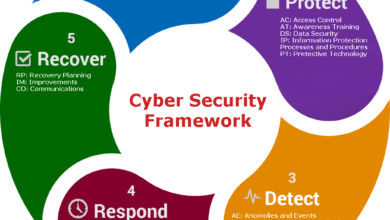
Data Responsibility Trust Drives Growth
A data responsibility leveraging the power of trust to drive growth – Data Responsibility: Trust Drives Growth – that’s the core message, and it’s more crucial than ever. In today’s data-driven world, simply collecting information isn’t enough; it’s how we
-handle* that data that truly matters. This isn’t just about compliance – it’s about building genuine trust with customers, partners, and even employees. This post dives into the practical steps and ethical considerations needed to leverage data responsibly, fostering a culture of transparency and ultimately, fueling sustainable business growth.
We’ll explore how establishing clear data responsibility policies, prioritizing data security and privacy, and fostering open communication can lead to stronger customer relationships, increased loyalty, and a significant boost to your bottom line. We’ll also look at the potential pitfalls of neglecting data responsibility and how to navigate the complexities of data privacy regulations.
Defining Data Responsibility
Data responsibility isn’t just about complying with regulations; it’s about building trust and fostering sustainable growth. It’s a proactive approach to data management that prioritizes ethical considerations, security, and the overall well-being of individuals whose data is being handled. This approach recognizes that data is a valuable asset, but also a powerful tool that must be used responsibly.
At its core, responsible data handling involves a commitment to transparency, accountability, and respect for individual privacy. It requires organizations to understand the data they collect, how it’s used, and the potential risks associated with its handling. This understanding forms the foundation for building robust data governance frameworks and fostering a culture of data ethics within the organization.
Core Principles of Responsible Data Handling
These principles guide ethical and secure data management. They emphasize transparency, user control, and data minimization. Adherence to these principles helps build and maintain trust with data subjects.
The core principles are built around several key areas: transparency in data collection and use, meaningful consent from individuals, data security and privacy protection measures, accountability for data breaches and misuse, and ongoing compliance with relevant regulations and best practices. Organizations must be clear about what data they collect, why they collect it, and how it will be used.
They must also provide users with control over their data, allowing them to access, correct, and delete their information.
Ethical Considerations in Data Management
Ethical data management requires careful consideration of potential biases, fairness, and the societal impact of data usage. Ignoring these aspects can lead to discriminatory outcomes and erode public trust.
Building trust is key to responsible data handling, and that trust fuels business growth. One way to efficiently manage and leverage data responsibly is through streamlined application development, which is where the power of domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes into play. By creating robust, secure apps quickly, we can ensure data integrity and transparency, further solidifying that crucial trust with our users and ultimately driving sustainable growth.
Ethical considerations extend beyond simply complying with regulations. They involve proactively identifying and mitigating potential harms associated with data use. For example, algorithms used in decision-making processes should be carefully audited to ensure they are free from bias and do not perpetuate inequalities. Data privacy must be respected, and individuals should have control over their personal information.
The potential for misuse of data, such as for surveillance or manipulation, must be carefully considered and mitigated.
Best Practices for Data Security and Privacy
Implementing robust security measures and privacy-enhancing technologies is crucial for protecting data from unauthorized access and misuse.
Strong security measures are essential. This includes employing encryption, access controls, regular security audits, and incident response plans. Data minimization – collecting only the data necessary – is also a crucial principle. Privacy-enhancing technologies, such as differential privacy and federated learning, can allow for data analysis while preserving individual privacy. Regular employee training on data security and privacy best practices is also critical.
Finally, organizations should establish clear data retention policies to ensure that data is not kept longer than necessary.
Framework for Establishing a Data Responsibility Policy
A well-defined policy provides a roadmap for responsible data handling, outlining roles, responsibilities, and procedures.
A comprehensive data responsibility policy should include: a clear definition of data ownership and responsibilities; detailed procedures for data collection, storage, and processing; a robust data security plan; mechanisms for handling data breaches and complaints; a process for obtaining and managing consent; a framework for ongoing monitoring and improvement. This policy should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in technology, regulations, and best practices.
Furthermore, it should be easily accessible to all employees and stakeholders.
The Role of Trust in Data Management
Data responsibility isn’t just about adhering to regulations; it’s about fostering a culture of trust. This trust, built upon transparency and accountability, is the bedrock of successful data management, enabling effective collaboration and driving significant growth. Without it, data initiatives stall, collaboration falters, and the potential value of data remains untapped.Trust significantly influences how readily data is shared and used collaboratively.
When stakeholders trust the data’s integrity, accuracy, and the ethical practices surrounding its collection and use, they are more likely to share their own data, contributing to a richer, more comprehensive dataset. This collaborative environment fuels innovation and allows for the development of more accurate and insightful analyses. Conversely, a lack of trust can lead to data silos, hindering progress and limiting the potential benefits of data-driven decision-making.
Transparency and Trust in Data Practices
Transparency is intrinsically linked to trust in data management. Open communication about data collection methods, storage procedures, usage policies, and any limitations or potential biases is crucial. When individuals understand how their data is being handled and why, they are more likely to trust the organization and its processes. This transparency also helps to build accountability, as it allows for scrutiny and ensures that data is used responsibly and ethically.
For instance, a company publicly disclosing its data privacy policy, including how user data is collected, used, and protected, demonstrates a commitment to transparency and fosters user trust. Conversely, secretive or opaque data practices breed suspicion and undermine confidence.
Strategies for Building and Maintaining Trust with Data Stakeholders
Building and maintaining trust requires a multifaceted approach. Consistent adherence to ethical guidelines and regulations is paramount. This includes obtaining informed consent, ensuring data security, and implementing robust data governance frameworks. Regular communication with stakeholders, providing clear and accessible information about data practices, is also essential. This could involve publishing regular reports on data usage, responding promptly to queries, and actively soliciting feedback.
Furthermore, actively involving stakeholders in data governance processes, allowing them a voice in how their data is used, can significantly enhance trust. For example, establishing a data ethics board with representatives from different stakeholder groups can help ensure that data is used responsibly and ethically.
Risks Associated with a Lack of Trust in Data Management
A lack of trust in data management carries significant risks. Data breaches and security incidents become more likely when trust is eroded. This is because stakeholders may be less likely to cooperate with security measures or report suspicious activity if they don’t trust the organization’s handling of their data. Similarly, a lack of trust can lead to inaccurate data and biased analyses, as individuals may be hesitant to share their data or provide accurate information.
This can have serious consequences for decision-making, leading to flawed strategies and potentially harming the organization’s reputation. For example, if customers don’t trust a company’s data privacy practices, they may be less likely to do business with that company, leading to a loss of revenue and market share. The damage to reputation can be long-lasting and difficult to repair.
Leveraging Trust to Drive Growth
Responsible data use isn’t just an ethical imperative; it’s a powerful engine for business growth. By prioritizing transparency, security, and user control over data, companies can cultivate trust, leading to increased customer loyalty, stronger brand reputation, and ultimately, higher revenue. This trust, built on a foundation of responsible data practices, unlocks opportunities for deeper customer engagement and more effective marketing strategies.Building trust with customers is paramount in today’s data-driven world.
When customers trust a company with their data, they’re more likely to engage with its products and services, share information willingly, and become brand advocates. This trust translates directly into increased sales, improved customer lifetime value, and a more resilient business model.
Responsible Data Use Fosters Business Growth
Companies that demonstrate a commitment to data responsibility often experience significant business advantages. For instance, a company that transparently explains how it uses customer data, provides easy-to-understand privacy policies, and offers clear options for data control is more likely to attract and retain customers. This proactive approach to data management fosters a positive brand image, driving customer acquisition and reducing churn.
Consider a hypothetical scenario where Company A prioritizes data transparency, offering granular control over data sharing preferences to its users. This results in higher customer satisfaction scores, increased user engagement, and a significant boost in positive online reviews, all contributing to revenue growth. Conversely, Company B, which has a less transparent data policy, experiences higher customer churn and negative publicity, impacting its bottom line.
Trust Improves Customer Relationships and Loyalty
Trust is the bedrock of strong customer relationships. When customers feel their data is being handled responsibly and ethically, they are more likely to develop a deeper connection with the brand. This leads to increased customer loyalty and advocacy. For example, a subscription service that uses customer data to personalize recommendations but also provides clear opt-out options will likely see higher retention rates compared to a service that uses data aggressively without transparency.
Customers who feel respected and valued are more likely to remain loyal, becoming repeat purchasers and recommending the service to others. This loyalty translates to increased revenue and reduced marketing costs.
Case Study: The Positive Impact of Data Responsibility on Revenue
Let’s imagine a fictional e-commerce company, “GreenThumb Gardens,” specializing in gardening supplies. Initially, GreenThumb Gardens collected customer data but lacked a clear data responsibility policy. This resulted in low customer trust and several data breaches. Following a significant re-evaluation, GreenThumb Gardens implemented a comprehensive data responsibility strategy, including transparent data usage policies, robust security measures, and a user-friendly data control dashboard.
Within a year, customer trust significantly improved, leading to a 20% increase in customer acquisition, a 15% reduction in customer churn, and a 25% boost in average order value. This demonstrates the direct correlation between responsible data handling and improved financial performance. The enhanced trust also allowed GreenThumb Gardens to effectively personalize marketing campaigns, resulting in higher conversion rates and increased revenue.
Benefits of a Trust-Based Data Strategy
A trust-based data strategy offers several key benefits. It reduces the risk of data breaches and associated legal and reputational damage. It improves customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to increased revenue and reduced marketing costs. It enhances brand reputation, attracting new customers and strengthening the brand’s competitive position. Finally, it allows for more effective and personalized marketing campaigns, driving higher conversion rates and ultimately, boosting the bottom line.
These benefits highlight the strategic importance of prioritizing data responsibility and building trust with customers.
Practical Applications of Responsible Data Practices: A Data Responsibility Leveraging The Power Of Trust To Drive Growth
Responsible data practices aren’t just ethical considerations; they’re crucial for building trust, fostering innovation, and driving sustainable growth. By actively incorporating ethical principles into data management, organizations can unlock significant competitive advantages while safeguarding their reputation and the interests of their stakeholders. This section explores practical applications of responsible data handling, focusing on ethical decision-making, data integrity, monitoring systems, and stakeholder communication.
Implementing responsible data practices requires a multifaceted approach. It’s not enough to simply collect and analyze data; organizations must ensure that every step of the process, from data collection to analysis and use, aligns with ethical guidelines and legal requirements. This involves careful consideration of privacy, security, fairness, and transparency.
Data-Driven Decision-Making with Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations should be at the forefront of every data-driven decision. For example, a company using customer data to personalize marketing campaigns must ensure it’s doing so in a way that respects individual privacy and avoids discriminatory practices. This means obtaining explicit consent, offering transparency about data usage, and implementing measures to prevent bias in algorithms used for targeting.
Consider a hypothetical scenario where a bank uses credit scoring models. A responsible approach would involve regularly auditing the model for biases that might unfairly discriminate against certain demographic groups, actively working to mitigate these biases, and providing clear explanations to customers about how their creditworthiness is assessed.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Integrity
Maintaining data accuracy and integrity is fundamental to responsible data management. This involves implementing robust data governance policies and procedures, including data validation checks, regular data quality audits, and mechanisms for detecting and correcting errors. For instance, a healthcare provider must ensure the accuracy of patient records to avoid misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment. This can involve using data validation rules to prevent incorrect entries, implementing double-checking procedures, and regularly auditing data for inconsistencies.
Furthermore, using version control systems for data and employing checksums or hashing algorithms can help ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized modifications.
Monitoring and Evaluating Data Responsibility Initiatives
Establishing a system for monitoring and evaluating data responsibility initiatives is critical for continuous improvement. This involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) related to data quality, privacy compliance, and ethical considerations. Regular reporting and analysis of these KPIs provide insights into the effectiveness of implemented practices and highlight areas for improvement. For example, KPIs could include the percentage of data breaches prevented, the number of privacy complaints received, and the accuracy rate of data entries.
Regular audits, both internal and potentially external, can provide an independent assessment of data responsibility practices.
Communicating Data-Related Risks and Mitigations to Stakeholders
Open and transparent communication about data-related risks and mitigations is crucial for building and maintaining trust with stakeholders. This involves providing clear and accessible information about data collection practices, data security measures, and potential risks. For instance, a social media platform should clearly communicate its data privacy policy to users, explaining how their data is collected, used, and protected.
Regular updates on data security incidents and mitigation strategies should also be provided. This transparent communication fosters trust and demonstrates a commitment to responsible data handling.
Building a Culture of Data Responsibility

Building a culture of data responsibility isn’t a one-time project; it’s an ongoing commitment that requires consistent effort and a top-down approach. It’s about embedding responsible data handling into the very fabric of your organization, ensuring it’s not just a policy but a lived experience for every employee. This involves integrating data responsibility into company values, providing comprehensive training, assessing organizational readiness, and establishing methods to measure the program’s effectiveness.Integrating data responsibility into a company’s values and culture requires a multifaceted approach.
It starts with leadership buy-in. Executives must champion data responsibility, modeling the desired behaviors and making it clear that ethical data handling is not just expected but is crucial for the company’s success. This commitment needs to be reflected in performance reviews, reward systems, and internal communications. Furthermore, clear and concise data governance policies should be developed and readily accessible to all employees.
These policies should Artikel acceptable data practices, responsibilities, and consequences for non-compliance. Regular communication and reinforcement of these policies are essential to ensure they remain relevant and understood.
Data Responsibility Training Programs
Effective training programs are crucial for educating employees on responsible data handling. These programs should be tailored to different roles and responsibilities within the organization. For example, data scientists might need in-depth training on privacy-preserving techniques, while marketing personnel might focus on compliance with advertising regulations and data subject rights. The training should go beyond theoretical knowledge and incorporate practical exercises and real-life scenarios to reinforce learning.
Regular refresher courses should be provided to ensure employees stay up-to-date with evolving regulations and best practices. A blended learning approach, combining online modules with in-person workshops, can maximize engagement and knowledge retention. Finally, the effectiveness of the training should be regularly assessed through quizzes, feedback mechanisms, and observation of employee behavior.
Organizational Readiness Assessment Checklist
Before launching large-scale data responsibility initiatives, it’s crucial to assess the organization’s readiness. This involves evaluating various aspects of the company’s infrastructure and culture. The following checklist can help:
- Leadership Commitment: Is there clear, visible support from senior leadership for data responsibility initiatives?
- Data Governance Framework: Does the organization have a well-defined data governance framework with clear policies and procedures?
- Technology Infrastructure: Does the technology infrastructure support data security, privacy, and compliance requirements?
- Employee Awareness: Are employees aware of data responsibility policies and procedures?
- Training and Development: Are there adequate training programs in place to educate employees on responsible data handling?
- Monitoring and Enforcement: Are there mechanisms in place to monitor compliance and enforce data responsibility policies?
- Incident Response Plan: Does the organization have a plan in place to respond to data breaches or other incidents?
This checklist helps identify areas for improvement and prioritize initiatives to build a strong foundation for data responsibility.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Data Responsibility Programs
Measuring the effectiveness of data responsibility programs requires a multi-pronged approach. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be established to track progress and identify areas needing improvement. These KPIs could include:
- Number of data breaches or security incidents: A decrease in these incidents indicates improved data security practices.
- Employee compliance with data responsibility policies: This can be measured through audits, surveys, and monitoring of employee behavior.
- Customer satisfaction with data privacy practices: Positive feedback reflects increased trust and confidence in the organization’s handling of customer data.
- Number of data-related complaints or legal challenges: A reduction in these indicates improved compliance with regulations.
Regular monitoring of these KPIs allows for continuous improvement and ensures the data responsibility program remains effective and aligned with organizational goals. Regular audits and internal reviews should be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement. The results of these assessments should be used to refine the program and enhance its effectiveness over time.
Addressing Data Responsibility Challenges
Implementing data responsibility initiatives, while crucial for growth and trust, often encounters significant hurdles. These challenges stem from various sources, including organizational culture, technological limitations, and the ever-evolving regulatory landscape. Successfully navigating these obstacles requires proactive planning, strategic communication, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Common Obstacles in Implementing Data Responsibility Initiatives
Several common obstacles hinder the effective implementation of data responsibility initiatives. These include a lack of executive sponsorship and insufficient resource allocation, which can significantly impact progress. Furthermore, siloed data management practices and a lack of clear accountability often lead to inconsistencies and inefficiencies. Finally, the complexity of data privacy regulations and the evolving threat landscape necessitate ongoing adaptation and investment in robust security measures.
Overcoming these obstacles requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing leadership buy-in, improved data governance structures, and continuous investment in security and compliance.
Strategies for Overcoming Resistance to Change Within an Organization
Resistance to change is a common challenge when implementing new data responsibility initiatives. Effective strategies for overcoming this resistance include clear communication of the benefits of responsible data practices, emphasizing the positive impact on the organization’s reputation and bottom line. Providing comprehensive training and support to employees is crucial to ensure a smooth transition and foster buy-in. Engaging employees early in the process through participatory design and feedback mechanisms can help address concerns and build consensus.
Finally, celebrating successes and acknowledging the efforts of individuals and teams involved in the implementation can reinforce positive behavior and build momentum. A phased approach to implementation, starting with pilot projects and gradually scaling up, can also help mitigate resistance.
Solutions for Managing Data Breaches and Other Security Incidents
Data breaches and security incidents can have severe consequences, impacting an organization’s reputation, financial stability, and customer trust. A robust incident response plan is essential for mitigating the impact of such events. This plan should include clear procedures for identifying, containing, and remediating security incidents, as well as communication protocols for notifying affected individuals and regulatory bodies. Regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Investing in advanced security technologies, such as intrusion detection systems and data loss prevention tools, is also crucial. Finally, employee training on security best practices is vital to prevent human error, a major contributor to many security incidents. For example, a well-defined incident response plan might include a dedicated team with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, a communication protocol outlining how to inform stakeholders, and a process for forensic analysis to identify the root cause of the breach.
Best Practices for Navigating Complex Data Privacy Regulations
Navigating the complex landscape of data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. This includes conducting thorough data mapping exercises to understand what data is collected, how it is used, and where it is stored. Implementing appropriate data protection measures, such as data minimization and encryption, is crucial to ensure compliance. Regularly reviewing and updating data privacy policies and procedures is essential to keep pace with evolving regulations and best practices.
Finally, appointing a dedicated data protection officer (DPO) can help organizations navigate the complexities of data privacy and ensure compliance. For example, a company might implement a data minimization policy to collect only the necessary personal data for a specific purpose, thereby reducing the risk of a breach and minimizing the potential harm.
Future Trends in Data Responsibility
The landscape of data responsibility is constantly evolving, driven by rapid technological advancements, shifting societal expectations, and increasingly stringent regulations. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for organizations aiming to not only comply but also thrive in a data-driven world. This section explores key future directions in data responsibility, highlighting the challenges and opportunities ahead.
The intersection of data and technology is rapidly expanding, creating both exciting possibilities and significant ethical considerations. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain are fundamentally altering how data is collected, processed, and used, demanding a proactive and adaptive approach to data responsibility.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Data Responsibility, A data responsibility leveraging the power of trust to drive growth
The proliferation of AI, IoT, and blockchain presents unique challenges to data responsibility. AI systems, for example, can perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. IoT devices generate massive volumes of data, often without clear consent mechanisms or robust security measures. Blockchain technology, while promising increased transparency and security, also raises concerns about data immutability and the potential for misuse of sensitive information.
Responsible development and deployment of these technologies require careful consideration of ethical implications and robust governance frameworks. For instance, the development of explainable AI (XAI) aims to increase transparency and accountability in AI decision-making processes, directly addressing concerns about bias and fairness. Similarly, the implementation of privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) helps mitigate data privacy risks associated with the massive data collection by IoT devices.
Potential Future Challenges Related to Data Ethics and Governance
Several significant challenges are expected to emerge in the future. One major concern is the increasing complexity of data ecosystems, making it difficult to track data flows and ensure accountability. Another challenge lies in the growing volume and velocity of data, which strains existing data governance frameworks and necessitates the development of more agile and scalable solutions. Furthermore, the evolving legal landscape surrounding data privacy and security presents ongoing challenges for organizations, requiring continuous adaptation to new regulations and standards.
For example, the increasing complexity of cross-border data transfers necessitates the development of international standards and agreements to ensure consistent data protection across jurisdictions. The lack of harmonization across global data protection laws poses a significant challenge for multinational companies operating in multiple jurisdictions.
A Roadmap for Adapting to Evolving Data Responsibility Landscapes
Adapting to the evolving data responsibility landscape requires a multi-faceted approach. Organizations should prioritize continuous monitoring of emerging technologies and regulatory changes. Investing in robust data governance frameworks, including clear data policies, ethical guidelines, and data security protocols, is essential. Furthermore, fostering a culture of data responsibility through employee training and awareness programs is crucial. Building strong partnerships with data protection authorities and industry stakeholders can facilitate best practice sharing and collaborative problem-solving.
Regular audits and assessments of data practices are necessary to identify and address potential risks and vulnerabilities. Finally, proactive engagement with stakeholders, including customers and the wider community, is essential to building trust and ensuring responsible data use.
Predictions for the Future of Data Responsibility in Various Industries
The future of data responsibility will vary across industries, shaped by specific data usage patterns and regulatory environments. In healthcare, we can expect increasing focus on data security and patient privacy, driven by regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. The financial services sector will likely see enhanced scrutiny of algorithmic fairness and bias in lending and investment decisions. In the retail sector, personalized advertising will face increased scrutiny, necessitating more transparent data usage practices and robust consent mechanisms.
The rise of synthetic data and differential privacy techniques will likely play a significant role in mitigating data privacy risks across multiple industries. For example, the use of synthetic data for training AI models can reduce the reliance on real personal data, minimizing privacy risks while maintaining model accuracy.
Final Conclusion
Ultimately, building a data-driven business that thrives relies heavily on cultivating trust. By prioritizing ethical data handling, transparency, and robust security measures, organizations can unlock the true potential of their data while fostering lasting relationships with stakeholders. It’s not just about the numbers; it’s about building a reputation built on integrity and responsible stewardship of valuable information. Embrace data responsibility, and watch your growth flourish.
FAQ Explained
What are the biggest risks associated with poor data responsibility?
Reputational damage, legal penalties (fines, lawsuits), loss of customer trust, decreased revenue, and security breaches leading to data loss or theft are all major risks.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my data responsibility initiatives?
Track key metrics like the number of data breaches, customer satisfaction related to data privacy, employee training completion rates, and improvements in data accuracy and integrity. Regular audits and assessments are also crucial.
What’s the difference between data privacy and data security?
Data privacy focuses on how personal data is handled and protected, adhering to regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Data security focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
How can I create a culture of data responsibility within my organization?
Start with leadership buy-in, develop clear policies and procedures, provide comprehensive training, implement strong monitoring and accountability systems, and foster open communication about data risks and best practices.