Android Mobile Security Alert SMS Stealer Malware
Android mobile security alert against sms stealer malware – Android Mobile Security Alert: SMS Stealer Malware. Ever felt that creepy feeling your phone is being watched? This isn’t just paranoia; SMS stealer malware is a real threat silently lurking, snatching your personal data from right under your nose. We’re diving deep into the world of these sneaky little digital thieves, exploring how they work, what they steal, and, most importantly, how to protect yourself.
This isn’t just about tech jargon; it’s about securing your life.
From understanding the mechanisms these malicious programs use to infiltrate your Android device to identifying the vulnerabilities they exploit, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll examine real-world examples of SMS theft and the devastating consequences, equipping you with the knowledge to prevent becoming a victim. Think of this as your personal guide to mobile security, empowering you to take control and stay safe.
Understanding SMS Stealer Malware
SMS stealer malware represents a significant threat to Android users, silently siphoning sensitive personal information from text messages. These malicious applications employ various deceptive techniques to gain access to your device and exploit vulnerabilities in the Android operating system to steal your data. Understanding their mechanisms is crucial for effective protection.SMS stealers primarily infiltrate Android devices through seemingly innocuous methods.
They often disguise themselves as legitimate apps available on third-party app stores or are spread through phishing campaigns, promising enticing features or updates to popular applications. Once downloaded and installed, these malicious apps often request excessive permissions, which, if granted unknowingly, grant them access to your SMS messages. Another common infiltration method is through compromised websites or malicious links embedded in spam emails or text messages.
Clicking these links can trigger the download and installation of the malware without the user’s explicit knowledge.
Mechanisms for Data Extraction
SMS stealers employ several techniques to extract sensitive information from SMS messages. They might directly access the SMS database on the device, copying the contents of all messages. Alternatively, they can use accessibility services, a legitimate Android feature intended to aid users with disabilities, to monitor and record incoming and outgoing messages in real-time. Some advanced SMS stealers even intercept messages at a network level, capturing them before they reach the device itself.
This makes detection more difficult as the message never actually appears in the device’s SMS inbox. Once obtained, this data—which may include banking details, one-time passwords (OTPs), personal identification numbers (PINs), and location information—is often exfiltrated to a remote server controlled by the malware authors.
Examples of SMS Stealer Malware
Numerous SMS stealer malware families exist, each with unique characteristics and capabilities. For example, “FluBot” is known for its sophisticated phishing capabilities, targeting users with convincing messages to trick them into revealing their banking credentials. “FakeInstaller” is notorious for its ability to masquerade as legitimate system update apps, thereby deceiving users into granting it the necessary permissions to access their SMS messages.
Another example is “Joker,” which is known for its ability to subscribe users to premium SMS services without their knowledge, generating revenue for the attackers.
Comparison of SMS Stealer Malware Families
| Malware Family | Primary Infection Vector | Data Extraction Method | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| FluBot | Phishing SMS messages, malicious websites | Direct access to SMS database, Accessibility services | Sophisticated phishing, ability to bypass security measures |
| FakeInstaller | Disguised as legitimate apps on third-party app stores | Direct access to SMS database | Masquerades as system updates, requests excessive permissions |
| Joker | Malicious apps disguised as legitimate apps | Direct access to SMS database, premium SMS subscription | Stealthy operation, ability to subscribe users to premium services |
Vulnerabilities Exploited by SMS Stealers
SMS stealer malware relies on exploiting weaknesses in the Android operating system and user behavior to gain access to sensitive information. These vulnerabilities often involve a combination of technical flaws and human susceptibility to social engineering tactics. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for effective protection against these malicious apps.Android’s open nature, while offering flexibility, also presents opportunities for malicious actors.
Many vulnerabilities stem from poorly designed apps, outdated operating systems, and users falling prey to deceptive tactics. The malware often leverages these vulnerabilities to silently infiltrate devices and harvest SMS messages containing sensitive data like banking credentials, two-factor authentication codes, and personal identifiers.
Common Android Vulnerabilities
SMS stealers often exploit several common vulnerabilities in Android. These vulnerabilities can range from outdated system components to vulnerabilities within individual applications. A key vulnerability lies in the permissions granted to apps. Many apps request excessive permissions, and if users grant these without careful consideration, the malware can easily access SMS data. Another common weakness is the use of insecure coding practices within apps, leading to vulnerabilities that can be exploited by the malware to gain unauthorized access.
Furthermore, insufficient security measures on the part of app developers can lead to malware being easily installed through compromised app stores or deceptive websites.
Bypassing Security Measures
Once a vulnerability is identified, the malware uses various techniques to bypass Android’s built-in security mechanisms. This might involve exploiting a known vulnerability in the Android system itself or using obfuscation techniques to hide the malware’s malicious code from security scanners. The malware can also utilize root exploits to gain elevated privileges, allowing it to access protected system resources, including SMS messages, without triggering security alerts.
Finally, the malware might use techniques to disable or circumvent security applications installed on the device, effectively removing any obstacles to data theft.
The Role of Social Engineering
Social engineering plays a significant role in the success of SMS stealer attacks. Often, users are tricked into installing malicious apps disguised as legitimate ones. These deceptive apps might be promoted through fraudulent advertisements, phishing websites, or even through seemingly harmless SMS messages. The malware might also be disguised as a system update or a necessary security patch, prompting users to grant it the necessary permissions.
This highlights the importance of user awareness and caution when downloading and installing apps. For example, a user might receive a text message claiming to be from their bank, asking them to update their banking app through a provided link. This link actually leads to a malicious app containing the SMS stealer.
Typical Infection Process
The following flowchart illustrates a typical infection process:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a user receiving a deceptive SMS message (e.g., a phishing link or a fake update notification). The next step would be the user clicking the link or downloading the malicious app. This leads to the installation of the malware, which then requests permissions (potentially excessive ones).
The malware then gains access to SMS messages, exfiltrates the data (often sending it to a remote server), and continues to operate covertly in the background. Finally, the flowchart concludes with the stolen data being used for malicious purposes, such as identity theft or financial fraud.]
Impact and Consequences of Infection
Having an SMS stealer on your Android device isn’t just an inconvenience; it’s a serious security breach with far-reaching consequences. These malicious apps can quietly siphon off sensitive data, leaving you vulnerable to identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage. The impact extends beyond just the immediate theft; it can create long-term problems that are difficult and costly to resolve.The insidious nature of SMS stealers lies in their ability to operate silently in the background.
You might not even realize your phone is compromised until the damage is done. This stealthy operation makes them particularly dangerous, as the victim often remains unaware of the ongoing data breach until significant harm has occurred. Understanding the potential impact is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation.
Types of Stolen Data
SMS stealers target a wide range of sensitive information transmitted via text message. This includes one-time passwords (OTPs) used for banking and other online services, confirmation codes for account verification, and even personal details like addresses and contact information. Criminals can exploit this stolen information to access bank accounts, online shopping accounts, social media profiles, and other sensitive personal information.
Financial details, such as credit card numbers and bank account details, are also prime targets if they are ever transmitted via SMS, although this is less common due to increased security protocols.
Real-World Scenarios Illustrating the Impact
Imagine receiving a seemingly legitimate text message from your bank, requesting you to verify a transaction via an embedded link. An SMS stealer could intercept this message and replace the legitimate link with a malicious one, leading you to a fake website designed to steal your login credentials. Once compromised, your bank account could be emptied within minutes.
Another scenario involves a two-factor authentication code being intercepted. This code, intended to secure your online accounts, is now in the hands of criminals, granting them unauthorized access. The consequences could range from stolen funds to compromised personal information used for identity theft.
Financial and Reputational Damages
The financial consequences of an SMS stealer infection can be devastating. This can include:
- Direct financial losses due to unauthorized transactions from compromised bank accounts and online shopping accounts.
- Costs associated with rectifying fraudulent activities, such as credit report monitoring and identity theft protection services.
- Potential losses due to compromised business accounts, impacting business operations and financial stability.
Beyond financial losses, the reputational damage can be significant. For instance:
- Damage to personal reputation due to identity theft, leading to difficulties in obtaining loans or credit.
- Potential legal repercussions if the stolen information is used for illegal activities, resulting in investigations and legal fees.
- Loss of trust from friends, family, and colleagues due to the compromise of personal information.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Protecting your Android device from SMS stealer malware requires a multi-layered approach encompassing proactive measures and vigilant practices. By understanding the vulnerabilities and employing effective strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of infection and protect your sensitive personal information. This involves careful app selection, diligent permission management, and the use of robust security software.
The most effective defense against SMS stealers lies in a combination of preventative measures and proactive security habits. Ignoring even one aspect of this approach can leave your device vulnerable. A holistic approach is crucial for comprehensive protection.
App Permission Management
Understanding and controlling app permissions is paramount in preventing malware infections. Many malicious apps request excessive permissions, often under the guise of legitimate functionality. For example, an app claiming to be a simple flashlight might request access to your contacts, SMS messages, and location data – far beyond what’s necessary. Carefully review the permissions requested by each app before installation.
Only install apps from trusted sources like the Google Play Store, and always check user reviews for red flags indicating potentially malicious behavior. Regularly review the permissions granted to already installed apps and revoke any that seem unnecessary or suspicious. This proactive approach significantly reduces the attack surface available to malicious actors.
Using Reputable App Stores and Verification
Downloading apps only from official app stores like Google Play Store drastically reduces the risk of encountering malicious software. While not foolproof, the Google Play Store employs security measures to vet apps before they’re made available. However, even within official stores, exercise caution. Carefully examine app descriptions, developer information, and user reviews before installing. Look for any inconsistencies or red flags that might indicate a malicious app.
Verifying the developer’s identity and checking for independent security reviews can provide an additional layer of protection.
Security Software and Regular Updates
Employing a reputable mobile security application provides an additional layer of defense. These apps often include features like real-time malware scanning, phishing detection, and anti-theft capabilities. Regularly updating your security software is crucial, as new malware threats constantly emerge. Keep your Android operating system and all apps updated to the latest versions. These updates frequently include security patches that address known vulnerabilities, making your device less susceptible to attack.
Think of security updates as armor against newly discovered weaknesses.
Identifying and Avoiding Suspicious SMS Messages, Android mobile security alert against sms stealer malware
Suspicious SMS messages often contain shortened URLs, unusual grammar, or urgent requests for personal information. Never click on links in unsolicited SMS messages, especially those promising rewards or threatening consequences. If you receive an SMS message from an unknown number requesting sensitive information, such as banking details or login credentials, it’s almost certainly a scam. Report such messages to your mobile carrier and relevant authorities.
Be wary of messages that create a sense of urgency or fear, as these tactics are often employed to manipulate users into acting quickly without thinking. For example, a message claiming your account has been compromised and requiring immediate action is highly suspicious.
Detection and Removal of SMS Stealer Malware
So, you suspect your Android phone might be infected with SMS stealer malware. It’s a scary thought, but thankfully, there are ways to detect and remove this nasty stuff. Early detection is key to minimizing the damage, so let’s dive into how to identify the problem and get rid of it.
Identifying an SMS stealer isn’t always straightforward. These malicious apps often operate in the background, subtly stealing your data without obvious signs. However, certain red flags can indicate their presence. Paying close attention to these warning signs is crucial for timely intervention.
Symptoms of SMS Stealer Malware Infection
Unexpected and unusual SMS activity is a major indicator. This could manifest as a sudden surge in the number of text messages being sent, messages being sent to unfamiliar numbers, or messages being sent without your knowledge or consent. You might also notice unusually high mobile data usage, unexplained charges on your phone bill, or unexpected app permissions granted.
Additionally, your phone might run slower than usual, or you may experience frequent crashes or freezes. These symptoms, while not conclusive on their own, should trigger a closer examination of your device’s security.
That scary Android SMS stealer malware alert got me thinking about app security. Building robust, secure apps is crucial, and that’s where learning more about domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes in handy. Understanding the development process, from low-code to pro-code solutions, helps developers build better defenses against these kinds of threats, ultimately making our phones safer from SMS-based malware.
Detecting and Removing Malware Using Available Tools
Several methods exist to identify and remove SMS stealer malware. One approach involves using a reputable mobile security app. These apps often perform regular scans for malicious software, alerting you to any threats found and offering removal options. Many offer real-time protection, blocking malicious links and downloads. Another approach involves manually reviewing your installed apps, looking for anything suspicious – apps you don’t remember installing, apps with unusual permissions, or apps with poor reviews mentioning malicious behavior.
If you suspect an app is malicious, uninstall it immediately. Finally, a factory reset, as detailed below, can be a last resort to completely wipe the device clean.
Resources and Tools for Malware Removal
Several reputable antivirus and security apps are available on the Google Play Store. Look for apps with high ratings and positive user reviews, paying attention to features like real-time protection, malware scanning, and app permission monitoring. Some examples include Lookout, McAfee Mobile Security, and Avast Mobile Security. Remember to always download apps from the official Google Play Store to minimize the risk of downloading malware.
Be cautious of apps promising unrealistic features or those with suspiciously low ratings.
Performing a Factory Reset to Eliminate Malware
A factory reset is a drastic measure, erasing all data and settings on your device, restoring it to its original state. It’s a highly effective method for removing persistent malware, but remember to back up any important data beforehand.
It is crucial to understand that a factory reset will delete
-all* data on your device. This includes photos, videos, documents, and app data. Ensure you have a backup of anything important before proceeding.
- Back up your important data to a cloud service or computer.
- Turn off your device completely.
- Power on your device while holding down the appropriate button combination to access the recovery mode. (This varies depending on the Android device model; consult your device’s manual.)
- Use the volume buttons to navigate to the “Wipe data/factory reset” option and select it using the power button.
- Confirm the factory reset when prompted.
- Once the process is complete, select “Reboot system now.”
- After rebooting, your device will be restored to its factory settings. You will need to set it up again as a new device.
Illustrative Examples of SMS Stealer Attacks

Understanding how SMS stealers operate requires looking at real-world examples. These attacks often leverage social engineering and exploit vulnerabilities in Android’s security mechanisms. Let’s examine a hypothetical scenario and delve into the technical aspects of these malicious programs.
A Hypothetical SMS Stealer Attack
Imagine Sarah receives a text message appearing to be from her bank. The message informs her of a suspicious transaction and requests her to click a link to verify her account details. This link, however, leads to a malicious website designed to download an SMS stealer disguised as a security update app. Once installed, the malware silently operates in the background, intercepting all incoming and outgoing SMS messages, including those containing one-time passwords (OTPs) and banking details.
The attacker then remotely accesses this stolen data through a command-and-control server, potentially emptying Sarah’s bank account or gaining access to other sensitive information. The entire process happens seamlessly, leaving Sarah unaware of the compromise until it’s too late.
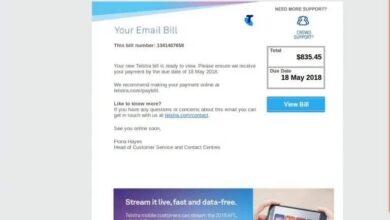
Visual Representation of a Phishing SMS Message
The phishing SMS message would mimic a legitimate bank notification. The sender ID might appear as “YourBank,” and the message would contain a short, urgent message like, “Urgent Security Alert! Suspicious activity detected on your account. Verify details here: [malicious link]”. The message might also include a sense of urgency, using phrases like “Act now” or “Your account may be suspended.” The link itself would be subtly disguised, perhaps shortened using a URL shortener service to obscure its true destination.
The overall appearance aims to look authentic, using the bank’s logo (potentially a poorly copied version) and official-sounding language. The message would lack any grammatical errors to maintain credibility.
Bypassing Android Security Measures
A sophisticated SMS stealer might bypass Android’s security measures by exploiting vulnerabilities in older Android versions. For example, a flaw in Android 4.4’s permission system might allow the malware to request only limited permissions during installation, but then gain access to SMS data through a backdoor or by exploiting other vulnerabilities within the system. The malware could leverage root privileges (if the device is rooted) to gain unrestricted access, bypassing permission checks entirely.
Furthermore, it might use techniques like code obfuscation to make its malicious code difficult to detect by antivirus software.
Comparison of Two SMS Stealer Methods
Let’s consider two hypothetical SMS stealers: “Stealer A” and “Stealer B”. Stealer A utilizes a direct access method. Upon installation, it immediately requests the SMS read permission and gains direct access to the SMS database. This is a straightforward approach but easily detectable by security software if it doesn’t use code obfuscation. Stealer B employs a more stealthy approach.
It might initially gain access through a different vulnerability, perhaps exploiting a flaw in a seemingly unrelated app. Once established, it subtly monitors the SMS data without directly accessing the database, using techniques like intercepting data at a lower system level. This method is more difficult to detect as it doesn’t trigger the same alerts as Stealer A.
Closing Notes
In the digital age, our phones hold our lives – our finances, our relationships, our identities. SMS stealer malware is a serious threat, but with awareness and proactive measures, we can significantly reduce our risk. Remember, staying informed is the first step to staying secure. By understanding how these threats work and implementing the preventative strategies discussed, you can safeguard your personal information and peace of mind.
Don’t wait for disaster to strike; take charge of your digital security today!
User Queries: Android Mobile Security Alert Against Sms Stealer Malware
What are the signs my phone is infected with SMS stealer malware?
Unusual high SMS usage, unexpected premium SMS charges, receiving strange messages you didn’t send, and apps behaving erratically are all potential indicators.
Can I recover stolen data after an infection?
Unfortunately, recovering stolen data after an infection is difficult. Focus on securing your accounts and reporting the theft to relevant authorities.
Is rooting my phone more susceptible to SMS stealers?
Yes, rooting your phone removes security measures, making it significantly more vulnerable to malware.
How often should I update my Android OS and apps?
Regularly! Updates often include security patches that protect against known vulnerabilities. Aim for updates as soon as they’re released.