CDK Cyber Incident Auto Dealerships Under Attack
CDK cyber incident auto dealerships – it sounds like a headline ripped from tomorrow’s news, doesn’t it? The reality is, these incidents are happening now, silently crippling businesses and exposing sensitive customer data. This isn’t just a tech problem; it’s a threat to the very heart of the auto industry, impacting everything from sales and service to customer trust and financial stability.
We’ll delve into the vulnerabilities, the attacks, and – most importantly – how dealerships can protect themselves.
From ransomware attacks that lock down entire systems to sophisticated phishing campaigns targeting employees, the threats facing dealerships reliant on CDK systems are diverse and constantly evolving. We’ll explore real-world examples, the legal ramifications of data breaches, and the crucial steps dealerships must take to bolster their cybersecurity defenses. This isn’t about fear-mongering; it’s about equipping you with the knowledge and strategies to safeguard your business.
CDK Global Systems Vulnerabilities in Auto Dealerships

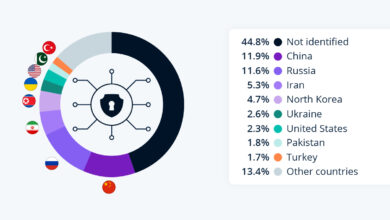
The recent surge in cyberattacks targeting auto dealerships highlights significant vulnerabilities within CDK Global’s systems, a leading provider of dealership management software. These attacks not only disrupt dealership operations but also expose sensitive customer data, leading to significant financial and reputational damage. Understanding the nature of these vulnerabilities and the methods used in these attacks is crucial for improving cybersecurity defenses within the automotive industry.
Common Vulnerabilities in CDK Global Systems
Several common vulnerabilities in CDK Global systems have been exploited in cyberattacks. These often involve outdated software, weak passwords, and insufficient security configurations. Phishing attacks, targeting employees with malicious emails containing malware, are a frequently used entry point. Exploitation of known vulnerabilities in CDK’s software, before patches are applied, is another common tactic. Furthermore, a lack of robust multi-factor authentication leaves systems susceptible to unauthorized access.
The consequences can be severe, ranging from data breaches exposing customer personal information (like driver’s licenses, social security numbers, and financial details) to ransomware attacks crippling dealership operations, halting sales, and preventing access to critical business data.
Impact of Vulnerabilities on Dealership Operations and Customer Data
The impact of successful cyberattacks on CDK Global systems can be devastating for auto dealerships. Ransomware attacks can lead to significant downtime, halting sales processes, preventing access to customer records, and disrupting service appointments. Data breaches can result in substantial financial losses due to regulatory fines, legal fees, and the cost of credit monitoring services for affected customers.
Reputational damage from a data breach can also be significant, leading to a loss of customer trust and impacting future sales. Furthermore, the theft of intellectual property, such as pricing strategies and sales data, can provide a competitive advantage to attackers or their associates.
Technical Methods Used in Attacks Targeting CDK Systems
Attackers utilize various technical methods to exploit vulnerabilities in CDK Global systems. Phishing remains a primary vector, often using sophisticated techniques to bypass email security filters. Once initial access is gained, attackers may use lateral movement techniques to gain access to other systems within the dealership’s network. Exploitation of known vulnerabilities in CDK software, particularly those that haven’t been patched, is another common tactic.
This often involves using automated tools to scan for vulnerable systems and then deploying exploits to gain unauthorized access. After gaining access, attackers may deploy ransomware to encrypt critical data, demanding a ransom for its release. Data exfiltration, the unauthorized copying and transfer of data, is another common objective.
Comparison of Cyberattacks Against CDK Systems
| Attack Type | Method | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Malicious emails containing malware | Data breach, malware infection | Security awareness training, multi-factor authentication, email filtering |
| Ransomware | Encryption of critical data | System downtime, data loss, financial loss | Regular backups, patching vulnerabilities, endpoint detection and response |
| Exploit of Software Vulnerabilities | Exploiting known vulnerabilities in CDK software | Unauthorized access, data breach | Regular software updates, vulnerability scanning |
| Data Exfiltration | Unauthorized copying and transfer of data | Data loss, intellectual property theft | Network segmentation, data loss prevention (DLP) tools |
Types of Cyber Incidents Affecting CDK Users
The reliance of many auto dealerships on CDK Global systems makes them a prime target for cybercriminals. These attacks can range from relatively minor disruptions to devastating data breaches, each carrying significant financial and reputational risks. Understanding the common types of incidents and implementing robust mitigation strategies is crucial for dealership survival in today’s digital landscape. This section will explore the most prevalent cyber threats facing CDK users and offer practical advice for safeguarding against them.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks are a major concern for CDK users. These attacks involve malicious software encrypting dealership data, rendering it inaccessible unless a ransom is paid. The encrypted data often includes critical operational information, customer data, and financial records. A successful ransomware attack can bring a dealership’s operations to a standstill, resulting in lost revenue, customer dissatisfaction, and significant recovery costs.
For example, in 2022, a significant number of dealerships using CDK experienced ransomware attacks that crippled their operations for days, leading to substantial financial losses and negative media coverage. The cost of recovery, including ransom payments (if made), data recovery services, and lost business, can easily run into the hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- Implement robust endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
- Regularly back up all critical data to an offline, secure location.
- Educate employees on phishing and social engineering tactics.
- Maintain up-to-date security patches for all software and hardware.
- Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks remain a persistent threat. These attacks typically involve deceptive emails or messages designed to trick employees into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial data. Once compromised, attackers can gain access to the dealership’s CDK system and potentially deploy ransomware or exfiltrate data. A successful phishing campaign against a dealership using CDK could lead to significant data breaches, financial losses, and regulatory fines.
One example involved a dealership employee clicking a malicious link in a seemingly legitimate email, granting attackers access to the CDK system and resulting in the theft of customer payment information.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts.
- Conduct regular security awareness training for all employees.
- Utilize email filtering and anti-spam solutions.
- Develop clear policies regarding email security and data handling.
- Promptly report any suspicious emails or messages.
Data Breaches
Data breaches, often resulting from ransomware attacks or phishing scams, pose a severe threat. The unauthorized access and disclosure of sensitive customer data, including personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, and driving records, can lead to significant financial penalties, legal action, and reputational damage. A well-publicized data breach can severely damage a dealership’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and future business.
A hypothetical example: A breach exposing customer credit card information could lead to millions of dollars in chargeback fees and legal settlements, alongside considerable damage to the dealership’s brand image.
- Encrypt all sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
- Implement strict access control measures to limit data access to authorized personnel.
- Regularly monitor and audit system logs for suspicious activity.
- Develop a comprehensive data breach response plan that includes notification procedures.
- Comply with all relevant data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The reliance of auto dealerships on CDK Global systems for managing crucial business operations introduces significant data security and privacy concerns. These systems house a wealth of sensitive customer information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Understanding the types of data involved, the legal ramifications of breaches, and implementing robust security measures are paramount for protecting both the dealership and its customers.
Types of Sensitive Customer Data Stored in CDK Systems
CDK systems typically store a wide range of sensitive customer data, including Personally Identifiable Information (PII). This encompasses names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, driver’s license numbers, social security numbers, and financial information like credit card details and bank account numbers. Beyond PII, CDK systems may also contain vehicle identification numbers (VINs), purchase history, service records, and even insurance details.
The breadth of this data underscores the critical need for stringent security protocols.
Legal and Regulatory Implications of Data Breaches
Data breaches involving CDK systems can trigger significant legal and regulatory repercussions. Depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the breach, dealerships could face hefty fines under laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and other state and federal regulations. Furthermore, dealerships could face class-action lawsuits from affected customers seeking compensation for damages, including financial losses, identity theft, and emotional distress.
The reputational damage resulting from a breach can also be substantial, impacting future business.
Best Practices for Securing Customer Data within CDK Environments
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for protecting customer data within CDK environments. This includes regularly updating CDK software to patch known vulnerabilities, employing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication, implementing robust access control measures to limit access to sensitive data based on roles and responsibilities, and regularly backing up data to secure offsite locations. Employee training on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing awareness and social engineering tactics, is equally vital.
Finally, regular security audits and penetration testing can identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Comprehensive Data Security Policy for an Auto Dealership Using CDK
A comprehensive data security policy should Artikel clear roles and responsibilities for data protection, including who is responsible for implementing and maintaining security controls. It should detail procedures for incident response, outlining steps to take in the event of a data breach, including notification procedures for customers and regulatory bodies. The policy should also specify data encryption methods for both data at rest and in transit, regular security awareness training for all employees, and a schedule for regular security assessments and penetration testing.
Furthermore, the policy should address data retention policies, outlining how long data is stored and how it is securely disposed of when no longer needed. Finally, the policy should mandate regular review and updates to remain current with evolving threats and best practices. A well-defined and enforced data security policy is the cornerstone of protecting sensitive customer information within a CDK environment.
Incident Response and Recovery Strategies: Cdk Cyber Incident Auto Dealerships
A robust incident response plan is crucial for auto dealerships reliant on CDK systems. A swift and effective response minimizes downtime, data loss, and reputational damage following a cyberattack. This plan should be regularly tested and updated to reflect evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
A comprehensive incident response plan needs to be proactive, not reactive. It should detail clear roles, responsibilities, and escalation procedures to ensure a coordinated and efficient response. Furthermore, regular security awareness training for all employees is vital to mitigate human error, a frequent entry point for cyberattacks.
Roles of IT Security Professionals and External Cybersecurity Firms
IT security professionals within the dealership play a frontline role in incident response. Their responsibilities include initial threat detection, containment, and eradication efforts. They are responsible for implementing and maintaining security controls, conducting vulnerability assessments, and managing security tools. However, the complexity and sophistication of modern cyberattacks often necessitate the involvement of external cybersecurity firms. These firms bring specialized expertise, advanced tools, and a broader perspective, offering crucial support during the investigation, remediation, and recovery phases.
They can provide forensic analysis, incident containment strategies, and assistance with legal and regulatory compliance. The collaboration between internal IT staff and external experts is often key to a successful response.
Data Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning
Regular data backups are the cornerstone of any effective disaster recovery plan. This includes both system backups and data backups, stored securely offsite and ideally in a geographically separate location to protect against physical damage or widespread outages. The frequency of backups should be determined by the criticality of the data and the acceptable level of data loss.
Disaster recovery planning goes beyond simple backups; it encompasses a detailed strategy for restoring systems and data in the event of a major incident. This plan should include a clear recovery process, system restoration procedures, and communication protocols to keep stakeholders informed during the recovery process. Regular testing of the disaster recovery plan is essential to ensure its effectiveness and identify any weaknesses.
For example, a dealership might conduct a simulated ransomware attack to test their ability to restore systems and data from backups. Failure to adequately plan for data recovery could lead to significant financial losses and operational disruption.
Sample Incident Response Plan Flowchart
The following describes a sample incident response plan flowchart. The process begins with Detection: An incident is detected, either through security monitoring systems, employee reports, or external notifications. This leads to Analysis: The nature and scope of the incident are assessed. Next is Containment: Steps are taken to isolate the affected systems and prevent further damage or spread of the incident.
Eradication: The root cause of the incident is identified and removed. This is followed by Recovery: Systems and data are restored from backups, and normal operations are resumed. Finally, Post-Incident Activity: Lessons learned are documented, security controls are reviewed and improved, and the entire process is evaluated to identify areas for improvement. The entire process is iterative, with feedback loops incorporated at each stage to refine the response and improve future preparedness.
This flowchart represents a simplified model; a real-world plan would be far more detailed and specific to the organization’s needs and infrastructure.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
Proactive security measures are crucial for auto dealerships using CDK systems to mitigate the risk of cyberattacks. Implementing a multi-layered approach encompassing technological solutions, employee training, and regular security audits significantly reduces vulnerability and minimizes the impact of potential incidents. This section details key preventative measures and best practices to safeguard your dealership’s data and operations.
Key Preventative Measures for Reducing Cyber Risk
Dealerships must adopt a layered security approach. This includes robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor and block malicious network traffic targeting the CDK system. Regular software updates for both the CDK system and all connected devices are paramount to patch known vulnerabilities. Strong password policies, enforced multi-factor authentication (MFA), and access control lists (ACLs) limiting user permissions based on their roles restrict unauthorized access.
Data backups should be performed regularly and stored securely offsite, allowing for quick recovery in case of data loss or corruption. Finally, regular security audits and penetration testing identify weaknesses in the system before attackers can exploit them. A well-defined incident response plan is also crucial, outlining procedures to follow in the event of a cyberattack.
Cybersecurity Solutions for Protecting CDK Systems, Cdk cyber incident auto dealerships
Several cybersecurity solutions can protect CDK systems. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions monitor endpoints for malicious activity, providing real-time alerts and automated responses. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, identifying potential threats and providing valuable insights into security posture. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools prevent sensitive data from leaving the network unauthorized.
Vulnerability scanners regularly assess the system for weaknesses, allowing for timely remediation. Finally, managed security service providers (MSSPs) offer comprehensive security services, including monitoring, incident response, and security awareness training. The choice of solution depends on the dealership’s size, budget, and specific needs. A smaller dealership might opt for a cloud-based solution, while a larger one might prefer an on-premise system integrated with their existing infrastructure.
Security Awareness Training Topics for Dealership Employees
Comprehensive security awareness training is essential. Training should cover phishing and social engineering tactics, emphasizing the importance of verifying email authenticity and avoiding suspicious links or attachments. Employees need to understand password security best practices, including the use of strong, unique passwords and the importance of MFA. Data security policies and procedures, including proper handling of sensitive customer information, should be clearly communicated and regularly reinforced.
Recognizing and reporting suspicious activity is also crucial, enabling prompt response to potential threats. Regular training sessions, incorporating real-world examples and simulated phishing attacks, ensure ongoing awareness and reinforce good security habits.
Security Controls Checklist for Implementation and Regular Review
A regular security review is essential. This checklist should be reviewed and updated at least annually or after any significant system changes.
- Firewall Configuration: Regularly review and update firewall rules to ensure only authorized traffic is allowed.
- Software Updates: Implement a system for automatically updating all software, including the CDK system and operating systems.
- Access Control: Implement strong access controls, using role-based access to limit user privileges.
- Password Management: Enforce strong password policies and multi-factor authentication.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up all data and test the recovery process.
- Security Awareness Training: Conduct regular security awareness training for all employees.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan for vulnerabilities and promptly address any identified issues.
- Security Monitoring: Implement security monitoring tools to detect and respond to threats.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
The Role of Insurance and Legal Counsel
Navigating the complex landscape of cybersecurity, especially for auto dealerships reliant on CDK systems, necessitates a robust understanding of the crucial roles insurance and legal counsel play in mitigating risks and managing the aftermath of a cyber incident. Proactive planning and a well-defined strategy are paramount to minimizing financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.Cyber insurance is no longer a luxury but a necessity for auto dealerships utilizing CDK systems.
These systems hold vast amounts of sensitive customer data, making dealerships prime targets for cyberattacks. A comprehensive cyber insurance policy can provide financial protection against the considerable costs associated with data breaches, including incident response, legal fees, regulatory fines, and notification costs. Furthermore, it can offer crucial support services, such as access to cybersecurity experts and public relations professionals, to help manage the crisis effectively.
Cyber Insurance Coverage for CDK-Related Incidents
Many cyber insurance providers offer policies specifically designed to address the risks associated with automotive dealership management systems like CDK. These policies typically cover a range of incidents, including ransomware attacks, data breaches, system failures, and business interruption resulting from cyberattacks. Specific coverage details vary widely between insurers and policy types, so careful review of the policy wording is crucial.
For example, some policies might offer coverage for the costs of restoring CDK systems, while others might focus on covering the costs of notifying affected customers. It’s vital to ensure that the policy explicitly covers the types of incidents most likely to affect your dealership’s use of CDK, such as data exfiltration or system compromise. A common exclusion, for example, is coverage for pre-existing vulnerabilities that were known to the dealership prior to the policy inception.
Therefore, regular security audits are a critical aspect of risk management.
The Role of Legal Counsel in Cyber Incident Management
Legal counsel plays a vital role throughout the entire lifecycle of a cyber incident, from the initial detection to the long-term recovery and prevention efforts. Their expertise is crucial in navigating the complex legal landscape surrounding data breaches, regulatory compliance, and potential litigation. Legal counsel can assist in: conducting internal investigations, determining the scope of the breach, complying with data breach notification laws, communicating with affected parties, and managing potential legal actions.
They can also advise on the implementation of effective incident response plans and ensure that all actions taken are compliant with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and state-specific data breach notification laws.
Data Breach Notification Laws and Requirements
Data breach notification laws vary by jurisdiction, but they generally require organizations to notify affected individuals and, in some cases, regulatory authorities, within a specific timeframe after discovering a data breach. These laws often specify the information that must be included in the notification, such as the type of information compromised, the number of individuals affected, and steps taken to mitigate the harm.
Failure to comply with these laws can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage. For instance, California’s CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) mandates notification within 45 days of discovery, whereas other states may have different timelines and requirements. Understanding these specific legal obligations is paramount for minimizing legal risk and demonstrating a commitment to data protection.
Legal counsel can provide guidance on complying with these laws, ensuring that notifications are timely, accurate, and legally compliant.
Conclusion
The threat of a CDK cyber incident is real, but it’s not insurmountable. By understanding the vulnerabilities, implementing robust security measures, and developing a comprehensive incident response plan, auto dealerships can significantly reduce their risk. Remember, proactive security is an investment, not an expense. It’s about protecting your business, your customers, and your future. Don’t wait for a crisis; prepare for it.
Take control of your cybersecurity now.
FAQ Resource
What types of data are most at risk in a CDK data breach?
Customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII) like names, addresses, driver’s license numbers, Social Security numbers, and financial data are all highly vulnerable.
What is the role of my insurance provider after a cyber incident?
Your cyber insurance policy should cover costs associated with incident response, legal fees, data recovery, and notification of affected customers. Contact your provider immediately after an incident.
How often should I update my security protocols?
Security protocols should be reviewed and updated at least annually, and more frequently if significant changes occur within the dealership’s IT infrastructure or if new threats emerge.
What is the best way to train employees on cybersecurity best practices?
Regular, interactive training sessions, phishing simulations, and clear communication of security policies are essential for employee awareness.