10 Ways to Know Your Smartphone Has Spying Malware
10 ways to know your smart phone has spying malware – 10 Ways to Know Your Smartphone Has Spying Malware: Ever felt like your phone is acting strangely? Maybe your battery drains faster than usual, or you’re getting weird text messages from unknown numbers. These could be signs that something sinister is lurking in your device – spying malware. This isn’t just a techy problem; it’s a privacy violation that can expose your personal data, location, and even your conversations.
Let’s dive into ten key indicators that your phone might be compromised and what you can do about it.
From unexplained battery drain and suspicious data usage spikes to unfamiliar apps and strange text messages, we’ll cover a range of symptoms that point towards a potential malware infection. We’ll also explore how malware can secretly access your microphone, camera, and location data, and what steps you can take to regain control of your privacy and secure your phone.
Unexpected Battery Drain
Your smartphone’s battery life is a crucial indicator of its overall health and security. Understanding typical battery consumption patterns can help you quickly identify when something is amiss, potentially pointing to malicious software. A sudden and significant decrease in battery life, even with minimal usage, is a strong warning sign.Unexpectedly rapid battery depletion can manifest in several ways.
For instance, you might notice your phone draining significantly faster than usual, even when you’re not actively using it. Another sign is the phone getting excessively hot, even when performing simple tasks. This heat generation is often a byproduct of intense background processes, which could be indicative of malware.
So, you’re worried about those 10 ways to know your smartphone has spying malware? It’s a valid concern in today’s digital world. Building secure apps is crucial, which is why I’ve been diving into the world of app development lately, specifically checking out domino app dev the low code and pro code future and how it impacts security.
Understanding these development processes helps us appreciate the complexities of securing our own devices from malicious software, so we can better identify those sneaky 10 signs of a compromised phone.
Apps and Processes Indicating Malware Activity
Certain apps or processes consuming excessive resources might hint at malware. For example, an unknown app running in the background, constantly using data or GPS, could be a major red flag. Similarly, unusually high CPU or memory usage, even when the phone is idle, can indicate malicious activity. Background processes that you don’t recognize or cannot identify should be investigated carefully.
Also, be wary of apps that request excessive permissions, especially those that seem unrelated to the app’s stated function. For example, a flashlight app requesting access to your contacts is suspicious.
Comparison of Normal and Suspicious Battery Usage Patterns
| Feature | Normal Usage | Suspicious Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Drain Rate | Gradual depletion over several hours, depending on usage. | Rapid depletion within an hour or two, even with minimal use. | Phone at 80% at 9 AM, down to 20% by noon, even with only a few text messages sent. |
| Background Processes | Few apps actively running in the background; mostly system processes. | Many unknown or suspicious apps consuming significant resources. | Multiple apps with names like “SystemUpdate123” or “MobileOptimizerPro” consuming high CPU and data. |
| Temperature | Slightly warm to the touch during extended use. | Excessively hot, even during idle periods. | Phone becomes uncomfortably hot even while on the charging stand and not actively used. |
| Data Usage | Data usage consistent with typical activities (browsing, streaming, etc.). | Unexpectedly high data usage, even with minimal app activity. | Data usage spikes overnight even though Wi-Fi is off and no data-intensive apps were running. |
Data Usage Spikes

Unexpectedly high data consumption on your smartphone can be a major red flag indicating the presence of malicious software. Understanding your typical data usage patterns is crucial to recognizing when something is amiss. This allows you to quickly identify potential threats and take action before significant damage occurs.Most smartphone users experience relatively consistent data usage patterns depending on their habits.
Someone who streams videos daily will naturally consume more data than someone who primarily uses their phone for texting and occasional web browsing. However, sudden and dramatic increases in data usage, far exceeding your typical consumption, are cause for concern.
Factors Contributing to Sudden Data Usage Increases, 10 ways to know your smart phone has spying malware
Several legitimate factors can cause a temporary spike in data usage. These include downloading large files (like apps or videos), streaming high-definition content, using data-intensive apps like cloud backups, or traveling to areas with poor Wi-Fi connectivity, forcing your phone to rely more on cellular data. However, these are typically temporary and predictable. A sustained, unexplained increase in data usage points towards a more serious issue.
Malware Causing High Data Consumption
Certain types of malware are designed specifically to consume large amounts of data without the user’s knowledge. This often happens through actions like:
- Sending spam messages: Malware can secretly send numerous text messages or emails, each consuming a small amount of data, but accumulating to a significant total over time.
- Uploading stolen data: Some malware steals personal information, such as photos, contacts, or location data, and uploads it to remote servers, resulting in substantial data usage.
- Operating in the background: Many malicious apps operate silently in the background, constantly communicating with command-and-control servers, draining your data without any visible activity on your screen. This is a common tactic employed by spyware.
- Cryptojacking: This type of malware secretly uses your phone’s processing power to mine cryptocurrency, requiring significant data transfer for communication with the mining pools. This often goes unnoticed until you see a dramatic increase in your data bill.
Investigating Unusual Data Usage
If you notice a significant and unexplained increase in your data usage, here’s how to investigate:
- Check your data usage reports: Most mobile carriers provide detailed reports showing your daily or weekly data consumption. Compare your current usage with your average usage over the past few months.
- Review your installed apps: Identify apps that have been recently installed or updated, and pay attention to apps with unusual permissions, particularly those accessing your contacts, location, or microphone.
- Monitor background data usage: Go into your phone’s settings and review which apps are consuming the most data even when they’re not actively open. This is often a key indicator of background malware activity.
- Run a malware scan: Use a reputable antivirus or anti-malware app to thoroughly scan your device for malicious software. Make sure to update your security software regularly.
- Factory reset (as a last resort): If you suspect a serious infection and other steps haven’t worked, a factory reset can remove malware, but remember to back up your essential data first. This should only be considered as a final step.
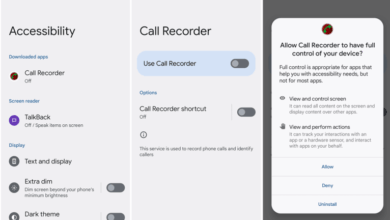
Unfamiliar Apps or Processes
Discovering unexpected apps or processes running on your smartphone can be a strong indicator of a malware infection. Spyware often disguises itself, making it crucial to regularly check your device for unauthorized software. This proactive approach can significantly reduce your risk of privacy breaches.Your smartphone’s operating system provides tools to review both installed apps and currently active processes.
Understanding how to use these tools is a vital step in maintaining your device’s security.
Accessing Installed Apps and Running Processes
Locating installed applications is generally straightforward. On Android devices, you can typically find a list of installed apps within the settings menu, often under “Apps” or “Applications.” iOS users can view their installed apps on the home screen and within the App Library. To see running processes (background apps), the method varies depending on the operating system and version.
Android often requires navigating to the “Developer options” (which need to be enabled first in the settings) to view a detailed list of active processes. iOS provides less direct access to this information, with limited visibility through the App Switcher or by observing unusual resource consumption.
Identifying Unfamiliar or Suspicious Apps
When reviewing your installed apps, be wary of anything you don’t recognize. Spyware often mimics legitimate apps, using names and icons that look similar to well-known software. Pay close attention to app names that are slightly misspelled or have unusual characters. For example, an app called “Faceboook” or “GoogIe Maps” should immediately raise suspicion. Also, look for apps with generic names or those lacking clear descriptions of their function.
If an app’s purpose isn’t immediately apparent, it’s worth investigating further.
Characteristics of Spyware Apps
Spyware apps frequently share certain characteristics. They often operate in the background, consuming significant resources without obvious user interaction. They might request extensive permissions, such as access to your contacts, location, microphone, and camera, even if these permissions seem irrelevant to the app’s stated function. Some spyware apps might even disable uninstall options, making them difficult to remove.
Another telltale sign is the presence of apps that lack developer information or have very few downloads or reviews.
Checking App Permissions and Identifying Potentially Harmful Access Requests
Before installing an app, carefully review the requested permissions. Legitimate apps generally only request permissions necessary for their function. An app requesting access to your contacts, location, and microphone when it claims to be a simple calculator should be viewed with extreme skepticism. On both Android and iOS, the permission requests are usually displayed during the installation process.
After installation, you can often review and modify app permissions within your device’s settings. If an app requests access to sensitive data that seems unjustified, it’s advisable to uninstall it immediately.
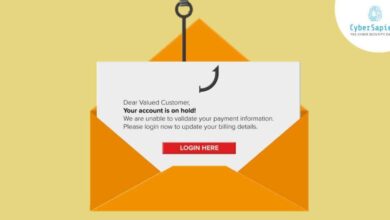
Strange Text Messages or Calls
Receiving unexpected or unusual text messages and calls can be a significant indicator of spyware on your smartphone. These communications often deviate from your normal contact patterns and contain elements designed to trick you into revealing personal information or downloading malicious software. Understanding the characteristics of these suspicious communications is crucial for protecting your data and privacy.Spyware can manifest itself through unsolicited calls or messages in several ways, often mimicking legitimate communication to gain your trust.
These messages might appear to be from your bank, a delivery service, or even a government agency, urging you to click a link or call a number. The goal is always to exploit your trust and gain access to your device.
Characteristics of Suspicious Communications
Suspicious messages frequently contain grammatical errors, urgent or threatening language, and requests for personal information such as passwords, bank details, or social security numbers. Phishing messages often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of your name. Links embedded in these messages may lead to fake websites designed to steal your credentials. Similarly, unsolicited calls might involve automated systems attempting to gain access through voice commands or pressure tactics to obtain sensitive information.
Examples of Suspicious Communication Patterns
Imagine receiving a text message claiming your bank account has been compromised and requiring you to click a link to verify your information. Or consider a series of missed calls from unknown numbers followed by a text message urging you to call back immediately to avoid consequences. These scenarios are red flags. Another example would be receiving a message promising a large sum of money if you provide your banking details.
These tactics are commonly employed by spyware distributors.
Actions to Take Upon Receiving Suspicious Communications
If you receive a suspicious message or call, it’s crucial to act promptly.
- Do not click any links or call back any unfamiliar numbers.
- Report the message or call to your service provider and relevant authorities.
- Delete the message immediately.
- Run a full malware scan on your device using a reputable antivirus application.
- Change your passwords for all online accounts, especially banking and email.
- Monitor your accounts for any unauthorized activity.
Slow Performance and Freezing
Malware can significantly degrade your smartphone’s performance, leading to frustrating slowdowns and unexpected freezes. This happens because malicious software often consumes significant system resources, such as processing power, memory (RAM), and storage space. The more resource-intensive the malware, the more noticeable the performance impact will be. Understanding the signs and troubleshooting steps is crucial for identifying and resolving this issue.Malicious software impacts smartphone performance in several ways.
It can run background processes that constantly consume CPU cycles, leading to sluggishness even when you’re not actively using any apps. Malware can also hog RAM, leaving less available for your legitimate apps, resulting in frequent app crashes or freezes. Additionally, some malware might fill up your storage space with unnecessary files, further slowing down your device. Finally, some malware actively interferes with your operating system’s core functions, hindering its overall efficiency.
Signs of Slow Performance Due to Malware
A sudden and unexplained decrease in your phone’s speed is a key indicator. This might manifest as longer loading times for apps, noticeable lags when scrolling through menus, or significant delays when opening files. Apps might crash more frequently than usual, or the entire system might freeze intermittently, requiring a hard reset. You might also notice increased heat generation from your phone, as the CPU works overtime to combat the malware’s resource consumption.
For example, a phone that used to open apps instantly might now take several seconds, or a game that previously ran smoothly might now experience frequent stutters and lag. These are clear signs that something is consuming your phone’s resources beyond normal usage.
Troubleshooting Performance Problems
A systematic approach is essential when troubleshooting performance issues. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Restart your phone: A simple restart can often resolve temporary glitches and free up resources consumed by rogue processes.
- Check your storage space: Malware can consume significant storage. Check your phone’s storage usage and delete unnecessary files or apps.
- Uninstall recently installed apps: If performance issues started after installing a new app, uninstall it immediately as a precaution.
- Close unnecessary background apps: Many apps run in the background, consuming resources. Close any apps you aren’t actively using.
- Scan your phone with a reputable antivirus app: Use a trusted mobile antivirus app to perform a thorough scan for malware. Many offer free versions with basic scanning capabilities.
- Perform a factory reset (last resort): If other steps fail, a factory reset can eliminate malware but will erase all your data. Make sure to back up important files before attempting this.
Remember to always download apps from official app stores and be cautious about clicking on unknown links or downloading files from untrusted sources. Proactive measures are key to preventing malware infections.
Overheating
Your smartphone generates heat during normal operation, but excessive heat can be a telltale sign of malicious activity. Understanding the typical temperature range and recognizing when things get too hot is crucial for identifying potential malware.Malware can cause excessive heat generation by forcing your phone’s processor to work harder than usual. This increased workload, often involving complex calculations or data encryption/decryption for nefarious purposes, translates directly into more heat.
Imagine your phone’s processor as a tiny engine; the malware is like flooring the gas pedal constantly, leading to overheating.
Malware Causing Overheating
Certain types of malware are particularly notorious for their heat-generating activities. Cryptojacking malware, for instance, secretly uses your phone’s processing power to mine cryptocurrency. This process is incredibly demanding and can significantly increase your device’s temperature. Other malware might involve complex data processing or continuous background tasks designed to remain undetected, resulting in similar overheating issues. Examples include spyware that constantly monitors your activity or adware that relentlessly displays advertisements.
Normal vs. Malware-Induced Temperatures
It’s difficult to give exact temperature figures because they vary based on phone model, ambient temperature, and usage. However, we can establish a general comparison. Feel your phone after a period of heavy use (gaming, video streaming). If it’s noticeably hotter than usual and remains so even after a period of inactivity, it warrants investigation.
| Condition | Typical Temperature Range (°C) | Feel | Potential Malware Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Use (e.g., browsing, messaging) | 25-35 | Slightly warm to the touch | No |
| Heavy Use (e.g., gaming, video streaming) | 35-45 | Warm to moderately hot | Possibly, if heat persists after use ceases |
| Malware Activity (suspected) | >45 | Hot to the touch, potentially uncomfortable to hold | Yes, investigate immediately |
Pop-up Ads and Notifications
Pop-up ads and notifications are a common part of the online experience, but their sudden appearance can be a telltale sign of something more sinister lurking on your smartphone. While some pop-ups are harmless advertisements, others can be a symptom of malware actively trying to exploit your device. Understanding the difference is crucial for protecting your privacy and security.Legitimate pop-up ads typically appear on specific apps or websites you’ve visited and are usually related to the content you’re viewing.
Malicious pop-ups, on the other hand, often appear unexpectedly and aggressively, even when you’re not using any apps or browsing the web. They often promote fake software updates, prize giveaways, or other scams designed to trick you into downloading more malware.
Distinguishing Legitimate and Malicious Pop-up Ads
Legitimate pop-up ads are generally contextually relevant to your browsing activity. For example, if you’re looking at hiking gear online, you might see ads for related products. Malicious pop-ups, however, are indiscriminate and often unrelated to your current activity. They may contain grammatical errors, misleading promises, or aggressive language urging immediate action. Their design is usually crude and unprofessional compared to legitimate ads.
Another key difference lies in their persistence. Legitimate ads typically appear once or twice and then disappear, while malicious pop-ups frequently reappear, even after you’ve closed them.
Malware’s Generation of Intrusive Notifications
Spyware and other forms of malware can generate intrusive notifications in several ways. They might inject code into existing apps to display unwanted ads or create their own background processes that constantly send notifications. These notifications often mimic system messages or alerts to make them seem legitimate, making it difficult to identify them as malicious. For example, a notification claiming your device is infected with a virus and prompting you to download a “cleaner” is a classic example of this tactic.
These notifications frequently lead to phishing websites or attempts to install further malware.
Examples of Pop-up Ads Associated with Spyware
Examples of pop-up ads commonly associated with spyware include those promoting fake antivirus software, offering free gifts or prizes requiring personal information, or displaying sexually suggestive content. These ads often lack a clear source or company information, and attempts to close them might lead to further unwanted pop-ups or redirects. For example, a pop-up claiming you’ve won a lottery and asking for your bank details is a clear indication of a potential spyware infection.
Similarly, pop-ups with hyper-sexualized content, especially those that persist despite closing the app or browser, are often linked to adware or spyware.
Blocking or Removing Intrusive Ads and Notifications
Blocking or removing intrusive ads and notifications requires a multi-pronged approach. First, update your operating system and all apps to the latest versions. Many updates include security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by malware. Second, install a reputable ad blocker. These apps can significantly reduce the number of unwanted ads and pop-ups you encounter.
Third, regularly review your installed apps and remove any that you don’t recognize or haven’t used recently. Fourth, run a full scan with a reputable antivirus or anti-malware program. Finally, if the problem persists, consider a factory reset of your device, but remember to back up your important data beforehand. This step should be considered a last resort, as it will erase all data on your phone.
Microphone or Camera Activity
Unexpected microphone or camera activation is a chilling sign of potential malware. While legitimate apps might request access, unusual activity – especially when no app appears to be using these features – is a major red flag. This indicates that something malicious might be running in the background, secretly recording your conversations or capturing images without your knowledge or consent.Malware can secretly access and use your phone’s microphone and camera through various methods.
It often exploits vulnerabilities in the operating system or apps to gain unauthorized access. Once inside, it can monitor your surroundings, record conversations, capture images, or even stream live video without any visible indication to the user. This covert access can be particularly dangerous as it compromises your privacy and security in a significant way.
Malware Activation Scenarios
Malware might activate your microphone or camera in several scenarios. For example, a spyware program could continuously record your conversations to steal sensitive information, such as banking details or personal conversations. Another scenario could involve a stalkerware app secretly capturing images or videos of you without your consent. In some cases, malware might activate the camera to steal your login credentials by recording you typing passwords or PINs.
The data collected can then be sent to a remote server controlled by the attackers. These scenarios highlight the severe consequences of having your phone compromised.
Preventing Unauthorized Access
Preventing unauthorized access to your microphone and camera requires a multi-pronged approach. Regularly updating your phone’s operating system and apps is crucial, as these updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities malware might exploit. Carefully review app permissions before installing any app, paying close attention to microphone and camera access requests. Only grant these permissions to apps you trust and understand the need for such access.
Additionally, regularly check your device’s settings to ensure that no suspicious apps have been granted access to your microphone or camera. Consider using a reputable antivirus app to scan for and remove malware. Finally, be cautious about clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from untrusted sources, as these can often lead to malware infections.
Location Tracking Discrepancies: 10 Ways To Know Your Smart Phone Has Spying Malware

Your smartphone’s location services are incredibly useful for navigation, finding nearby businesses, and sharing your whereabouts with friends and family. However, this convenience comes with a potential security risk: malicious apps can exploit these services to track your movements without your knowledge or consent. Discrepancies in your recorded location history can be a strong indicator of spyware.Location data on most smartphones is accessible through the device’s settings menu.
The exact steps vary slightly depending on the operating system (Android or iOS), but generally involve navigating to “Settings,” then “Location,” or a similarly named option. Within these settings, you can view your recent location history, which may be displayed as a map or a list of timestamps and coordinates. Additionally, you can manage which apps have access to your location data.Malware can surreptitiously access and transmit your location data through various methods.
Some malware might directly interact with the device’s location services API, while others might use more indirect methods such as capturing screen data or exploiting vulnerabilities in other apps. This location data is then typically transmitted to a remote server controlled by the malware authors, allowing them to monitor your movements in real-time or access your historical location data.
Examples of Suspicious Location Data
Unexpected location entries, such as your phone reporting your location as being in a different country while you’re at home, are a major red flag. Similarly, consistent location tracking when the location services are supposedly turned off, or an unusually high frequency of location updates, especially when no location-based apps are in use, can signal malware activity. For example, imagine your phone consistently reports your location as being near a competitor’s office when you are clearly at home.
This could suggest a competitor is using spyware to track your business activities. Another example would be if your phone shows you were at a remote location at 3 AM, when you know you were asleep at home.
Reviewing and Managing Location Permissions
Regularly reviewing and managing location permissions for your apps is crucial for maintaining your privacy and security. On both Android and iOS, you can access a list of apps that have requested access to your location. Review this list carefully, revoking access for any apps that you don’t recognize or that don’t require location data for their intended functionality.
For example, a calculator app shouldn’t need access to your location. It’s also wise to enable location services only when necessary, disabling them when not actively using location-based apps. This limits the potential impact of any malware that might attempt to access your location data.
Changes in Network Settings
Your smartphone’s network settings are a crucial aspect of its online activity, controlling how it connects to the internet and other devices. Malware can subtly manipulate these settings, often without your knowledge, to facilitate its malicious activities, such as data theft or unauthorized communication. Understanding how to access and review these settings is essential for detecting and preventing such attacks.Network settings control aspects like Wi-Fi connectivity, mobile data usage, VPN connections, and proxy servers.
Malware can alter these settings to redirect your internet traffic through malicious servers, intercept your data, or even prevent you from accessing certain websites or services. This can compromise your privacy, security, and overall online experience.
Accessing and Reviewing Network Settings
Accessing your network settings varies slightly depending on your phone’s operating system (Android or iOS). On Android devices, you typically find these settings within the “Settings” app, often under a section labeled “Network & internet,” “Wi-Fi,” or “Connections.” iOS devices usually have network settings accessible through the “Settings” app, with options for Wi-Fi, Cellular, and VPN. Within these sections, you’ll find details about connected networks, data usage, and other network-related configurations.
Regularly reviewing these settings allows you to identify any unauthorized changes.
Malware Alterations to Network Settings
Malware can make several sneaky alterations to your network configuration. For instance, it might automatically connect to a specific Wi-Fi network, even if you haven’t selected it, or activate a VPN without your consent, routing your internet traffic through an unknown server. It could also change your mobile data settings, increasing data usage or even disabling your data connection entirely.
Furthermore, malware can configure proxy servers to intercept your web traffic and steal sensitive information.
Examples of Suspicious Network Setting Changes
Imagine finding a new, unfamiliar VPN connection activated on your phone. Or perhaps you notice your phone automatically connecting to a public Wi-Fi hotspot named something like “FreePublicWiFi,” even when you are at home. Another red flag would be a significant increase in mobile data usage without any corresponding increase in your app usage. These are all potential indicators of malware tampering with your network settings.
Unexpected changes to proxy server settings, such as the appearance of a proxy address you don’t recognize, also suggest malicious activity.
Restoring Default Network Settings and Identifying Unauthorized Changes
If you suspect malware has altered your network settings, restoring your network settings to their factory defaults can be a helpful step. This usually involves finding a “Reset Network Settings” option within the network settings menu. This action will erase saved Wi-Fi passwords and other network configurations, requiring you to re-enter them. Before doing this, make a note of any important network credentials.
By comparing your network settings before and after the reset, you can identify any unauthorized changes made by the malware. For example, if a specific VPN connection reappears after a reset, it strongly suggests the presence of persistent malware.
Final Conclusion
So, there you have it – ten telltale signs that your smartphone might be harboring spying malware. Remember, staying vigilant is key. Regularly check your phone’s activity, be cautious about the apps you download, and keep your software updated. By being aware of these potential threats and taking proactive steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim.
Don’t let your phone become a window into your private life – take control and secure your digital privacy today!
Q&A
Q: Can antivirus software prevent spying malware?
A: Yes, a good antivirus app can significantly reduce your risk, but it’s not a foolproof solution. Some malware is very sophisticated and can evade detection.
Q: What should I do if I suspect my phone is infected?
A: Immediately back up any essential data (if you can safely do so), then factory reset your phone. This will wipe all data, including the malware. Consider professional help if you’re not comfortable performing a factory reset yourself.
Q: How often should I check for malware?
A: Regularly! At least once a month is a good starting point. Pay close attention to your phone’s behavior and any unusual changes.
Q: Are all free apps safe?
A: No. Free apps can contain malware, so always read reviews and check the app developer’s reputation before installing anything.