How to Draft an Effective Data Protection Strategy
How to draft an effective data protection strategy is crucial in today’s digital landscape. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps, from defining your strategy to adapting it to future needs. We’ll explore key elements like risk assessment, implementation of controls, building a data-protection culture, and ongoing monitoring and adaptation.
A robust data protection strategy isn’t just about meeting regulatory requirements; it’s about safeguarding your valuable information and fostering trust with your users. This guide will provide actionable insights and practical examples to help you create a strategy that works for your specific organization.
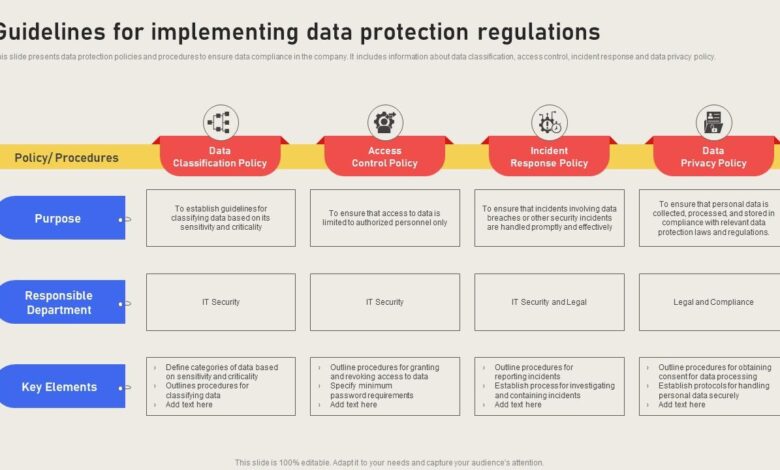
Defining Data Protection Strategy

A robust data protection strategy is crucial for any organization navigating the complex landscape of data privacy. It’s not just about adhering to regulations; it’s about establishing a comprehensive framework that safeguards sensitive information throughout its lifecycle, from collection to disposal. This framework encompasses both technical measures and organizational policies to ensure data security and compliance.This strategy goes beyond simply preventing unauthorized access; it proactively addresses the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with data handling.
It establishes clear guidelines and responsibilities, ensuring that all employees understand and follow the rules, minimizing the risk of data breaches and associated financial and reputational damage.
Defining Data Protection Strategy
A data protection strategy is a comprehensive plan that Artikels how an organization manages and safeguards sensitive data. It encompasses technical controls, like encryption and access management, as well as organizational policies, including employee training and incident response procedures. A well-defined strategy proactively addresses potential risks and vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and minimizing potential damage from data breaches.
Key Objectives and Goals
The primary objectives of a data protection strategy are to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. This involves protecting data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. Furthermore, a strong strategy aims to build trust with customers and stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to data privacy. This commitment fosters a positive reputation and contributes to business success.
Importance of Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with relevant regulations, such as the GDPR and CCPA, is paramount. These regulations dictate specific requirements for data processing and storage, providing a baseline for data protection. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties and reputational damage. A well-structured strategy ensures that all data handling practices align with the mandates of applicable regulations, fostering trust and maintaining legal compliance.
Types of Data Requiring Protection
Organizations handle diverse types of data, each requiring varying levels of protection. This includes customer data, financial records, intellectual property, and personal health information. The sensitivity of the data dictates the specific safeguards required. A thorough inventory of all data types, along with their sensitivity levels, is a vital step in developing a robust data protection strategy.
Comparison of Data Protection Approaches
| Approach | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Converting data into an unreadable format without a key. | Strong protection against unauthorized access; effective for sensitive data. | Requires key management; potentially impacts performance. |
| Access Controls | Restricting access to data based on roles and permissions. | Minimizes the risk of unauthorized access; easily implemented. | Requires careful role definition; may not fully protect against insider threats. |
| Data Masking | Replacing sensitive data with dummy data while maintaining the original data structure. | Allows testing and analysis without compromising sensitive information. | Requires expertise to ensure accurate masking. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Monitoring and controlling the flow of sensitive data. | Identifies and prevents sensitive data from leaving the organization. | Can be complex to implement and manage. |
Assessing Data Protection Risks
Understanding and mitigating data protection risks is crucial for any organization. A robust data protection strategy hinges on a thorough risk assessment. This involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, analyzing their impact, and developing appropriate countermeasures. Failing to address these risks can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
Identifying and Categorizing Potential Data Breaches and Vulnerabilities
A critical first step in risk assessment is identifying potential data breaches and vulnerabilities. This requires a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s data assets, their sensitivity, and the systems used to store and process them. Common vulnerabilities include weak passwords, outdated software, insecure configurations, and inadequate access controls. Analyzing historical data breaches, industry best practices, and emerging threats provides a solid foundation for identifying vulnerabilities.
Crafting a robust data protection strategy involves meticulous planning and a deep understanding of potential threats. One crucial aspect is recognizing vulnerabilities like those detailed in the Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details here. Understanding these specific weaknesses is essential for developing preventative measures and ultimately fortifying your overall data protection strategy.
Thorough inventorying of data assets, including their location, sensitivity level, and usage, is vital for a complete picture.
Risk Assessment Methodologies and Tools
Several methodologies and tools facilitate the risk assessment process. Qualitative methods, such as checklists and questionnaires, can provide a high-level overview of potential risks. Quantitative methods, on the other hand, assign numerical values to the likelihood and impact of each risk. Tools like risk matrices, vulnerability scanners, and penetration testing platforms offer valuable support in identifying and prioritizing potential threats.
Utilizing a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches provides a more comprehensive risk assessment.
Steps to Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment
A systematic approach to risk assessment is essential. The steps typically include:
- Identifying data assets: This involves cataloging all sensitive data, including its location, type, and usage.
- Identifying threats and vulnerabilities: Analyze potential threats, such as malicious attacks, human error, and natural disasters, and assess their impact on the identified data assets.
- Assessing the likelihood and impact of risks: Determine the probability of each threat occurring and the potential damage to the organization if it does.
- Evaluating existing controls: Assess the effectiveness of existing security controls in mitigating identified risks.
- Developing mitigation strategies: Propose solutions to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks, incorporating best practices and industry standards.
- Documenting and reporting: Creating a comprehensive risk register detailing identified risks, their likelihood, impact, and mitigation strategies is essential.
Criticality of Identifying and Mitigating Risks
Identifying and mitigating risks within an organization is paramount. Failing to address potential threats can result in severe consequences, ranging from financial penalties to legal action and reputational damage. A proactive approach to risk management helps prevent data breaches, safeguards sensitive information, and ensures business continuity. Prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and potential impact enables organizations to allocate resources effectively.
Examples of Potential Data Breaches
Numerous examples highlight the potential impact of data breaches. A breach affecting a financial institution can result in substantial financial losses, while a breach in a healthcare organization can compromise patient confidentiality and privacy. A breach affecting a government agency could compromise sensitive national security information. Real-world case studies of data breaches serve as valuable learning resources.
Table of Common Data Breach Scenarios and Their Impact
| Data Breach Scenario | Impact |
|---|---|
| Phishing attack targeting employee accounts | Unauthorized access to sensitive data, potential financial loss |
| Malware infection of a company server | Data theft, disruption of business operations |
| Third-party vendor breach | Compromise of customer data, reputational damage |
| Insider threat | Unauthorized disclosure of confidential information |
| Natural disaster impacting data centers | Data loss, business interruption |
Implementing Data Protection Controls
Putting a data protection strategy into action requires a multifaceted approach. Simply defining and assessing risks isn’t enough; you need concrete steps to safeguard sensitive information. This involves implementing various technical controls, establishing robust access management, and fostering a culture of security awareness. A proactive and well-structured implementation process is crucial to achieving the desired level of data protection.Implementing these controls is a dynamic process, not a one-time event.
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, requiring organizations to adapt and refine their security measures. Regular reviews and updates to the strategy are essential to maintaining its effectiveness.
Technical Controls for Enhanced Data Protection
Implementing robust technical controls is paramount to a successful data protection strategy. These controls form the foundation for safeguarding data and preventing unauthorized access. Effective technical controls encompass a range of measures, including encryption, access controls, security audits, and incident response plans.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest is a cornerstone of data protection. Data encryption renders data unreadable to unauthorized individuals, significantly reducing the risk of breaches. The use of strong encryption algorithms is vital for ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive information. Examples include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and data at rest encryption using tools like BitLocker.
- Access Control Mechanisms: Implementing strict access control mechanisms is critical to limit data exposure. These mechanisms define who can access specific data and what actions they are permitted to perform. This includes using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to only authorized personnel. Granular control over access permissions ensures data confidentiality and minimizes the impact of potential security breaches.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Routine security audits and penetration testing are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities in your data protection infrastructure. These assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of your security posture and pinpoint potential weaknesses. Penetration testing, in particular, simulates real-world attacks to evaluate the effectiveness of your defenses. Regular audits ensure that your controls remain effective against evolving threats.
Results from audits and tests should be used to prioritize and address vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Planning and Procedures: Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is vital for managing security incidents. This plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach or security incident, including notification procedures, containment strategies, and recovery plans. This ensures a structured approach to handling incidents, minimizing damage, and adhering to regulatory compliance.
A clear incident response plan can significantly reduce the impact of a security incident.
- Security Awareness Training Programs: Employee training is a critical component of a strong data protection strategy. Regular security awareness training programs help educate employees about potential threats and best practices for protecting sensitive data. These programs should cover topics such as phishing scams, social engineering, password security, and data handling protocols. Training programs are crucial in fostering a culture of security awareness within the organization.
Examples include simulated phishing attacks to identify vulnerabilities and training on handling sensitive data.
Implementation Steps of Data Protection Controls
This table Artikels the key steps for implementing each data protection control.
| Data Protection Control | Implementation Steps |
|---|---|
| Data Encryption |
|
| Access Control Mechanisms |
|
| Security Audits and Penetration Testing |
|
| Incident Response Planning and Procedures |
|
| Security Awareness Training Programs |
|
Building a Data Protection Culture: How To Draft An Effective Data Protection Strategy
A robust data protection strategy isn’t just about implementing technical controls; it’s fundamentally about fostering a culture of data protection awareness and responsibility within an organization. This involves shifting from a reactive approach to a proactive one, where data protection is ingrained in the daily operations and decision-making processes of every employee. A strong data protection culture minimizes risks, enhances compliance, and ultimately safeguards sensitive information.A data protection culture is cultivated through consistent training, clear policies, proactive communication, and strong leadership.
Employees must understand the importance of their role in protecting data, and they must be equipped with the knowledge and tools to do so effectively. This creates a unified front against potential breaches and ensures compliance with regulations.
Employee Training
A critical component of establishing a strong data protection culture is comprehensive employee training. Training programs should be tailored to different roles and responsibilities within the organization. For instance, customer service representatives require training on handling sensitive customer data, while IT personnel need instruction on data security best practices. Regular updates and refresher courses are also crucial to maintain a high level of awareness.
Training should not be a one-time event but an ongoing process, reinforcing data protection principles and keeping employees informed of evolving threats and regulations.
Crafting a robust data protection strategy is crucial these days. Consider the recent Department of Justice Safe Harbor policy for Massachusetts transactions, Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions , as a real-world example. It highlights the need for clear, legally compliant protocols within your data handling processes. Ultimately, a well-structured data protection strategy needs to be proactive, adaptable, and consistently monitored for maximum effectiveness.
Clear Policies and Procedures
Clearly defined policies and procedures for data protection are essential. These documents should be easily accessible, concise, and readily understandable by all employees. They should Artikel acceptable data handling practices, procedures for reporting suspected breaches, and guidelines for responding to data requests. Regular reviews and updates of these policies are vital to reflect changes in regulations and best practices.
Crafting a strong data protection strategy involves more than just policies; it’s about anticipating potential threats. A crucial part of that is understanding how to implement secure coding practices, like the ones highlighted in Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed. Ultimately, a robust data protection strategy needs to adapt to emerging technologies and threats to ensure data remains safe and secure.
Employees should be held accountable for adhering to these policies, fostering a culture of shared responsibility in protecting sensitive information.
Regular Communication and Awareness Campaigns
Regular communication and awareness campaigns are vital to maintaining a proactive data protection culture. These campaigns should use various methods, including email newsletters, posters, and internal meetings, to keep employees informed about data protection best practices. They should also address common data protection misconceptions and concerns, fostering a culture of knowledge and understanding. Data breaches and security incidents can be used as learning opportunities to highlight potential vulnerabilities and reinforce the importance of vigilance.
Examples of Successful Data Protection Awareness Programs, How to draft an effective data protection strategy
Several organizations have implemented successful data protection awareness programs. For instance, some companies have developed interactive online modules that test employee knowledge and reinforce data protection principles. Others have created posters and infographics that visually depict data protection best practices. Many companies also recognize and reward employees who demonstrate a commitment to data protection, further incentivizing proactive measures.
Leadership’s Role in Fostering a Data Protection-Conscious Culture
Leadership plays a pivotal role in establishing a data protection-conscious culture. Senior management must demonstrate commitment to data protection through their actions and decisions. They should actively participate in training programs, communicate the importance of data protection, and ensure that resources are allocated to support these efforts. A visible and demonstrable commitment from leadership sets the tone for the entire organization.
Effectiveness of Different Communication Strategies
| Communication Strategy | Effectiveness Factors | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Email Newsletters | Wide reach, cost-effective, regular updates | Weekly updates on data protection best practices |
| Internal Meetings | Direct interaction, opportunity for Q&A, focused discussions | Regular data protection training sessions |
| Posters and Infographics | Visual aids, easily accessible, reminder of best practices | Data protection posters displayed in common areas |
| Interactive Online Modules | Engaging, interactive, self-paced learning | Online quizzes and simulations on data protection |
Monitoring and Evaluating the Strategy
A robust data protection strategy isn’t a one-time project; it’s a continuous process of adaptation and improvement. Monitoring and evaluating your strategy ensures that controls remain effective in the face of evolving threats and technological advancements. This phase allows you to identify weaknesses, refine your approach, and demonstrate your commitment to data protection to stakeholders.
Monitoring the Effectiveness of Data Protection Controls
Continuous monitoring of data protection controls is crucial to identify any gaps or vulnerabilities that could compromise the security of sensitive data. This involves regularly checking the status of security measures, such as access controls, encryption protocols, and incident response plans. This proactive approach allows for timely adjustments to your strategy, minimizing potential breaches and their impact.
Importance of Regular Reviews and Audits
Regular reviews and audits play a vital role in maintaining the effectiveness of your data protection strategy. These assessments help identify areas where controls are not functioning as intended, enabling you to implement corrective measures promptly. They also provide an objective evaluation of your current posture, allowing you to benchmark against industry best practices and identify potential weaknesses that may not have been apparent through routine monitoring.
Metrics to Track for Data Protection Success
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential to measure the success of your data protection strategy. These metrics offer insights into the effectiveness of your controls and the overall health of your data protection program. They should be chosen based on your specific organizational needs and risk profile.
Evaluating Strategy Effectiveness in Relation to Risks
Evaluating the effectiveness of the strategy requires a comparison against the identified data protection risks. The metrics collected should be analyzed to determine if the controls implemented are adequately mitigating the identified risks. This involves a thorough examination of the effectiveness of controls in relation to the likelihood and impact of each risk. If controls are not effectively mitigating risks, adjustments to the strategy are necessary.
Examples of Data Protection Metrics and Their Interpretation
Several metrics can help gauge the success of your data protection program. For instance, the number of security incidents reported, the time taken to respond to incidents, and the number of successful security audits all contribute to an overall picture of effectiveness. Analyzing these metrics can highlight trends and areas requiring improvement. A high number of security incidents, for example, may indicate a need for enhanced training or stronger security controls.
Key Metrics for Measuring Data Protection Strategy Success
This table Artikels key metrics for measuring the success of a data protection strategy. Regular monitoring and analysis of these metrics will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your controls and allow for timely adjustments to your strategy.
| Metric | Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Number of security incidents | Number of reported security incidents (e.g., unauthorized access attempts, data breaches). | High number suggests weaknesses in controls; low number indicates effective controls. |
| Time to respond to incidents | Time taken to contain and resolve security incidents. | Longer response times can lead to increased data exposure; shorter times indicate effective incident response procedures. |
| Security audit pass rate | Percentage of successful security audits. | Low pass rate indicates deficiencies in controls and processes; high pass rate suggests effective controls. |
| Data breach cost | Financial cost associated with data breaches (e.g., legal fees, regulatory fines, lost revenue). | Lower cost indicates successful risk mitigation; higher cost necessitates adjustments to the strategy. |
| Employee training completion rate | Percentage of employees who have completed required data protection training. | Low completion rate suggests a need for improved training programs; high rate indicates employee awareness and commitment. |
Adapting to Changes
A robust data protection strategy isn’t a static document; it’s a living entity that needs constant adaptation to the dynamic landscape of regulations, technologies, and threats. This adaptation is crucial to maintain compliance, mitigate risks, and ensure the long-term effectiveness of the strategy. Failing to adapt can lead to significant vulnerabilities and potential legal repercussions.Evolving data protection regulations necessitate a proactive approach to strategy updates.
Organizations must stay informed about changes in legislation, such as new privacy laws, enhanced penalties, and evolving requirements for data breach notification. This proactive approach ensures that the organization remains compliant and minimizes the risk of penalties.
Adapting to Evolving Regulations
Staying current with the latest data protection regulations is paramount. Organizations must regularly review and update their policies and procedures to reflect changes in legislation. This includes understanding the implications of new regulations and ensuring all personnel are aware of the updated requirements.
Updating and Enhancing Data Protection Controls
Regularly assessing and updating data protection controls is essential. This involves evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls, identifying gaps, and implementing new or improved measures. Regular audits and penetration testing help in identifying potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
Staying Informed About Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
Keeping abreast of emerging threats and vulnerabilities is critical. This includes staying informed about new attack vectors, sophisticated malware, and evolving social engineering techniques. Subscribing to industry newsletters, attending cybersecurity conferences, and engaging with cybersecurity experts can aid in maintaining awareness.
Adapting to New Technologies
The rapid evolution of technology demands that data protection strategies be flexible enough to adapt. Cloud computing, IoT devices, and AI present unique data protection challenges. Strategies need to incorporate safeguards for data stored in the cloud, secure data transmission between devices, and ensure responsible use of AI. Organizations must proactively address the data protection implications of new technologies as they emerge.
Ensuring Long-Term Relevance
A data protection strategy must remain relevant over time. This involves regular reviews and updates, incorporating lessons learned from incidents, and adapting to changing organizational needs. Regular audits and risk assessments are essential to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the strategy’s continued efficacy.
Key Steps for Updating and Maintaining the Data Protection Strategy
Regular reviews of the strategy are crucial for its ongoing relevance and efficacy. Implementing a structured approach to these updates will guarantee the strategy remains current.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Regular Review | Schedule regular reviews of the data protection strategy, ideally annually or more frequently based on risk assessments and regulatory changes. |
| 2. Risk Assessment | Conduct regular risk assessments to identify new or emerging threats and vulnerabilities. |
| 3. Policy Updates | Update policies and procedures to reflect regulatory changes and technological advancements. |
| 4. Control Enhancement | Enhance or implement new data protection controls to address identified risks and vulnerabilities. |
| 5. Training and Awareness | Provide regular training and awareness programs to ensure all personnel understand and comply with the updated data protection strategy. |
| 6. Monitoring and Evaluation | Monitor the effectiveness of the strategy and evaluate its impact on reducing risks. |
| 7. Documentation | Maintain thorough documentation of all updates, changes, and rationale behind decisions. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, crafting a successful data protection strategy requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not a one-time task but an ongoing process of assessment, implementation, and adaptation. By understanding the key elements, proactively managing risks, and fostering a strong culture of data protection, you can effectively safeguard your organization’s valuable data and maintain user trust. The insights presented in this guide will help you build a strategy that’s not just compliant, but truly effective.
FAQ Section
What are some common data breach scenarios?
Common data breach scenarios include phishing attacks, malware infections, insider threats, and vulnerabilities in software or hardware. Each scenario has varying degrees of impact, depending on the type and sensitivity of the data compromised.
How often should security audits and penetration testing be performed?
Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. The frequency should be determined based on the specific risks and vulnerabilities identified, as well as industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
What metrics can be used to measure the effectiveness of a data protection strategy?
Key metrics include the number of security incidents, the time taken to respond to incidents, the cost of security breaches, and user satisfaction with security measures. A comprehensive analysis of these metrics will help evaluate the effectiveness of your strategy.
How can a data protection strategy be adapted to new technologies?
Data protection strategies must be adaptable to evolving technologies. This includes regularly reviewing and updating policies and controls to address new threats and vulnerabilities associated with emerging technologies.





