Fortifying Defenses Cybersecurity in the Dawn of AI Hornetsecurity
Fortifying defences cybersecurity in the dawn of ai hornetsecurity – Fortifying defenses cybersecurity in the dawn of AI Hornetsecurity – it sounds like a sci-fi thriller, right? But the reality is even more dramatic. Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping the cybersecurity landscape, creating both incredible opportunities and terrifying new threats. Attackers are leveraging AI to craft more sophisticated and evasive malware, while simultaneously, defenders are using AI to build smarter, more proactive security systems.
This post dives into the heart of this evolving battle, exploring how we can effectively fortify our defenses against the AI-powered threats of tomorrow, with a particular focus on the innovative solutions offered by Hornetsecurity.
We’ll examine how AI is amplifying existing cyberattacks, making phishing campaigns more convincing and malware more difficult to detect. But don’t worry, it’s not all doom and gloom! We’ll also delve into the powerful ways AI is being used to bolster our defenses, from enhancing intrusion detection systems to strengthening endpoint security. Get ready to explore network segmentation strategies, AI-powered EDR solutions, and the crucial role of human expertise in this new era of cybersecurity.
The Evolving Threat Landscape

The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming nearly every aspect of our lives, and cybersecurity is no exception. While AI offers incredible potential for improving security, it also introduces a new and complex threat landscape. Attackers are increasingly leveraging AI’s capabilities to create more sophisticated and effective cyberattacks, forcing defenders to adapt and innovate to stay ahead.
This necessitates a deep understanding of how AI is reshaping the cybersecurity battlefield.AI’s impact on cybersecurity is multifaceted, creating both opportunities and challenges. The increasing sophistication of AI-powered attacks demands a corresponding increase in the sophistication of our defenses. This isn’t simply about adding more layers of security; it’s about fundamentally changing how we approach cybersecurity, integrating AI into our strategies to combat the threats it creates.
New Attack Vectors and Vulnerabilities Introduced by AI
AI introduces several new attack vectors and vulnerabilities. For example, AI can be used to generate highly convincing phishing emails, tailored to individual targets and designed to bypass traditional spam filters. Deepfakes, created using AI, can be used for social engineering attacks, impersonating trusted individuals to gain access to sensitive information or systems. Furthermore, AI can automate the discovery and exploitation of vulnerabilities in software and systems at a scale and speed previously unimaginable.
This includes the development of highly targeted and polymorphic malware that can evade traditional signature-based detection methods. The automation of these processes allows attackers to scale their operations, targeting many victims simultaneously. Finally, AI can be used to analyze vast amounts of data to identify weaknesses in security systems and develop customized attacks to exploit those weaknesses.
AI’s Enhancement of Existing Cyberattacks
AI significantly enhances the effectiveness of existing cyberattacks. Consider phishing: AI can analyze massive datasets of personal information to create highly personalized and convincing phishing emails. These emails are far more likely to succeed than generic phishing attempts. Similarly, AI can automate the creation and deployment of malware, creating variations that evade traditional antivirus software. The ability to rapidly generate and adapt malware based on observed defenses makes it exceptionally difficult to counteract.
AI can also be used to automate reconnaissance, identifying vulnerabilities in target systems more efficiently and effectively than human attackers. This allows attackers to launch more focused and successful attacks.
AI-Powered Defenses to Mitigate New Threats
Fortunately, AI can also be used to bolster our defenses. AI-powered security systems can analyze network traffic and identify anomalies that might indicate a cyberattack. They can also learn to recognize patterns of malicious activity, improving their ability to detect and respond to threats over time. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to identify and block malicious emails and websites, improving the effectiveness of spam filters and web security tools.
AI can also automate incident response, helping security teams to quickly identify and contain breaches. Furthermore, AI can be used to analyze security logs and identify potential vulnerabilities in systems before attackers can exploit them.
Comparison of Traditional and AI-Enhanced Security Methods
| Method | Traditional Approach | AI-Enhanced Approach | Advantages of AI Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malware Detection | Signature-based detection; relies on known malware signatures. | Behavioral analysis; uses machine learning to identify malicious behavior regardless of signature. | Detects zero-day exploits and polymorphic malware; adapts to evolving threats. |
| Phishing Detection | filtering; relies on identifying known phishing s. | Content analysis and behavioral analysis; uses machine learning to identify suspicious patterns in emails and websites. | Detects highly personalized and sophisticated phishing attacks; adapts to evolving phishing techniques. |
| Vulnerability Management | Manual vulnerability scanning; relies on human analysts to identify and assess vulnerabilities. | Automated vulnerability scanning and prioritization; uses AI to identify and prioritize critical vulnerabilities. | Faster and more efficient vulnerability identification; allows for proactive mitigation. |
| Intrusion Detection | Rule-based intrusion detection systems; relies on pre-defined rules to detect intrusions. | Anomaly detection; uses machine learning to identify unusual network activity. | Detects unknown and zero-day attacks; adapts to evolving attack techniques. |
Fortifying Network Defenses Against AI-Driven Attacks

The rise of AI has ushered in a new era of cybersecurity threats. Malicious actors are increasingly leveraging AI’s capabilities to automate attacks, making them more sophisticated, persistent, and difficult to detect. This necessitates a proactive and multi-layered approach to network defense, focusing on resilience and advanced threat detection. Fortifying our networks against these AI-driven attacks is no longer a luxury, but a critical necessity.
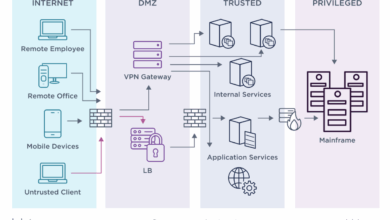
Robust Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is a crucial strategy for limiting the impact of breaches. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, we can prevent attackers from easily moving laterally across the system. If one segment is compromised, the damage is contained, preventing widespread infection. Implementing effective network segmentation requires careful planning and execution, considering factors like business needs and the sensitivity of data housed within each segment.
This involves using firewalls, VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), and other network security tools to create these isolated zones. A well-segmented network significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the potential for catastrophic data loss. For example, separating the guest Wi-Fi network from the internal corporate network prevents a compromised guest device from gaining access to sensitive internal systems.
Deploying AI-Powered Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Deploying AI-powered intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) is a vital step in bolstering network defenses. These systems utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze network traffic patterns and identify anomalies indicative of malicious activity. Here’s a step-by-step procedure for deployment:
- Needs Assessment: Analyze network traffic patterns and identify potential vulnerabilities to determine the specific needs and requirements for an AI-powered IDPS.
- System Selection: Choose an IDPS solution that aligns with the organization’s needs, considering factors like scalability, integration capabilities, and the level of AI sophistication offered.
- Installation and Configuration: Install the chosen IDPS and configure it according to the organization’s specific network architecture and security policies. This includes defining thresholds for alerts and defining actions to take upon detection of malicious activity.
- Integration: Integrate the IDPS with other security tools, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, to provide a holistic view of security events and enhance threat response capabilities.
- Monitoring and Tuning: Continuously monitor the IDPS for performance and effectiveness. Adjust settings and update rules as needed to adapt to evolving threat landscapes and ensure optimal performance. Regularly review false positives and refine the system’s learning process.
Securing Cloud Infrastructure Against AI-Based Attacks
The cloud presents unique challenges in the face of AI-driven attacks. However, by implementing robust security measures, organizations can mitigate these risks significantly.
- Employ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access to cloud resources, even if they obtain credentials.
- Implement Strong Access Control Policies: Restrict access to cloud resources based on the principle of least privilege. Only grant users the necessary permissions to perform their tasks, limiting the potential damage from a compromised account.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regularly assess the security posture of cloud infrastructure to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify weaknesses.
- Utilize Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools: CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud environments for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, providing alerts and recommendations for remediation. This proactive approach helps identify and address security risks in real-time.
- Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit: Encrypting data both when it’s stored and when it’s being transmitted protects it from unauthorized access, even if an attacker gains access to the cloud infrastructure.
- Regular Software Updates and Patching: Keeping all software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches is crucial to protect against known vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
Strengthening Endpoint Security in the Age of AI: Fortifying Defences Cybersecurity In The Dawn Of Ai Hornetsecurity
The rise of AI has ushered in a new era of sophisticated cyber threats. Attackers are leveraging AI’s capabilities to automate attacks, evade traditional security measures, and target vulnerabilities with unprecedented precision. This necessitates a fundamental shift in our approach to endpoint security, moving beyond reactive measures to a proactive, AI-powered defense. Strengthening endpoint security is no longer optional; it’s paramount for survival in this evolving threat landscape.Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions are becoming increasingly crucial in this AI-driven threat environment.
EDR goes beyond traditional antivirus, offering advanced threat hunting capabilities, real-time monitoring, and automated response mechanisms. This allows security teams to identify and neutralize threats before they can cause significant damage, a crucial advantage when facing the speed and complexity of AI-powered attacks. The ability to analyze endpoint behavior, detect anomalies, and automatically respond to malicious activity is essential in mitigating the risks posed by increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Integrating AI-Powered Security Tools into Existing Endpoint Security Infrastructure
A phased approach to integrating AI-powered security tools is recommended to minimize disruption and maximize effectiveness. This involves a careful assessment of the current endpoint security infrastructure, identifying gaps and prioritizing areas for improvement. The initial phase could focus on deploying AI-driven threat intelligence platforms to enhance existing threat detection capabilities. This provides valuable insights into emerging threats and allows for proactive adjustments to security policies.
Subsequent phases could involve the gradual integration of AI-powered EDR solutions, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) tools. Continuous monitoring and refinement are vital throughout this process, ensuring that the integrated system operates effectively and adapts to the ever-changing threat landscape. Successful integration requires careful planning, robust testing, and ongoing training for security personnel.
For example, a company might start by integrating an AI-powered malware detection tool into their existing antivirus software, followed by the deployment of an AI-driven EDR solution a few months later.
Comparison of Endpoint Security Approaches Against AI-Based Threats
The following table compares three different approaches to securing endpoints against AI-based threats. Each approach offers unique strengths and weaknesses, and the optimal choice depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the specific threat landscape.
| Approach | Strengths | Weaknesses | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Antivirus with AI Enhancements | Relatively low cost, familiar to security teams, improved detection rates with AI additions. | Limited proactive capabilities, may struggle with advanced, AI-driven attacks, relies on signature-based detection in part. | Low to Medium |
| AI-Powered EDR | Advanced threat detection and response, proactive threat hunting, automated incident response. | Higher cost, requires specialized expertise to manage and interpret data, potential for false positives. | Medium to High |
| Comprehensive Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) with AI | Centralized security monitoring and analysis, correlation of events across multiple sources, improved threat detection and response through AI-driven analytics. | High cost, requires significant expertise to manage and interpret data, complex implementation. | High |
The Role of Human Expertise in AI-Fortified Defenses
The rise of AI in cybersecurity offers incredible potential, automating threat detection and response at speeds far beyond human capabilities. However, relying solely on AI is a dangerous gamble. Human expertise remains crucial, providing the critical thinking, contextual understanding, and ethical considerations that AI currently lacks. A truly effective cybersecurity strategy leverages the strengths of both AI and human intelligence, creating a synergistic defense.AI-powered security systems, while powerful, are only as good as the data they are trained on.
They can identify patterns and anomalies, but they struggle with nuanced interpretations, particularly when dealing with novel or sophisticated attacks. Human analysts are needed to interpret these alerts, validate findings, and make informed decisions about the appropriate response. This human-in-the-loop approach is essential for mitigating the risks associated with false positives and ensuring the effectiveness of the overall security posture.
Key Skills and Knowledge Gaps in Cybersecurity Teams
Addressing the skills gap requires a multi-faceted approach. Cybersecurity teams need professionals proficient in both traditional security practices and AI-related technologies. This includes a deep understanding of machine learning algorithms, data analysis techniques, and the ethical implications of using AI in security. Furthermore, strong communication and collaboration skills are vital, as AI-driven security often involves working across different teams and departments.
A significant knowledge gap exists in understanding the limitations of AI in security, including bias in algorithms and the potential for adversarial attacks designed to fool AI systems. Bridging this gap requires specialized training and continuous professional development.
Improving the Accuracy and Effectiveness of AI-Based Security Systems Through Human Oversight
Human oversight significantly improves the accuracy and effectiveness of AI-based security systems in several key ways. First, humans can validate AI-generated alerts, distinguishing between true threats and false positives. This reduces the workload on security teams, allowing them to focus on genuine security incidents. Second, human analysts can provide context to AI-detected anomalies, enriching the data used to train and improve the AI system.
For example, a human might recognize a seemingly innocuous network activity as part of a larger, sophisticated attack, providing valuable feedback to the AI for future detection. Third, human intervention is critical in handling situations where AI systems lack sufficient data or encounter unexpected behaviors. Humans can leverage their experience and judgment to make informed decisions, even in ambiguous situations where AI may struggle.
This proactive approach significantly strengthens the overall resilience of the security system.
Fortifying our cybersecurity defenses in the age of AI, like Hornetsecurity’s solutions, requires a multi-layered approach. A crucial element is managing the ever-expanding cloud landscape, and understanding how platforms like Bitglass help; check out this insightful article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management to see how. Ultimately, strengthening cloud security is paramount to building robust, AI-ready defenses against modern threats.
A Training Program for Upskilling Cybersecurity Professionals
A comprehensive training program designed to upskill cybersecurity professionals in the use of AI-powered security tools should incorporate several key elements. The curriculum should begin with foundational courses in AI and machine learning, covering essential concepts such as supervised and unsupervised learning, neural networks, and deep learning. Subsequent modules should focus on the application of AI in specific cybersecurity domains, including threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management.
Hands-on training using real-world datasets and simulated attack scenarios is crucial to develop practical skills. The program should also emphasize ethical considerations and responsible AI practices, ensuring that professionals understand the potential biases and limitations of AI systems and how to mitigate these risks. Finally, continuous learning and professional development should be encouraged through ongoing training, workshops, and certifications, ensuring professionals stay abreast of the rapidly evolving landscape of AI in cybersecurity.
This ongoing education will be critical in adapting to new AI technologies and threat vectors.
The Future of Cybersecurity
The next 5-10 years will witness a dramatic reshaping of cybersecurity landscapes, driven largely by the accelerating advancements in artificial intelligence. AI’s potential to both enhance and threaten security is immense, demanding a proactive and adaptive approach from organizations worldwide. The integration of AI will be pivotal in detecting and responding to increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, while simultaneously raising concerns about the potential misuse of AI by malicious actors.AI’s transformative power in cybersecurity will manifest in several key areas.
It will allow for the automation of previously manual tasks, improving efficiency and reducing human error. Furthermore, AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets and identify patterns invisible to human analysts will lead to earlier threat detection and more effective incident response. This enhanced predictive capability will enable organizations to proactively mitigate risks rather than simply reacting to breaches.
Fortifying our cybersecurity defenses in the age of AI, with solutions like Hornetsecurity, is more crucial than ever. Recent news highlights the urgency; check out this article about Facebook potentially requesting bank account details and card transactions from users: facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users. This underscores the need for robust, proactive security measures to protect ourselves from increasingly sophisticated threats.
Strengthening our digital shields is no longer optional, it’s essential.
AI-Driven Threat Detection and Response
AI is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of modern threat detection systems. Machine learning algorithms can analyze network traffic, log files, and other data sources to identify anomalies indicative of malicious activity. For example, AI can detect unusual login attempts, identify phishing emails with high accuracy, and even predict potential vulnerabilities in software before they are exploited. This proactive approach significantly reduces the time it takes to detect and respond to threats, minimizing the impact of successful attacks.
Furthermore, AI-powered security information and event management (SIEM) systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, correlating security events across multiple sources to provide a comprehensive view of the threat landscape. This holistic approach allows for more effective incident response and reduces the risk of overlooking critical security events.
Innovative AI-Based Security Solutions
Several innovative AI-based security solutions are already being implemented or are in advanced stages of development. One example is the use of AI in vulnerability management. AI algorithms can scan code for vulnerabilities, prioritizing remediation efforts based on the severity of the risk. Another example is the use of AI in endpoint detection and response (EDR). AI-powered EDR solutions can analyze endpoint behavior in real-time, identifying and isolating malicious processes before they can cause significant damage.
Furthermore, AI is being used to improve the accuracy of threat intelligence, enabling security teams to better understand and respond to emerging threats. The development of AI-powered deception technologies is also gaining traction. These technologies create fake assets and data to lure attackers, allowing security teams to identify and analyze their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
Hornetsecurity’s Contribution to AI-Fortified Defenses, Fortifying defences cybersecurity in the dawn of ai hornetsecurity
Hornetsecurity leverages AI in several ways to strengthen its security solutions. Its email security platform utilizes machine learning algorithms to identify and block phishing emails, malware attachments, and other malicious content with high accuracy. This significantly reduces the risk of successful spear-phishing attacks and ransomware infections. Hornetsecurity’s cloud-based architecture also enables it to benefit from the scalability and processing power of cloud computing, allowing its AI algorithms to analyze massive amounts of data and adapt to evolving threats in real-time.
The company’s ongoing investment in research and development ensures that its AI-powered security solutions remain at the forefront of cybersecurity innovation, providing clients with robust and adaptable protection against increasingly sophisticated AI-driven attacks. Furthermore, Hornetsecurity integrates its AI capabilities with human expertise, combining the power of machine learning with the nuanced judgment of experienced security analysts. This hybrid approach ensures that its security solutions are both highly effective and adaptable to unforeseen circumstances.
Illustrating AI-Powered Threat Detection

AI-powered threat detection systems are revolutionizing cybersecurity by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify and respond to sophisticated attacks in real-time, far exceeding the capabilities of traditional signature-based methods. These systems leverage machine learning algorithms to learn from past attacks and adapt to new threats, providing a crucial layer of defense against increasingly complex cyberattacks. Let’s examine how such a system might detect a sophisticated phishing attack.An AI-powered system detecting a sophisticated phishing attack would employ a multi-layered approach, combining various data sources and analysis techniques.
The process begins with the collection of data from various points within the network, including email servers, web gateways, and endpoint devices. This data encompasses email headers, content, URLs, attachments, user behavior patterns, and network traffic.
AI Techniques Employed in Phishing Detection
The core of the system’s detection capabilities lies in its sophisticated algorithms. Machine learning models, specifically those based on deep learning neural networks, are trained on massive datasets of legitimate and malicious emails. These models learn to identify subtle patterns and anomalies indicative of phishing attempts. For example, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) excel at analyzing sequential data like email text, identifying unusual word choices, grammatical errors, or suspicious links within the email body.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are particularly effective at analyzing images, such as suspicious attachments, for malicious code or patterns. Furthermore, Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques are used to understand the semantic meaning of the email text, flagging emails with suspicious subject lines or body content that tries to manipulate the recipient.
Data Analysis and Threat Scoring
The system analyzes the collected data using a combination of techniques. Firstly, it performs static analysis on the email itself, examining its headers for inconsistencies or spoofed addresses. Secondly, dynamic analysis is conducted by simulating user interaction with suspicious links or attachments within a sandboxed environment. This allows the system to observe the behavior of the suspected malicious code without risking compromise of the actual network.
Fortifying our cybersecurity defenses in the age of AI, with Hornetsecurity’s help, is more critical than ever. We need robust, adaptable systems, and that includes considering how we build applications. Learning about efficient development methods, like those explored in this article on domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , can inform our choices in creating secure, scalable solutions.
Ultimately, secure app development directly impacts our overall cybersecurity posture in this AI-driven landscape.
The results of both static and dynamic analysis, along with user behavior patterns (e.g., unusual login times or locations), are combined to generate a threat score. This score represents the probability of the email being a phishing attempt, with higher scores triggering immediate alerts and automated responses, such as blocking the email or quarantining the attachment.
Example Scenario: A Spear Phishing Attack
Consider a spear phishing attack targeting a high-level executive. The AI system would analyze an incoming email, noticing that while the sender’s email address appears legitimate, subtle inconsistencies exist in the email headers. The system’s NLP component would identify the email’s content as highly personalized and persuasive, aiming to exploit the executive’s knowledge of company projects. Simultaneously, the system’s dynamic analysis reveals that a seemingly innocuous attachment contains malicious code designed to steal credentials.
By combining these factors, the AI system assigns a high threat score, triggering an immediate alert to the security team and automatically blocking the email from reaching the executive’s inbox. The system logs the event and provides detailed analysis to support further investigation. This detailed analysis includes the threat score, the specific indicators of compromise identified, and a timeline of the system’s actions.
Illustrating AI-Powered Threat Response
An AI-powered security system’s response to a ransomware attack is a multi-stage process, far more sophisticated and rapid than traditional methods. It leverages machine learning and advanced analytics to contain the threat, eradicate the malware, and restore affected systems with minimal downtime. This contrasts sharply with manual responses which can be slow and prone to human error.The system’s initial reaction hinges on real-time threat detection.
Upon identifying suspicious activity consistent with a ransomware infection (e.g., unusual file encryption patterns, mass file deletions, network communication spikes to known command-and-control servers), the AI initiates a series of automated responses.
Containment Procedures
The primary goal in the containment phase is to isolate the infected system or network segment to prevent the ransomware from spreading. This might involve automatically disconnecting the infected machine from the network, blocking specific network ports used by the malware, or temporarily halting critical services. The AI system might use network segmentation and micro-segmentation techniques to limit the impact.
For instance, if a workstation is infected, the AI might immediately isolate that workstation from the rest of the network, preventing lateral movement of the ransomware. This isolation is often accompanied by the creation of a forensic snapshot of the system’s state before any remediation is undertaken, crucial for later analysis and recovery. The AI also logs all actions taken during containment for auditing purposes.
Eradication Techniques
Once contained, the AI initiates the eradication phase. This involves identifying and removing the ransomware payload and any associated malicious files. The AI might employ several techniques, including:
- Signature-based detection: Matching known ransomware signatures against files on the system.
- Heuristic analysis: Identifying suspicious behavior indicative of malware, even if it hasn’t been seen before.
- Behavioral analysis: Monitoring the malware’s actions to understand its goals and develop targeted countermeasures.
- Sandboxing: Running suspicious files in a controlled environment to observe their behavior without risking damage to the main system.
The AI’s ability to correlate data from multiple sources (endpoint detection and response, network traffic analysis, security information and event management (SIEM) systems) allows for a more comprehensive eradication strategy. It might use machine learning models trained on vast datasets of ransomware samples to identify and neutralize even zero-day threats. The system might also leverage automated patching and vulnerability management to address any system weaknesses that allowed the initial infection.
Recovery Procedures
The final phase focuses on restoring affected systems and data. The AI leverages the forensic snapshot created during the containment phase to roll back the system to a clean state. If the snapshot is not viable, or if data has been encrypted, the AI might employ data recovery techniques, such as using backups or specialized decryption tools (if a decryptor is available for the specific ransomware variant).
The AI may prioritize restoring critical systems and data first, and may use automated workflows to restore user profiles and applications. The entire recovery process is tracked and logged, providing a complete audit trail of the incident response. The system also learns from the attack, updating its threat intelligence and machine learning models to improve its ability to prevent similar attacks in the future.
This iterative learning process is vital for adapting to the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Concluding Remarks
The future of cybersecurity is undeniably intertwined with the advancement of artificial intelligence. While AI presents significant challenges, it also offers unparalleled opportunities to strengthen our defenses. By strategically integrating AI-powered tools, implementing robust network security measures, and upskilling our cybersecurity teams, we can build a more resilient and secure digital world. Hornetsecurity’s commitment to innovation in this space is crucial, offering solutions that help organizations navigate this complex landscape and proactively protect themselves against the ever-evolving threats of AI-driven attacks.
The key takeaway? Proactive defense, continuous learning, and embracing innovative technologies like those offered by Hornetsecurity are essential for surviving and thriving in this new era.
Helpful Answers
What specific types of malware are becoming more sophisticated due to AI?
AI is enhancing malware by making it more polymorphic (changing its code to evade detection), self-learning (adapting to security measures), and capable of targeted attacks based on individual user profiles.
How can human oversight improve AI-based security systems?
Human expertise is vital for interpreting AI’s findings, addressing false positives, and making critical decisions during complex security incidents. Humans provide the context and judgment that AI currently lacks.
What are some examples of innovative AI-based security solutions?
Examples include AI-powered threat intelligence platforms, automated incident response systems, and sophisticated anomaly detection tools that identify unusual network behavior.
Is AI completely replacing human cybersecurity professionals?
No, AI is a powerful tool, but it’s not a replacement for human expertise. The future of cybersecurity relies on a collaborative approach where humans and AI work together.