Commerce 9.1 Monitoring and Metrics A Deep Dive
Commerce 9 1 monitoring and metrics – Commerce 9.1 monitoring and metrics – sounds a bit dry, right? Wrong! Understanding how to track and analyze your e-commerce platform’s performance is the key to unlocking serious growth. This isn’t just about numbers on a screen; it’s about understanding your customers, identifying bottlenecks, and ultimately, making more money. We’ll explore the crucial metrics, the tools you need, and how to turn data into actionable insights.
Get ready to level up your e-commerce game!
This post will walk you through everything from setting up a basic monitoring system to advanced techniques for analyzing transactional data. We’ll cover essential KPIs, troubleshooting common problems, and even delve into security monitoring. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to leverage data to optimize your Commerce 9.1 platform and drive significant improvements to your bottom line.
Prepare for some serious data-driven enlightenment!
Understanding Commerce 9.1 Monitoring Landscape
Effective monitoring is crucial for the success of any e-commerce platform, and Commerce 9.1 is no exception. A robust monitoring system ensures optimal performance, identifies potential issues proactively, and ultimately contributes to a positive customer experience. This section delves into the key aspects of building and maintaining a comprehensive Commerce 9.1 monitoring strategy.
Core Components of a Robust Commerce 9.1 Monitoring System
A robust Commerce 9.1 monitoring system typically comprises several key components working in concert. These include application performance monitoring (APM) tools to track the health and performance of the Commerce 9.1 application itself, server monitoring tools to oversee the underlying infrastructure (databases, web servers, etc.), and log management solutions to analyze system logs for errors and anomalies. Integration with a centralized monitoring dashboard provides a single pane of glass view for comprehensive oversight.
Finally, a robust alerting system is essential to notify administrators of critical issues in real-time.
Types of Data Collected in Commerce 9.1 Monitoring
Commerce 9.1 monitoring collects a wide range of data to provide a holistic view of system health and performance. This includes transactional data (order processing times, checkout completion rates), application performance metrics (response times, error rates, CPU utilization), server metrics (memory usage, disk I/O), and user experience data (page load times, bounce rates). Log data provides detailed insights into application events, errors, and security incidents.
The combination of these data types provides a complete picture of the system’s performance and identifies potential bottlenecks or issues.
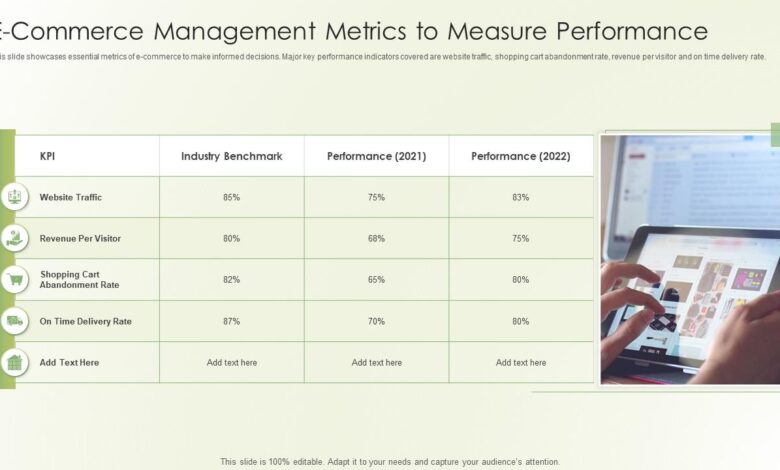
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Typically Tracked in a Commerce 9.1 Environment
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) are routinely monitored in a Commerce 9.1 environment. These include average order value (AOV), conversion rates, customer acquisition cost (CAC), website traffic, cart abandonment rate, and customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores. Monitoring these KPIs provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, website usability, and overall business performance. Analyzing trends in these metrics can help identify areas for improvement and optimization.
Comparison of Commerce 9.1 Monitoring Tools
Several monitoring tools are available for Commerce 9.1, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some popular options include tools like Dynatrace, New Relic, AppDynamics, and Datadog. The choice of tool often depends on factors such as budget, existing infrastructure, and specific monitoring requirements. For example, Dynatrace is known for its comprehensive APM capabilities, while Datadog offers a strong integration with various cloud platforms.
A thorough evaluation of each tool’s features and capabilities is crucial before making a selection.
Essential Steps for Setting Up a Basic Commerce 9.1 Monitoring System
Establishing a basic Commerce 9.1 monitoring system involves a series of key steps. The following table Artikels these steps, including the tools used, data collected, collection frequency, and alert thresholds.
| Step | Tool | Data Collected | Collection Frequency | Alert Thresholds |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Install Monitoring Agent | New Relic | Application performance metrics (response times, error rates) | Every minute | Response time > 500ms, error rate > 1% |
| Configure Server Monitoring | Nagios | Server metrics (CPU usage, memory usage, disk space) | Every 5 minutes | CPU usage > 80%, memory usage > 90%, disk space < 10% |
| Set up Log Monitoring | Graylog | Application and system logs | Real-time | Errors exceeding a predefined threshold per hour |
| Integrate with Alerting System | PagerDuty | Critical alerts from monitoring tools | Real-time | Based on pre-configured alert thresholds |
Key Metrics for Commerce 9.1 Performance
Monitoring the performance of your Commerce 9.1 platform is crucial for ensuring a smooth customer experience and maximizing business success. By tracking key metrics, you can proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact your bottom line. This allows for informed decision-making and optimization of your e-commerce operations.
Top Five Critical Metrics
The health of a Commerce 9.1 platform can be effectively assessed by focusing on five key metrics: Average Order Value (AOV), Conversion Rate, Website Load Time, Cart Abandonment Rate, and Customer Satisfaction (CSAT). These metrics provide a holistic view of platform performance, covering aspects from customer engagement to operational efficiency.
Average Order Value (AOV) Significance
AOV represents the average revenue generated per order. A higher AOV indicates successful upselling and cross-selling strategies, resulting in increased revenue. For example, a consistent increase in AOV might suggest the effectiveness of recently implemented product bundles or targeted promotions. Conversely, a declining AOV could signal a need to review pricing strategies, product offerings, or promotional campaigns.
Analyzing AOV trends helps in understanding customer purchasing behavior and optimizing revenue generation.
Conversion Rate Significance
The conversion rate measures the percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase. A high conversion rate signifies effective marketing and user experience design. A low conversion rate suggests potential problems with website navigation, checkout process, or overall user experience. For instance, a sudden drop in conversion rate might indicate issues with the website’s search functionality or a poorly designed checkout page.
Analyzing this metric helps identify areas for improvement in the customer journey.
Website Load Time Significance
Website load time directly impacts user experience. A slow-loading website leads to increased bounce rates and frustrated customers. Fast load times are crucial for maintaining user engagement and conversion rates. For example, a load time exceeding three seconds can result in a significant decrease in conversions, according to various studies on e-commerce website performance. Monitoring this metric helps ensure optimal website performance and a positive user experience.
Cart Abandonment Rate Significance
The cart abandonment rate reflects the percentage of shopping carts that are initiated but not completed. High abandonment rates suggest problems with the checkout process, payment options, or overall user experience. Analyzing the reasons behind cart abandonment (e.g., complicated checkout, unexpected shipping costs) allows for targeted improvements to reduce this rate and boost conversions. For example, offering guest checkout or highlighting shipping costs earlier in the process can significantly reduce cart abandonment.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Significance
CSAT measures customer satisfaction with the overall shopping experience. This metric provides valuable insights into customer perception and areas for improvement. Low CSAT scores might indicate problems with product quality, customer service, or the overall website experience. Actively collecting and analyzing CSAT feedback through surveys or reviews helps identify pain points and enhance the customer journey. For instance, a low CSAT score related to shipping could lead to a review of the shipping provider or delivery options.
Dashboard Visualization
| Metric | Current Value | Trend | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Order Value (AOV) | $75 | Increasing | Maintain current strategies |
| Conversion Rate | 2.5% | Decreasing | Review checkout process |
| Website Load Time | 2.1 seconds | Stable | Maintain current optimization |
| Cart Abandonment Rate | 15% | Decreasing | Continue current improvements |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | 4.2/5 | Increasing | Maintain current strategies |
Analyzing Transactional Data in Commerce 9.1: Commerce 9 1 Monitoring And Metrics
Understanding the transactional data within your Commerce 9.1 instance is crucial for optimizing performance, identifying areas for improvement, and ultimately, boosting revenue. This data provides a wealth of information about customer behavior, product popularity, and the overall health of your online store. Analyzing this data effectively allows for data-driven decision-making, leading to more targeted marketing campaigns and improved operational efficiency.
Types of Transactional Data in Commerce 9.1
Commerce 9.1 captures a wide array of transactional data. This includes information about individual transactions, such as order IDs, timestamps, customer IDs, product IDs, quantities purchased, prices, shipping addresses, payment methods, discounts applied, and any associated taxes. Beyond individual transactions, aggregated data provides insights into sales trends, popular products, average order value, and customer lifetime value. The system also logs data related to failed transactions, providing valuable information for troubleshooting and improving the checkout process.
Finally, detailed information on returns and refunds adds another layer of understanding to the overall customer experience.
Methods for Collecting and Storing Transactional Data
Commerce 9.1 utilizes a relational database system to collect and store transactional data. This data is typically captured in real-time as transactions occur, ensuring that the information is up-to-date and readily available for analysis. The database schema is designed to efficiently manage large volumes of data, allowing for quick retrieval and processing. The system often employs data warehousing techniques to consolidate data from various sources, creating a centralized repository for analysis.
This approach ensures data integrity and consistency across different analytical processes. Additionally, robust logging mechanisms ensure that all transactional events are recorded and stored securely.
Identifying Patterns and Trends Using Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics play a vital role in understanding the transactional data. Calculating metrics such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and percentiles allows for a comprehensive overview of key performance indicators (KPIs). For instance, analyzing the average order value over time can reveal seasonal trends or the impact of marketing campaigns. Similarly, examining the distribution of customer purchase frequencies can identify high-value customers and inform loyalty programs.
Visualizations like histograms and box plots are useful for representing this data and identifying outliers or unusual patterns. For example, a sudden spike in returns could indicate a problem with a specific product or a change in customer expectations.
Comparison of Transactional Data Analysis Techniques
Time series analysis is particularly useful for identifying trends and seasonality in transactional data. This technique allows for forecasting future sales based on historical patterns. For instance, analyzing past sales data for a particular product can help predict demand during the upcoming holiday season. Regression modeling, on the other hand, can be used to identify relationships between different variables.
For example, a regression model could be used to determine the relationship between marketing spend and sales revenue. While time series analysis focuses on the temporal aspect of the data, regression modeling explores the relationships between multiple variables, offering a broader perspective.
Common Transactional Data Analysis Techniques, Commerce 9 1 monitoring and metrics
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various techniques is key to effective analysis. Here are five common techniques:
- Cohort Analysis: Groups customers based on shared characteristics (e.g., signup date) to track behavior over time. Strength: Identifies trends specific to customer segments. Weakness: Requires sufficient data for meaningful segmentation.
- RFM Analysis (Recency, Frequency, Monetary Value): Segments customers based on their recent purchase, purchase frequency, and total spending. Strength: Simple yet effective for identifying high-value customers. Weakness: Doesn’t capture the full complexity of customer behavior.
- A/B Testing: Compares the performance of two different versions of a webpage or marketing campaign. Strength: Provides statistically significant results on the effectiveness of changes. Weakness: Requires careful experimental design and sufficient sample size.
- Market Basket Analysis: Identifies products frequently purchased together. Strength: Enables targeted product recommendations and promotions. Weakness: Assumes correlation implies causation.
- Time Series Decomposition: Separates a time series into its components (trend, seasonality, residuals). Strength: Allows for accurate forecasting and identification of seasonal patterns. Weakness: Can be complex to implement and interpret.
Troubleshooting and Optimization Based on Metrics
Understanding Commerce 9.1 metrics is crucial, but knowing how to use them for troubleshooting and optimization is even more vital. This section will delve into practical applications, showing how specific metrics pinpoint performance bottlenecks and guide optimization strategies to improve your Commerce 9.1 system’s efficiency and effectiveness. We’ll cover identifying problems, implementing solutions, and prioritizing efforts based on their impact on key business goals.
Identifying Performance Bottlenecks Through Metric Analysis
Analyzing Commerce 9.1 metrics reveals performance issues. High average order processing times, for example, indicate a problem within the order management system. A sharp increase in database query times points towards database performance issues, potentially due to inefficient queries or insufficient indexing. Similarly, a high error rate in specific API calls highlights problems within the integration layer.
By monitoring key metrics like page load times, conversion rates, and error rates, we can identify areas requiring attention. Analyzing trends over time provides further insight, allowing for proactive problem-solving before issues escalate. For instance, a gradual increase in average order processing time over several weeks might indicate a need for system scaling or code optimization.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Procedures
Let’s consider a scenario with consistently high average order processing times. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Identify the affected area: Detailed metric analysis pinpoints the bottleneck. Is it the payment gateway, inventory management, or order fulfillment? Specific error logs provide further clues.
- Isolate the cause: Once the affected area is identified, delve into the specifics. Are there specific product categories causing delays? Are certain payment methods slower than others? Thorough investigation is key.
- Gather relevant data: Collect data from various sources, including logs, databases, and monitoring tools. This provides a comprehensive picture of the issue.
- Implement a solution: Based on the root cause, implement a solution. This could involve code optimization, database tuning, or infrastructure upgrades. For example, if the bottleneck is in the database, optimizing queries or adding indexes can significantly improve performance.
- Monitor the results: After implementing a solution, closely monitor the relevant metrics to ensure the problem is resolved and performance has improved. Continuous monitoring prevents future issues.
Optimizing Commerce 9.1 Performance Based on Identified Issues
Optimization strategies depend on the identified issues. If database queries are slow, optimizing database indexes and queries is crucial. If the issue lies with slow API calls, improving API performance or optimizing the integration layer might be necessary. For high server response times, consider scaling the server infrastructure or optimizing the application code. In cases of low conversion rates, analyzing user behavior and website usability might lead to improvements in the user experience.
For instance, A/B testing different page layouts or checkout processes can identify areas for improvement.
Prioritizing Optimization Efforts Based on Business Objectives
Prioritizing optimization efforts involves assessing the impact on key business objectives. Focus on areas that significantly affect revenue, customer satisfaction, or operational efficiency. For example, improving checkout speed directly impacts conversion rates and revenue. Addressing issues that affect customer satisfaction, such as slow page load times or frequent errors, builds brand loyalty and reduces churn. Conversely, optimizing less critical aspects can be deferred to a later stage.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Troubleshooting and Optimization
This flowchart illustrates the decision-making process:
Prioritize optimizations impacting key metrics directly linked to revenue and customer satisfaction.
Continuously monitor metrics to identify emerging trends and proactively address potential issues.
Security Monitoring within Commerce 9.1
Securing your Commerce 9.1 environment is paramount. A robust security monitoring strategy is crucial not only for protecting sensitive customer data and financial transactions but also for maintaining the overall integrity and reputation of your business. This section will delve into the key aspects of security monitoring within the Commerce 9.1 platform, focusing on identifying vulnerabilities, implementing monitoring methods, and establishing best practices.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities in Commerce 9.1
Commerce 9.1, like any complex system, is susceptible to various security vulnerabilities. These can range from common web application vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) to more sophisticated attacks targeting system configurations or APIs. Specific vulnerabilities depend heavily on the system’s configuration, installed extensions, and the overall security posture of the surrounding infrastructure. For example, insufficient input validation can lead to SQL injection, allowing attackers to manipulate database queries.
Similarly, outdated software components can introduce known vulnerabilities that attackers actively exploit. Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital in identifying these weaknesses proactively.
Methods for Monitoring Security Vulnerabilities
Effective monitoring involves a multi-layered approach. This includes employing a web application firewall (WAF) to filter malicious traffic, implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor network activity for suspicious patterns, and leveraging security information and event management (SIEM) tools to aggregate and analyze security logs from various sources. Regular vulnerability scanning using automated tools is crucial for identifying known vulnerabilities in the system’s software and configurations.
Furthermore, proactive monitoring of system logs, both at the application and operating system levels, helps detect unusual activity that could indicate a security breach. Finally, real-time monitoring of critical system resources, such as CPU and memory usage, can reveal resource exhaustion attacks (DoS/DDoS).
Importance of Real-Time Security Monitoring
Real-time security monitoring in a Commerce 9.1 environment is non-negotiable. The immediate detection of security incidents minimizes the impact of attacks. Delayed detection can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Real-time monitoring allows for immediate response and mitigation, preventing data breaches, unauthorized access, and system compromise. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and reduces the overall cost associated with security incidents.
For example, immediate detection of a DDoS attack allows for swift mitigation strategies, preventing significant service disruptions.
Examples of Security Alerts and Remediation Steps
A SQL injection attempt detected by the WAF would trigger an alert indicating the source IP address, the attempted query, and the time of the event. Remediation would involve reviewing the application code for vulnerabilities, implementing parameterized queries, and potentially blocking the malicious IP address. An alert from the SIEM system showing unusual login attempts from multiple locations could indicate a credential stuffing attack.
The remediation steps would include implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), reviewing account access permissions, and potentially resetting compromised user credentials. A spike in error logs related to a specific API endpoint might indicate an attempt to exploit a vulnerability in that API. The remediation involves investigating the API for vulnerabilities, patching any identified flaws, and implementing rate limiting to prevent abuse.
Security Best Practices for Commerce 9.1
Implementing a robust security posture requires adherence to several best practices.
The following points Artikel key security best practices:
- Regularly update Commerce 9.1 and all associated software components to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Implement strong password policies and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts.
- Regularly back up your Commerce 9.1 system to ensure data recovery in case of a security incident.
- Utilize a web application firewall (WAF) to protect against common web application attacks.
- Implement robust input validation to prevent SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Monitor system logs and security alerts proactively to detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
- Train employees on security best practices and awareness to minimize the risk of human error.
- Establish an incident response plan to handle security incidents effectively and efficiently.
- Regularly review and update security policies and procedures to adapt to evolving threats.
Closure
Mastering Commerce 9.1 monitoring and metrics isn’t just about reacting to problems; it’s about proactively shaping your e-commerce success. By understanding the key metrics, analyzing transactional data, and implementing effective troubleshooting strategies, you gain a powerful advantage. Remember, data is your friend – use it wisely, and watch your business flourish. Happy monitoring!
FAQ Insights
What are the most common mistakes businesses make with Commerce 9.1 monitoring?
Failing to define clear KPIs, neglecting real-time monitoring, and not having a process for acting on the data are all common pitfalls.
How often should I review my Commerce 9.1 metrics?
Ideally, you should review key metrics daily, weekly, and monthly to identify trends and address issues promptly. The frequency depends on your business needs and the criticality of the metrics.
What if I don’t have a dedicated IT team? Can I still effectively monitor Commerce 9.1?
Yes! There are many user-friendly monitoring tools available that require minimal technical expertise. Consider outsourcing to a managed service provider if needed.
Are there any free tools available for Commerce 9.1 monitoring?
While many robust tools are paid, some free options offer basic monitoring capabilities. Look for open-source solutions or free tiers from established providers. However, be aware that free options may have limitations.
