5 Ways CCSP Can Help You Improve Cloud Security
5 Ways CCSP Can Help You Improve Cloud Security: Ever felt overwhelmed by the complexities of cloud security? The sheer volume of potential threats and ever-evolving compliance regulations can be daunting. But what if I told you there’s a proven path to navigating this landscape with confidence? This post explores five key ways the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification can dramatically boost your cloud security posture, empowering you to build a robust and resilient security framework.
From mastering risk management and achieving compliance to strengthening data protection and designing secure cloud architectures, the CCSP curriculum provides a comprehensive skillset. We’ll delve into practical applications, real-world examples, and actionable strategies you can implement immediately to elevate your organization’s cloud security game. Get ready to transform your approach to cloud security!
Enhanced Risk Management
The Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification significantly enhances your ability to identify, assess, and mitigate cloud security risks. It provides a structured framework and in-depth knowledge crucial for navigating the complex landscape of cloud security threats and vulnerabilities. This isn’t just about knowing theoretical concepts; it’s about applying practical methodologies to build robust and resilient cloud security postures.
CCSP equips you with the skills to understand the unique security challenges presented by various cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid, multi-cloud) and to tailor your risk management strategies accordingly. The certification emphasizes a proactive approach, moving beyond simple compliance checklists to a more holistic and dynamic risk assessment process.
Risk Assessment Methodologies
CCSP knowledge underpins the effective application of several risk assessment methodologies. These methods help systematically identify and analyze potential threats and vulnerabilities within your cloud environment. A solid understanding of these methodologies is critical for building a comprehensive risk management plan.
For example, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) provides a widely accepted approach to managing cybersecurity risk. CCSP training reinforces the importance of identifying assets, assessing threats, and developing appropriate responses based on risk tolerance. Another relevant methodology is the OCTAVE Allegro method, which focuses on a collaborative, iterative approach to risk assessment, perfectly aligned with the collaborative nature of cloud environments and multi-stakeholder responsibilities.
Finally, the FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) model, frequently used by organizations to quantify risk in financial terms, can be effectively leveraged with the risk management knowledge gained through CCSP certification. This allows for more data-driven decision-making around risk mitigation strategies.
Developing and Implementing a Cloud Security Risk Management Plan
A CCSP’s role extends beyond simply identifying risks; they are instrumental in developing and implementing a comprehensive cloud security risk management plan. This plan should cover all aspects of cloud security, from data protection and access control to incident response and compliance. This involves defining clear roles and responsibilities, establishing effective communication channels, and implementing monitoring and reporting mechanisms.
So, you’re looking at boosting your cloud security with those 5 key CCSP strategies? Smart move! But building secure apps is also crucial, and that’s where understanding the future of development comes in, as outlined in this insightful piece on domino app dev the low code and pro code future. Ultimately, strong app security complements a robust cloud security posture, making those 5 CCSP methods even more effective.
A CCSP-informed plan would include regular risk assessments, vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and security audits. It would also incorporate strategies for mitigating identified risks, such as implementing security controls (e.g., encryption, access control lists, intrusion detection systems), establishing incident response procedures, and conducting regular security awareness training for staff. The plan would be iterative, adapting to changes in the threat landscape and the evolving cloud environment.
Furthermore, the plan would incorporate strategies for continuous monitoring and improvement, leveraging automation and analytics to identify and respond to emerging threats in a timely manner.
Comparison of Traditional and Cloud-Specific Risk Management
Traditional risk management approaches often struggle to keep pace with the dynamic nature of cloud environments. CCSP training highlights the key differences and emphasizes the need for cloud-specific strategies. The following table illustrates some key distinctions:
| Feature | Traditional Risk Management | Cloud-Specific Risk Management (CCSP-Informed) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Primarily on-premises infrastructure | Encompasses multi-cloud, hybrid, and public cloud environments |
| Shared Responsibility | Clearly defined within the organization | Shared between the organization and cloud provider; requires precise contract definition and understanding of responsibilities |
| Automation | Limited automation | Extensive use of automation for security monitoring, incident response, and vulnerability management |
| Agility | Slower response to changes | Rapid adaptation to changes in cloud infrastructure and security threats |
Improved Compliance and Governance: 5 Ways Ccsp Can Help You Improve Cloud Security
Navigating the complex world of cloud security requires more than just technical expertise; it demands a deep understanding of regulatory compliance. The Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification equips you with the knowledge and skills to not only secure your cloud environment but also to ensure it adheres to relevant industry standards and regulations. This is crucial for maintaining trust with customers, avoiding hefty fines, and preventing reputational damage.
A robust compliance program is the cornerstone of a secure and trustworthy cloud operation.The importance of compliance standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS cannot be overstated. These frameworks establish specific requirements for data protection, privacy, and security, depending on the industry and the type of data handled. Failure to comply can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions.
For example, a healthcare provider violating HIPAA could face millions of dollars in fines and irreparable damage to its reputation. Similarly, a company failing to meet GDPR requirements could face substantial penalties for mishandling personal data.
Compliance Standard Adherence Through CCSP Knowledge
CCSP training provides a comprehensive understanding of these compliance frameworks and how they translate into practical cloud security measures. For instance, CCSP certification covers the technical and operational aspects of meeting HIPAA’s requirements for protecting Protected Health Information (PHI) in the cloud. This includes implementing appropriate access controls, data encryption, and audit trails. Similarly, CCSP professionals understand the principles of GDPR, including data subject rights, data minimization, and accountability, and can design and implement cloud security solutions that ensure compliance.
Understanding PCI DSS, a critical standard for organizations handling payment card data, is another area where CCSP knowledge proves invaluable, covering the secure handling of sensitive financial information within cloud infrastructure. This includes implementing strong encryption, regular vulnerability scanning, and rigorous access control mechanisms.
Designing and Implementing a Robust Cloud Governance Framework, 5 ways ccsp can help you improve cloud security
A well-defined cloud governance framework is essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring consistent security practices. The CCSP curriculum emphasizes the importance of establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing cloud security. This includes defining policies, procedures, and standards for access control, data security, incident response, and risk management. CCSP professionals are equipped to design and implement such frameworks, tailoring them to specific organizational needs and regulatory requirements.
This often involves leveraging cloud-native security tools and services, as well as integrating cloud security into the broader enterprise governance structure.
Key Compliance Requirements and CCSP Expertise
| Compliance Standard | Key Requirements | CCSP Expertise Addressing the Requirement | Example Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIPAA | Data encryption at rest and in transit, access controls, audit trails | Understanding of encryption algorithms, access control models (RBAC, ABAC), and logging mechanisms. | Implementing AES-256 encryption for PHI stored in cloud storage and using role-based access control to restrict access to sensitive data. |
| GDPR | Data minimization, data subject rights, data breach notification | Knowledge of data privacy principles, data lifecycle management, and incident response procedures. | Implementing data masking techniques to minimize the amount of personal data collected and stored, providing individuals with tools to access and modify their data, and establishing a process for handling data breaches. |
| PCI DSS | Strong encryption, regular vulnerability scanning, secure network architecture | Understanding of network security concepts, vulnerability management practices, and encryption technologies. | Implementing TLS/SSL encryption for all payment card data transactions, conducting regular penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities, and establishing a secure network segmentation strategy. |
Strengthened Data Security and Privacy

The cloud offers incredible scalability and flexibility, but it also introduces new security challenges. Protecting your sensitive data in this environment is paramount, and the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification equips you with the knowledge and skills to build a robust data security posture. This section will explore how CCSP principles directly contribute to stronger data security and privacy within your cloud infrastructure.Data breaches and unauthorized access cost organizations millions annually, impacting reputation and compliance.
Understanding common threats and vulnerabilities, and implementing appropriate preventive measures, are crucial for minimizing risk. The CCSP curriculum provides a comprehensive overview of these threats and Artikels practical, effective solutions.
Common Cloud Data Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
Cloud environments present a unique attack surface. Common threats include misconfigurations of cloud services leading to accidental data exposure, insider threats from malicious or negligent employees, and sophisticated attacks targeting vulnerabilities in cloud platforms or applications. Data breaches often stem from inadequate access control, weak encryption, or a lack of robust monitoring and logging. CCSP training emphasizes the importance of identifying and mitigating these vulnerabilities through rigorous security assessments and proactive security measures.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies Using CCSP Best Practices
Implementing effective DLP strategies is vital for preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. CCSP best practices advocate for a multi-layered approach, combining technical controls like data encryption and access controls with procedural controls such as data classification and employee training. For instance, using data classification schemes to label sensitive data allows for the implementation of granular access controls and automated DLP tools that monitor and prevent unauthorized data transfer.
This also facilitates better compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit Leveraging CCSP Knowledge
Encryption is a cornerstone of cloud data security. CCSP emphasizes the importance of encrypting data both at rest (while stored) and in transit (while being transmitted). At rest encryption involves encrypting data stored on cloud storage services, databases, and virtual machines. Transit encryption secures data during transmission between different cloud components or between on-premises and cloud environments.
CCSP provides guidance on choosing appropriate encryption algorithms and key management practices to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of your data. Examples include using TLS/SSL for transit encryption and AES-256 for data at rest.
Best Practices for Securing Sensitive Data in the Cloud Based on CCSP Principles
The following best practices, informed by CCSP principles, are crucial for securing sensitive data:
- Implement strong access control measures, using least privilege principles and multi-factor authentication.
- Regularly perform vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and remediate security weaknesses.
- Establish robust monitoring and logging capabilities to detect suspicious activities and security incidents promptly.
- Utilize cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to continuously assess and improve your cloud security posture.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) tools and strategies to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
- Regularly review and update your cloud security policies and procedures to adapt to evolving threats and best practices.
- Employ robust incident response planning to effectively handle security incidents and minimize their impact.
- Ensure compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards, such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR.
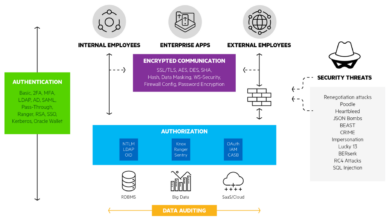
Secure Cloud Architecture and Design
A well-designed cloud architecture is the cornerstone of robust cloud security. It’s not simply about choosing a cloud provider; it’s about strategically planning and implementing your cloud infrastructure to minimize vulnerabilities and maximize resilience. A secure architecture proactively addresses potential threats, ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The CCSP certification plays a crucial role in this process, equipping professionals with the knowledge and skills to design and implement secure cloud environments.The principles of secure cloud architecture design emphasize a layered approach to security, incorporating various controls at different levels.
This includes network security, access control, data encryption, and regular security assessments. These principles ensure that even if one layer is compromised, others remain intact, minimizing the overall impact of a security breach. Understanding and applying these principles is essential for organizations seeking to protect their sensitive data and maintain business continuity in the cloud.
Secure Cloud Deployment Models
Organizations can choose from various cloud deployment models, each with its own security implications. The selection depends on factors like regulatory compliance, data sensitivity, and budget constraints.
| Deployment Model | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Shared infrastructure provided by a third-party provider. | Cost-effective, scalable, and readily available. | Shared responsibility model, potential for data breaches if security isn’t properly managed. |
| Private Cloud | Dedicated infrastructure managed either internally or by a third-party provider. | Enhanced security and control over data and infrastructure. | Higher upfront costs, requires dedicated IT expertise for management. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combines public and private cloud resources. | Flexibility to leverage the benefits of both models, increased resilience. | Increased complexity in management and security configuration. |
The CCSP’s Role in Secure Cloud Infrastructure Design and Implementation
CCSP professionals are instrumental in designing and implementing secure cloud infrastructures. Their expertise covers a wide range of security domains, including risk management, cryptography, identity and access management, and data loss prevention. They are responsible for developing and enforcing security policies, selecting appropriate security tools, and conducting regular security audits. A CCSP’s understanding of various cloud deployment models, security architectures, and compliance frameworks enables them to create secure, compliant, and efficient cloud environments.
They ensure that security is built into the cloud architecture from the ground up, rather than being an afterthought.
Effective Cloud Security Operations

Effective cloud security isn’t just about setting up initial defenses; it’s about continuous vigilance and rapid response. This fifth and final pillar of leveraging CCSP knowledge focuses on maintaining a robust security posture through proactive monitoring and efficient incident handling. A strong security operations program is critical for mitigating risks and ensuring the ongoing protection of your cloud environment.Continuous monitoring and incident response are paramount in today’s dynamic threat landscape.
Without these capabilities, even the most meticulously designed cloud security architecture can be vulnerable. A proactive approach, guided by CCSP best practices, ensures that potential threats are identified and addressed before they can cause significant damage.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tool Integration with CCSP Practices
SIEM tools are the cornerstone of effective cloud security monitoring. These systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a centralized view of activity across your cloud infrastructure. Examples of popular SIEM tools include Splunk, IBM QRadar, and Azure Sentinel. CCSP professionals leverage these tools to establish baselines of normal activity, identify anomalies that might indicate malicious activity, and trigger automated responses to security events.
Integration with CCSP practices involves configuring SIEM systems to monitor for specific threats identified in risk assessments, implementing appropriate alerting thresholds, and integrating the SIEM with other security tools such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms. This integrated approach allows for a more comprehensive and effective security posture.
Incident Handling and Response Procedures Based on CCSP Guidelines
The CCSP framework provides a structured approach to incident handling, emphasizing speed, efficiency, and minimizing impact. A typical incident response lifecycle, informed by CCSP best practices, includes: Preparation (developing incident response plans, defining roles and responsibilities, and establishing communication protocols); Identification (detecting and verifying security incidents); Containment (isolating affected systems and preventing further damage); Eradication (removing the threat and restoring systems to a secure state); Recovery (restoring data and systems to normal operation); and Post-Incident Activity (conducting a thorough review to identify lessons learned and improve future responses).
CCSP professionals play a critical role in each phase, ensuring that responses are aligned with organizational policies and regulatory requirements. For instance, a CCSP professional would be responsible for ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR during a data breach incident.
Improving Security Audits and Penetration Testing with CCSP Expertise
CCSP expertise significantly enhances the effectiveness of security audits and penetration testing. A CCSP professional brings a deep understanding of cloud security controls and best practices, enabling them to conduct more thorough and comprehensive assessments. During audits, a CCSP can identify gaps in security controls, assess the effectiveness of existing measures, and recommend improvements aligned with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Similarly, during penetration testing, a CCSP can design more effective test scenarios, identify vulnerabilities more accurately, and provide more actionable remediation advice. Their knowledge of cloud-specific vulnerabilities and attack vectors is crucial for identifying weaknesses that might be overlooked by less experienced security professionals.
Security Incident Lifecycle and the Role of CCSP
The following describes a visual representation of a security incident lifecycle and the role of a CCSP professional in each phase. Imagine a flowchart. Phase 1: Preparation: The flowchart begins with a box labeled “Preparation.” This phase involves establishing security policies, procedures, and incident response plans. A CCSP guides the development of these plans, ensuring alignment with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
Arrows point from this box to subsequent phases. Phase 2: Identification: A box labeled “Identification” shows the detection of a potential security incident through monitoring tools (like the SIEM mentioned earlier). A CCSP professional analyzes alerts, validating the incident and its severity. Phase 3: Containment: The next box is “Containment,” illustrating the isolation of affected systems to prevent further damage. A CCSP professional directs this process, utilizing cloud-native security controls.
Phase 4: Eradication: The “Eradication” box shows the removal of the threat. A CCSP professional guides the remediation process, ensuring complete removal of malware or vulnerabilities. Phase 5: Recovery: The “Recovery” box shows the restoration of systems to normal operation. A CCSP professional oversees data restoration and system validation. Phase 6: Post-Incident Activity: The final box is “Post-Incident Activity,” which encompasses lessons learned, documentation, and plan improvements.
A CCSP leads this phase, analyzing the incident to identify weaknesses and enhance future responses. A feedback loop is shown from this box back to the “Preparation” box, highlighting the iterative nature of the process. The CCSP is involved in each phase, ensuring a coordinated and effective response.
Conclusion
Ultimately, achieving robust cloud security isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about cultivating a proactive and informed approach. The CCSP certification isn’t just a credential; it’s a passport to a deeper understanding of cloud security best practices. By mastering the principles Artikeld in this certification, you’ll be well-equipped to not only mitigate risks but also proactively design and implement security measures that safeguard your valuable data and systems.
So, are you ready to elevate your cloud security expertise and confidently navigate the complexities of the cloud landscape? The CCSP certification is your key.
FAQ Section
What are the prerequisites for taking the CCSP exam?
Generally, you need at least five years of cumulative paid work experience in IT, with at least three years of experience in information security. Specific experience requirements in cloud security are also Artikeld by (ISC)².
How much does the CCSP certification cost?
The cost varies depending on your (ISC)² membership status and location. Check the (ISC)² website for the most up-to-date pricing information.
Is the CCSP certification globally recognized?
Yes, the CCSP is a globally recognized certification, highly valued by employers worldwide in the cloud security field.
How long is the CCSP certification valid?
The CCSP certification requires maintaining Continuing Professional Development (CPD) credits to remain current. Failure to maintain these credits will result in the certification lapsing.