
Whitepaper Global CDPs Shaping Customer Data Insights
Whitepaper global how cdps are shaping customer data insights worldwide – Whitepaper: Global CDPs Shaping Customer Data Insights dives headfirst into the exciting world of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs). Forget siloed data; we’re talking about a unified view of your customer, allowing for hyper-personalized experiences and smarter business decisions. This whitepaper explores the current global CDP landscape, highlighting key players, different CDP types, and the impact on various industries.
We’ll unpack how CDPs improve data quality, create a 360-degree customer view, and even tackle the crucial aspects of data privacy and security in this rapidly evolving market. Get ready to uncover how CDPs are transforming the way businesses understand and engage with their customers worldwide.
We’ll delve into real-world examples of successful CDP implementations across sectors like retail, finance, and healthcare, showcasing the unique challenges and opportunities each industry faces. From comparing leading CDPs and their features to predicting future trends in CDP technology, this whitepaper is your go-to guide for navigating the world of customer data intelligence.
Introduction: Global CDP Landscape
The global Customer Data Platform (CDP) market is experiencing explosive growth, driven by the increasing need for businesses to understand and leverage their customer data effectively. This surge is fueled by the rising volume of data generated from various sources, the growing demand for personalized customer experiences, and the imperative to improve marketing ROI. The market is characterized by a diverse range of vendors, offering solutions tailored to different business needs and scales.
Competition is fierce, with established players and innovative startups vying for market share.The current market is dominated by a few key players, although precise market share figures fluctuate depending on the research firm and methodology. However, companies like Adobe, Salesforce, Segment, and Tealium consistently rank among the leaders, each holding a significant portion of the market. Their dominance stems from their comprehensive feature sets, strong brand recognition, and extensive partner ecosystems.
Beyond these major players, a vibrant ecosystem of smaller, specialized CDPs caters to niche markets and specific industry requirements.
Types of CDPs
CDPs are available in various deployment models, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. Cloud-based CDPs are the most prevalent, offering scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. They are ideal for businesses of all sizes, particularly those with rapidly changing data needs. On-premise CDPs, on the other hand, provide greater control over data security and compliance, but they require significant upfront investment and ongoing IT maintenance.
Hybrid models, combining aspects of both cloud and on-premise solutions, are also gaining traction, offering flexibility and customized control. Furthermore, there are variations in the functionalities offered. Some CDPs are more focused on marketing automation, while others provide a more comprehensive view of the customer, integrating data from various touchpoints across the customer journey.
Comparison of Leading CDPs
The following table compares four leading CDPs, highlighting their key features, pricing models, and target customer segments. Note that pricing can vary significantly based on specific configurations and usage.
| CDP | Key Features | Pricing Model | Target Customer Segment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Experience Platform | Comprehensive customer data integration, real-time personalization, robust analytics, extensive integrations with Adobe’s marketing cloud. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Large enterprises with complex marketing needs |
| Salesforce Marketing Cloud | Strong integration with Salesforce ecosystem, robust automation capabilities, personalized journeys, advanced analytics. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Businesses using Salesforce CRM, ranging from mid-market to enterprise |
| Segment | Focus on data collection and unification, supports various data sources, flexible integrations, relatively easy to implement. | Usage-based pricing, tiered plans | Businesses of all sizes, particularly those needing a scalable solution |
| Tealium Customer Data Hub | Emphasis on real-time data integration, flexible data orchestration, strong focus on data governance and compliance. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Businesses with complex data needs and a focus on data security and privacy |
How CDPs Shape Customer Data Insights
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are revolutionizing how businesses understand and interact with their customers. By consolidating data from various sources and providing a unified view, CDPs empower organizations to make more informed decisions, personalize customer experiences, and ultimately, drive business growth. This section will delve into the specific ways CDPs enhance customer data insights.
CDPs dramatically improve data collection and unification by acting as a central hub for all customer data. Instead of data residing in disparate silos – marketing automation tools, CRM systems, website analytics, e-commerce platforms, and more – a CDP ingests and harmonizes this information, creating a single, unified customer profile. This eliminates the need for manual data integration and reconciliation, a process that is often time-consuming, error-prone, and costly.
Data Quality and Accuracy Enhancement
One of the key benefits of CDPs is their ability to cleanse and standardize data, resulting in significantly improved quality and accuracy. CDPs employ various techniques, such as deduplication, data matching, and data enrichment, to ensure data consistency and reliability. For example, a CDP might identify and merge duplicate customer records from different sources, resolving discrepancies in names, addresses, or email addresses.
It might also enrich existing data by adding information from external sources, such as demographic data or purchase history, creating a more complete and accurate customer profile. This enhanced data quality leads to more reliable insights and more effective marketing campaigns.
Creation of a Single Customer View
The core function of a CDP is to create a single, unified view of each customer. This 360-degree view consolidates all relevant customer data from various touchpoints into a single profile, providing a comprehensive understanding of individual customer behavior, preferences, and interactions. Imagine a customer who interacts with a company through its website, mobile app, and email marketing campaigns.
A CDP would integrate all this data, revealing a holistic picture of the customer’s journey, allowing businesses to understand their needs and preferences much better than relying on fragmented data sources. This holistic view is crucial for effective personalization and targeted marketing.
Facilitation of Personalized Customer Experiences
With a unified and accurate view of each customer, CDPs enable businesses to deliver highly personalized experiences. By leveraging customer data insights, organizations can tailor their messaging, offers, and product recommendations to individual customer needs and preferences. For instance, a retailer might use a CDP to identify customers who have recently viewed specific products and send them targeted email promotions with discounts or special offers.
A streaming service might utilize a CDP to recommend shows and movies based on a user’s viewing history and preferences. This level of personalization enhances customer engagement, improves satisfaction, and ultimately drives loyalty and increased revenue. The ability to create highly targeted and personalized experiences is a significant competitive advantage in today’s market.
CDP Impact on Specific Industries
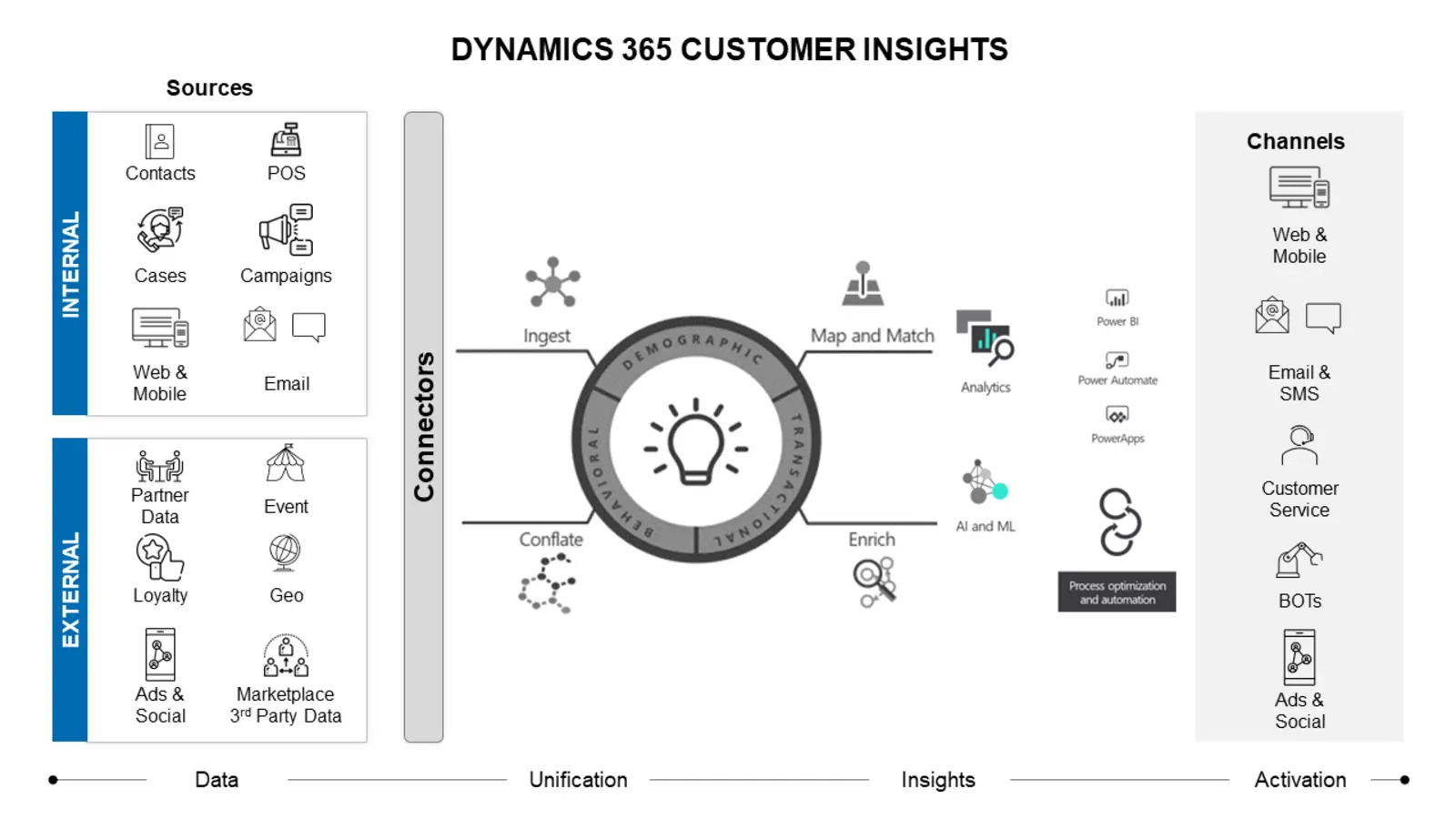
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are revolutionizing how businesses understand and interact with their customers, but their impact varies significantly across different sectors. The unique challenges and opportunities presented by a CDP depend heavily on the industry’s data landscape, regulatory environment, and customer expectations. This section explores the specific applications and implications of CDPs in several key industries.
CDP Implementation in Retail, Whitepaper global how cdps are shaping customer data insights worldwide
The retail industry has been an early adopter of CDPs, leveraging them to personalize the customer journey, optimize marketing campaigns, and improve customer retention. Successful implementations often involve integrating data from various sources – point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, loyalty programs, and social media – to create a unified customer profile. This allows retailers to deliver targeted promotions, personalized product recommendations, and customized email campaigns.
For example, a major clothing retailer might use a CDP to identify customers who frequently purchase a specific type of clothing and then target them with exclusive offers on similar items or new arrivals in that category. This targeted approach leads to increased conversion rates and improved customer lifetime value.
Challenges in the retail sector include data privacy concerns, the need for robust data governance, and the complexity of integrating disparate data systems. Opportunities lie in creating hyper-personalized experiences, improving customer service through proactive support, and optimizing inventory management based on real-time demand insights.
Hypothetical CDP Implementation for a Small Retail Business: A small, independent bookstore could use a CDP to track customer purchases, preferences (e.g., genre, author), and engagement with email marketing. This data could be used to personalize recommendations, offer targeted discounts on related books, and segment customers for more effective marketing campaigns. For instance, customers who frequently buy science fiction could receive emails about new releases in that genre, increasing the likelihood of a sale.
Benefits and Drawbacks of CDP Adoption in Retail:
- Benefits: Increased sales conversion, improved customer loyalty, enhanced personalization, better inventory management, targeted marketing campaigns.
- Drawbacks: High initial investment costs, complexity of implementation, data privacy concerns, need for skilled personnel.
CDP Implementation in Finance
The financial services industry faces stringent regulatory requirements and a strong emphasis on data security. CDPs help financial institutions comply with regulations while simultaneously enhancing customer experiences. By consolidating customer data from various banking systems, loan applications, and investment accounts, financial institutions can gain a 360-degree view of each customer. This allows for more accurate risk assessment, personalized financial advice, and proactive fraud detection.
A successful example might involve a bank using a CDP to identify customers at risk of churning and proactively offering them tailored retention offers.
Challenges include stringent data security and privacy regulations (like GDPR and CCPA), the need for robust data governance, and the complexity of integrating legacy systems. Opportunities exist in personalized financial planning, improved fraud detection, and enhanced customer service through proactive risk management and tailored financial advice.
Hypothetical CDP Implementation for a Small Financial Institution: A small credit union could use a CDP to analyze member transaction history, loan applications, and customer service interactions to identify members who might benefit from financial literacy programs or personalized financial advice. This proactive approach could improve member satisfaction and loyalty.
Benefits and Drawbacks of CDP Adoption in Finance:
- Benefits: Improved risk management, personalized financial advice, enhanced fraud detection, increased customer loyalty, better regulatory compliance.
- Drawbacks: High security and compliance costs, data privacy concerns, integration challenges with legacy systems.
CDP Implementation in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is characterized by complex data regulations (HIPAA) and a focus on patient privacy. CDPs in healthcare can help streamline patient care, improve operational efficiency, and personalize patient experiences while adhering to strict data privacy regulations. For example, a hospital system could use a CDP to integrate patient data from electronic health records, medical devices, and patient portals to provide a comprehensive view of each patient’s health history.
This allows for better diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and proactive health management.
Challenges include strict data privacy regulations (HIPAA), data security concerns, and the need for interoperability between different healthcare systems. Opportunities exist in personalized medicine, improved patient engagement, enhanced operational efficiency, and proactive disease management.
Hypothetical CDP Implementation for a Small Healthcare Provider: A small medical clinic could use a CDP to consolidate patient data from various sources, enabling them to send personalized appointment reminders, provide tailored health education materials, and proactively reach out to patients about preventative care based on their individual health profiles.
Benefits and Drawbacks of CDP Adoption in Healthcare:
- Benefits: Improved patient care, enhanced patient engagement, better operational efficiency, proactive disease management, better compliance with regulations.
- Drawbacks: High costs associated with security and compliance, integration challenges with legacy systems, stringent data privacy regulations.
Data Privacy and Security with CDPs

Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) offer unparalleled opportunities for businesses to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs. However, the increasing volume and sensitivity of data collected and processed by CDPs necessitate a robust approach to data privacy and security, especially in light of stringent global regulations. Ignoring these crucial aspects can lead to significant legal repercussions, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.The implementation of a CDP must be carefully planned and executed with data privacy and security at its core.
This requires a deep understanding of relevant regulations and the adoption of best practices to mitigate potential risks.
Data Privacy Regulations and CDP Implementation
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, along with other similar regulations worldwide, significantly impact how organizations can collect, store, and use personal data. These regulations grant individuals greater control over their data and impose strict obligations on companies regarding data processing. CDP implementation must be fully compliant with these laws, requiring careful consideration of data minimization, purpose limitation, data subject rights (access, rectification, erasure), and data security measures.
For example, a company implementing a CDP must ensure it has a lawful basis for processing personal data under GDPR, such as consent or legitimate interests, and must be able to demonstrate compliance to data protection authorities. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal action.
Best Practices for Data Security and Compliance within a CDP Environment
Robust data security is paramount when utilizing a CDP. This involves implementing a multi-layered security approach that encompasses technical, administrative, and physical safeguards. Technical safeguards include encryption of data both in transit and at rest, access control measures (role-based access control or RBAC is highly recommended), and regular security audits. Administrative safeguards include comprehensive data governance policies, employee training programs on data privacy and security best practices, and incident response plans.
Physical safeguards involve securing the physical location where the CDP is hosted and protecting the hardware from unauthorized access. Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments are also crucial to identify and address security weaknesses proactively.
Potential Risks Associated with Data Breaches and Mitigation Strategies
Data breaches can have devastating consequences for businesses, including financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities, and loss of customer trust. Potential risks associated with CDP data breaches include unauthorized access to sensitive customer data, identity theft, financial fraud, and regulatory penalties. Mitigation strategies include implementing robust access control mechanisms, employing strong encryption, regularly updating software and security patches, and conducting regular security awareness training for employees.
A comprehensive incident response plan should be in place to quickly contain and mitigate the impact of a data breach should one occur. This plan should include procedures for notifying affected individuals and regulatory authorities. Furthermore, investing in robust data loss prevention (DLP) tools can help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
Data Governance Procedures for a CDP: A Step-by-Step Guide
Establishing a comprehensive data governance framework is essential for ensuring data privacy and security within a CDP environment. This framework should encompass the following steps:
- Data Inventory and Mapping: A complete inventory of all data collected, processed, and stored within the CDP, along with a clear mapping of data flows, is crucial. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of data handling processes.
- Data Classification and Categorization: Data should be classified according to its sensitivity and criticality. This helps determine the appropriate level of security controls to be implemented.
- Policy Development and Implementation: Develop and implement clear data governance policies that address data collection, storage, processing, access, retention, and disposal. These policies must align with relevant data privacy regulations.
- Data Access Control: Implement robust access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), to restrict access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel.
- Data Retention and Disposal: Establish clear guidelines for data retention periods and secure data disposal procedures to ensure compliance with regulations and minimize risks.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly monitor the CDP environment for security vulnerabilities and compliance issues. Conduct periodic audits to verify the effectiveness of data governance procedures.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to effectively manage and mitigate data breaches or security incidents.
Future Trends in Global CDP Adoption
The global CDP market is experiencing explosive growth, driven by the increasing need for businesses to understand and leverage their customer data effectively. This isn’t just about collecting data; it’s about harnessing its power for personalized experiences, improved marketing ROI, and enhanced customer loyalty. Looking ahead, several key trends will shape the future of CDP adoption worldwide, impacting how businesses interact with their customers and navigate the ever-evolving data landscape.The convergence of advanced analytics, AI, and evolving privacy regulations will fundamentally alter the capabilities and applications of CDPs.
We’re moving beyond simple data aggregation towards a future where CDPs become intelligent platforms, proactively identifying customer insights and optimizing marketing strategies in real-time. This shift will require businesses to adapt their data strategies and invest in the necessary infrastructure and expertise to fully utilize these advanced functionalities.
AI-Powered Insights and Predictive Analytics
AI and machine learning are rapidly transforming CDP capabilities. We’re seeing a move beyond descriptive analytics (what happened?) and diagnostic analytics (why did it happen?) towards predictive analytics (what will happen?) and prescriptive analytics (what should we do?). For example, a retailer using a CDP with integrated AI could predict which customers are likely to churn based on their purchase history and browsing behavior, allowing proactive intervention through targeted offers or personalized support.
This predictive capability allows for more efficient resource allocation and improved customer retention. Furthermore, AI can automate tasks such as data cleansing and segmentation, freeing up marketers to focus on strategic initiatives.
Real-Time Personalization and Omnichannel Experiences
Real-time personalization is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a rapidly growing expectation among consumers. CDPs are at the heart of enabling this. By unifying customer data across all touchpoints, CDPs allow businesses to deliver personalized experiences in real-time, whether it’s a tailored product recommendation on a website, a personalized email based on recent browsing activity, or a customized in-app message.
Imagine a travel company using a CDP to instantly adjust flight recommendations based on a customer’s real-time location and search history, offering a truly seamless and personalized experience. This omnichannel approach, fueled by real-time data insights from the CDP, is crucial for building strong customer relationships in today’s digital landscape.
Enhanced Data Privacy and Security Features
As data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA become increasingly stringent, CDPs will need to integrate robust security and privacy features. This includes incorporating advanced encryption techniques, providing granular data access controls, and ensuring compliance with evolving privacy standards. We’ll see CDPs incorporating features like differential privacy and federated learning, which allow for the analysis of sensitive data without compromising individual privacy.
A strong focus on data governance and transparency will be crucial for maintaining customer trust and avoiding regulatory penalties.
Increased Integration with Other Martech Tools
The future of CDPs lies in their ability to seamlessly integrate with other marketing technology (Martech) tools. This will create a more unified and efficient marketing ecosystem. We’ll see greater interoperability between CDPs and tools like CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and analytics dashboards. This interconnectedness will allow for a more holistic view of the customer journey and enable more effective marketing campaigns.
For instance, a seamless integration between a CDP and a CRM system allows for real-time updates of customer data, ensuring consistent and accurate information across all marketing channels.
Potential Future Developments in the CDP Landscape
The following bullet points represent potential future developments, showcasing the dynamic nature of the CDP landscape:
- Decentralized CDPs: A shift towards more decentralized data management, potentially leveraging blockchain technology for enhanced security and data ownership.
- Serverless CDPs: Utilizing serverless architecture to offer greater scalability and cost-efficiency.
- Hyper-Personalization at Scale: Advanced AI and machine learning algorithms enabling highly granular personalization for millions of customers.
- Increased Focus on Customer Consent and Data Transparency: CDPs incorporating features that facilitate easy customer consent management and provide greater transparency about data usage.
- Advanced Data Quality and Governance Tools: Built-in tools for automated data cleansing, validation, and governance, minimizing human intervention.
Illustrative Example: A Detailed CDP Implementation: Whitepaper Global How Cdps Are Shaping Customer Data Insights Worldwide
Let’s explore the journey of “GreenThumb Gardens,” a fictional but realistic online plant retailer, as they implemented a CDP to enhance their customer understanding and engagement. GreenThumb Gardens experienced rapid growth but struggled with fragmented customer data spread across various platforms, hindering personalized marketing efforts. Their implementation provides a practical example of the challenges and successes involved in CDP adoption.
GreenThumb Gardens’ Data Sources
GreenThumb Gardens’ data resided in disparate systems. Their primary data sources included their e-commerce platform (Shopify), email marketing service (Mailchimp), CRM (Salesforce), and social media channels (Facebook and Instagram). Integrating these sources into a unified view was crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior. The initial challenge was the variety of data formats and structures across these platforms.
For example, customer IDs were inconsistent across platforms, leading to difficulty in merging data. To address this, GreenThumb Gardens employed a robust data integration platform that could handle various data formats and standardize customer identifiers using a hashing algorithm to ensure data privacy.
Data Transformation and Cleaning Processes
Once integrated, the data required significant cleaning and transformation. This involved handling missing values, standardizing data formats (e.g., date and address formats), and correcting inconsistencies in customer information. Data quality rules were established to flag and address inconsistencies. For example, if a customer’s shipping address differed significantly from their billing address, it was flagged for review to prevent delivery issues.
Duplicate records were identified and merged using advanced deduplication techniques. This process ensured data accuracy and reliability, which is essential for building accurate customer profiles. Data governance protocols were put in place to ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Improvements in Customer Insights and Engagement
Following the CDP implementation, GreenThumb Gardens experienced significant improvements in their customer insights and engagement. They gained a 360-degree view of each customer, enabling personalized recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns. For example, customers who frequently purchased succulents received personalized email campaigns promoting new succulent varieties. Customers who abandoned their online shopping carts received automated email reminders. This resulted in a 20% increase in conversion rates and a 15% increase in customer lifetime value.
Furthermore, they were able to segment their customers based on purchasing behavior, allowing them to tailor marketing messages to specific groups. This resulted in a more effective use of marketing budget and improved customer satisfaction. Real-time insights enabled proactive customer service interventions, such as addressing potential delivery issues before they impacted customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
In short, this whitepaper illuminates the transformative power of CDPs in the global marketplace. By unifying customer data, enhancing its quality, and facilitating personalized experiences, CDPs are no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. Understanding the intricacies of CDP implementation, data privacy regulations, and emerging trends is crucial for leveraging the full potential of this technology.
The journey toward a unified customer view is paved with opportunities, and this whitepaper provides the roadmap to navigate it successfully. So buckle up, and let’s unlock the power of customer data together!
Common Queries
What is the difference between a CDP and a CRM?
While both manage customer data, a CRM focuses on sales and customer relationship management, often lacking the robust data unification and real-time capabilities of a CDP. CDPs are specifically designed for creating a unified customer profile for improved personalization and marketing efforts.
How much does a CDP typically cost?
CDP pricing varies widely depending on features, data volume, and vendor. Expect a range from a few hundred dollars per month for smaller solutions to tens of thousands for enterprise-level platforms with extensive functionalities.
What are the biggest challenges in implementing a CDP?
Key challenges include data integration from disparate sources, ensuring data quality and accuracy, navigating data privacy regulations, and securing buy-in from different departments within an organization.
Is a CDP right for every business?
While CDPs offer immense benefits, they’re not a one-size-fits-all solution. Smaller businesses with simpler data needs might find alternative solutions more cost-effective. However, as data complexity grows, the value proposition of a CDP becomes increasingly compelling.
