How to Achieve Maximum Security in Virtualized Data Centers
How to achieve maximum security in virtualized data centers is a critical concern for organizations today. Virtualization offers agility and efficiency, but introduces new security complexities. This in-depth guide explores the multifaceted challenges and solutions, covering everything from network segmentation to physical security, to ensure a robust and secure virtualized data center environment.
From network security protocols to virtual machine hardening, this guide delves into the essential strategies for safeguarding your virtualized infrastructure. We’ll uncover the common vulnerabilities and demonstrate how to mitigate them, providing practical advice and actionable steps to build a fortress of security around your virtualized data.
Introduction to Virtualized Data Center Security
Virtualized data centers, while offering significant benefits like scalability and resource efficiency, introduce unique security challenges. The dynamic nature of virtual machines (VMs) and the shared infrastructure they operate on demand new security strategies. Traditional security approaches, often designed for physical servers, often fall short in this environment. Proactive security measures are paramount to mitigating risks and ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data within these complex systems.The importance of proactive security measures in virtualized data centers cannot be overstated.
Traditional security methods, relying on physical access controls and perimeter defenses, are insufficient in a virtualized environment. A proactive approach focuses on identifying potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, implementing robust security policies at the hypervisor level, and continuously monitoring the environment for anomalies. This approach enables organizations to adapt to the evolving threat landscape and maintain a strong security posture.
Security Challenges in Virtualized Environments
Virtualization introduces new attack vectors and complexities that traditional security models often fail to address. These vulnerabilities arise from the shared nature of resources, the dynamic nature of VMs, and the inherent complexity of hypervisor environments. Security professionals need to adopt a holistic approach that considers these unique aspects to effectively protect virtualized data centers.
Traditional vs. Virtualized Security Approaches
Traditional security approaches often focus on securing the physical hardware and network perimeter. Virtualized environments, however, demand a different strategy. Virtualized security approaches must encompass the entire virtual infrastructure, including the hypervisor, VMs, and the underlying physical infrastructure. This requires a shift from a reactive to a proactive security posture. It involves implementing robust access controls, intrusion detection systems, and vulnerability management procedures at the hypervisor level, and implementing security policies that encompass the virtualized infrastructure as a whole.
Common Security Vulnerabilities in Virtualized Environments
A proactive approach to security requires understanding the common vulnerabilities inherent in virtualized environments. These vulnerabilities often exploit the shared nature of resources and the dynamic nature of VMs. A robust security strategy needs to address these specific challenges.
| Vulnerability Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hypervisor Vulnerabilities | Weaknesses in the hypervisor software itself, such as vulnerabilities in the operating system kernel or security features. | A security flaw in the hypervisor allows unauthorized access to the entire virtualized environment. |
| VM Escape | An attacker gains unauthorized access to a VM and then escapes to the underlying physical infrastructure or other VMs. | Exploiting a vulnerability in a VM to gain access to other VMs or the host server. |
| Guest VM Attacks | Malicious software or attacks originating from within a virtual machine can impact other VMs or the host system. | A compromised VM spreading malware to other VMs on the same hypervisor. |
| Misconfigurations | Incorrect or inadequate security settings within VMs or the hypervisor. | A VM is configured with weak passwords or has open ports. |
| Shared Resource Attacks | Attacks exploiting the shared resources of the virtualized environment. | A compromised VM monopolizes CPU or memory resources, impacting other VMs. |
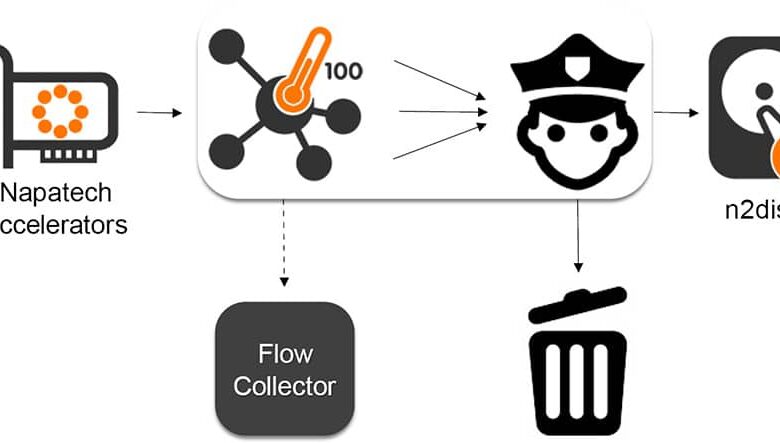
Network Security in Virtualized Environments
Virtualized data centers, while offering agility and scalability, introduce new security challenges. Traditional network security approaches often fall short in these dynamic environments. Effective network security in a virtualized setting demands a proactive and adaptable strategy, encompassing secure segmentation, robust intrusion detection, and the protection of virtual network functions.A key aspect of this approach is the careful implementation of secure network segmentation.
This allows for isolating virtual machines (VMs) and applications based on their sensitivity and access requirements, significantly limiting the impact of potential breaches. This approach is crucial for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality within the virtualized environment.
Securing virtualized data centers demands a multi-layered approach. Strong encryption and robust access controls are crucial, but understanding the legal landscape surrounding data transfers is equally vital. For example, recent developments like the Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions highlight the importance of staying informed about regulations.
Ultimately, a comprehensive security strategy encompassing both technical measures and legal compliance is key to achieving maximum protection.
Secure Network Segmentation within Virtualized Data Centers
Network segmentation is fundamental to isolating virtualized resources. Proper segmentation controls lateral movement of threats within the data center. It restricts unauthorized access and limits the scope of any potential compromise. Virtual networks can be segmented logically, creating isolated zones for different applications or departments. This granular control is critical for minimizing the risk of a breach impacting other parts of the data center.
Different Network Security Technologies Suitable for Virtualized Environments
Several technologies cater to the unique demands of virtualized environments. Virtual firewalls, often integrated with hypervisors, allow for dynamic firewall rules based on VM movement and application states. Network access control (NAC) solutions can enforce policies at the network level, controlling which VMs can access specific resources. Software-defined networking (SDN) controllers provide centralized control and automation for network configurations, facilitating rapid response to security threats.
Implementation of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) in a Virtualized Network
IDS/IPS systems are essential for detecting and preventing malicious activities. Implementing these systems within a virtualized environment requires specialized tools. Virtualized IDS/IPS solutions are often integrated with the hypervisor, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis of network traffic across VMs. These solutions can provide detailed insights into suspicious activities, enabling swift responses to potential threats.
Securing Virtual Network Functions (VNFs)
VNFs, crucial components in cloud-based networking, require dedicated security measures. Implementing strong access controls to VNFs is vital. This includes limiting access to specific users or groups based on their roles and responsibilities. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential to ensure that VNFs remain secure.
Secure Network Protocols Applicable to Virtualized Environments
Secure network protocols, such as Secure Shell (SSH), Transport Layer Security (TLS), and IPsec, are vital for secure communication between VMs and network devices. These protocols provide encryption and authentication, protecting data in transit. Using these protocols is essential for maintaining confidentiality and integrity.
Network Security Controls and Effectiveness in a Virtualized Context
| Network Security Control | Effectiveness in Virtualized Environments |
|---|---|
| Virtual Firewalls | High; dynamic rules allow for rapid adaptation to VM movements. |
| Network Access Control (NAC) | High; controls access based on device posture and policies. |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | High; specialized virtualized solutions provide real-time monitoring. |
| VNF Security Measures | Moderate to High; requires careful implementation of access controls and regular audits. |
| Secure Protocols (SSH, TLS, IPsec) | High; crucial for secure communication between VMs and network devices. |
Virtual Machine Security
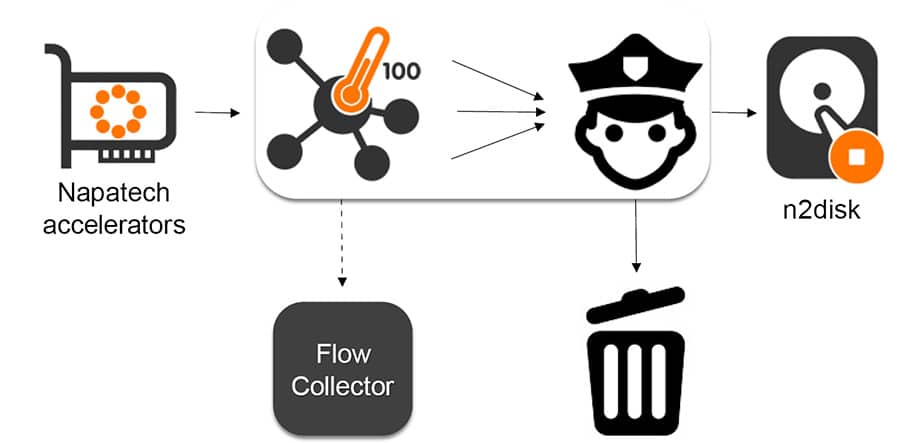
Securing virtual machines (VMs) is paramount in a virtualized data center. VM security isn’t just about the guest operating system; it extends to the hypervisor layer, the foundational software that manages and isolates VMs. A compromised hypervisor can expose all VMs running on it to potential attacks. This necessitates a layered approach to security, focusing on the hypervisor, individual VMs, and the network connections between them.The hypervisor, acting as the intermediary between the physical hardware and the VMs, plays a critical role in safeguarding the entire virtualized environment.
Securing virtualized data centers requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing everything from robust access controls to regular vulnerability assessments. A recent vulnerability in Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB, detailed in Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details , highlights the importance of staying ahead of potential threats. Ultimately, continuous monitoring and proactive patching remain crucial for maintaining maximum security in these environments.
Robust security configurations at this level prevent malicious code from spreading across VMs and compromising the entire infrastructure.
Hypervisor Security Configurations
Properly configuring the hypervisor is the cornerstone of VM security. This involves applying security patches promptly, restricting administrator access, and configuring robust logging and monitoring mechanisms. Security hardening of the hypervisor itself directly influences the security posture of all VMs. Careful attention to these configurations ensures the overall environment’s resilience against cyber threats.
- Patch Management: Regularly updating the hypervisor with security patches is essential. Vulnerabilities in the hypervisor can lead to widespread compromises if left unaddressed. Patches often address critical flaws that attackers can exploit. A timely patch management strategy reduces the attack surface and minimizes the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited.
- Access Control: Restricting access to the hypervisor to authorized personnel is crucial. Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls (RBAC) are fundamental for preventing unauthorized access. The hypervisor is the key to the entire virtualized environment; thus, restricting access is a first line of defense.
- Logging and Monitoring: Implementing robust logging and monitoring systems provides valuable insights into potential security breaches. These systems record actions and events, allowing administrators to detect and respond to suspicious activities promptly. Continuous monitoring of the hypervisor’s activities is vital for proactive threat detection and mitigation.
VM Security Configurations
Securing individual VMs involves implementing specific configurations to mitigate potential threats. These configurations should be tailored to the specific needs and workload of each VM.
- Least Privilege Principle: Granting VMs only the necessary permissions to perform their functions is a fundamental principle. This limits the impact of a potential compromise. Restricting unnecessary access privileges helps contain the damage in case of an attack.
- Firewall Rules: Implementing firewall rules on VMs controls network traffic, preventing unauthorized access and limiting potential exploitation vectors. This can be particularly important for VMs hosting sensitive data.
- Operating System Hardening: Applying security best practices to the guest operating system is vital. This includes disabling unnecessary services, configuring strong passwords, and applying security updates to the OS. The OS is a crucial part of the attack surface, so hardening it is an essential step.
Encryption for VM Data
Encrypting VM data protects sensitive information even if the VM or hypervisor is compromised. This involves encrypting data at rest and in transit.
Encryption ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Hardening VMs
Hardening VMs strengthens their security posture. This involves applying patches, disabling unnecessary services, and configuring secure network configurations. A hardened VM is less susceptible to exploitation attempts.
Securing virtualized data centers requires a multi-faceted approach. One crucial step is understanding potential vulnerabilities in your codebase, which can be helped by implementing tools like those discussed in Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed. Ultimately, a strong security posture in these environments hinges on proactive vigilance and the adoption of cutting-edge solutions.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in VMs is crucial. Regular assessments ensure that security measures are up-to-date and effective. Security audits can uncover potential weaknesses that attackers could exploit.
- Security Software Installation: Installing and configuring appropriate security software, such as antivirus and intrusion detection systems, on the VMs enhances their defenses. This software helps detect and respond to malicious activity.
Virtual Machine Escape Prevention
VM escape vulnerabilities allow malicious code to escape the confines of a VM and compromise the host system. This is a serious threat to the entire virtualized environment.
- Hypervisor-Level Controls: Implementing hypervisor-level controls can prevent unauthorized access to host resources. This includes isolation mechanisms and access restrictions to the underlying hardware.
- VM Isolation: Robust VM isolation mechanisms limit the potential for one VM to compromise others or the host system. Isolation prevents the spread of malicious code.
VM Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures
| Vulnerability Type | Description | Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|
| Hypervisor vulnerabilities | Exploitable flaws in the hypervisor software. | Regular hypervisor updates and security hardening. |
| VM escape vulnerabilities | Malicious code escaping the VM boundaries. | Strong VM isolation and hypervisor security controls. |
| Guest OS vulnerabilities | Exploitable flaws in the guest OS. | Regular OS updates and hardening. |
| Misconfigurations | Incorrect or inadequate security settings. | Regular security audits and configuration reviews. |
Data Security in Virtualized Environments: How To Achieve Maximum Security In Virtualized Data Centers
Virtualized data centers offer significant advantages in terms of flexibility and scalability, but they also introduce new security challenges. Protecting data within these dynamic environments requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on encryption, access control, prevention of data loss, and rigorous compliance with industry regulations. Robust backup and restoration strategies are crucial to ensure business continuity in case of unforeseen events.Data security in virtualized environments is paramount.
Effective strategies must address the unique characteristics of virtualization, including the dynamic nature of virtual machines and the potential for data breaches across multiple layers of the infrastructure. Implementing a comprehensive security posture requires careful consideration of the entire data lifecycle, from encryption at rest and in transit to data loss prevention and disaster recovery.
Data Encryption
Data encryption, both at rest and in transit, is a fundamental component of safeguarding sensitive information in a virtualized data center. Encryption at rest protects data stored on virtual disks, while encryption in transit protects data transmitted across networks. Robust encryption algorithms and key management protocols are essential.
- Encryption at rest ensures data confidentiality even if unauthorized access occurs to the storage systems. This is achieved by encrypting data within virtual disks, ensuring that even if a virtual machine or physical server is compromised, the data remains protected.
- Encryption in transit safeguards data transmitted between virtual machines, servers, and other network components. This protects against eavesdropping and data breaches during transmission. SSL/TLS protocols are commonly used for securing network communications.
Access Control Mechanisms
Implementing robust access control mechanisms is crucial for restricting access to sensitive data within virtualized environments. Granular access control policies ensure that only authorized users can access specific data or resources. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common method for managing access rights.
- Virtual machine-level access control can restrict access to specific virtual machines based on user roles or permissions. This isolates sensitive data within individual virtual machines and limits potential exposure in case of a compromise.
- Data-level access control allows fine-grained control over access to specific files or databases. This ensures that only authorized users can view, modify, or delete specific data within the virtualized environment.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools
Data loss prevention (DLP) tools are essential for identifying and preventing sensitive data from leaving the virtualized environment. These tools can monitor network traffic, user activities, and data storage for unauthorized access or breaches.
- DLP tools monitor user actions and system logs to detect suspicious activities, such as attempts to copy or export sensitive data. These tools can be configured to identify specific s or patterns associated with sensitive data, enabling proactive prevention measures.
- Examples of DLP tools include those that monitor network traffic for sensitive data exfiltration, and those that scan files for confidential information. These tools can be deployed within the virtualized environment to proactively identify and prevent data loss.
Backup and Restore Methods
Robust backup and restore procedures are critical for ensuring business continuity in case of data loss or system failure. Virtualized environments offer several methods for backing up and restoring data efficiently.
- Virtual machine backups can be performed to protect the entire virtual machine state, including the operating system, applications, and data. This allows for a complete recovery in case of failure.
- Snapshotting enables point-in-time backups, capturing the state of a virtual machine at a specific moment. This allows for quick recovery to a previous stable state.
Compliance with Data Security Regulations
Compliance with data security regulations like GDPR and HIPAA is crucial for organizations operating in virtualized environments. These regulations mandate specific requirements for data protection, and failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
- GDPR mandates strict data protection measures, including data minimization, purpose limitation, and data security. Implementing encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention measures are essential to comply with these regulations within a virtualized environment.
- HIPAA regulations dictate specific requirements for protecting protected health information (PHI). These regulations require implementing robust security controls to safeguard patient data in virtualized environments.
Data Security Measures and Implications
| Data Security Measure | Description | Implications in Virtualized Environments |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption at Rest | Encrypting data stored on virtual disks | Protects data even if VMs or servers are compromised |
| Encryption in Transit | Encrypting data transmitted across networks | Safeguards data during transmission, preventing eavesdropping |
| Access Control | Restricting access to data based on roles and permissions | Limits exposure of sensitive data and improves security posture |
| DLP Tools | Identifying and preventing sensitive data loss | Proactive detection of data exfiltration and unauthorized access |
| Backup and Restore | Regularly backing up and restoring data | Ensures business continuity and data recovery in case of failures |
| Compliance with Regulations | Adherence to industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) | Avoids penalties and maintains trust with customers and stakeholders |
Identity and Access Management (IAM) in Virtualized Environments
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is critical in securing virtualized data centers. It dictates who has access to what virtual resources, ensuring only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive data and systems. Effective IAM policies are paramount to preventing unauthorized access and data breaches in the dynamic landscape of virtualization. Strong IAM practices mitigate risks and protect the integrity of virtualized environments.Robust IAM in virtualized environments establishes a comprehensive framework for managing user access to virtual resources, ensuring only authorized personnel interact with sensitive data and systems.
This framework encompasses the entire lifecycle of user interaction, from initial authentication to resource access and eventual termination of access.
The Role of IAM in Virtualized Data Center Security
IAM plays a crucial role in the overall security posture of a virtualized data center. It acts as a gatekeeper, controlling who can access specific virtual machines, networks, and data. A well-implemented IAM system enhances security by enforcing policies that define permitted actions and resources. This mitigates the risks associated with unauthorized access, misuse, and data breaches.
IAM is directly tied to the principle of least privilege, where users are granted only the necessary access to perform their job functions.
Methods for Managing User Access to Virtual Resources
Several methods exist for managing user access to virtual resources. These methods include but are not limited to:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This method defines roles with specific permissions and assigns users to those roles. This granular control ensures users only access resources necessary for their tasks. For instance, a system administrator role might have broader access than a regular user role.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): This method leverages attributes (like user location, device type, or time of day) to determine access permissions. This allows for dynamic access policies based on real-time conditions. For example, access to sensitive data might be restricted to users within the corporate network.
- Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC): This method defines rules for access based on predefined policies. The policies can be complex, considering multiple attributes and conditions. A PBAC system could enforce access restrictions based on user role and time constraints.
Implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Virtualized Environments
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances security in virtualized environments. It requires users to provide multiple forms of verification (e.g., password, security token, biometric data) before granting access. This approach makes it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they obtain a user’s password. Implementing MFA across virtualized resources is a critical step in protecting sensitive data and systems.
Comparison of IAM Solutions for Virtualized Environments
Different IAM solutions cater to various needs and security requirements. Choosing the right solution depends on factors like the scale of the virtualized environment, budget constraints, and specific security needs. Some popular solutions include:
- Commercial IAM platforms: These platforms provide comprehensive IAM functionalities, including authentication, authorization, and user management. They often integrate with existing infrastructure and offer extensive customization options.
- Open-source IAM solutions: These solutions offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness. They may require more technical expertise for implementation and ongoing maintenance.
- Cloud-based IAM services: These services provide a scalable and readily available IAM solution, often integrated with cloud platforms. They are typically managed by the cloud provider.
Importance of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Virtualized Environments
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is vital in virtualized environments. It ensures that users have only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks. This principle of least privilege reduces the potential damage from unauthorized access or malicious actions. A well-defined RBAC system is fundamental to maintaining a secure virtualized data center.
Contrasting IAM Approaches and Their Security Benefits
| IAM Approach | Security Benefits in Virtualized Environments |
|---|---|
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Granular control over access, enforcing least privilege, easier to manage complex access requirements. |
| Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) | Dynamic access policies based on real-time attributes, adapting to changing conditions, improving responsiveness to security threats. |
| Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC) | Complex access rules, encompassing multiple conditions, enhancing security posture. |
Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Virtualized data centers, while offering agility and efficiency, introduce unique security challenges. Continuous monitoring and a robust incident response plan are crucial to proactively identify and mitigate threats. Effective security monitoring goes beyond simple alerts; it requires a holistic approach that combines automated tools with human expertise.The dynamic nature of virtualized environments demands a proactive security posture, constantly adapting to evolving threats.
This necessitates comprehensive monitoring to identify anomalies and potential breaches in real-time. The ability to quickly contain and resolve incidents is paramount to minimizing disruption and maintaining business continuity.
Importance of Continuous Security Monitoring
Continuous security monitoring in virtualized data centers is essential for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they escalate into significant breaches. Real-time threat detection allows for immediate responses and reduces the potential for data loss or service disruptions. Monitoring tools can track critical system metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory consumption, and network traffic, helping to identify anomalies that could indicate malicious activity.
Use of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools play a critical role in virtualized environments. They aggregate security logs from various sources, including virtual machines, network devices, and security appliances, correlating them to identify patterns indicative of malicious activity. SIEM tools can automatically generate alerts for suspicious events, allowing security teams to quickly respond to potential threats. The ability to analyze historical data is crucial for identifying trends and understanding the attack surface.
Incident Response Procedure in Virtualized Environments
A well-defined incident response procedure is critical for containing and resolving security incidents in virtualized environments. This procedure should Artikel roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and escalation paths. It should also detail steps for isolating affected systems, gathering evidence, and restoring services. A key element is establishing clear communication protocols between security teams, IT operations, and other stakeholders.
- Preparation: Establish clear communication protocols, define roles and responsibilities, and develop a documented incident response plan. This plan should address various types of incidents and provide specific procedures for each.
- Detection: Implement robust security monitoring tools to identify suspicious activity and potential breaches in real-time.
- Analysis: Analyze the detected incident, gather relevant data, and determine the scope and impact of the incident.
- Containment: Isolate affected systems and prevent further damage or propagation of the incident.
- Eradication: Eliminate the root cause of the incident and remediate any vulnerabilities exploited.
- Recovery: Restore affected systems and services to their pre-incident state. This includes data recovery and system reconfiguration.
- Post-Incident Activity: Conduct a thorough review of the incident response process, identify areas for improvement, and update procedures as needed.
Importance of Log Management in a Virtualized Data Center
Log management is fundamental to security monitoring in a virtualized data center. Logs from virtual machines, hypervisors, and network devices provide crucial insights into system activity, enabling security analysts to detect suspicious patterns and respond effectively to security threats. Comprehensive log management is essential for forensic analysis in case of a security breach.
Methods for Detecting and Responding to Security Breaches
Detecting and responding to security breaches in virtualized environments requires a multi-layered approach. This includes leveraging intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to identify and block malicious activity. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are crucial for identifying and patching weaknesses in virtualized infrastructure. Monitoring for unusual network traffic patterns and user behavior is also vital.
For example, sudden spikes in network traffic from a particular IP address could indicate a potential attack.
Security Monitoring Tools and Applicability
| Tool | Description | Applicability in Virtualized Environments |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | A widely used SIEM tool that aggregates and analyzes security logs from various sources. | Excellent for correlating events across virtual machines, hypervisors, and network devices. |
| Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana (ELK Stack) | An open-source suite for log aggregation, analysis, and visualization. | Highly adaptable and cost-effective for virtualized environments, particularly in custom deployments. |
| SolarWinds Security | A comprehensive security management platform offering various monitoring tools. | Provides a centralized view of security across virtual and physical infrastructure, useful for large-scale deployments. |
| Wireshark | A network protocol analyzer that captures and analyzes network traffic. | Useful for identifying unusual network activity and potential malicious communication within the virtualized environment. |
Physical Security Considerations in Virtualized Data Centers
Virtualized data centers, while offering flexibility and scalability, are still vulnerable to physical threats. Proper physical security is crucial to protecting the valuable data and infrastructure housed within these environments. A robust physical security plan acts as a crucial first line of defense against unauthorized access, theft, and environmental damage, safeguarding the entire virtualized infrastructure.Physical security in virtualized data centers goes beyond just locking doors.
It involves a comprehensive approach encompassing access control, environmental controls, and a carefully designed server room layout, all integrated to maintain the integrity and availability of the virtualized systems. This intricate web of physical protections is vital for safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
Access Control Systems
Implementing robust access control systems is paramount for restricting physical access to the data center. This involves more than just a simple security guard; it necessitates a multi-layered approach. Keycard systems, biometric authentication, and video surveillance are all essential components. Combining these methods creates a strong deterrent against unauthorized individuals. Access logs are crucial for tracking and auditing personnel movements, facilitating accountability and investigation in case of security breaches.
Regularly reviewing and updating access lists ensures only authorized personnel have entry.
Environmental Controls, How to achieve maximum security in virtualized data centers
Maintaining optimal environmental conditions is critical for the proper functioning of virtualized servers and the longevity of the equipment. Unstable temperatures, fluctuating humidity levels, or inadequate ventilation can lead to equipment malfunctions and data loss. Thus, careful attention to environmental controls is a crucial aspect of physical security. Climate control systems, including HVAC systems, are essential for maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels.
Regular monitoring of these systems and proactive maintenance schedules minimize potential disruptions. Redundant systems, such as backup power supplies and cooling units, are vital for maintaining operations during unforeseen outages.
Server Room Design and Layout
The design and layout of the server room significantly influence the effectiveness of physical security measures. A well-designed server room prioritizes minimizing vulnerabilities and maximizing security. Strategic placement of security cameras, strategically positioned fire suppression systems, and clear pathways for emergency evacuation are all critical design considerations. Using raised floors for cabling management allows for easier access to the underlying infrastructure and prevents unauthorized access to equipment.
A clear demarcation between authorized and unauthorized areas, coupled with restricted access points, further enhances security.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning
Disaster recovery and business continuity planning (BCP) are essential for mitigating the impact of potential disruptions, including physical security incidents. BCP planning should Artikel procedures for data backup, disaster recovery sites, and business resumption strategies. These plans should account for various scenarios, from power outages to natural disasters. Regular testing and validation of BCP plans are critical for ensuring they remain effective and resilient to evolving threats.
This proactive approach minimizes downtime and maintains business operations during unforeseen circumstances.
Physical Security Measures Table
| Security Measure | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control Systems | Keycard systems, biometric authentication, video surveillance | Restrict physical access, enhance accountability |
| Environmental Controls | Temperature, humidity, ventilation | Ensure optimal equipment performance, prevent damage |
| Server Room Design | Strategic placement of equipment, security cameras, fire suppression | Minimize vulnerabilities, maximize security |
| Disaster Recovery/BCP | Data backup, recovery sites, resumption strategies | Mitigate disruption, maintain business continuity |
Compliance and Regulations
Navigating the virtualized data center landscape requires a deep understanding of compliance and regulatory frameworks. These frameworks ensure data security, privacy, and operational integrity, protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust with stakeholders. Failing to adhere to these regulations can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage.Virtualization, while offering flexibility and efficiency, introduces unique security considerations that must be addressed through compliance.
This involves meticulous planning, rigorous implementation, and ongoing monitoring to ensure adherence to industry standards and legal mandates.
Key Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Understanding the specific requirements of various regulations is crucial for building a secure virtualized data center. These regulations often cover aspects like data protection, privacy, security incident reporting, and auditing. Compliance is a multifaceted process that demands careful attention to detail and a proactive approach.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This EU regulation mandates stringent data protection measures, particularly concerning the collection, processing, and storage of personal data. It emphasizes user consent, data minimization, and data security.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): In healthcare, HIPAA regulations are paramount, requiring strict confidentiality and security protocols for protected health information (PHI). It dictates specific measures for protecting electronic data from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): This standard is critical for organizations handling credit card information, demanding secure processing and storage procedures to prevent breaches. It Artikels technical and operational safeguards for protecting sensitive financial data.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): For publicly traded companies, SOX mandates financial reporting controls, requiring accurate and reliable financial data. It also emphasizes internal controls and audits to ensure the integrity of financial information.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework: NIST provides a comprehensive framework for managing cybersecurity risks. It offers a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate risks across various aspects of an organization’s security posture. This framework is widely applicable to virtualized data centers.
Steps to Ensure Compliance
Implementing a robust compliance strategy involves several crucial steps. Proactive measures are essential for avoiding penalties and maintaining a positive reputation.
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment: Identify potential vulnerabilities and risks specific to the virtualized environment. This assessment should consider the unique aspects of virtualization, such as the potential for unauthorized access through virtual machines.
- Develop and implement security policies: Create comprehensive security policies that clearly define responsibilities, procedures, and acceptable use guidelines. These policies must address specific security controls relevant to virtualized environments, including access controls and data encryption.
- Implement appropriate security controls: Deploy robust security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls. Ensure these controls are tailored to the virtualization platform and address the specific threats and vulnerabilities in virtualized environments.
- Regularly monitor and audit: Establish a system for regularly monitoring security events and conducting security audits. This allows for identification of any deviations from established policies and regulations, and allows for timely remediation.
- Stay informed and updated: The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving. Organizations must stay informed about emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and updates to regulations. This continuous learning process is crucial to maintaining compliance and adapting to new security challenges.
Importance of Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are critical for identifying gaps in security controls and ensuring ongoing compliance. They are vital for proactive security management and risk mitigation.Regular audits provide a snapshot of the current security posture, revealing potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses that might not be apparent through other means. This allows for proactive measures to be implemented before a breach occurs.
Furthermore, they provide evidence of adherence to compliance standards, protecting against penalties and maintaining stakeholder trust.
Role of Security Policies in a Virtualized Environment
Security policies play a crucial role in guiding actions and establishing standards within a virtualized data center. These policies should address specific aspects of virtualization.Security policies in a virtualized environment must clearly define responsibilities and procedures regarding the creation, management, and termination of virtual machines. These policies should include guidelines for access controls, data encryption, and incident response procedures.
They should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the changing security landscape.
Comparison of Compliance Frameworks
Various compliance frameworks provide different approaches to security. A comparison highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Provides a structured, risk-based approach applicable to various organizations and industries. It emphasizes a continuous improvement cycle.
- ISO 27001: A globally recognized standard for information security management systems. It offers a comprehensive set of security controls applicable to any organization.
- HIPAA: Specifically focused on protecting health information, this framework requires strict security measures to protect patient data.
Compliance Regulations and Applicability
The table below illustrates the applicability of various compliance regulations to virtualized data centers. This table is not exhaustive but provides a general overview.
| Compliance Regulation | Applicability to Virtualized Data Centers |
|---|---|
| GDPR | Applicable; requires stringent data protection measures for personal data processed in virtualized environments. |
| HIPAA | Applicable; strict confidentiality and security protocols are required for protected health information processed within virtualized environments. |
| PCI DSS | Applicable; secure processing and storage of payment card information within virtualized environments. |
| SOX | Applicable; requires robust internal controls and financial reporting processes for publicly traded companies using virtualized environments. |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | Highly applicable; provides a structured approach for managing cybersecurity risks in virtualized environments. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, achieving maximum security in virtualized data centers requires a holistic approach, encompassing network, machine, data, identity, monitoring, and physical security considerations. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key strategies, highlighting the importance of proactive measures, robust security configurations, and a culture of continuous improvement. By understanding and implementing these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and protect their sensitive data in this evolving digital landscape.
Question & Answer Hub
What are some common security vulnerabilities specific to virtualized environments?
Virtualized environments introduce vulnerabilities related to hypervisors, virtual machines, and the network. These can include VM escape vulnerabilities, misconfigurations in the hypervisor, inadequate network segmentation, and insufficient access controls.
What role does encryption play in protecting data within a virtualized environment?
Encryption is crucial for safeguarding data at rest and in transit. Encrypting data both on storage devices and during transmission helps protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
How can I ensure compliance with data security regulations in a virtualized environment?
Compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA requires meticulous attention to data protection. This includes implementing strong access controls, encryption, and robust incident response plans. Organizations must also document their security policies and procedures to demonstrate compliance.
What are some best practices for hardening virtual machines?
Hardening virtual machines involves minimizing attack surface, using strong passwords, and regularly updating software. This includes disabling unused services and configuring appropriate firewall rules.