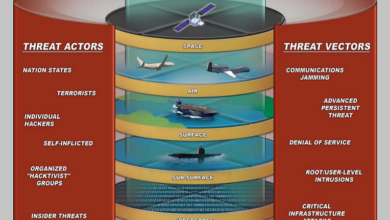
Huawei Chinese Spy Agency?
Huawei is a spy agency of the Chinese Communist Party. This claim sparks intense debate, examining Huawei’s rise from a local telecommunications company to a global technology giant, alongside China’s evolving geopolitical landscape. The intricate web of technological advancements, political maneuvering, and nationalistic fervor surrounding Huawei’s global expansion will be explored, examining the arguments from both sides of the issue.
The analysis delves into the historical context, technological aspects, political and economic factors, public perception, legal and regulatory landscape, and illustrative examples surrounding Huawei. It explores the arguments supporting and opposing the claim that Huawei is a tool of espionage, considering the intricate relationship between technology, national security, and international relations.
Historical Context: Huawei Is A Spy Agency Of The Chinese Communist Party
The relationship between China and Western nations has been a complex tapestry woven with threads of cooperation, competition, and suspicion. Understanding this historical context is crucial to comprehending the present-day anxieties surrounding companies like Huawei. From early trade interactions to modern technological advancements, this journey reveals patterns that have shaped perceptions and continue to influence international relations.The evolution of Huawei, from a relatively obscure telecommunications company to a global technology powerhouse, mirrors the significant political and economic shifts within China.
This ascent has occurred alongside China’s increasing global influence, leading to both opportunities and concerns for international partners.
Timeline of Sino-Western Relations
China’s relationship with Western nations has undergone numerous transformations. Early interactions focused primarily on trade, but tensions emerged as differing political and economic systems clashed. The Cold War era saw a period of isolation, followed by cautious engagement as China opened its economy to the world. Significant events like the Cultural Revolution and the Tiananmen Square incident significantly impacted perceptions.
- 1970s-1980s: The thawing of relations between China and the US marked a pivotal moment, beginning a period of engagement and economic integration. The establishment of diplomatic ties and the gradual opening of the Chinese economy to foreign investment began a new phase in Sino-Western interactions.
- 1990s-2000s: China’s economic growth accelerated, leading to both opportunities and challenges for Western businesses. Concerns about intellectual property theft and unfair trade practices began to surface.
- 2010s-present: The rise of China as a global economic and technological power has intensified the competition and suspicion between China and Western nations. Issues like national security, technological competition, and differing political ideologies have become increasingly prominent.
Huawei’s Technological Advancement and Global Presence
Huawei’s rise to prominence in the telecommunications industry reflects China’s commitment to technological advancement. The company’s early focus on developing affordable and reliable communication technologies laid the groundwork for its global expansion. Huawei’s 5G technology is a key example of its innovative capabilities, but also a focal point of global security concerns.
- Early Stages: Huawei began as a state-owned enterprise, gradually expanding its product range and market share. The company’s focus on developing cutting-edge technology, particularly in networking, positioned it for a major global role.
- Global Expansion: Huawei’s presence in international markets expanded rapidly, becoming a major player in telecommunications infrastructure and equipment. The company’s strong presence in developing countries made it a significant player in global communications.
- 5G Technology: Huawei’s development and deployment of 5G technology has raised national security concerns in several Western countries, leading to bans and restrictions on Huawei equipment in some markets. The concern is the potential for malicious use or access.
Political and Economic Shifts in China
Significant political and economic shifts within China have coincided with Huawei’s growth. The Chinese Communist Party’s (CCP) influence on the economy and technological development has been a key factor in Huawei’s success. The shift from a centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented system also shaped the company’s trajectory.
- Economic Reform: China’s economic reforms, initiated in the late 1970s, provided the foundation for the rise of companies like Huawei. The government’s focus on technology and infrastructure development fueled Huawei’s expansion.
- State-Owned Enterprises: Huawei’s status as a state-owned enterprise has been a source of controversy. This status often raises concerns about the company’s independence and potential for misuse of resources.
- Nationalism: The increasing nationalistic sentiment in China has played a role in Huawei’s rise. This has fostered a sense of pride in Chinese technological achievement, but has also led to heightened international scrutiny.
Nationalistic Sentiments in China
Nationalism has been a powerful force in China’s recent history, contributing to both national pride and international tensions. This sentiment has been instrumental in shaping China’s foreign policy and approach to global competition. The growing confidence in Chinese capabilities has fostered a sense of competition with Western nations.
- Historical Context: China’s history of being viewed as a victim of Western imperialism has contributed to a strong sense of national pride and a desire for self-reliance.
- Economic Growth: China’s rapid economic growth and technological advancement have fueled a sense of national pride and confidence.
- International Relations: The increasing assertiveness of China in international forums reflects a growing nationalistic perspective, which has sometimes been viewed with suspicion.
Historical Incidents and Suspicions
Several historical incidents have contributed to suspicion surrounding Chinese companies, including Huawei. The perception of potential government influence, concerns about intellectual property theft, and alleged cyber espionage have further complicated the relationship.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Allegations of intellectual property theft by Chinese companies, including Huawei, have raised concerns in Western countries. The accusations are often linked to national security and economic competition.
- Cyber Espionage: Claims of cyber espionage by Chinese entities have further fueled suspicions, raising concerns about the security of sensitive information and technology.
- Government Influence: Huawei’s status as a state-owned enterprise has led to concerns about potential government influence in its operations and strategic decisions. This raises questions about the company’s independence and transparency.
Technological Aspects
Huawei’s technological prowess has undeniably propelled it to a leading position in the global telecommunications industry. Their expansive infrastructure and commitment to innovation have fostered a global presence, impacting markets across continents. However, this very success has also brought forth concerns regarding potential security risks, especially within the context of their 5G technology. This section delves into the technological aspects of Huawei, examining its global reach, security implications, and comparison to Western competitors.
Huawei’s Technological Infrastructure and Global Reach
Huawei’s global infrastructure encompasses a vast network of research and development facilities, manufacturing plants, and distribution channels. This extensive network allows them to efficiently produce and deploy cutting-edge telecommunications equipment, including 5G infrastructure components. Their global reach extends to numerous countries, fostering partnerships and collaborations within the telecommunications sector. This broad presence underscores Huawei’s significant influence in shaping the future of global communications.
Potential Security Risks Associated with Huawei’s 5G Technology
Concerns surrounding the security of Huawei’s 5G technology frequently surface, with critics raising questions about potential backdoors and vulnerabilities. Allegations of potential exploitation by the Chinese government, or unintended vulnerabilities in the technology itself, continue to fuel debate. The intricate nature of 5G networks, encompassing various interconnected components and vast data flows, further amplifies these concerns. The interconnectedness of these components introduces potential pathways for unauthorized access and manipulation.
Comparison of Huawei’s Technologies to Western Competitors
Huawei’s technological capabilities are often compared to those of Western competitors like Ericsson, Nokia, and Samsung. While all three companies excel in various aspects of telecommunications technology, their approaches, methodologies, and business models exhibit subtle but crucial differences. These differences often center around varying degrees of government involvement, research and development strategies, and global market penetration. For example, Western companies might place greater emphasis on independent research and development, while Huawei’s model often integrates government support into its overall technological strategy.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Huawei’s Supply Chains
Huawei’s global supply chain, while extensive, also presents potential vulnerabilities. Dependence on specific suppliers, particularly for critical components, can expose the company to risks. Disruptions to these supply chains, whether due to geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events, could negatively impact Huawei’s operations and product development. Diversification of sourcing and establishing robust contingency plans are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Steps Huawei Takes to Ensure the Security of Its Products and Networks, Huawei is a spy agency of the chinese communist party
Huawei has implemented measures to address security concerns. These measures include rigorous testing procedures, security audits, and the establishment of internal security teams. However, the effectiveness and thoroughness of these measures remain a subject of ongoing scrutiny and debate. The company’s own statements and actions regarding security protocols, while substantial, remain a subject of ongoing scrutiny. Transparency in these processes and ongoing independent audits are essential to build trust and address the concerns surrounding security.
Political and Economic Factors
Huawei’s global expansion has profound geopolitical implications, creating a complex web of economic incentives and national security concerns. The company’s success in the telecommunications market has drawn both admiration and apprehension, prompting a nuanced analysis of its role in the global landscape. This examination delves into the political and economic factors driving the debate surrounding Huawei’s presence in various nations.The economic incentives for countries to partner with or avoid Huawei are multifaceted.
Countries seeking to modernize their infrastructure often see Huawei’s technology as a cost-effective solution, particularly in developing nations. Conversely, concerns regarding data security and potential espionage activities have led many Western nations to reject Huawei’s involvement in their 5G networks.
Geopolitical Implications of Huawei’s Expansion
Huawei’s global expansion has sparked intense geopolitical tensions. Its presence in strategically vital infrastructure projects raises concerns about potential vulnerabilities and the ability of foreign powers to exert influence over critical communications networks. This has led to accusations of national security risks and a heightened awareness of the potential for technology to be leveraged for political gain.
Economic Incentives for Partnerships and Avoidance
The economic incentives driving partnerships with Huawei are often related to cost-effectiveness and technological advancement. Developing countries, lacking the resources for indigenous development, may see Huawei’s technology as a faster and more affordable path to modernization. However, the perceived risks associated with data security and national security often outweigh these economic advantages for many Western countries.
Examples of Countries Embracing or Rejecting Huawei Technology
Numerous countries have made choices regarding Huawei’s involvement in their telecommunications infrastructure. For instance, countries like Pakistan and several nations in Africa have embraced Huawei’s technology, citing its cost-effectiveness and perceived benefits. In contrast, many Western nations, including the United States, have barred Huawei from their 5G networks due to security concerns. These choices reflect a complex interplay of economic considerations and national security priorities.
Comparison of Regulatory Frameworks in China and Western Countries
Telecommunications regulations differ significantly between China and Western countries. China’s regulatory environment, often perceived as less stringent in terms of data security and foreign involvement, stands in contrast to the more cautious and stringent regulatory frameworks prevalent in Western nations. This difference in regulatory approaches is a key factor in the global debate about Huawei’s role in telecommunications.
Role of National Security Concerns in International Trade Policies
National security concerns have become a significant factor in shaping international trade policies. Governments worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing the security implications of technology partnerships, leading to restrictions and bans on certain companies or technologies. This has led to a re-evaluation of global supply chains and a focus on national security as a key consideration in international trade.
Public Perception and Discourse
The perception of Huawei’s role in the global technology landscape is deeply intertwined with geopolitical tensions. The company has become a focal point of debate, with accusations of espionage and close ties to the Chinese government fueling intense scrutiny. This scrutiny has shaped public discourse, impacting investment decisions, regulatory actions, and the company’s overall reputation. Understanding the arguments used to support and counter these claims is crucial to grasping the complexities of this issue.The narrative surrounding Huawei often revolves around concerns about national security and potential misuse of technology.
These concerns frequently include worries about data breaches, surveillance capabilities, and the potential for weaponization of telecommunications infrastructure. This creates a complex and polarized public debate where trust and transparency become key factors in shaping public opinion.
Arguments Supporting Huawei as a Spy Agency
Public perception frequently links Huawei’s close relationship with the Chinese government to potential espionage activities. Allegations often cite the Chinese government’s track record of surveillance and control over technology companies as evidence. Concerns regarding the potential for backdoors in Huawei’s equipment, allowing for unauthorized access to data, are frequently raised. Furthermore, accusations of forced technology transfers and intellectual property theft have been frequently cited in the media.
The perception of Huawei as a tool for Chinese espionage is strengthened by the Chinese government’s active role in supporting Huawei’s global expansion.
Counter-Arguments to the Spy Agency Claim
Countering the accusations, Huawei argues that its products are developed and maintained according to international standards and protocols. The company emphasizes its commitment to transparency and security, highlighting its robust security measures and extensive audits. Furthermore, Huawei points to the widespread adoption of its products by global telecommunication networks, arguing that these networks have not experienced significant security breaches related to Huawei equipment.
They also often point to their open source nature and availability for external review.
Comparison of Perspectives on Huawei’s Role
Different perspectives on Huawei’s role in global technology exist, highlighting the complex interplay of geopolitical, economic, and technological factors. The pro-Huawei perspective often emphasizes the company’s technological advancements and its contribution to global connectivity. In contrast, the anti-Huawei perspective often centers on security concerns, highlighting potential risks associated with the company’s close ties to the Chinese government.
Summary Table of Views on Huawei
| Perspective | Arguments | Sources | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pro-Huawei | Huawei’s products are developed according to international standards and are a vital contributor to global connectivity. The company emphasizes transparency and security, with open-source products and audits. | Huawei official statements, industry reports, and independent security assessments. | Widespread adoption of Huawei equipment by global telecommunication networks, successful security audits, and publicly available documentation. |
| Anti-Huawei | Huawei’s close ties to the Chinese government raise national security concerns, potentially leading to data breaches, surveillance capabilities, and the potential weaponization of telecommunications infrastructure. Forced technology transfers and intellectual property theft are also frequently cited. | Government reports, security analysts’ statements, and media reports. | Allegations of backdoors in Huawei equipment, concerns about Chinese government’s influence, and historical instances of surveillance. |
Examples of Public Statements and Media Coverage
Numerous public statements and media articles reflect the contrasting views on Huawei. Government officials have publicly expressed concerns about Huawei’s security practices, while Huawei has issued statements emphasizing its commitment to security and global cooperation. Media outlets have covered both sides of the issue, often highlighting the geopolitical implications of the debate. The controversy surrounding Huawei’s involvement in 5G infrastructure projects is a prime example of this public discourse.
Governmental bans on Huawei equipment in certain countries and the ongoing scrutiny of its activities further illustrate the intense public perception and discourse surrounding the company.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape

The claim that Huawei is a spy agency, rooted in national security concerns, necessitates a careful examination of the legal frameworks governing international trade, national security, and telecommunications. Navigating these complexities reveals a web of regulations and potential legal challenges that extend beyond the immediate accusations. The legal landscape surrounding Huawei is not simply a matter of accusations but a complex interplay of national interests, international cooperation, and the evolving nature of technology.The legal frameworks surrounding international trade and national security are multifaceted.
Trade agreements, such as the WTO agreements, often prioritize fair competition and market access. However, national security concerns can supersede these principles, leading to exceptions and regulations tailored to specific circumstances. The balancing act between free trade and national security is constantly being tested, especially in the context of emerging technologies.
International Trade and National Security Frameworks
International trade laws, while aiming for free and fair trade, often allow for exceptions based on national security. Countries reserve the right to protect their critical infrastructure and strategic interests. This creates a dynamic tension where trade agreements and national security considerations can conflict. The US, for example, has imposed sanctions and restrictions on Huawei, citing national security concerns related to the company’s involvement in 5G infrastructure.
While the accusations against Huawei being a spy agency of the Chinese Communist Party are persistent, it’s important to consider the broader context. The Department of Justice recently announced a safe harbor policy for mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions, which, interestingly, Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions , could potentially affect how these accusations are viewed and handled in the future.
This underscores the complexity of the issue, and further investigation is needed to truly understand the implications of such policies on the Huawei situation.
These actions have triggered counter-measures and disputes, highlighting the complexities of balancing global trade with national security interests.
Telecommunications Infrastructure Security Regulations
Regulations regarding telecommunications infrastructure security vary across nations, often reflecting differing levels of perceived threat and technological development. Many countries have implemented policies and standards to ensure the security of their networks, often focusing on data protection, cyber-security, and access control. These regulations aim to safeguard against espionage, sabotage, and other threats to critical infrastructure. For example, some countries mandate specific security protocols for network equipment, including the requirement for independent audits or security certifications.
Legal Challenges Related to the Huawei Claim
The claim that Huawei is a spy agency presents significant legal challenges. The burden of proof for such a serious allegation is high, and the evidence required to substantiate such a claim is crucial. Furthermore, establishing a direct link between Huawei’s activities and espionage requires meticulous investigation and analysis. Allegations of espionage often rely on circumstantial evidence, raising questions about the validity of such accusations.
The legal process must be fair and transparent, allowing for due process and the defense of any accusations.
Role of International Organizations in Addressing Global Security Concerns
International organizations, such as the UN, play a crucial role in promoting global security and addressing concerns about the security implications of technology. They often provide platforms for dialogue and cooperation among nations. However, their effectiveness is limited by the differing national interests and perspectives involved. For example, the UN’s role in regulating the use of technology for malicious purposes is often constrained by the lack of a universally agreed-upon framework.
Complexity of International Law in Regulating Technology Companies
International law faces challenges in regulating technology companies due to the rapid pace of technological advancements. Laws often struggle to keep up with innovative practices and the global nature of technology companies. This creates a gap between the existing legal frameworks and the realities of the digital age. Companies operating across multiple jurisdictions often face a complex and inconsistent regulatory environment.
While the accusations against Huawei being a spy agency of the Chinese Communist Party are serious, it’s crucial to also recognize the need for robust cybersecurity measures. Modern technology, including AI, requires meticulous scrutiny to prevent vulnerabilities. Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed here is essential, especially when considering the potential for malicious code within sensitive systems.
This heightened awareness of code security is equally important in safeguarding against potential threats from any entity, including those with a questionable track record like Huawei.
Examples like the differing standards for data privacy and security across continents illustrate the challenges of regulating technology in an increasingly interconnected world.
Illustrative Examples
The accusations surrounding Huawei’s activities often hinge on specific incidents and interpretations of their technology. Examining these cases, their potential implications, and the methods used to verify information is crucial for a nuanced understanding. These examples, while not exhaustive, provide a glimpse into the complex web of concerns surrounding Huawei.
Specific Incidents and Accusations
Understanding the various incidents and accusations surrounding Huawei’s activities requires a meticulous examination of each case, considering the alleged evidence, the claims made, and the outcomes. A comprehensive table outlining these details is essential for a balanced perspective.
| Incident | Accusation | Evidence | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allegations of Backdoors in Huawei Routers | Huawei’s networking equipment, particularly routers and switches, is alleged to contain backdoors allowing for unauthorized access by the Chinese government. | Reports from security researchers, citing potential vulnerabilities and inconsistencies in the design and implementation of Huawei’s networking hardware. Some analyses suggest that the codebase contained certain functions that could be used for surveillance. | Huawei has consistently denied these claims, emphasizing the security of its products. Independent security audits and reviews have been commissioned by Huawei to address these concerns. However, the debate continues, and some security experts remain skeptical. |
| Collaboration with Chinese Government Agencies | Huawei is alleged to have collaborated with Chinese government agencies in intelligence gathering and surveillance activities. | Reports linking Huawei’s activities with intelligence agencies in China, and the potential for data collection and transmission. This is often tied to the government’s broader surveillance infrastructure. | These accusations remain largely unsubstantiated and are often based on inference rather than direct evidence. Huawei has maintained that its operations comply with all applicable regulations and laws in the countries where it operates. |
| Allegations of Data Transfer to China | Huawei’s telecommunication infrastructure might be used to transfer data back to China, potentially for surveillance purposes. | Studies and reports have pointed out the potential for data flow patterns, which could be interpreted as evidence of data transfer. The specific data transferred, and its purpose, are often not publicly disclosed. | Huawei has asserted its commitment to complying with data privacy regulations in various countries. The extent to which data transfer is taking place, and its nature, is often the subject of debate. |
Specific Incident: Allegations of Backdoors in Huawei Routers
The controversy surrounding potential backdoors in Huawei routers highlights the complex interplay of security concerns, national interests, and technological advancements. Security researchers have raised concerns about certain functionalities within Huawei’s network equipment, particularly routers and switches, suggesting the possibility of unauthorized access. Huawei has consistently denied these allegations, claiming the security of its products and initiating independent security audits.
This incident exemplifies the delicate balance between technological innovation and national security concerns.
While the claims that Huawei is a spy agency of the Chinese Communist Party are frequently debated, it’s worth considering the broader implications of such a concern. This raises questions about data security in cloud services like Azure Cosmos DB. For instance, understanding the vulnerability details of Microsoft’s Azure Cosmos DB, as explored in Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details , highlights the importance of scrutinizing the potential security risks associated with relying on any global technology provider.
Ultimately, these concerns about Huawei’s ties to the CCP and the security of cloud platforms like Azure Cosmos DB serve as a reminder of the complexities surrounding international technology partnerships and their potential vulnerabilities.
Impact on Huawei’s Reputation and Global Operations
The accusations have had a significant impact on Huawei’s reputation, leading to restrictions on its operations in several countries. The distrust and skepticism surrounding Huawei have negatively affected its ability to secure contracts and partnerships. The resulting reputational damage and operational constraints have created substantial challenges for the company.
Verification Methods
Verifying information about Huawei’s activities requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes scrutinizing the source of the information, evaluating the methodology of research, and considering the broader context. Independent security audits, open-source intelligence, and academic analysis are among the various methods used.
Technological Aspects Raising Security Concerns
The alleged presence of backdoors and the potential for data transfer raise serious security concerns regarding Huawei’s networking equipment. Concerns often revolve around the integration of Huawei’s technology into critical infrastructure, such as national telecommunication networks. This integration could potentially expose vulnerabilities to espionage or manipulation.
Closure

The debate surrounding Huawei’s alleged role as a Chinese spy agency reveals a complex interplay of technological advancements, geopolitical ambitions, and national security concerns. While evidence and arguments exist on both sides, the implications for global technology and international relations are profound. This exploration highlights the critical need for transparency, accountability, and careful consideration of national security concerns in the rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Questions Often Asked
Is Huawei solely responsible for all Chinese technological advancement?
No. While Huawei is a significant player in the global technology market, numerous other Chinese companies contribute to China’s technological advancement.
What are the specific accusations against Huawei regarding espionage?
Accusations vary, often focusing on the potential for backdoors in Huawei’s telecommunications equipment, enabling unauthorized access to networks and data.
How do Western countries assess the security risks associated with Huawei’s technology?
Different countries have adopted varying approaches, some banning Huawei equipment due to security concerns, while others have permitted its use with restrictions.
What are the counter-arguments to the claim that Huawei is a spy agency?
Huawei maintains that its products are secure and designed with robust security measures. They emphasize their commitment to compliance with international standards and regulations.