Can Ransomware Gangs Be Neutralized? Exploring Cyber Extortion Strategies
Can ransomware gangs be neutralized exploring strategies to combat cyber extortion – Can ransomware gangs be neutralized? Exploring strategies to combat cyber extortion is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Ransomware attacks are escalating, impacting businesses and individuals alike, leading to significant financial losses and data breaches. This post delves into the complex world of ransomware gangs, examining their operations, the challenges faced by law enforcement, and the multifaceted strategies needed to effectively combat this growing threat.
We’ll explore everything from understanding the lifecycle of a ransomware attack to the crucial role of international cooperation and the importance of robust cybersecurity defenses.
From the sophisticated techniques employed by these criminal organizations to the innovative solutions being developed to counter them, we’ll dissect the key elements of this cyber war. We’ll examine the effectiveness of current strategies, highlight their limitations, and propose avenues for improvement. The goal? To paint a comprehensive picture of the fight against ransomware and offer insights into how we can better protect ourselves and our data.
Understanding Ransomware Gangs’ Operations: Can Ransomware Gangs Be Neutralized Exploring Strategies To Combat Cyber Extortion
Ransomware gangs operate as sophisticated criminal enterprises, employing a range of techniques and exploiting vulnerabilities to achieve their objectives. Understanding their operational lifecycle and methods is crucial in developing effective countermeasures. This section delves into the intricacies of ransomware gang operations, examining their attack lifecycles, techniques, and business models.
The Ransomware Attack Lifecycle
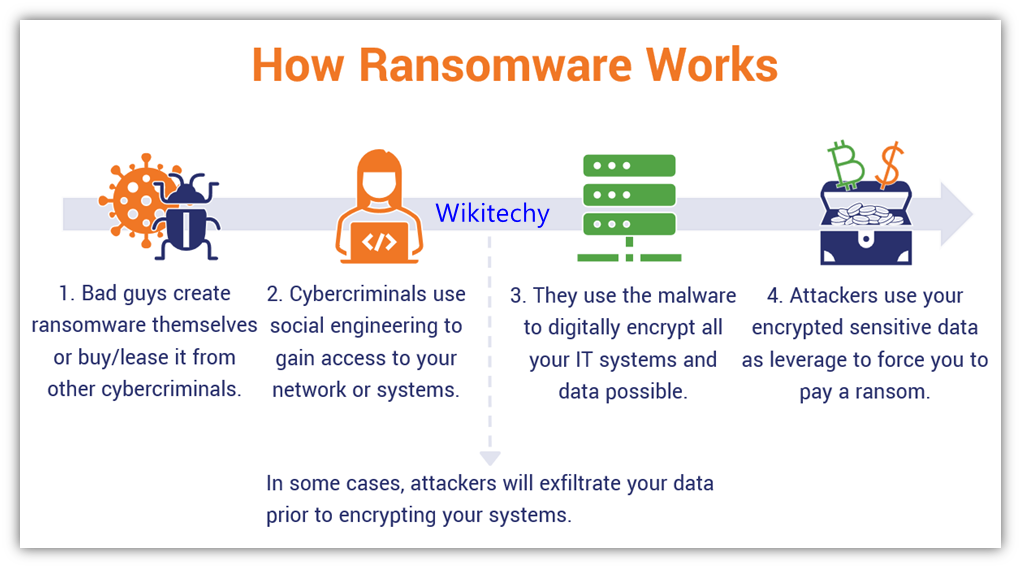
A typical ransomware attack follows a predictable lifecycle. It begins with initial infiltration, often through phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links. This leads to system compromise, where the attackers gain unauthorized access. Once inside, they may deploy lateral movement techniques to spread the ransomware across the network. Data exfiltration follows, where sensitive data is stolen as leverage or for resale on dark web marketplaces.
Finally, the ransomware is deployed, encrypting critical files and rendering them inaccessible. The attackers then demand a ransom for decryption keys and/or promise to not release the stolen data. Failure to pay often results in data being published online or sold to other malicious actors.
Techniques Used by Ransomware Gangs
Ransomware gangs utilize a variety of techniques to compromise systems. Phishing remains a highly effective entry point, exploiting human error through deceptive emails or websites. Exploiting known vulnerabilities in software and operating systems is another common method, often achieved through automated scanning tools. Social engineering, manipulating individuals to reveal sensitive information or grant access, also plays a significant role.
These techniques are often combined for maximum impact, creating multi-layered attacks that are difficult to detect and prevent.
Types of Ransomware and Encryption Methods
Ransomware varies in its encryption methods and data destruction capabilities. Some ransomware employs symmetric encryption, using a single key for both encryption and decryption. Others use asymmetric encryption, involving a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, held by the attackers. Certain ransomware strains go beyond simple encryption; they may also delete shadow copies, preventing data recovery through system restore points.
Neutralizing ransomware gangs requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on prevention and response. A key element is robust cloud security, and understanding how to manage it effectively is crucial. For insights into this, check out this great article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management , which highlights the importance of proactive security measures. Ultimately, strengthening our cloud defenses is a vital step in the fight against cyber extortion.
The sophistication of the encryption and data destruction techniques can significantly impact the difficulty of recovery and the cost of remediation.
Business Models of Prominent Ransomware Gangs
Different ransomware gangs operate under various business models. Some operate as affiliates, distributing ransomware developed by others in exchange for a cut of the ransom. Others develop and deploy their own ransomware, maintaining full control over the operation. The sophistication of their operations, including the use of double extortion (data encryption and data theft), varies greatly. Profit maximization is the primary driver, with some gangs focusing on high-value targets and others targeting a broader range of victims.
The evolution of these business models is continuous, with gangs adapting to countermeasures and evolving their techniques to maintain profitability.
Ransomware Gang Infrastructure, Can ransomware gangs be neutralized exploring strategies to combat cyber extortion
The infrastructure used by ransomware gangs is typically distributed and designed for anonymity. This includes command-and-control (C2) servers for communication and control, data leak sites to publish stolen data, and cryptocurrency wallets for receiving ransom payments. The use of anonymizing services like VPNs and the Tor network is commonplace to hinder tracking and investigation.
| Infrastructure Component | Description | Purpose | Security Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Command-and-Control (C2) Servers | Servers used to communicate with infected systems. | Issue commands, receive stolen data, deliver ransomware updates. | Often hosted on compromised servers or using anonymizing services. |
| Data Leak Sites | Websites used to publish stolen data as leverage for ransom payments. | Publicly expose sensitive information to pressure victims. | Hosted on the dark web, using strong security measures. |
| Cryptocurrency Wallets | Digital wallets used to receive ransom payments. | Enable untraceable transactions. | Utilize various techniques to obscure the origin and destination of funds. |
| Bulletproof Hosting Providers | Hosting providers that do not cooperate with law enforcement investigations. | Provide anonymity and protection from takedown attempts. | Often operate outside of legal jurisdictions. |
Law Enforcement and International Cooperation
Combating ransomware gangs requires a multifaceted approach, and law enforcement plays a crucial role, particularly given the transnational nature of these criminal enterprises. The challenges are immense, requiring sophisticated investigative techniques and unprecedented levels of international collaboration. Success hinges on overcoming jurisdictional barriers, coordinating intelligence gathering, and developing effective strategies for disrupting ransomware operations and bringing perpetrators to justice.The challenges faced by law enforcement agencies in combating ransomware attacks across national borders are significant.
Ransomware gangs often operate from countries with weak cybercrime laws or limited law enforcement capacity, making extradition difficult. The decentralized and anonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions used for ransom payments further complicates investigations. Different legal frameworks and data protection regulations across countries hinder the seamless sharing of crucial information necessary for effective joint investigations. Moreover, the rapidly evolving tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by ransomware gangs require continuous adaptation and innovation from law enforcement.
International Cooperation in Disrupting Ransomware Operations
International cooperation is paramount in disrupting ransomware operations. Information sharing between law enforcement agencies across countries is crucial for identifying patterns, tracking the movements of ransomware gangs, and building strong cases for prosecution. Joint investigations allow for the pooling of resources and expertise, leading to more effective takedowns. Agreements on mutual legal assistance (MLAs) and data sharing are essential for facilitating these collaborations.
Neutralizing ransomware gangs requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on prevention and response. Strong security practices are crucial, but equally important is the development of robust, secure applications. This is where exploring the potential of platforms like Domino, as discussed in this insightful article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , becomes vital.
By building more secure applications, we can reduce the attack surface and make it harder for ransomware to take hold, ultimately strengthening our defenses against cyber extortion.
Furthermore, coordinated actions, such as simultaneous raids across multiple jurisdictions, can significantly disrupt ransomware gangs’ operations and send a strong deterrent message.
Examples of Successful Law Enforcement Actions Against Ransomware Gangs
Several successful law enforcement actions against ransomware gangs demonstrate the effectiveness of international cooperation. Operation “Trojan Shield,” a multinational operation involving law enforcement agencies from various countries, successfully disrupted the activities of several ransomware gangs by seizing their infrastructure and disrupting their command-and-control servers. This operation involved coordinated raids, the seizure of cryptocurrency, and the arrest of key individuals involved in the ransomware operations.
Another notable example is the disruption of the REvil ransomware gang, which involved international collaboration and resulted in the recovery of millions of dollars in ransom payments. These successes highlight the importance of intelligence sharing, joint investigations, and coordinated law enforcement actions.
Framework for Improved International Cooperation to Combat Ransomware
A robust framework for improved international cooperation requires strengthened legal frameworks that address the jurisdictional challenges posed by cross-border cybercrime. This includes harmonizing laws related to cybercrime, establishing clear mechanisms for extradition and mutual legal assistance, and addressing the legal complexities surrounding cryptocurrency transactions. Furthermore, standardized data sharing agreements, with appropriate safeguards for privacy and data protection, are essential for facilitating the timely and secure exchange of information between law enforcement agencies.
This framework should also include mechanisms for capacity building and training for law enforcement agencies in developing countries to enhance their ability to investigate and prosecute ransomware-related crimes.
Strategies for Tracing and Seizing Cryptocurrency Payments
Tracing and seizing cryptocurrency payments used by ransomware gangs is a complex but increasingly important aspect of law enforcement efforts. Techniques employed include analyzing blockchain transactions to identify the flow of funds, collaborating with cryptocurrency exchanges to freeze or seize assets, and using specialized forensic tools to trace cryptocurrency movements. Successful strategies often involve working with cryptocurrency exchanges and blockchain analytics companies to identify and track the movement of ransom payments.
This requires close cooperation between law enforcement agencies and the private sector to develop effective methods for tracing and seizing cryptocurrency assets. For instance, law enforcement agencies have successfully traced ransomware payments by analyzing transaction patterns on the blockchain, identifying intermediary wallets, and ultimately tracing the funds to accounts controlled by the perpetrators.
Cybersecurity Defenses and Mitigation Strategies
Ransomware attacks are a significant threat to organizations of all sizes. Effective cybersecurity defenses are crucial for mitigating the risk and minimizing the impact of such attacks. This section explores key vulnerabilities, mitigation strategies, and best practices for building a robust ransomware defense.
Key Vulnerabilities and Mitigation
Ransomware gangs exploit various vulnerabilities to gain access to systems and encrypt data. Commonly targeted weaknesses include outdated software with known exploits, weak or stolen credentials, phishing attacks, and vulnerabilities in network infrastructure. Mitigation involves a multi-layered approach. Regular patching and updating of software and operating systems is paramount. Implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and robust access control mechanisms are crucial to prevent unauthorized access.
Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Finally, employee training on identifying and avoiding phishing attempts is essential.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Robust data backup and recovery strategies are critical in mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks. A 3-2-1 backup strategy is recommended: three copies of data, on two different media types, with one copy offsite. This ensures that even if one backup is compromised, other copies remain available for recovery. Regular testing of backup and recovery procedures is vital to ensure their effectiveness in a real-world scenario.
Consider immutable backups, which cannot be altered or deleted, offering an extra layer of protection against ransomware. The recovery process should be well-documented and regularly practiced to minimize downtime in case of an attack. For example, a financial institution might use a geographically diverse cloud storage solution for their offsite backup, ensuring business continuity even in a major disaster.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities at the endpoint level. EDR solutions monitor system activity for malicious behavior, such as unusual file access patterns or suspicious network connections, indicative of a ransomware infection. They can detect ransomware even before encryption begins, allowing for immediate remediation. Many EDR solutions offer features like automated response capabilities, such as isolating infected endpoints or automatically quarantining malicious files.
Real-time threat intelligence feeds help EDR solutions stay ahead of the curve, identifying and responding to emerging ransomware variants. For instance, an EDR system might detect unusual encryption activity on a server and automatically block the malicious process, preventing data encryption.
Security Awareness Training Programs
Effective security awareness training programs are vital in reducing the risk of ransomware attacks. Training should focus on educating employees about various attack vectors, including phishing emails, malicious attachments, and suspicious websites. Simulations and phishing exercises can help reinforce learning and test employee awareness. Regular updates on emerging threats and best practices are also crucial. Different training methods can be employed, including online modules, interactive workshops, and gamified learning experiences.
Tailoring the training to the specific roles and responsibilities of employees can maximize its effectiveness. For example, a program might use realistic phishing emails to test employee vigilance and provide immediate feedback on their responses.
Ransomware Prevention Best Practices Checklist
Implementing a comprehensive set of best practices is essential for minimizing the risk of ransomware attacks.
- Regularly update software and operating systems.
- Implement strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Utilize a robust firewall and intrusion detection/prevention system.
- Employ a 3-2-1 backup strategy and regularly test backups.
- Implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Educate employees through comprehensive security awareness training.
- Restrict administrative privileges to only authorized personnel.
- Segment networks to limit the impact of a breach.
- Develop an incident response plan and regularly test it.
The Role of Private Sector Initiatives
The private sector plays a crucial, often overlooked, role in the fight against ransomware. Cybersecurity companies, insurance providers, and collaborative initiatives are all vital components in building a robust defense against these increasingly sophisticated attacks. Their contributions extend beyond individual responses to encompass proactive measures and strategic partnerships that strengthen overall cybersecurity posture.Cybersecurity companies are at the forefront of developing and deploying anti-ransomware technologies.
This includes creating advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, threat intelligence platforms, and security awareness training programs. These tools are critical for identifying and mitigating ransomware threats before they can cause significant damage. Furthermore, the constant evolution of ransomware tactics necessitates continuous innovation and adaptation within the private sector.
Anti-Ransomware Technology Development and Deployment
Cybersecurity firms invest heavily in research and development to stay ahead of the evolving ransomware landscape. This involves creating sophisticated detection mechanisms, employing advanced machine learning algorithms to identify malicious activity, and developing tools to decrypt data affected by ransomware attacks. Companies like CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, and Palo Alto Networks are examples of organizations actively engaged in developing and deploying these critical technologies.
Their solutions range from proactive threat hunting to automated incident response capabilities, reducing the impact of ransomware infections. These technologies are often tailored to specific industries and organizational needs, enhancing their effectiveness.
Threat Intelligence Sharing Among Private Sector Organizations
The sharing of threat intelligence is paramount in combating ransomware effectively. Private sector organizations, often possessing unique insights into attacker tactics and techniques, can significantly benefit from collaboration. Information sharing enables a collective defense, allowing companies to proactively defend against known threats and adapt their security strategies in response to emerging trends. This collaboration can take various forms, from informal information exchanges between security professionals to participation in industry-specific information sharing and analysis centers (ISACs).
The more effectively this information is shared, the better the collective ability to neutralize ransomware threats.
Successful Private Sector Initiatives Against Ransomware
Collaborative threat hunting and incident response are two examples of successful private sector initiatives. Collaborative threat hunting involves multiple organizations working together to proactively identify and neutralize threats across their networks. This collaborative approach allows for a wider range of expertise and resources to be brought to bear on the problem. Similarly, coordinated incident response ensures a faster and more effective response to ransomware attacks.
This coordinated effort minimizes the damage and facilitates faster recovery. For instance, industry consortia and shared threat intelligence platforms facilitate these collaborative efforts.
The Role of Cybersecurity Insurance in Mitigating Financial Impact
Cybersecurity insurance plays a crucial role in mitigating the financial impact of ransomware attacks. By providing financial protection against data breaches, system downtime, and legal costs, insurance incentivizes organizations to invest in robust cybersecurity measures and provides financial support during recovery. However, the effectiveness of cybersecurity insurance hinges on the clarity of policy terms, the adequacy of coverage, and the insurer’s capacity to provide effective support during a ransomware incident.
The insurance industry is continuously adapting its policies to address the evolving ransomware threat, reflecting the increased risk and the need for comprehensive coverage.
A Model for Public-Private Partnership to Enhance Cybersecurity Defenses
A successful model for public-private partnership requires clear communication channels, defined roles and responsibilities, and a shared understanding of objectives. The government can contribute by providing regulatory frameworks, supporting research and development, and sharing threat intelligence. The private sector can contribute by developing and deploying advanced security technologies, sharing threat intelligence, and investing in cybersecurity training and awareness programs.
This collaborative approach should focus on information sharing, joint training exercises, and coordinated incident response. A clear governance structure and a mechanism for resolving disputes are also essential for the long-term success of such a partnership. This model fosters a stronger collective defense against ransomware, leveraging the strengths of both the public and private sectors.
Analyzing the Effectiveness of Current Strategies
Combating ransomware is a multifaceted challenge requiring a coordinated global effort. While significant strides have been made, the effectiveness of current strategies varies considerably, highlighting the need for continuous adaptation and improvement. This analysis examines the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches, focusing on their impact and suggesting avenues for enhanced efficacy.Law enforcement actions, cybersecurity defenses, and international cooperation represent the primary pillars of the current anti-ransomware strategy.
However, the effectiveness of each is contingent upon several factors, including technological advancements, jurisdictional limitations, and the evolving tactics employed by ransomware gangs.
Effectiveness of Law Enforcement Actions
Law enforcement’s role focuses on disrupting ransomware operations through investigations, arrests, and asset seizures. Success stories exist, such as the takedown of specific infrastructure used by ransomware gangs, leading to disruptions in their activities. However, the decentralized and often transnational nature of these groups poses significant challenges. Jurisdictional issues, difficulties in tracing cryptocurrency transactions, and the ephemeral nature of online infrastructure hinder effective prosecution.
Furthermore, the sheer volume of attacks makes it impossible for law enforcement to respond to every incident effectively. Improvements require enhanced international cooperation, improved cryptocurrency tracing capabilities, and a focus on proactive disruption rather than solely reactive investigations.
Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Defenses
Cybersecurity defenses, including robust patching, endpoint detection and response (EDR), security awareness training, and data backups, are crucial in mitigating ransomware attacks. Strong cybersecurity postures significantly reduce the likelihood of successful attacks and limit the impact of breaches. However, the sophistication of ransomware techniques, including the use of zero-day exploits and advanced evasion tactics, continues to challenge even the most robust defenses.
The human element remains a critical vulnerability, with phishing and social engineering attacks frequently succeeding in bypassing technical safeguards. Improvements necessitate continuous investment in advanced threat detection technologies, robust security awareness training programs, and the adoption of proactive threat hunting methodologies.
Effectiveness of International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential for effectively combating ransomware, given the transnational nature of these criminal enterprises. Sharing intelligence, coordinating law enforcement actions, and establishing legal frameworks for extradition and asset recovery are crucial. Several international initiatives are underway, but inconsistencies in legal frameworks and varying levels of resources across nations pose significant challenges. The lack of a universally accepted legal definition of ransomware and difficulties in obtaining evidence across borders further complicate efforts.
Enhanced cooperation requires standardized legal frameworks, increased resource allocation to international task forces, and the development of effective mechanisms for sharing threat intelligence.
Case Study: The Neutralization of REvil
The disruption of the REvil ransomware operation in 2021 serves as a notable example of successful neutralization. A coordinated international effort, involving law enforcement agencies and private sector partners, played a key role in seizing infrastructure and disrupting the gang’s operations. Key factors contributing to this success included: the proactive identification and disruption of the gang’s infrastructure, effective collaboration between law enforcement agencies and private sector companies, and the successful tracing and seizure of cryptocurrency assets.
This case highlights the potential of collaborative efforts, but also underscores the need for continuous vigilance and adaptation.
Impact of the Evolving Cryptocurrency Landscape
The use of cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, has significantly facilitated ransomware operations by providing a relatively anonymous and untraceable payment method. While efforts to track and seize cryptocurrency are ongoing, the decentralized nature of blockchain technology poses significant challenges. The development of techniques like coin mixing and the use of decentralized exchanges make tracing transactions increasingly difficult. Countermeasures include improved cryptocurrency tracing techniques, enhanced collaboration with cryptocurrency exchanges to identify and freeze suspicious transactions, and the exploration of alternative payment methods for ransom demands, such as using escrow services with increased transparency.
Last Word

The fight against ransomware is an ongoing battle, demanding constant vigilance and adaptation. While complete neutralization of all ransomware gangs might remain a distant goal, significant progress can be made through a multi-pronged approach involving robust cybersecurity measures, effective international cooperation, and proactive private sector initiatives. By understanding the intricacies of ransomware operations and implementing comprehensive strategies, we can significantly reduce the impact of these attacks and create a safer digital world.
The future of cybersecurity hinges on our collective ability to stay ahead of these ever-evolving threats.
FAQ Overview
What is the most common method ransomware gangs use to infiltrate systems?
Phishing emails remain a highly effective method, often exploiting social engineering techniques to trick users into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments.
How can individuals protect themselves from ransomware attacks?
Regularly update software, be cautious of suspicious emails and links, back up your data regularly, and consider using robust anti-malware software.
What role does insurance play in ransomware mitigation?
Cybersecurity insurance can help organizations mitigate the financial impact of ransomware attacks by covering costs associated with recovery, legal fees, and potentially even ransom payments (though this is often debated).
Are there any legal ramifications for paying a ransom?
Paying a ransom is generally discouraged by law enforcement as it encourages further attacks. There may also be legal implications depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances.