Five Strategies for IT & Security Leaders Against AI Threats
Five strategies for it and security leaders to defend against ai powered threats – Five Strategies for IT and security leaders to defend against AI-powered threats – it’s a headline that’s becoming increasingly relevant in our rapidly evolving digital landscape. AI is transforming everything, including the methods used by cybercriminals. This means traditional security measures often fall short. We’re facing sophisticated, adaptive threats that require equally sophisticated defenses. This post dives into five crucial strategies that IT and security leaders need to adopt to stay ahead of the curve and protect their organizations from the ever-growing threat of AI-powered attacks.
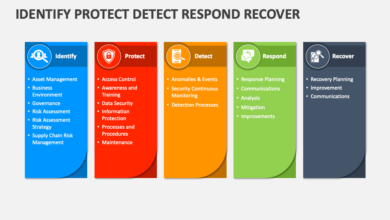
The rise of AI presents both opportunities and significant challenges in cybersecurity. While AI can enhance our defenses, malicious actors are leveraging it to create more powerful and evasive attacks. This means we need to proactively hunt for threats, strengthen our data security, secure our AI systems themselves, and build a robust incident response plan. Finally, a strong security awareness culture among employees is paramount.
Let’s explore these strategies in detail.
Proactive Threat Hunting and Detection
Proactive threat hunting is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity in today’s AI-powered threat landscape. Reactive security measures simply can’t keep pace with the sophistication and speed of modern attacks. By actively searching for threats before they cause damage, organizations can significantly reduce their risk profile and minimize the impact of successful breaches. This involves leveraging advanced technologies and employing a strategic approach that combines technical expertise with threat intelligence.
Effectively hunting for AI-powered threats requires a multi-faceted approach. This involves combining advanced technologies with a deep understanding of threat actors’ tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). By proactively searching for indicators of compromise (IOCs) and unusual activity, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to sophisticated attacks. A key element is the integration of threat intelligence feeds, which provide valuable context and insights into emerging threats.
Methods for Proactive Identification of AI-Powered Threats
Several methods can be employed to proactively identify AI-powered threats. These methods are complementary and should be used in conjunction with each other for optimal effectiveness.
| Method | Description | Example | Technology/Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-powered Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Utilizes machine learning to analyze security logs and identify anomalies indicative of malicious activity, including those too subtle for human analysts to detect. | An AI-powered SIEM detects unusual access patterns from a specific IP address correlating with known botnet activity, flagging it as suspicious even before a full-scale attack occurs. | Splunk, IBM QRadar, Elastic Stack |
| Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs) | Consolidates threat intelligence feeds from various sources, enabling proactive identification of emerging threats and potential attack vectors. | A TIP identifies a new malware variant targeting a specific industry, allowing organizations in that sector to proactively implement mitigation strategies. | Recorded Future, ThreatConnect, Palo Alto Networks Cortex XSOAR |
| Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing | Regularly assesses systems for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by AI-powered attacks, simulating real-world attacks to identify weaknesses. | Penetration testing reveals a vulnerability in a web application that could be exploited by an AI-powered botnet to launch a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack. | Nessus, OpenVAS, Metasploit |
| Deception Technology | Deploys decoys and traps to lure attackers, revealing their tactics and providing early warning of potential breaches. | Deception technology identifies a malicious actor attempting to access sensitive data through a decoy server, revealing their presence and allowing for rapid response. | Attivo Networks, Scythe, Darktrace |
| Behavioral Analytics | Monitors user and system behavior to detect deviations from established baselines, identifying anomalies that could indicate malicious activity. | Behavioral analytics detects unusual login attempts from an employee’s account originating from an unfamiliar location, potentially indicating account compromise. | Exabeam, Splunk User Behavior Analytics (UBA), CrowdStrike Falcon |
Utilizing Technologies and Tools for Proactive Threat Hunting
The technologies and tools listed in the table above are crucial components of a robust proactive threat hunting strategy. However, simply implementing these tools is insufficient. It’s essential to have skilled security personnel capable of interpreting the data generated by these tools and translating that data into actionable insights. This requires a combination of technical expertise, threat intelligence knowledge, and a deep understanding of the organization’s specific security landscape.
Integrating Threat Intelligence Feeds
Integrating threat intelligence feeds is paramount for effective proactive threat hunting. These feeds provide valuable context, enabling security teams to prioritize threats, understand attacker motivations, and anticipate future attacks. By correlating threat intelligence with internal security data, organizations can significantly improve their ability to identify and respond to AI-powered threats before they cause significant damage. This includes real-time feeds of IOCs, emerging malware variants, and attack techniques, enabling rapid identification and response to evolving threats.
Strengthening Data Security and Privacy
AI-powered threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, demanding a robust and proactive approach to data security and privacy. The traditional security measures are often insufficient to counter the advanced capabilities of these threats. Strengthening our defenses requires a multi-layered strategy encompassing data encryption, strict access control, and proactive data loss prevention, all while leveraging the power of AI itself to enhance our security posture.The rise of AI-powered attacks necessitates a shift in our approach to data security.
Simply relying on perimeter defenses is no longer sufficient. We need to embrace a more granular, context-aware approach that anticipates and mitigates threats before they can cause significant damage. This involves implementing robust data security practices, leveraging AI-powered security tools, and adopting a zero-trust security model.
Best Practices for Securing Sensitive Data
Implementing strong data security practices is paramount in mitigating AI-powered attacks. The following five best practices focus on protecting sensitive data through encryption, access control, and data loss prevention.
So, you’re thinking about those five strategies for IT and security leaders to defend against AI-powered threats? A strong cloud security posture is crucial, and that’s where understanding tools like Bitglass comes in. Check out this great resource on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management to bolster your defenses. Implementing robust cloud security directly impacts your overall ability to effectively counter AI-driven attacks, making it a key component of those five strategies.
- Employ robust data encryption at rest and in transit: Encrypt all sensitive data, both when stored (at rest) and while being transmitted (in transit). This includes using strong encryption algorithms like AES-256 and implementing secure protocols like TLS/SSL for communication. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the decryption key.
- Implement granular access control: Restrict access to sensitive data based on the principle of least privilege. Only authorized personnel should have access to specific data, and their access should be limited to what is absolutely necessary for their roles. This can be achieved through role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) systems.
- Utilize data loss prevention (DLP) tools: Implement DLP tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. These tools can scan emails, files, and network traffic for sensitive information and block attempts to transmit it outside the organization’s perimeter. Modern DLP solutions often incorporate AI and machine learning to identify and classify sensitive data more effectively.
- Regularly conduct data security audits and penetration testing: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your security measures through audits and penetration testing. These assessments should simulate real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your data security posture. This allows for proactive identification and remediation of potential security gaps.
- Implement data masking and anonymization techniques: For data used for testing or development purposes, employ data masking and anonymization techniques to protect sensitive information. This involves replacing sensitive data elements with non-sensitive substitutes while preserving the data’s structure and utility for testing.
The Role of AI in Enhancing Data Security and Privacy, Five strategies for it and security leaders to defend against ai powered threats
AI can significantly enhance data security and privacy by automating threat detection, improving incident response, and providing more granular access control. AI-powered security tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify anomalies and potential threats that might be missed by traditional security systems.Examples of AI-powered security tools include:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems with AI capabilities: These systems use AI algorithms to analyze security logs and identify suspicious activities in real-time. They can correlate events from various sources to detect complex attacks and provide faster incident response.
- AI-powered intrusion detection and prevention systems: These systems use machine learning to identify malicious traffic and block attacks before they can cause damage. They can learn from past attacks to improve their ability to detect and prevent future attacks.
- AI-driven threat intelligence platforms: These platforms collect and analyze threat data from various sources to identify emerging threats and vulnerabilities. They can provide organizations with timely warnings about potential attacks and help them prioritize their security efforts.
Implementing Zero-Trust Security Principles
A zero-trust security model assumes no implicit trust and verifies every user and device before granting access to resources. This is crucial in mitigating the impact of AI-powered breaches, as even compromised accounts within the network can be restricted.Implementing zero-trust requires:
- Microsegmentation: Divide the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the impact of a breach. If one segment is compromised, the attacker will have limited access to other parts of the network.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Require multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password, one-time code, biometric) to verify user identity before granting access.
- Continuous monitoring and access control: Constantly monitor user activity and access patterns to detect anomalies and potential threats. Implement dynamic access control policies that adjust access based on real-time risk assessment.
- Data encryption and access control: Utilize robust encryption and granular access control mechanisms to protect sensitive data, even within the network.
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address security gaps and weaknesses.
Securing AI Systems and Models
AI is rapidly becoming the backbone of many critical systems, from healthcare to finance. However, this increasing reliance also exposes us to new and sophisticated threats. Securing these AI systems and the models they utilize is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Malicious actors are actively seeking vulnerabilities to exploit, demanding a proactive and comprehensive approach to security.
So, you’re thinking about five strategies for IT and security leaders to defend against AI-powered threats? It’s a crucial topic, and building robust defenses requires a multifaceted approach. One key aspect is ensuring your application development keeps pace with evolving threats; this is where understanding the potential of domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes into play.
Efficient development cycles allow for quicker patching and updates, a vital part of those five strategies for combating AI-driven attacks.
AI System Vulnerabilities
Understanding the specific vulnerabilities that AI systems face is crucial for effective defense. These vulnerabilities can be broadly categorized into data poisoning, model extraction, adversarial attacks, backdoors, and data breaches. The following table details five key vulnerabilities and their potential impacts.
| Vulnerability | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Poisoning | Introducing malicious data into the training dataset to manipulate the model’s behavior. | Inaccurate predictions, biased outputs, compromised decision-making. For example, a self-driving car’s training data could be poisoned to cause it to misinterpret stop signs. |
| Model Extraction | Illegally obtaining a copy of a trained model, potentially through API access or inference attacks. | Intellectual property theft, unauthorized replication, potential for malicious use of the model. A competitor could steal a proprietary financial prediction model. |
| Adversarial Attacks | Introducing carefully crafted inputs designed to fool the AI model into making incorrect predictions. | Misclassifications, incorrect diagnoses (in medical AI), compromised security systems. A stop sign could be subtly altered to be misclassified by a self-driving car’s vision system. |
| Backdoors | Introducing hidden triggers within the model that activate malicious behavior under specific conditions. | Unauthorized access, data theft, sabotage. A seemingly benign image processing model could be triggered to reveal sensitive data under a specific watermark. |
| Data Breaches | Unauthorized access to the data used to train or operate the AI model. | Data leaks, privacy violations, model retraining with compromised data. A breach of patient data used to train a medical diagnosis model could lead to serious privacy issues. |
Model Validation and Testing
Robust model validation and testing are paramount to mitigating the risks associated with AI systems. Thorough testing ensures that the model performs as expected, identifies potential vulnerabilities, and reduces the likelihood of manipulation or compromise. This involves rigorous evaluation using diverse datasets, including adversarial examples, to expose weaknesses before deployment. Without comprehensive testing, even the most sophisticated AI model can be vulnerable to exploitation.
Strategies for Securing the AI Development Lifecycle
A multi-layered security approach is needed throughout the AI development lifecycle. Here are five key strategies:
Effective security begins with data. Secure data collection, storage, and processing are fundamental. Implementing strong access controls, encryption, and data anonymization techniques are crucial steps.
- Secure Data Handling: Implement robust data governance policies, encryption at rest and in transit, and access control mechanisms to protect training data.
- Model Monitoring and Anomaly Detection: Continuously monitor the model’s performance for anomalies that could indicate malicious activity or degradation.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and proactively address potential weaknesses.
- Secure Model Deployment and Management: Deploy models in secure environments with appropriate access controls and monitoring capabilities. Regularly update and patch the underlying infrastructure.
- Develop Secure AI Development Practices: Integrate security considerations into every stage of the development process, from design to deployment. This includes secure coding practices, regular code reviews, and vulnerability scanning.
Developing and Implementing Robust Incident Response Plans
AI-powered attacks present unique challenges to traditional cybersecurity strategies. Their sophisticated nature, ability to adapt, and potential for widespread damage necessitate a robust and well-rehearsed incident response plan specifically designed to address these threats. Failing to adequately prepare can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions. This section Artikels the crucial elements of such a plan.
AI-Powered Attack Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan should be a living document, regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving threats and technological advancements. The following steps provide a framework for handling an AI-powered attack:
- Preparation: This involves identifying potential attack vectors, establishing clear roles and responsibilities within the incident response team, and pre-configuring tools and systems for rapid response. Regular security awareness training for all personnel is crucial.
- Detection and Analysis: This stage focuses on identifying the attack, understanding its nature (e.g., adversarial AI, data poisoning, model theft), and determining the extent of the compromise. This might involve analyzing logs, network traffic, and AI model performance metrics.
- Containment: Once an attack is confirmed, immediate steps must be taken to isolate affected systems and prevent further damage. This could involve shutting down affected AI models, isolating compromised networks, or disabling access to sensitive data.
- Eradication: This involves removing the malicious code or AI component, restoring compromised systems to a known good state, and patching vulnerabilities exploited during the attack. This may require specialized forensic analysis and remediation techniques.
- Recovery: This stage involves restoring normal operations, ensuring data integrity, and validating the effectiveness of security controls. This may involve deploying updated AI models or security patches.
- Post-Incident Activity: This critical step includes a thorough post-incident analysis to identify weaknesses, improve security measures, and update the incident response plan. This may involve conducting penetration testing and vulnerability assessments.
Comparison of Incident Response for Traditional and AI-Powered Attacks
While both traditional and AI-powered attacks require swift and decisive action, there are key differences in their incident response procedures. Traditional attacks often focus on identifying malware, removing malicious code, and restoring compromised systems. AI-powered attacks, however, may involve sophisticated techniques like adversarial machine learning, where the attacker manipulates the AI model’s inputs to produce incorrect or malicious outputs.
So, I’ve been diving into five strategies for IT and security leaders to defend against AI-powered threats, and it’s a wild west out there. One thing that immediately springs to mind is the alarming news of facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users , which perfectly illustrates how sophisticated these attacks can become. Understanding these evolving tactics is crucial when developing those five crucial defense strategies against AI-driven cybercrime.
This requires specialized expertise in AI and machine learning to detect, analyze, and remediate the attack effectively. For example, a traditional attack might involve a ransomware infection, while an AI-powered attack might involve an adversary manipulating a self-driving car’s AI system to cause an accident.
Post-Incident Analysis and Improvement
A thorough post-incident analysis is crucial for learning from past events and improving future security measures. This involves examining the timeline of the attack, identifying the vulnerabilities exploited, and assessing the effectiveness of the incident response plan. The analysis should also identify areas for improvement in security controls, processes, and training. For example, a post-incident analysis might reveal a weakness in the data validation process that allowed an attacker to inject poisoned data into an AI model, leading to inaccurate predictions.
This would necessitate implementing stronger data validation techniques and retraining the model with clean data. The findings of the analysis should be documented and used to update the incident response plan and overall security posture.
Building a Culture of Security Awareness and Training
In today’s threat landscape, a strong security posture relies not just on robust technology, but also on a workforce that understands and actively participates in mitigating risks. AI-powered threats are particularly insidious, often bypassing traditional security measures, making employee awareness and training paramount. A comprehensive security awareness program is the cornerstone of a resilient defense against these sophisticated attacks.
This involves educating employees about the evolving threat landscape, equipping them with the knowledge to identify and report suspicious activities, and fostering a culture where security is everyone’s responsibility.The effectiveness of any security measure hinges on the human element. Even the most advanced security systems can be compromised by a single click on a malicious link or the disclosure of sensitive information.
By investing in comprehensive security awareness training, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to AI-powered attacks and build a more resilient security ecosystem.
Key Training Modules for AI-Powered Threat Awareness
A successful training program should address the specific challenges posed by AI-powered threats. These modules should be delivered in a variety of formats, catering to different learning styles and incorporating interactive elements to maximize engagement. The following five modules provide a strong foundation:
- Module 1: Understanding AI-Powered Threats: This module introduces the various types of AI-powered threats, including deepfakes, sophisticated phishing attacks, and AI-driven malware. It explains how these threats work and the potential consequences of falling victim to them. Examples of real-world AI-powered attacks will be included to illustrate the severity of the threats.
- Module 2: Identifying and Reporting Suspicious Activities: This module focuses on practical skills, teaching employees how to identify suspicious emails, websites, and attachments. It emphasizes the importance of reporting any suspicious activity promptly through established channels. Specific examples of phishing emails and malicious websites will be used for practical exercises.
- Module 3: Data Security and Privacy Best Practices: This module covers the importance of protecting sensitive data, both personal and organizational. It emphasizes strong password hygiene, secure data handling practices, and the importance of adhering to data privacy regulations. Case studies of data breaches caused by human error will be analyzed.
- Module 4: Safe Use of Social Media and Personal Devices: This module addresses the risks associated with using social media and personal devices for work-related activities. It highlights the importance of maintaining professional boundaries online and avoiding the sharing of sensitive information on unsecured platforms. Best practices for using personal devices for work purposes will be discussed.
- Module 5: Responding to Security Incidents: This module Artikels the procedures to follow in the event of a security incident. It emphasizes the importance of reporting incidents promptly and cooperating with incident response teams. A simulated phishing exercise will be used to practice incident response procedures.
Creating Engaging and Effective Security Awareness Campaigns
Security awareness training shouldn’t be a dry, one-off event. To truly build a culture of security, ongoing engagement is crucial. Effective campaigns use a variety of methods to reach employees and keep security top-of-mind. These include:
- Interactive Training: Gamification, simulations, and scenario-based learning make training more engaging and memorable. For instance, a simulated phishing attack allows employees to experience the threat firsthand and learn from their mistakes in a safe environment.
- Regular Communication: Regular newsletters, emails, and internal communications keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices. Sharing real-world examples of attacks makes the information more relevant and impactful.
- Visual Aids: Infographics, videos, and short animations can effectively communicate complex information in an easily digestible format. For example, an infographic explaining the different types of AI-powered threats can be easily understood by employees of all technical backgrounds.
- Incentives and Recognition: Rewarding employees for their participation in training and for reporting suspicious activity fosters a culture of security awareness and encourages proactive engagement. For instance, recognizing employees who successfully identify phishing attempts can motivate others to be more vigilant.
Comprehensive Security Awareness Program Implementation
A robust program is more than just training; it’s a continuous cycle of education, reinforcement, and improvement. Key components include:
- Regular Training: Annual or bi-annual refresher training ensures that employees stay up-to-date on the latest threats and best practices. This includes updates on new AI-powered threats and evolving security techniques.
- Phishing Simulations: Regular phishing simulations test employee awareness and identify vulnerabilities in the organization’s security posture. Analyzing the results helps to improve training and refine security policies.
- Ongoing Education: Providing access to online resources, security bulletins, and other educational materials allows employees to continue learning and stay informed outside of formal training sessions. This can include access to online security awareness platforms and regular updates on security best practices.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, defending against AI-powered threats requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not enough to simply rely on traditional security measures; we need to proactively hunt for threats, bolster our data security with AI-powered tools, secure our own AI systems, and develop comprehensive incident response plans. Crucially, fostering a strong culture of security awareness among your team is vital.
By implementing these five strategies, IT and security leaders can significantly reduce their organization’s vulnerability to AI-driven attacks and build a more resilient security posture in the face of this evolving threat landscape. The future of cybersecurity depends on our ability to adapt and innovate, and these strategies offer a strong foundation for doing just that.
Key Questions Answered: Five Strategies For It And Security Leaders To Defend Against Ai Powered Threats
What are some common examples of AI-powered attacks?
Examples include sophisticated phishing campaigns using deepfakes, AI-driven malware that adapts to evade detection, and autonomous botnets carrying out large-scale attacks.
How can we measure the effectiveness of our AI security strategies?
Key metrics include the number of detected and mitigated AI-powered attacks, reduction in data breaches, and improvement in incident response times. Regular security assessments and penetration testing are crucial.
What’s the role of human expertise in an AI-driven security landscape?
Human expertise remains crucial for interpreting AI alerts, making critical decisions, and developing adaptable strategies. AI augments human capabilities, but it doesn’t replace them.
How often should security awareness training be conducted?
Regular training, ideally quarterly or even more frequently, is recommended to keep employees updated on the latest threats and best practices.