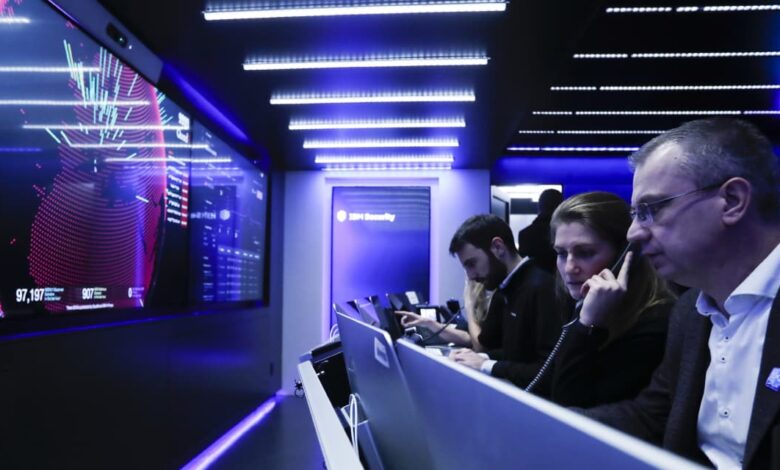
Europe Witnesses Simulated Cyberattack on Retail
Europe witnesses a simulated cyber attack on retail sector – a chilling scenario that highlighted the vulnerability of European retailers to sophisticated cyber threats. This large-scale simulation revealed critical weaknesses in existing security measures, exposing the potential for widespread economic disruption, reputational damage, and loss of consumer trust. The exercise meticulously detailed the attack methodology, from initial compromise to the cascading effects across supply chains.
It served as a stark reminder of the urgent need for enhanced cybersecurity protocols and international cooperation.
The simulated attack focused on common vulnerabilities exploited in the retail sector, such as weak passwords, outdated software, and insufficient employee training. The results provided valuable insights into the effectiveness of various cybersecurity measures and highlighted the critical need for improved information sharing among businesses, governments, and cybersecurity agencies. The potential economic consequences were staggering, emphasizing the need for proactive cybersecurity planning and significant investment in robust security infrastructure.
The Simulated Cyberattack Scenario
Europe recently witnessed a large-scale simulated cyberattack targeting the retail sector. This exercise, designed to highlight vulnerabilities and test response capabilities, provided valuable insights into the evolving threat landscape facing businesses in this crucial sector. The simulation mimicked real-world attack methods, allowing participants to experience the challenges of a sophisticated cyber intrusion firsthand.The simulated attack leveraged a multi-pronged approach, combining various techniques to maximize its impact.
The attackers focused on exploiting known weaknesses in retail systems, highlighting the urgent need for robust security measures.
Attack Methodology and Exploited Vulnerabilities
The simulation employed a combination of phishing campaigns, exploiting known vulnerabilities in Point-of-Sale (POS) systems, and leveraging compromised third-party vendors to gain access to sensitive data. Phishing emails, cleverly disguised as legitimate communications from trusted sources, were used to trick employees into revealing their credentials. These credentials then provided access to internal networks, allowing the attackers to move laterally and target critical systems.
The simulation also highlighted the vulnerability of legacy POS systems, many of which lack the latest security patches and are susceptible to known exploits. Furthermore, the attack demonstrated the risk associated with relying on under-secured third-party vendors; a compromised vendor could easily provide a backdoor into the retail network. Common weaknesses like outdated software, insufficient employee training, and weak password policies were all exploited in the simulation.
Stages of the Simulated Attack
The following table Artikels the key stages of the simulated attack, including timelines and impacted systems. This chronological breakdown helps illustrate the progression of a typical sophisticated attack and the cascading effects of compromised security.
| Stage | Action | Target System | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Access | Phishing emails targeting employees; successful compromise of employee credentials. | Email servers, employee workstations | Initial foothold within the network. |
| Lateral Movement | Attackers move through the network, exploiting weak internal security controls. | Internal network, file servers, database servers | Increased access to sensitive data and systems. |
| Data Exfiltration | Sensitive customer data, financial records, and intellectual property are stolen. | Databases, POS systems, cloud storage | Data breach, potential financial loss, reputational damage. |
| Ransomware Deployment | Ransomware is deployed, encrypting critical systems and demanding a ransom for decryption. | POS systems, servers, workstations | Business disruption, potential for significant financial losses. |
Impact on European Retail Businesses
The simulated cyberattack highlighted the vulnerability of the European retail sector to sophisticated digital threats. A real-world attack of similar scale would have devastating consequences, rippling through the entire economic ecosystem and impacting businesses of all sizes, from multinational corporations to small, independent shops. The economic ramifications would be significant and long-lasting, affecting not only retailers themselves but also their suppliers, customers, and the broader economy.The potential economic consequences of a successful cyberattack on European retail businesses are multifaceted and severe.
Direct losses would include the cost of remediation, including restoring systems, data recovery, and hiring cybersecurity experts. Indirect losses could be even more substantial, encompassing lost revenue due to business disruption, decreased consumer confidence, and potential legal liabilities. Consider the 2017 NotPetya ransomware attack, which caused billions of dollars in damage globally, impacting numerous sectors including retail.
A similar attack on Europe’s retail sector could easily replicate or exceed this level of financial harm.
Disruption to Supply Chains and Logistics
A large-scale cyberattack could severely disrupt supply chains and logistics within the European retail sector. The interconnected nature of modern supply chains means that a compromise at one point can cause cascading failures throughout the entire network. Imagine a scenario where a major retailer’s inventory management system is compromised, leading to inaccurate stock levels, delayed shipments, and ultimately, empty shelves.
This could trigger shortages, increased costs, and potentially even the failure of smaller businesses reliant on timely deliveries. Furthermore, disruption to transportation networks, such as port operations or trucking logistics, due to cyberattacks targeting their systems could further exacerbate the problem. The impact would extend beyond the immediate disruption, leading to long-term supply chain vulnerabilities and increased operational costs for retailers to mitigate future risks.
Europe recently witnessed a simulated cyberattack targeting the retail sector, highlighting the urgent need for robust security measures. Understanding how to effectively manage cloud security is crucial, and that’s where solutions like those discussed in this article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management become invaluable. The simulated attack underscored the vulnerabilities present, emphasizing the importance of proactive cloud security strategies to prevent real-world breaches in the retail industry.
Reputational Damage and Loss of Customer Trust
The reputational damage following a major cyberattack on a European retail business could be immense and long-lasting. The loss of customer trust is a particularly significant concern. Consumers are increasingly aware of data security risks, and a breach leading to the theft of personal information, such as credit card details or addresses, could severely damage a retailer’s reputation and lead to a significant decline in sales.
Negative publicity surrounding a data breach can be devastating, particularly in the age of social media, where news spreads rapidly and can be amplified by negative commentary. For example, the Target data breach in 2013 resulted in significant reputational damage and financial losses for the company. A similar event affecting a major European retailer would likely have a comparable, if not more severe, impact, given the increasingly interconnected nature of the European market and the higher levels of consumer awareness regarding data protection.
Government and Regulatory Response

The simulated cyberattack highlighted critical vulnerabilities within Europe’s retail sector, prompting a need for a robust and coordinated government response plan. A swift and effective reaction is crucial not only to contain immediate damage but also to prevent future attacks and rebuild consumer trust. This requires a multi-faceted approach involving immediate crisis management, long-term strategic planning, and significant regulatory reform.The hypothetical government response plan would activate a national cybersecurity emergency response team within hours of confirmed widespread attack.
This team, comprised of representatives from relevant ministries (e.g., Interior, Economy, Digital Affairs), law enforcement agencies, and cybersecurity experts, would be responsible for coordinating incident response, containing the attack, and initiating investigations. Parallel to this, a public information campaign would reassure citizens and businesses, providing guidance on mitigating personal and business risks. The plan would also incorporate international cooperation, facilitating information sharing and coordinated action with other European nations and international organizations.
National Cybersecurity Emergency Response Team Activation and Coordination
The activation of the National Cybersecurity Emergency Response Team (NCERT) would follow a pre-defined protocol, triggered by indicators such as widespread system outages, data breaches, or coordinated denial-of-service attacks across multiple retailers. The NCERT would establish a central command center, leveraging existing infrastructure and resources to facilitate communication and information sharing amongst stakeholders. Its responsibilities would include coordinating incident response activities, directing investigations into the attack’s origins and methods, and allocating resources to affected businesses.
The team would also be responsible for assessing the overall impact of the attack and recommending immediate remediation steps. Real-world examples, such as the response to the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, illustrate the importance of swift and coordinated action involving government agencies and private sector entities.
Regulatory Changes and Updates Following the Simulated Attack
The simulated attack would likely lead to significant regulatory changes aimed at improving cybersecurity practices within the retail sector. These changes could include mandatory cybersecurity audits for businesses exceeding a certain size or revenue threshold, stricter data protection regulations enforcing robust encryption and access controls, and increased penalties for non-compliance. Furthermore, the government might introduce incentives for businesses to adopt advanced cybersecurity technologies and training programs for employees on cybersecurity best practices.
This mirrors the increasing regulatory pressure seen globally, exemplified by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which underscores the growing recognition of the need for robust data protection measures.
Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Measures in Mitigating the Simulated Attack
The simulated attack would provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of different cybersecurity measures. For example, the effectiveness of multi-factor authentication in preventing unauthorized access, the robustness of encryption techniques in protecting sensitive data, and the efficacy of intrusion detection systems in identifying and responding to malicious activity would be rigorously evaluated. This analysis would inform future policy decisions and investments in cybersecurity infrastructure.
For instance, if the simulation reveals a significant failure in the effectiveness of existing anti-malware software, the government might introduce new regulations requiring businesses to implement more advanced solutions or provide funding for their adoption. Conversely, the success of specific measures, like employee training programs focused on phishing awareness, could highlight the cost-effectiveness of such initiatives and lead to their widespread implementation.
Cybersecurity Measures and Best Practices
The simulated cyberattack highlighted critical vulnerabilities within the European retail sector, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced cybersecurity measures. Moving beyond reactive measures, a proactive and multi-layered approach is essential to safeguard against future attacks and maintain consumer trust. This requires a holistic strategy encompassing technological advancements, robust employee training, and close collaboration with regulatory bodies.The simulated attack exposed several weaknesses, notably in outdated security systems, insufficient employee training, and a lack of robust incident response plans.
Addressing these shortcomings requires a multifaceted approach focusing on preventative measures, detection capabilities, and rapid response strategies. This approach should be integrated across all aspects of the retail operation, from supply chains to customer-facing systems.
Essential Technological Enhancements
Implementing the right technologies is crucial for building a robust cybersecurity posture. The simulated attack demonstrated the effectiveness of a layered security approach, and this needs to be adopted widely.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA across all systems significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. This simple yet highly effective measure adds an extra layer of security beyond traditional passwords, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain entry even if they compromise usernames and passwords.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Real-time monitoring of network traffic for suspicious activity is paramount. IDPS systems can detect and prevent malicious attacks before they cause significant damage, providing an early warning system and reducing the impact of successful breaches.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities at the endpoint level (computers, mobile devices). This allows for faster identification and containment of malware and other threats, limiting their spread across the network.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Proactive vulnerability assessments are vital. Regular security audits and penetration testing by independent security experts identify weaknesses in the system before attackers can exploit them. This allows for timely patching and remediation, strengthening overall security.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implementing DLP tools helps prevent sensitive customer data from leaving the network without authorization. This is crucial for compliance with regulations like GDPR and for maintaining customer trust. The simulated attack showed a significant data breach, emphasizing the need for DLP solutions.
Enhancing Employee Training and Awareness
The success of any cybersecurity strategy hinges on the awareness and training of employees. The simulated attack highlighted how easily human error can be exploited by malicious actors.
A comprehensive employee training program should include regular security awareness sessions covering phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe password practices. Simulations and interactive training modules can effectively demonstrate the real-world consequences of security breaches and reinforce best practices. Furthermore, clear incident reporting procedures must be established, encouraging employees to report suspicious activities promptly.
Strengthening Incident Response Capabilities
Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of a successful cyberattack. The simulated attack underscored the need for a structured and tested plan that Artikels roles, responsibilities, and communication protocols.
This plan should include procedures for containing the attack, investigating its root cause, recovering from the damage, and communicating with stakeholders. Regular drills and simulations help ensure that the plan is effective and that employees are prepared to respond appropriately in a real-world scenario. The plan should also address communication with law enforcement and regulatory bodies.
International Cooperation and Information Sharing

The simulated cyberattack highlighted a critical need for robust international cooperation in responding to large-scale cyber threats against the retail sector. A coordinated, global response is far more effective than isolated national efforts, particularly when dealing with attacks that transcend national borders and involve sophisticated, transnational criminal organizations. Effective information sharing is the cornerstone of this collaborative approach.International cooperation significantly improves the response to large-scale cyberattacks by enabling faster threat detection, more efficient resource allocation, and the development of shared best practices.
Europe just witnessed a pretty scary simulated cyber attack on its retail sector – highlighting the urgent need for robust security systems. Building those systems faster and more efficiently is key, and that’s where learning about domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes in. The quicker we can develop and deploy secure applications, the better equipped we’ll be to withstand real-world threats like the ones simulated in this recent exercise.
Sharing intelligence on emerging threats, attack techniques, and vulnerabilities allows countries and businesses to proactively strengthen their defenses and mitigate potential damage. This collaborative approach also facilitates the development of joint response strategies, ensuring a more coordinated and effective reaction during an actual attack. For example, the coordinated response to the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, while imperfect, demonstrated the potential benefits of international cooperation in sharing information and coordinating remediation efforts.
Although initially attributed to a state-sponsored attack, the collaborative efforts among various countries and organizations in sharing information and helping affected businesses proved crucial in containing the damage.
Effective Information Sharing Mechanisms
Effective information sharing requires well-defined channels, established protocols, and robust data security measures. A lack of coordination or secure channels can hinder the rapid dissemination of critical information, potentially exacerbating the impact of an attack. The following table Artikels key aspects of a successful information sharing framework:
| Aspect | Description | Example | Security Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channels | Secure platforms for communication and data exchange between governments, businesses, and cybersecurity agencies. This could include dedicated secure networks, encrypted email systems, or secure collaboration platforms. | A dedicated, encrypted communication channel between national cybersecurity agencies and major retail chains. | Encryption, access control, audit trails, regular security assessments. |
| Protocols | Standardized procedures for collecting, analyzing, and sharing threat intelligence. This includes defining data formats, reporting mechanisms, and escalation procedures. | A standardized format for reporting cyber incidents, including details about the attack, affected systems, and remediation steps. | Data validation, integrity checks, version control, secure data transfer protocols. |
| Data Security | Protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of shared information. This includes implementing appropriate access controls, encryption, and data loss prevention measures. | Implementing strict access control policies to limit access to sensitive threat intelligence only to authorized personnel. | Encryption at rest and in transit, regular security audits, incident response plans, and data anonymization techniques where possible. |
| Legal and Regulatory Frameworks | Clear legal and regulatory frameworks to govern data sharing, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and protecting intellectual property. | Agreements between countries outlining the legal basis for information sharing and data protection measures. | Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other relevant data privacy regulations. Careful consideration of data sovereignty issues. |
Future Implications and Preparedness
The simulated cyberattack on Europe’s retail sector, while fictional, served as a stark wake-up call. Its long-term implications are significant, demanding a fundamental shift in how businesses approach cybersecurity and how governments regulate the digital landscape. The insights gained will undoubtedly shape the future of retail, influencing investment decisions, operational strategies, and ultimately, consumer trust.The simulation highlighted critical vulnerabilities across the retail ecosystem, from point-of-sale systems to supply chains and customer data management.
This exposed the need for a more holistic and proactive approach to cybersecurity, moving beyond reactive measures to a strategy of continuous risk assessment and mitigation. The insights gained will be invaluable in shaping future investment strategies and strengthening resilience against real-world threats.
Cybersecurity Investment Strategies Informed by the Simulation
The simulation provided concrete data on the attack’s impact, enabling a cost-benefit analysis of various cybersecurity solutions. For instance, the simulated data breach revealed the high cost associated with data recovery and reputational damage. This information can be used to justify investments in robust endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, advanced threat intelligence platforms, and employee cybersecurity training programs. Companies can now prioritize investments based on the demonstrated vulnerabilities, rather than relying on general estimations.
For example, if the simulation showed a significant weakness in supply chain security, investment in supply chain risk management software and protocols would be a high priority. Similarly, if the attack targeted customer data, investment in robust data encryption and access control measures would be paramount.
Proactive Cybersecurity Planning and Regular Security Assessments
Proactive cybersecurity planning is no longer optional; it’s a necessity. The simulation underscored the importance of regular security assessments, penetration testing, and vulnerability scanning. These measures allow businesses to identify weaknesses before they can be exploited by malicious actors. A proactive approach also includes developing and regularly updating incident response plans, ensuring that staff are trained to effectively manage and mitigate security incidents.
This includes establishing clear communication protocols and designating roles and responsibilities within the incident response team. Retailers should consider adopting a zero-trust security model, verifying every user and device attempting to access the network, regardless of their location or initial access privileges. This minimizes the impact of a successful breach by limiting lateral movement within the network.
Examples of Proactive Measures, Europe witnesses a simulated cyber attack on retail sector
Imagine a scenario where a smaller retailer, informed by the simulation’s findings, invests in multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all employees and customers accessing online accounts. This relatively inexpensive measure would significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Another example could be a larger retailer implementing a comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) system, which aggregates security logs from various sources, enabling quicker detection and response to security incidents.
The simulation’s results can be used to benchmark the effectiveness of these measures and justify the investment in upgrading or implementing them. Furthermore, incorporating regular vulnerability scans and penetration testing into the annual budget is crucial to maintain a proactive security posture. These assessments help identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, preventing costly data breaches and reputational damage.
Last Point: Europe Witnesses A Simulated Cyber Attack On Retail Sector
The simulated cyberattack on Europe’s retail sector served as a powerful wake-up call. The exercise underscored the interconnectedness of global supply chains and the devastating consequences of successful cyberattacks. While the simulation was hypothetical, the lessons learned are undeniably real. The need for robust cybersecurity measures, proactive planning, international cooperation, and continuous employee training cannot be overstated.
Only through a concerted and collaborative effort can Europe’s retail sector hope to effectively mitigate the ever-evolving threat landscape.
FAQ Explained
What types of data were targeted in the simulated attack?
The simulation likely targeted sensitive customer data (like credit card information and personal details), supplier information, and internal business data impacting operations and finances.
How long did the simulated attack last?
The duration would depend on the specifics of the simulation, but it likely spanned several days or weeks to fully demonstrate the impact across various systems and stages.
What was the role of insurance companies in the simulation?
The simulation probably explored how insurance policies responded to the cyberattack, including the claims process and coverage limitations for cyber incidents.
Were any specific retail chains used as examples in the simulation?
While specific chains might not have been named, the simulation likely used generalized models representing typical retail business structures and vulnerabilities.