Cyber Threat to Over 50,000 UK SMEs
Cyber threat to over 50000 uk smes – Cyber threat to over 50,000 UK SMEs is a chilling reality, not a distant threat. Imagine the domino effect – a single successful cyberattack crippling a large business, impacting its supply chain, and ultimately shaking the UK economy. This isn’t science fiction; it’s a very real and present danger facing thousands of UK businesses. We’ll dive into the specifics of the threats, the vulnerabilities they exploit, and – most importantly – how to protect your business.
This post will explore the five most common cyber threats targeting large UK SMEs, examining their vulnerabilities and the devastating consequences of a successful attack. We’ll look at real-world examples, explore effective protective measures, and discuss the legal and regulatory landscape. Get ready to arm yourself with the knowledge you need to safeguard your business.
Types of Cyber Threats Facing UK SMEs

The cyber landscape is increasingly perilous for businesses of all sizes, but UK SMEs, particularly those employing over 50,000 people, face unique challenges due to their often limited IT budgets and security expertise. Understanding the prevalent threats and their vulnerabilities is crucial for effective mitigation. This post will explore five key cyber threats targeting large UK SMEs and the significant consequences of successful attacks.
Five Prevalent Cyber Threats Targeting Large UK SMEs
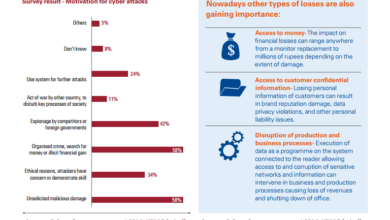
The five most common and impactful cyber threats targeting UK SMEs with significant employee numbers include phishing attacks, ransomware attacks, malware infections, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and data breaches resulting from inadequate security practices. These threats exploit various vulnerabilities, leading to substantial financial and reputational damage.
Vulnerabilities Exploited by Each Threat Type
- Phishing Attacks: These rely on social engineering, exploiting human error. Employees are tricked into clicking malicious links or downloading attachments containing malware, often disguised as legitimate communications from trusted sources. Vulnerabilities include insufficient employee training on phishing recognition and a lack of robust email security filters.
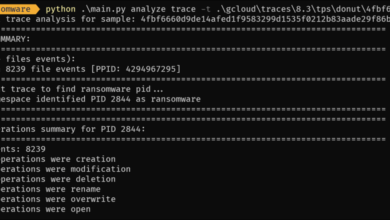
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware encrypts critical data, rendering it inaccessible unless a ransom is paid. Vulnerabilities include outdated software with unpatched security flaws, weak passwords, and a lack of regular data backups. Successful attacks can cripple operations.
- Malware Infections: Malware encompasses various malicious software, including viruses, worms, and trojans, that can damage systems, steal data, or disrupt operations. Vulnerabilities stem from inadequate endpoint protection, insufficient software updates, and unsecured network access.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: DoS attacks flood a target system with traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users. Vulnerabilities include insufficient network bandwidth and a lack of robust DDoS mitigation strategies. These attacks can severely impact business continuity.
- Data Breaches Due to Inadequate Security Practices: Weak security measures, such as inadequate access controls, poor password management, and lack of data encryption, create vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches. These breaches can expose sensitive customer information and intellectual property, resulting in legal and financial repercussions.
Comparison of Phishing and Ransomware Attacks
Phishing attacks often serve as a precursor to other attacks, such as ransomware. A successful phishing campaign might deliver malware that subsequently encrypts data, leading to a ransomware attack. While phishing exploits human error, ransomware exploits technical vulnerabilities. The impact on SME operations differs; phishing can lead to data theft or malware infection, while ransomware directly disrupts operations by encrypting critical data and demanding payment for its release.
Both, however, can severely damage reputation and cause significant financial losses.
Financial and Reputational Consequences of a Successful Cyberattack
The financial consequences of a successful cyberattack on a large SME can be devastating. This includes direct costs such as ransom payments (in the case of ransomware), incident response costs, legal fees, and regulatory fines. Indirect costs include lost revenue due to business disruption, damage to reputation, loss of customer trust, and potential legal action from affected customers.
For example, a data breach exposing customer data could lead to significant fines under GDPR regulations, costing millions of pounds and severely impacting the company’s reputation, potentially leading to customer churn and loss of future business. The reputational damage can be long-lasting, impacting the company’s ability to attract investors and partners.
Vulnerabilities of Large UK SMEs
Large UK SMEs, employing over 50,000 individuals, often face unique cybersecurity challenges due to their complex infrastructure and extensive data holdings. While benefiting from potentially larger budgets for security, these organizations frequently struggle to implement and maintain effective security practices across their sprawling operations, leaving them vulnerable to a range of sophisticated attacks. This often stems from a combination of factors including rapid growth, legacy systems, and a dispersed workforce.
Network Security Weaknesses
Inadequate network security is a significant vulnerability for large UK SMEs. The sheer scale of their networks, often encompassing multiple locations, diverse technologies, and numerous interconnected systems, creates a vast attack surface. Common weaknesses include insufficient network segmentation, outdated firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and a lack of robust network monitoring and logging capabilities. This allows attackers to easily move laterally within the network once an initial breach has occurred.
For example, a lack of proper segmentation could allow a compromised server in one department to access sensitive data in another.
Endpoint Security Deficiencies
Endpoint security, encompassing the protection of individual computers, laptops, mobile devices, and servers, is often overlooked or poorly implemented in large UK SMEs. This can involve inadequate endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, insufficient patch management practices, and a lack of employee training on safe computing practices. The use of outdated or unsupported operating systems and applications is also prevalent, creating easy entry points for malicious actors.
For instance, a failure to regularly patch software vulnerabilities can leave endpoints vulnerable to ransomware attacks.
Data Security Gaps
Protecting sensitive data is paramount, yet many large UK SMEs fall short in this area. Common data security weaknesses include insufficient data encryption, both in transit and at rest, inadequate access control mechanisms, and a lack of comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) strategies. The failure to properly classify and protect sensitive data leaves organizations vulnerable to data breaches and regulatory fines.
For example, a failure to encrypt sensitive customer data stored on cloud servers could lead to a significant data breach if those servers are compromised.
| Vulnerability | Impact | Mitigation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insufficient Network Segmentation | Lateral movement of attackers within the network, leading to wider data breaches. | Implement robust network segmentation using VLANs and firewalls. | A compromised server in the marketing department gaining access to financial data. |
| Outdated Firewalls | Inability to block modern threats, leading to successful intrusions. | Regularly update firewall firmware and rules, and consider next-generation firewalls (NGFWs). | Exploitation of known vulnerabilities in an outdated firewall leading to a successful breach. |
| Inadequate Patch Management | Exploitation of known software vulnerabilities, leading to malware infections and data breaches. | Implement a robust patch management system with automated patching and vulnerability scanning. | Ransomware infection due to an unpatched vulnerability in a widely used application. |
| Lack of Data Encryption | Exposure of sensitive data in case of a breach, leading to regulatory fines and reputational damage. | Encrypt sensitive data both in transit (using HTTPS) and at rest (using disk encryption). | Exposure of customer credit card details due to lack of encryption in a database. |
Impact on Business Operations
A significant cyberattack can cripple even a large SME, causing widespread disruption and potentially irreparable damage. The interconnected nature of modern business means that a single point of failure, such as compromised servers or stolen data, can have cascading effects throughout the entire operation. The impact extends far beyond immediate financial losses, affecting reputation, customer trust, and long-term sustainability.The disruption to daily operations can manifest in numerous ways.
Consider the immediate impact of a ransomware attack encrypting critical data: production halts, customer orders are delayed or cancelled, and internal communications are severely hampered. Beyond the immediate shutdown, the process of recovery – data restoration, system rebuilds, and regulatory compliance – can take weeks or even months, incurring significant costs and potentially losing valuable market share.
Real-World Cyberattack Consequences
Several high-profile cyberattacks on UK businesses illustrate the devastating consequences. For example, the 2017 NotPetya ransomware attack impacted global businesses, including several large UK firms. The attack, which spread rapidly through infected software, caused widespread operational disruption, data loss, and significant financial losses due to downtime and recovery efforts. Another example is the TalkTalk data breach in 2015, which exposed the personal data of millions of customers.
This resulted in significant reputational damage, regulatory fines, and substantial costs associated with improving security and notifying affected customers. These incidents demonstrate that even well-established businesses are vulnerable to significant cyberattacks and that the repercussions can be far-reaching and long-lasting.
Supply Chain Disruptions
A cyberattack on a large SME can create significant ripples throughout its supply chain. If a key supplier is compromised, it can lead to delays in the delivery of goods or services, impacting production schedules and potentially causing shortages. Conversely, if a large SME is attacked and its operations are disrupted, it can impact its own customers and suppliers, creating a chain reaction of disruptions.
For instance, a manufacturing SME that provides crucial components to a larger automotive company could halt the entire production line if its systems are compromised and its ability to deliver parts is affected. This highlights the interconnectedness of modern business and the potential for widespread disruption from a seemingly isolated incident.
Hypothetical Scenario: Cascading Effects
Imagine a large UK SME, “Acme Manufacturing,” specializing in precision engineering components for the aerospace industry. A sophisticated phishing attack compromises a senior employee’s email account, granting attackers access to the company’s internal network. The attackers deploy ransomware, encrypting critical design files, production schedules, and customer databases. Acme’s production immediately halts. Unable to fulfill orders, Acme loses contracts with key clients, impacting their revenue streams.
With over 50,000 UK SMEs facing crippling cyber threats, robust security is no longer optional. The increasing reliance on cloud services makes solutions like those offered by Bitglass crucial; check out this insightful article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management to understand how they work. Ultimately, strengthening cloud security is key to protecting these vulnerable businesses from devastating attacks.
Furthermore, the compromised data includes sensitive customer information and intellectual property, leading to potential legal liabilities and reputational damage. The disruption extends to Acme’s suppliers, who rely on consistent orders and face delays and potential losses due to Acme’s inability to meet its obligations. Down the supply chain, the aerospace manufacturer relying on Acme’s components experiences delays in its own production, potentially impacting delivery schedules and creating a domino effect of disruptions.
The entire incident highlights how a single cyberattack can have a far-reaching and devastating impact on multiple businesses and industries.
Protective Measures and Best Practices
Protecting your large UK SME from cyber threats requires a multi-layered approach encompassing technology, processes, and, crucially, your people. Investing in robust security measures isn’t just about mitigating risk; it’s about safeguarding your business’s future, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining customer trust. Ignoring cybersecurity best practices can lead to devastating financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
A proactive and comprehensive strategy is vital, incorporating regular security assessments, employee training, and a well-defined incident response plan. This proactive approach will not only protect against immediate threats but also help build a resilient cybersecurity posture for the long term.
Best Practices for Enhancing Cybersecurity Posture
Implementing these best practices will significantly strengthen your cybersecurity defenses and reduce your vulnerability to attacks. A layered approach, combining multiple security measures, is the most effective strategy.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify weaknesses in your systems and infrastructure before attackers do. This proactive approach allows for timely remediation of identified vulnerabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all user accounts, especially those with access to sensitive data. This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access even if they obtain passwords.
- Strong Password Policies and Password Management: Enforce strong password policies, including length, complexity, and regular changes. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage passwords for employees.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. This ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains unreadable to unauthorized individuals.
- Regular Software Updates and Patching: Maintain up-to-date software and operating systems across all devices and applications. Promptly apply security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation: Segment your network to isolate critical systems and data from less sensitive areas. This limits the impact of a breach by preventing attackers from easily moving laterally across your network.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP measures to prevent sensitive data from leaving your network without authorization. This includes monitoring email, file transfers, and other data transmission channels.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Use a SIEM system to collect and analyze security logs from various sources, enabling the detection of suspicious activities and potential security incidents.
- Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning: Regularly back up your data to a secure offsite location and develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of a cyberattack or other unforeseen event. This includes testing your backup and recovery procedures regularly.
The Importance of Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employees are often the weakest link in a company’s cybersecurity defenses. Phishing attacks, social engineering, and other forms of human error are responsible for a significant percentage of cyber breaches. Investing in comprehensive employee training programs is crucial to mitigating this risk.
Effective training programs should cover topics such as phishing awareness, password security, safe browsing habits, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities. Regular training sessions and simulated phishing attacks can help employees stay vigilant and recognize potential threats.
The Role of Robust Incident Response Planning
Even with the best preventative measures in place, cyberattacks can still occur. A well-defined incident response plan is essential for minimizing the impact of a breach and ensuring a swift and effective recovery. This plan should Artikel clear procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, recovering from, and learning from a security incident.
The plan should include designated roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and procedures for working with law enforcement and other relevant authorities. Regular testing and updates of the incident response plan are crucial to ensure its effectiveness.
Comparison of Cybersecurity Solutions
Several cybersecurity solutions are available to large UK SMEs, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right combination of solutions depends on your specific needs and resources.
- Firewalls: Act as the first line of defense, controlling network traffic and preventing unauthorized access. They can be hardware-based or software-based and range in complexity from basic to highly sophisticated.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Monitor network traffic for malicious activity, alerting administrators to potential threats or automatically blocking them. IDS passively monitors, while IPS actively blocks malicious traffic.
- Endpoint Protection: Provides security for individual devices (computers, laptops, mobile devices), protecting against malware, viruses, and other threats. This often includes antivirus software, anti-malware software, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities.
Choosing the right combination of these solutions requires careful consideration of factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the specific threats faced by your organization. It is often advisable to seek expert advice from a cybersecurity consultant to determine the most appropriate security architecture for your specific needs.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance

Navigating the legal landscape of cybersecurity can feel daunting for any business, but especially for SMEs juggling multiple priorities. Understanding and adhering to relevant regulations isn’t just about avoiding penalties; it’s about building trust with customers, protecting your business reputation, and ensuring long-term sustainability. Non-compliance can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage, far outweighing the cost of proactive compliance.
The UK has a robust legal framework designed to protect data and safeguard businesses from cyber threats. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in substantial fines, legal action, and damage to brand credibility. This section Artikels key regulations and their implications for SMEs.
Key UK Cybersecurity Regulations and Legal Frameworks
The UK’s legal framework surrounding cybersecurity is multifaceted, drawing from both domestic legislation and EU-derived regulations that remain applicable post-Brexit. Key regulations impacting SMEs include the UK GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), the Data Protection Act 2018, the Network and Information Systems (NIS) Regulations 2018, and the Computer Misuse Act 1990. These regulations cover various aspects of data protection, network security, and the handling of sensitive information.
Potential Legal Liabilities Following a Data Breach
A data breach can expose an SME to significant legal liabilities. Under the UK GDPR, organisations are obligated to report breaches to the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) within 72 hours. Failure to do so can result in substantial fines. Furthermore, affected individuals may pursue legal action for compensation due to the breach, leading to further financial and reputational damage.
The severity of the penalties depends on factors such as the nature of the data breached, the number of individuals affected, and the organisation’s preparedness and response to the incident. For example, a breach involving sensitive personal data, such as medical records or financial information, will likely attract more severe penalties than a breach involving less sensitive data.
Importance of Data Protection and Privacy in the Context of Cyber Threats
Data protection and privacy are paramount in mitigating the risks associated with cyber threats. The UK GDPR places a strong emphasis on the principle of data minimisation, requiring organisations to only collect and process the minimum amount of personal data necessary. Strong data protection measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, are crucial in preventing data breaches and ensuring compliance.
Furthermore, organisations must implement appropriate technical and organisational measures to protect personal data against unauthorised access, loss, alteration, or destruction. A robust data protection policy, coupled with employee training on data security best practices, is essential for mitigating risks and demonstrating compliance.
Key Regulations, Requirements, and Penalties, Cyber threat to over 50000 uk smes
| Regulation | Requirements | Penalties | Relevant SME Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| UK GDPR | Data protection by design and default; lawful basis for processing; data subject rights; notification of breaches; appropriate security measures. | Fines up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover (whichever is higher). | Implement a comprehensive data protection policy; conduct regular data protection impact assessments; provide employee training; appoint a Data Protection Officer (if required). |
| Data Protection Act 2018 | Compliance with UK GDPR; data security measures; processing of special category data; subject access requests. | Fines up to £17.5 million. | Ensure compliance with UK GDPR; implement appropriate technical and organisational measures; respond promptly to subject access requests. |
| NIS Regulations 2018 | Security risk management; incident reporting; cooperation with authorities. | Fines up to £17.5 million. | Develop and implement a cybersecurity risk management plan; report significant incidents to the relevant authorities; maintain accurate records of security incidents. |
| Computer Misuse Act 1990 | Prohibits unauthorized access to computer systems and data; prohibits unauthorized modification or deletion of data. | Up to 10 years imprisonment and/or unlimited fine. | Implement robust access controls; regularly update software and systems; educate employees on cyber security threats. |
Government Initiatives and Support
The UK government recognises the significant threat cyberattacks pose to SMEs and has implemented various initiatives to bolster their cybersecurity posture. These programs offer a range of resources, from financial assistance to practical guidance, aiming to equip businesses with the tools and knowledge necessary to defend against increasingly sophisticated threats. The level of support available reflects the government’s commitment to fostering a resilient digital economy.The government’s approach is multifaceted, combining direct financial support with access to expert advice and training.
This strategy acknowledges that improving cybersecurity isn’t solely about technological solutions; it also requires a cultural shift within businesses, promoting a proactive and informed approach to risk management.
Cybersecurity Resources and Tools for SMEs
Several resources and tools are available to help UK SMEs enhance their cyber resilience. These resources are designed to be accessible and practical, catering to businesses of varying sizes and technical capabilities. The government understands that a one-size-fits-all approach isn’t effective, and therefore provides a diverse range of options.
With over 50,000 UK SMEs facing crippling cyber threats, robust security is paramount. Building secure, scalable applications is crucial, and that’s where exploring options like domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes in. Investing in secure development practices, regardless of the approach, is the best defense against these increasing threats to UK businesses.
- The Cyber Essentials scheme: This government-backed scheme provides a clear and concise framework for improving basic cybersecurity. It involves a self-assessment and, optionally, certification, demonstrating a commitment to good cybersecurity practices to customers and partners. The scheme covers five key areas: boundary firewalls, secure configuration, access control, malware protection, and patch management.
- The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) website: The NCSC, a part of GCHQ, offers a wealth of free and readily accessible resources, including practical guidance, toolkits, and alerts. Their website is a valuable starting point for SMEs seeking to improve their cybersecurity. They offer advice on everything from password management to incident response.
- Cybersecurity skills training: Various government-funded programs and initiatives offer cybersecurity training and development opportunities for SME employees. This helps upskill staff and build internal expertise in managing cyber risks.
Accessing Cybersecurity Advice and Guidance
SMEs can access cybersecurity advice and guidance from various government agencies and programs. This support ranges from online resources to direct consultations with cybersecurity experts. The aim is to provide tailored support based on the specific needs and circumstances of each business.
- The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC): The NCSC provides direct support and guidance to SMEs through various channels, including their helpline and online resources. They offer tailored advice based on individual business needs and can assist with incident response in the event of a cyberattack.
- Local Growth Hubs: These hubs often provide access to local cybersecurity experts and support programs, offering a more localised and accessible point of contact for SMEs.
- Industry-specific advice: The government often works with industry bodies to provide tailored cybersecurity guidance for specific sectors, addressing the unique challenges faced by different types of businesses.
Final Wrap-Up
The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, but with the right knowledge and proactive measures, UK SMEs can significantly reduce their risk. Remember, prevention is far cheaper than the cure. By understanding the vulnerabilities, implementing robust security practices, and staying informed about the latest threats, you can protect your business, your reputation, and your bottom line. Don’t wait for a disaster to strike; take control of your cybersecurity today.
FAQ Explained: Cyber Threat To Over 50000 Uk Smes
What is the average cost of a cyberattack on a UK SME?
The cost varies wildly depending on the type of attack and the size of the business, but it can range from thousands to millions of pounds, including financial losses, legal fees, and reputational damage.
How can I report a cybercrime?
You should report cybercrimes to Action Fraud (the UK’s national reporting centre for fraud and cybercrime) and potentially involve the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) if a data breach has occurred.
What is the role of insurance in mitigating cyber risks?
Cyber insurance can help cover the costs associated with a cyberattack, such as data recovery, legal fees, and business interruption. It’s crucial to understand the policy’s coverage before purchasing.
Are there any free resources available to help UK SMEs improve their cybersecurity?
Yes, the UK government provides numerous free resources and guidance through organizations like the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC). Their website offers valuable advice and tools.