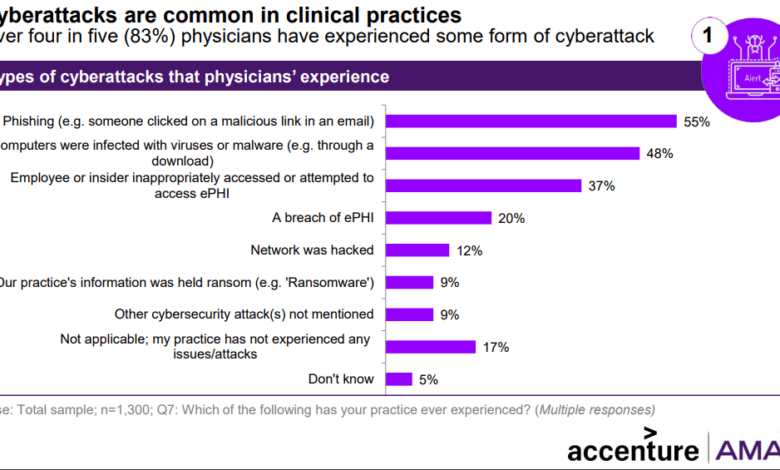
Eight in Ten Doctors Faced Clinical Cyberattacks
Eight in ten doctors have experienced cyber attack in their clinical practice – Eight in ten doctors have experienced a cyberattack in their clinical practice – a staggering statistic that highlights a critical vulnerability in our healthcare system. This isn’t just about stolen data; it’s about compromised patient care, eroded trust, and significant financial losses for medical professionals. We’ll delve into the types of attacks, the vulnerabilities exploited, and most importantly, the steps doctors can take to protect themselves and their patients.
From ransomware crippling operations to phishing scams targeting sensitive patient information, the threats are real and diverse. The consequences can range from hefty fines and legal battles to irreparable damage to a doctor’s reputation. This post aims to shed light on this growing problem, offering practical advice and insights to help navigate this increasingly complex digital landscape.
The Scope of the Cyberattack Problem

The increasing reliance on digital systems in healthcare has unfortunately made doctors’ clinical practices prime targets for cybercriminals. The consequences of successful attacks extend far beyond simple data breaches; they represent a significant threat to patient safety, operational efficiency, and the overall integrity of the healthcare system. The scale of the problem is alarming, with a substantial portion of medical professionals facing these threats firsthand.The potential impact of cyberattacks on patient data security and healthcare operations is profound.
Breaches can expose highly sensitive patient information, including medical histories, insurance details, and even social security numbers. This exposure can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and emotional distress for patients. Beyond patient data, attacks can disrupt critical healthcare operations, leading to delays in treatment, compromised diagnostic accuracy, and even potential harm to patients if essential systems are offline.
Types of Cyberattacks Targeting Doctors’ Clinical Practices
Cyberattacks against doctors’ offices vary widely in their methods and objectives. Common threats include ransomware attacks, where malicious software encrypts data and demands a ransom for its release; phishing scams, designed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive login credentials; and malware infections, which can compromise systems and steal data. Denial-of-service attacks can overwhelm a practice’s network, making it inaccessible to patients and staff.
Sophisticated attacks may involve exploiting vulnerabilities in software or hardware to gain unauthorized access to systems.
Seriously, the stat that eight in ten doctors have faced cyberattacks is terrifying. It highlights the urgent need for robust, secure healthcare systems. This is why I’ve been researching better solutions, and exploring options like the innovative approaches discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , which could help improve security and efficiency.
Ultimately, protecting patient data requires a multi-pronged approach, and stronger tech solutions are a vital part of that. That eight in ten statistic really drives home the point.
Real-World Consequences of Cyberattacks on Medical Practices, Eight in ten doctors have experienced cyber attack in their clinical practice
The consequences of these attacks can be devastating. Consider the case of a small cardiology practice in Ohio that suffered a ransomware attack, resulting in a week of downtime and a significant financial loss to recover their data and rebuild their systems. The cost of recovery, including IT support, legal fees, and lost revenue, far exceeded the ransom demand.
The shocking statistic that eight in ten doctors have faced cyberattacks in their practice highlights a critical need for robust security measures. This underscores the importance of solutions like cloud security posture management, and learning more about platforms such as bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is crucial. Ultimately, strengthening cybersecurity in healthcare is vital to protect patient data and prevent further attacks on already vulnerable professionals.
Beyond financial losses, the practice experienced reputational damage, leading to a loss of patient trust and a decline in new patient referrals. Another example is a large multi-specialty clinic in California that experienced a data breach exposing the personal information of thousands of patients. The resulting legal battles and regulatory fines imposed significant financial burdens on the clinic and eroded public confidence.
Impact of Cyberattacks on Medical Practices and Patients
| Type of Attack | Frequency | Impact on Patients | Impact on Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware | High | Delayed or interrupted care, potential exposure of PHI, loss of trust in the practice | Significant financial losses, operational disruption, reputational damage, legal liabilities |
| Phishing | Very High | Potential exposure of PHI, loss of trust in the practice if the breach is related to their data | Compromised systems, potential data breaches, operational disruption |
| Malware | High | Delayed or interrupted care, potential exposure of PHI | System instability, data breaches, financial losses due to downtime and recovery efforts |
| Denial-of-Service | Moderate | Inability to access care, disruption of appointments | Loss of revenue, reputational damage |
Vulnerabilities in Clinical Practices
The shocking statistic – eight in ten doctors experiencing cyberattacks – highlights a critical vulnerability within healthcare. This isn’t just about inconvenience; it’s about compromised patient data, disrupted services, and potentially life-threatening consequences. Understanding the weaknesses in clinical practices is the first step towards building robust defenses.The reality is that many doctors’ offices lack the comprehensive security measures needed to protect sensitive patient information.
This vulnerability stems from a combination of factors, including outdated technology, insufficient employee training, and a lack of awareness about evolving cyber threats. The consequences of these weaknesses can be devastating, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage and legal repercussions. Let’s delve into some of the most common vulnerabilities.
Outdated Software and Hardware
Outdated software and hardware are significant security risks. Older systems often lack the latest security patches, making them easy targets for malware and other cyber threats. For example, an outdated operating system might contain known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to the network. Similarly, aging hardware might lack the encryption capabilities necessary to protect sensitive data.
The use of unsupported software, like older versions of EHR systems, also creates significant vulnerabilities. These older systems might not have the capacity to incorporate modern security protocols or receive critical security updates. This creates a massive entry point for malicious actors.
Insufficient Employee Training
Human error is a major contributor to cyberattacks. Employees who lack adequate cybersecurity training are more likely to fall victim to phishing scams, malware infections, and other social engineering attacks. A simple click on a malicious link in an email can compromise the entire network. Comprehensive training programs that cover topics such as phishing awareness, password security, and data protection best practices are crucial for mitigating this risk.
Regular refresher courses are also essential to keep employees up-to-date on the latest threats and techniques.
Weak Password Policies
Weak or easily guessable passwords are a significant security vulnerability. Many medical practices still rely on weak passwords that are easily cracked by hackers. This is especially concerning given the sensitive nature of the data they protect. Implementing strong password policies, including password complexity requirements and regular password changes, is essential for enhancing security. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code generated by an authenticator app.
Lack of Data Encryption
Data encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive patient information both in transit and at rest. Without encryption, patient data is vulnerable to interception and theft. Healthcare providers should implement strong encryption protocols to protect data stored on servers, laptops, and other devices. This includes encrypting both EHRs and other sensitive patient data, like medical images and billing information.
The implementation of encryption should cover all aspects of data handling, ensuring comprehensive protection at every stage.
Inadequate Network Security
Many clinical practices lack robust network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software. These measures are crucial for preventing unauthorized access to the network and protecting against cyberattacks. A firewall acts as a barrier between the network and the internet, preventing unauthorized access. Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, and antivirus software protects against malware infections.
Regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that the network is adequately protected.
Five Key Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
The following list summarizes five key vulnerabilities and corresponding mitigation strategies:
- Vulnerability: Outdated software. Mitigation: Implement a regular software update schedule and utilize automated patching systems where possible.
- Vulnerability: Weak passwords. Mitigation: Enforce strong password policies, including complexity requirements and regular password changes, and implement multi-factor authentication.
- Vulnerability: Insufficient employee training. Mitigation: Provide comprehensive cybersecurity training to all employees and conduct regular refresher courses.
- Vulnerability: Lack of data encryption. Mitigation: Implement strong encryption protocols for data both in transit and at rest.
- Vulnerability: Inadequate network security. Mitigation: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
The Impact on Patient Care: Eight In Ten Doctors Have Experienced Cyber Attack In Their Clinical Practice
Cyberattacks on medical practices don’t just affect computer systems; they directly impact the health and well-being of patients. The consequences ripple outwards, affecting the doctor-patient relationship, the quality of care, and even legal standing. Understanding these impacts is crucial for improving cybersecurity practices in healthcare.Data breaches erode the fundamental trust between patients and their doctors. When sensitive medical information—including diagnoses, treatment plans, and even personal details—is exposed, patients feel vulnerable and betrayed.
This breach of confidentiality can lead to reluctance to share information openly with their healthcare providers, hindering effective diagnosis and treatment. The fear of further exposure or misuse of their data can also cause significant emotional distress.Compromised patient care is a direct result of disrupted systems or data loss. Imagine a scenario where a hospital’s electronic health record (EHR) system is down due to a ransomware attack.
Doctors may be unable to access vital patient information, leading to delays in treatment, incorrect diagnoses, or even medication errors. Loss of data, such as radiology images or lab results, can further complicate matters, resulting in potentially dangerous consequences for patients.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Data Breaches Involving PHI
Data breaches involving Protected Health Information (PHI) trigger significant legal and ethical ramifications. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, and similar regulations globally, impose strict requirements on healthcare providers to protect patient data. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage. Beyond the legal aspects, ethical considerations demand that healthcare providers prioritize patient privacy and data security.
A breach of trust not only jeopardizes the doctor-patient relationship but also undermines the public’s confidence in the healthcare system.
Hypothetical Scenario: Cyberattack Disrupting Patient Care
Imagine Dr. Anya Sharma, a cardiologist, whose practice is hit by a sophisticated phishing attack. The attackers gain access to her practice management software and encrypt all patient data, including EKG results and medication lists. The ransomware demand is substantial, and Dr. Sharma is unable to pay immediately.
For several days, her practice is effectively shut down. Patients with scheduled appointments cannot be seen, and critical information needed for ongoing care is inaccessible. A patient with a history of heart failure misses a crucial follow-up appointment, resulting in a potentially life-threatening delay in treatment. The incident highlights the devastating consequences of a cyberattack on patient care, underscoring the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures in healthcare settings.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Protecting small medical practices from cyberattacks requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing technological safeguards, employee training, and robust insurance coverage. Ignoring these strategies leaves practices vulnerable to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and, most critically, compromised patient care. This section details key strategies for bolstering cybersecurity defenses.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification to access systems and data. Instead of relying solely on a password, MFA adds another layer, such as a one-time code sent to a mobile device, a biometric scan (fingerprint or facial recognition), or a security token. This makes it exponentially more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access, even if they obtain a password through phishing or other means.
For example, a doctor attempting to access their patient records might need to enter their password and then verify their identity using a code sent to their smartphone. The added layer of authentication dramatically reduces the risk of successful breaches. Implementing MFA across all systems and accounts is a crucial first step in any cybersecurity strategy for a medical practice.
Cybersecurity Solutions for Small Medical Practices
Small medical practices have diverse cybersecurity needs and budgets. Several solutions cater to these varying requirements. Cloud-based security solutions offer scalable protection, often including features like firewall management, intrusion detection, and data backup. These solutions can be particularly beneficial for practices with limited IT staff. On-premise solutions, requiring dedicated hardware and IT expertise, provide greater control but often involve higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance.
Antivirus and anti-malware software are essential components, requiring regular updates to remain effective against evolving threats. Finally, dedicated cybersecurity consultants can offer tailored assessments and guidance, helping practices identify vulnerabilities and implement appropriate solutions. The choice depends on the practice’s size, budget, and technical capabilities. A smaller practice might opt for a comprehensive cloud-based solution, while a larger one might prefer a more customized on-premise system managed by an external consultant.
Software Updates and Employee Training
Regular software updates are paramount in patching known vulnerabilities exploited by attackers. Failing to update software leaves systems susceptible to malware and exploits. For example, outdated operating systems or applications might contain security flaws that hackers can leverage. A proactive approach involves establishing a schedule for automatic updates, ensuring all software, including operating systems, applications, and antivirus programs, are consistently updated.
Complementing software updates is comprehensive employee training. This training should cover phishing awareness, password security, safe internet browsing practices, and recognizing and reporting suspicious activity. Regular simulated phishing campaigns can help identify employees who are vulnerable to social engineering attacks. A well-trained workforce forms the first line of defense against many common cyber threats.
Cybersecurity Insurance
Cybersecurity insurance offers crucial financial protection against the substantial costs associated with data breaches and cyberattacks. These policies can cover expenses related to incident response, legal fees, regulatory fines, and notification costs to affected individuals. For instance, if a medical practice experiences a ransomware attack, insurance can cover the costs of data recovery, paying the ransom (though this is not always recommended), and notifying patients of the breach.
The cost of cybersecurity insurance varies depending on the practice’s size, risk profile, and the level of coverage desired. It is a vital investment, mitigating potential financial ruin from a successful cyberattack.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Ramifications
The increasing frequency of cyberattacks targeting healthcare providers necessitates a thorough understanding of the legal landscape surrounding data breaches and the critical role of regulatory compliance. Failure to adhere to regulations like HIPAA can result in severe financial penalties and reputational damage, impacting not only the practice but also patient trust. This section explores the legal ramifications of data security failures in healthcare.
HIPAA Regulations and Patient Data Protection
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 establishes national standards for protecting sensitive patient health information (PHI). Specifically, the HIPAA Security Rule Artikels administrative, physical, and technical safeguards that covered entities (healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses) must implement to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic PHI (ePHI). These safeguards encompass a wide range of security measures, including risk assessments, employee training, access controls, and data encryption.
A key aspect of HIPAA compliance in the face of cyberattacks is the requirement for breach notification. If a breach occurs, covered entities must notify affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and potentially others, depending on the circumstances. Failure to comply with these notification requirements can lead to significant penalties.
Potential Legal Consequences for Doctors Following a Data Breach
The legal consequences of a data breach for doctors can be substantial. Beyond the potential for HIPAA violations, which can result in hefty fines from the HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR), doctors may face civil lawsuits from patients whose PHI has been compromised. These lawsuits could allege negligence, breach of contract, or violations of state privacy laws.
Furthermore, doctors could face professional disciplinary actions from state medical boards, potentially leading to license suspension or revocation. The severity of the consequences will depend on several factors, including the nature and extent of the breach, the steps taken to mitigate the damage, and the level of cooperation with investigations.
Examples of Successful Legal Actions Against Healthcare Providers
Several high-profile cases illustrate the potential legal repercussions of data security failures in healthcare. For instance, the settlement reached between the OCR and a healthcare provider who experienced a ransomware attack resulted in a significant financial penalty for failing to implement adequate security measures. In another case, a hospital faced multiple class-action lawsuits after a data breach exposed the PHI of thousands of patients.
These examples highlight the importance of proactive security measures and prompt response protocols in preventing and mitigating the legal risks associated with cyberattacks.
Steps a Medical Practice Should Take Following a Cyberattack
The following flowchart Artikels the critical steps a medical practice should take following a cyberattack:[Diagram Description: A flowchart would be presented here. It would begin with a “Cyberattack Detected” box, branching to “Assess the Damage” (determine the extent of the breach and affected data), then to “Secure the System” (isolate affected systems, change passwords, etc.), followed by “Notify Affected Parties” (patients, HHS, etc.), then “Conduct a Forensic Investigation” (determine the cause and extent of the breach), then “Implement Remedial Measures” (strengthen security, improve training, etc.), and finally “Document Everything” (maintain thorough records of the incident and response).]
The Future of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
The healthcare industry faces an ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, demanding proactive and innovative solutions. The increasing reliance on interconnected systems, the rise of telehealth, and the growing volume of sensitive patient data create a fertile ground for sophisticated attacks. Understanding these emerging threats and adopting advanced security measures are crucial for protecting patient privacy, maintaining operational integrity, and ensuring the future of healthcare delivery.
Emerging Cybersecurity Threats and Vulnerabilities
The healthcare sector is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high value of patient data and the often-fragmented nature of its IT infrastructure. Ransomware attacks remain a significant threat, capable of crippling hospital operations and potentially endangering patient lives. Furthermore, the increasing use of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices, such as insulin pumps and pacemakers, introduces new vulnerabilities, as these devices may lack robust security features.
Phishing attacks, exploiting human error, continue to be a major entry point for malicious actors. Advanced persistent threats (APTs), involving sophisticated and persistent attacks by state-sponsored or organized crime groups, also pose a serious and evolving challenge. Data breaches, whether through hacking or insider threats, remain a constant concern, potentially leading to significant financial penalties and reputational damage.
Finally, the rise of artificial intelligence itself introduces new vulnerabilities if not properly secured. Malicious actors could leverage AI to create more sophisticated and harder-to-detect attacks.
Predictions for Future Trends in Cybersecurity Solutions
We can anticipate several key trends shaping the future of cybersecurity in healthcare. Zero Trust security architectures, which assume no implicit trust and verify every access request, will become increasingly prevalent. This approach minimizes the impact of breaches by limiting access to sensitive data. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play a crucial role in threat detection and response, enabling faster identification and mitigation of attacks.
Blockchain technology, with its inherent security and immutability, offers potential for securing sensitive patient data and improving data integrity. Enhanced cybersecurity training for healthcare professionals will be essential to combat phishing and social engineering attacks, improving human factors in security. Finally, greater collaboration and information sharing among healthcare organizations will strengthen the collective defense against cyber threats.
For example, the sharing of threat intelligence between hospitals could allow for quicker identification and response to emerging threats.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Cybersecurity Defenses
AI and ML are poised to revolutionize healthcare cybersecurity. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify anomalies and potential threats in real-time, far exceeding human capabilities. These systems can detect patterns indicative of malicious activity, such as unusual login attempts or data exfiltration attempts, allowing for rapid response. Furthermore, AI can automate security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and patching, freeing up human analysts to focus on more complex threats.
The use of AI in threat hunting proactively searches for threats rather than simply reacting to alerts, significantly improving the overall security posture. For instance, an AI system might detect a subtle pattern in network traffic indicative of a sophisticated attack that would be missed by traditional security systems.
Predicted Future Trends and Their Potential Impact on Clinical Practices
| Trend | Potential Impact on Clinical Practices |
|---|---|
| Increased adoption of Zero Trust security | Improved data protection, reduced impact of breaches, enhanced compliance |
| AI-powered threat detection and response | Faster identification and mitigation of attacks, reduced downtime, improved security posture |
| Blockchain technology for data security | Enhanced data integrity, improved patient privacy, reduced risk of data breaches |
| Enhanced cybersecurity training for staff | Reduced vulnerability to phishing and social engineering attacks, improved overall security awareness |
| Increased collaboration and information sharing | Faster response to emerging threats, improved collective security, stronger industry resilience |
Wrap-Up
The cybersecurity landscape for medical practices is constantly evolving, demanding vigilance and proactive measures. While the statistic of eight in ten doctors facing cyberattacks is alarming, it’s not a death sentence. By understanding the vulnerabilities, implementing robust security protocols, and staying informed about emerging threats, doctors can significantly reduce their risk. Investing in cybersecurity isn’t just a cost; it’s an investment in patient safety, professional integrity, and the long-term viability of their practice.
Helpful Answers
What is the most common type of cyberattack against doctors’ offices?
Phishing emails and malware infections are among the most prevalent, often targeting employees to gain access to systems.
How can I know if my practice has been compromised?
Look for unusual activity like slow systems, unauthorized access attempts, or unusual email activity. Regular security audits are crucial.
What is the role of HIPAA in all this?
HIPAA mandates specific security measures to protect patient health information (PHI). Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties.
Is cybersecurity insurance worth it for a small practice?
Absolutely. It provides crucial financial protection in the event of a successful attack, covering legal fees, recovery costs, and potential fines.





