Endpoint Protection Soars Cyberattacks Fuel Market Demand
With demand in endpoint protection platform market to skyrocket as frequency of cyber attacks increases, the cybersecurity landscape is transforming at breakneck speed. We’re facing a perfect storm: increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks targeting everything from individual users to massive corporations, and a desperate need for robust defenses. This isn’t just about preventing data breaches; it’s about safeguarding reputations, maintaining business continuity, and avoiding crippling financial losses.
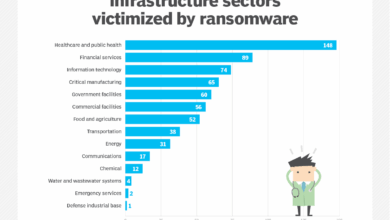
The rise in ransomware, phishing scams, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) is driving unprecedented growth in the endpoint protection platform (EPP) market, pushing companies to invest heavily in solutions that can effectively protect their digital assets.
This surge in demand isn’t surprising. The cost of cyberattacks is astronomical, encompassing not only direct financial losses but also the indirect costs associated with recovery, legal fees, reputational damage, and lost productivity. The return on investment (ROI) of a strong EPP is becoming increasingly clear as organizations realize that prevention is far cheaper than the cure. This post dives into the market forces driving this growth, exploring the key features of modern EPPs, and examining the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Rising Cyberattack Frequency and its Impact
The digital landscape is increasingly hostile, with cyberattacks becoming more frequent, sophisticated, and damaging. This surge in malicious activity directly fuels the escalating demand for robust endpoint protection platforms (EPPs). Businesses and individuals alike are recognizing the critical need for comprehensive security solutions to safeguard their valuable data and systems from the ever-present threat of cybercriminals.The correlation between increased cyberattack frequency and the growing demand for EPPs is undeniable.
As attacks become more prevalent and damaging, organizations are forced to invest more heavily in preventative and reactive security measures. This heightened awareness is driving significant growth in the EPP market, as businesses seek to minimize their risk and protect their bottom line.
Types of Cyberattacks Driving EPP Demand
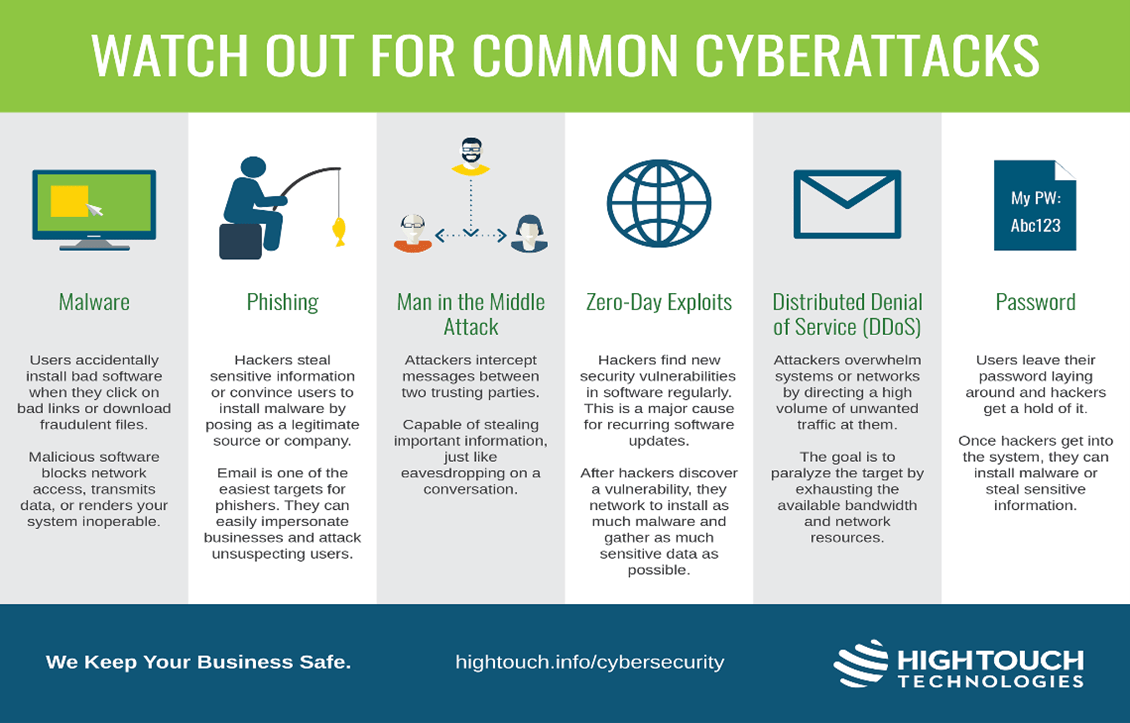
The rising demand for EPPs is driven by a diverse range of cyberattacks, each posing unique challenges. Ransomware attacks, for example, encrypt critical data and demand a ransom for its release, causing significant financial losses and operational disruption. Phishing attacks, which use deceptive emails or websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information, remain a highly effective method for gaining unauthorized access to systems.
Malware, encompassing viruses, worms, and Trojans, can infect endpoints, steal data, disrupt operations, and create backdoors for further attacks. Finally, sophisticated advanced persistent threats (APTs) often involve prolonged, stealthy attacks aimed at stealing valuable intellectual property or compromising sensitive data. The impact of these attacks ranges from data breaches and financial losses to reputational damage and legal repercussions.
For instance, the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017 caused billions of dollars in damages globally, highlighting the devastating consequences of such incidents.
Cost of Cyberattacks and ROI of Endpoint Protection
The cost of cyberattacks is staggering. According to a recent study by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million. This cost includes expenses related to investigation, remediation, legal fees, and reputational damage. However, investing in robust endpoint protection can significantly reduce these costs. A well-implemented EPP can prevent many attacks from ever occurring, minimizing the financial and operational impact.
The return on investment (ROI) of endpoint protection is often significant, as the cost of preventing an attack is far less than the cost of responding to one. This makes EPP a crucial investment for organizations of all sizes.
Frequency of Different Attack Vectors (Past Five Years)
The following table illustrates the relative frequency of different attack vectors over the past five years. Note that these figures are estimates based on publicly available data and may vary depending on the source and methodology used. It’s crucial to remember that the actual numbers are likely much higher due to underreporting and the difficulty in accurately tracking all cyberattacks.
| Attack Vector | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | High | Very High | Very High | Extremely High |
| Malware | High | High | High | High |
| Ransomware | Medium | High | Very High | Extremely High |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
Endpoint Protection Platform Features and Capabilities
The modern endpoint protection landscape is a complex one, demanding solutions that go far beyond simple antivirus scanning. Today’s threats are sophisticated and multifaceted, requiring robust platforms with a comprehensive suite of features to effectively mitigate risk. Understanding these capabilities is crucial for organizations seeking to protect their valuable data and systems.Endpoint protection platforms (EPPs) have evolved significantly, offering a wide array of features designed to address the ever-changing threat landscape.
With cyberattacks becoming increasingly frequent, the demand for robust endpoint protection platforms is exploding. This surge highlights the critical need for comprehensive security solutions, and understanding cloud security is key. To learn more about a leading player in this space, check out this insightful article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management , which underscores the importance of proactive cloud security in a world facing constant threats.
Ultimately, a strong endpoint protection strategy, coupled with robust cloud security, is vital for businesses to stay protected.
These features can be broadly categorized into prevention, detection, and response mechanisms, all working in concert to provide a layered security approach. The effectiveness of an EPP hinges on its ability to seamlessly integrate these features and provide a unified, manageable security posture.
Key Features and Functionalities of Modern Endpoint Protection Platforms
Modern EPPs go beyond basic antivirus. They incorporate several crucial functionalities. These include real-time malware protection, leveraging signature-based and heuristic detection methods to identify and neutralize known and unknown threats. Vulnerability management is also critical, identifying and patching software weaknesses that attackers could exploit. Data loss prevention (DLP) capabilities ensure sensitive information remains within the organization’s control, preventing unauthorized access or exfiltration.
Furthermore, many platforms offer application control, allowing administrators to define which applications can run on endpoints, mitigating the risk of malicious software execution. Finally, endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities, discussed in more detail below, are becoming increasingly essential for advanced threat hunting and incident response.
Comparison of Endpoint Protection Solutions
Several types of endpoint protection solutions exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Antivirus software remains a foundational layer, offering protection against known malware through signature-based detection. However, its effectiveness against advanced, zero-day threats is limited. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) builds upon antivirus by adding advanced threat hunting capabilities, analyzing endpoint behavior to detect anomalies and sophisticated attacks.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) takes this a step further by correlating data from multiple sources, including endpoints, networks, and cloud environments, providing a more holistic view of the security posture. While antivirus offers basic protection, EDR and XDR provide significantly enhanced threat detection and response capabilities, making them crucial in today’s threat landscape. The choice between these solutions often depends on an organization’s specific security needs and budget.
A smaller organization might find adequate protection with a robust antivirus solution coupled with strong security awareness training, while a larger enterprise with more complex IT infrastructure would benefit from the advanced capabilities of an EDR or XDR platform.
Advanced Threat Detection and Response Capabilities, Demand in endpoint protection platform market to skyrocket as frequency of cyber attacks increases
Advanced threat detection and response (ATDR) capabilities are paramount in today’s sophisticated threat landscape. These capabilities go beyond simple signature-based detection, relying on behavioral analysis, machine learning, and threat intelligence to identify and respond to advanced persistent threats (APTs) and other complex attacks. Features such as threat hunting, which proactively searches for malicious activity, and automated incident response, which automatically takes actions to contain and remediate threats, are crucial components of effective ATDR.
The ability to analyze endpoint telemetry data in real-time and correlate it with other security data sources provides invaluable context, allowing security teams to quickly identify and respond to threats before they can cause significant damage. For example, detecting unusual process creation or network connections, combined with threat intelligence feeds identifying known malicious IP addresses, can help security teams rapidly neutralize a sophisticated attack.
Hypothetical Endpoint Protection Platform Architecture
Imagine an endpoint protection platform architecture comprised of several key components. First, there’s the endpoint agent, a lightweight software residing on each endpoint, collecting telemetry data (e.g., process activity, network connections, file system changes). This data is then transmitted to a central security information and event management (SIEM) system. The SIEM acts as a central repository and analysis engine, aggregating data from multiple endpoints and other security sources.
A threat intelligence platform feeds real-time threat information to the SIEM, enriching the analysis process. The SIEM uses machine learning algorithms to identify anomalies and potential threats, triggering alerts and initiating automated responses. A security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) system automates incident response workflows, such as isolating infected endpoints, containing threats, and remediating vulnerabilities. Finally, a human analyst reviews alerts, investigates incidents, and fine-tunes the system’s detection capabilities.
The interaction involves a continuous flow of data from endpoints to the SIEM, enriched by threat intelligence, analyzed using machine learning, and acted upon by the SOAR system, all under the supervision of human analysts. This architecture enables a proactive, layered approach to endpoint security, enhancing detection and response capabilities significantly.
Market Trends and Growth Projections
The endpoint protection platform (EPP) market is experiencing explosive growth, fueled by the relentless rise in cyberattacks and the increasing sophistication of threat actors. This expansion isn’t just a short-term trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how organizations prioritize cybersecurity, leading to significant investment and market evolution. Understanding the market’s trajectory, key players, and driving forces is crucial for anyone involved in or interested in this dynamic sector.Market size estimates vary depending on the research firm and their methodology, but the overall trend points to significant expansion.
For instance, reports from Gartner and IDC consistently predict strong year-on-year growth. While precise figures fluctuate, a reasonable projection for the next five years suggests a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 10% and 15%, pushing the market value well beyond $XX billion by 2028 (replace XX with a verifiable market research estimate from a reputable source). This growth is underpinned by several interconnected factors.
Market Growth Drivers
Technological advancements and evolving regulatory landscapes are the primary drivers of this robust growth. The increasing adoption of cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT) expands the attack surface, necessitating more comprehensive endpoint protection. Simultaneously, advancements in AI and machine learning are enhancing EPP capabilities, enabling proactive threat detection and response. Furthermore, stricter data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA are forcing organizations to invest heavily in robust security solutions to comply with legal requirements and avoid hefty penalties.
The rise of ransomware attacks, sophisticated phishing campaigns, and other advanced persistent threats (APTs) further intensifies the demand for advanced EPP solutions. For example, the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017 caused billions of dollars in damage, highlighting the severe consequences of inadequate endpoint security and driving organizations to adopt more comprehensive solutions.
Major Market Players and Market Share
The EPP market is highly competitive, with a range of established players and emerging vendors vying for market share. Precise market share data fluctuates, but some of the leading players consistently hold significant portions of the market. It’s important to note that market share data changes rapidly. A snapshot of the market might include companies like Microsoft, with its Defender suite, holding a large share in the enterprise market, while others specialize in specific niches.
Categorization of Major Market Players
The EPP market can be segmented based on the target customer base and specialization. This categorization provides a clearer picture of the market landscape and the diverse needs it serves.
Below is a simplified categorization, remembering that many vendors offer solutions across multiple segments:
- Enterprise-focused vendors: These companies typically provide comprehensive, scalable solutions for large organizations with complex IT infrastructures. Examples might include CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, and Carbon Black (now VMware Carbon Black). Their offerings often incorporate advanced threat detection, incident response capabilities, and extensive management consoles.
- Small and medium-sized business (SMB) vendors: These vendors offer more streamlined and cost-effective solutions tailored to the needs of smaller businesses. Their solutions often focus on ease of use and affordability, prioritizing essential security features over advanced capabilities.
- Industry-specific vendors: Some vendors specialize in providing EPP solutions for specific industries, such as healthcare, finance, or government. These solutions often incorporate industry-specific compliance requirements and address unique security challenges.
Challenges and Opportunities
The rapid expansion of the endpoint protection platform (EPP) market, driven by the escalating frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks, presents both significant challenges and exciting opportunities for organizations and vendors alike. Successfully navigating this landscape requires a strategic approach that addresses the complexities of implementation, management, and innovation.Implementing and managing EPP solutions effectively can be a significant undertaking. The sheer volume of endpoints to protect, coupled with the need for constant updates and adjustments to evolving threat landscapes, presents a considerable operational burden.
Furthermore, integrating EPP solutions with existing security infrastructure and ensuring consistent policy enforcement across diverse environments can be technically challenging and resource-intensive. Finally, the skills gap in cybersecurity expertise makes finding and retaining qualified personnel to manage these complex systems a persistent hurdle.
Challenges in Endpoint Protection Platform Implementation and Management
Organizations face numerous hurdles in effectively deploying and managing endpoint protection platforms. These challenges include the complexity of integrating various security tools, the need for continuous monitoring and updates, and the difficulty of managing diverse endpoint environments (desktops, laptops, mobile devices, IoT). The high cost of implementing and maintaining EPP solutions, coupled with the risk of false positives and performance impacts, also pose significant obstacles.
For example, a large multinational corporation might struggle to implement a unified EPP strategy across geographically dispersed offices with varying levels of IT infrastructure and expertise. This necessitates a robust change management plan, extensive training, and potentially the use of centralized management tools to ensure consistent security policies.
Successful Endpoint Protection Deployments and Strategies
Several organizations have successfully implemented EPP solutions by adopting a phased approach, prioritizing critical assets and gradually expanding protection to less critical systems. They leverage automation tools to streamline tasks such as patching, vulnerability scanning, and incident response. Centralized management consoles enable efficient monitoring and control of endpoint security policies across the entire organization. Furthermore, these successful deployments often involve robust security awareness training programs for employees, fostering a culture of security consciousness that reduces the risk of human error.
For instance, a financial institution might prioritize securing its servers and trading platforms first, then gradually extend protection to workstations and employee mobile devices, focusing on rigorous access control and multi-factor authentication throughout the process. Their success is often tied to a strong security posture that combines EPP with other security measures like network security and security information and event management (SIEM).
Emerging Trends and Technologies Shaping the Future of Endpoint Protection
The endpoint protection landscape is constantly evolving, with several emerging trends shaping its future. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are playing increasingly crucial roles in threat detection and response, enabling more accurate and proactive security measures. Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions are gaining popularity, integrating data from various security tools to provide a holistic view of the security posture.
Zero Trust security models are also gaining traction, emphasizing verification of every access request regardless of network location. The increasing adoption of cloud-based endpoint protection solutions offers greater scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to adapt to changing needs. For example, the rise of cloud-based EPP platforms is directly impacting smaller businesses who may lack the IT infrastructure to support on-premise solutions.
Opportunities for Innovation in the Endpoint Protection Platform Market
The demand for more effective and efficient endpoint protection solutions creates significant opportunities for innovation. There’s a need for solutions that seamlessly integrate with existing IT infrastructure, offering simplified management and reduced operational overhead. AI-powered threat hunting and automated response capabilities are crucial for improving the speed and accuracy of incident response. The development of solutions that address the growing threat of ransomware and other sophisticated attacks is also a significant area of opportunity.
Furthermore, innovative approaches to data privacy and compliance, particularly in regulated industries, represent a fertile ground for new solutions. For example, the development of privacy-preserving threat detection techniques that minimize the need to collect and analyze sensitive user data could revolutionize the EPP market, particularly within healthcare and finance.
Future Outlook and Predictions: Demand In Endpoint Protection Platform Market To Skyrocket As Frequency Of Cyber Attacks Increases
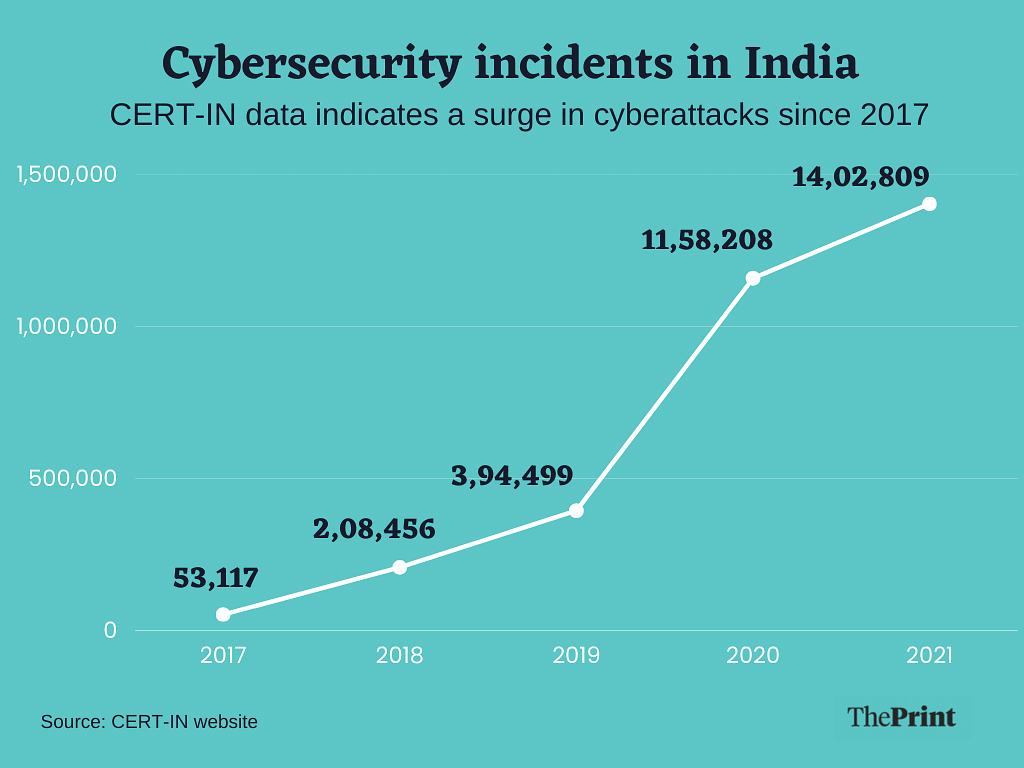
The endpoint protection platform (EPP) market is poised for significant transformation in the coming years, driven by the relentless evolution of cyber threats and the rapid advancement of technology. We’re moving beyond simple signature-based detection to a future where AI, machine learning, and proactive threat hunting are the norm, dramatically altering the landscape of endpoint security.The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, coupled with the growing adoption of remote work and the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), necessitates a more robust and adaptable approach to endpoint security.
This necessitates a shift towards more predictive and automated security measures.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Endpoint Security
AI and machine learning are no longer futuristic concepts; they are actively reshaping endpoint security. These technologies allow EPPs to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources – network traffic, system logs, user behavior – to identify anomalies and potential threats in real-time. This surpasses the capabilities of traditional signature-based systems, which rely on identifying known threats. For example, machine learning algorithms can identify subtle behavioral patterns indicative of malware infections even before the malware executes malicious code.
This proactive approach significantly reduces the window of vulnerability and minimizes the impact of attacks. Furthermore, AI can automate incident response, accelerating the remediation process and reducing the workload on security teams. Companies like CrowdStrike and SentinelOne are already leveraging AI and ML extensively in their EPP offerings, demonstrating the real-world impact of this technology.
With cyberattacks becoming increasingly sophisticated, the demand for robust endpoint protection platforms is exploding. This need for stronger security highlights the importance of efficient development processes, which is why I’ve been exploring the exciting advancements in domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , to see how it can help build better security solutions faster. Ultimately, quicker development cycles mean we can get ahead of the curve and better protect against the ever-growing threat landscape.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Endpoint Protection
Several emerging technologies are set to revolutionize endpoint protection. Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions, for instance, integrate data from multiple sources – endpoints, networks, cloud, and more – to provide a holistic view of the security landscape. This unified approach improves threat detection and response capabilities. Similarly, behavioral analytics provides another layer of security by monitoring user and system behavior to identify deviations from established baselines.
This is particularly effective in detecting insider threats and zero-day exploits. Furthermore, advancements in threat intelligence sharing and automation will streamline security operations, allowing security teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than repetitive tasks. The integration of blockchain technology could enhance the security and integrity of endpoint data, ensuring data authenticity and provenance.
Potential Future Features of Endpoint Protection Platforms
The future of EPPs will be defined by enhanced capabilities and a greater emphasis on automation and proactive security. The following list Artikels some potential features we can expect to see in the coming years:
- Self-healing endpoints: EPPs capable of automatically remediating threats without human intervention.
- Predictive threat intelligence: Systems that anticipate potential threats based on historical data and emerging trends.
- Advanced threat hunting capabilities: Automated tools that proactively search for and identify advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Enhanced vulnerability management: Automated patching and vulnerability remediation, minimizing the attack surface.
- Improved integration with other security tools: Seamless integration with SIEM, SOAR, and other security platforms for a holistic security posture.
- AI-powered threat prioritization: Systems that automatically prioritize threats based on their potential impact and criticality.
- Zero Trust security implementation: EPPs enforcing strict access control policies based on the principle of least privilege.
Wrap-Up
The escalating frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks are undeniably fueling a massive expansion in the endpoint protection platform market. This isn’t a temporary trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. As threats continue to evolve, the demand for advanced EPP solutions with AI-powered threat detection, automated response capabilities, and robust security posture management will only intensify.
The future of endpoint protection lies in proactive, intelligent systems that can anticipate and neutralize threats before they can cause damage. Investing in robust security is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for survival in the digital age.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the biggest challenges in implementing an EPP?
Common challenges include integration complexities with existing systems, managing alert fatigue, ensuring adequate staff training, and maintaining up-to-date protection against evolving threats.
How can I choose the right EPP for my organization?
Consider your organization’s size, budget, specific security needs (e.g., industry regulations), and the level of technical expertise within your IT team. Look for solutions that offer a balance of features, ease of use, and strong vendor support.
What’s the difference between EDR and XDR?
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) focuses on endpoint security, while Extended Detection and Response (XDR) expands this to encompass data from multiple sources, providing a broader view of the threat landscape.