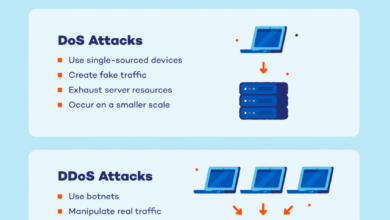
A Synopsis of Simjacker Mobile Security Vulnerability
A synopsis of Simjacker mobile security vulnerability: Ever felt your phone was being spied on? Simjacker isn’t science fiction; it’s a chillingly real threat that exploits vulnerabilities in your SIM card to remotely control your device. This isn’t just about reading your texts; we’re talking about complete access – location tracking, call interception, even microphone activation. Let’s dive into this terrifyingly sophisticated attack and uncover how it works, its impact, and what you can do to protect yourself.
Simjacker leverages weaknesses in the SS7 protocol, a system that underpins global mobile communication. By sending malicious commands through this network, attackers can bypass traditional security measures and directly target your SIM card. This allows them to execute commands on your phone without your knowledge or consent, potentially stealing sensitive data, tracking your movements, and compromising your privacy in significant ways.
The vulnerability affects various SIM card types, making a wide range of users potential victims.
Simjacker Overview
Simjacker, a sophisticated mobile security vulnerability, allowed attackers to remotely control mobile phones without user interaction, essentially turning them into surveillance devices. This wasn’t achieved through a simple app or malware download; it exploited a far deeper, more fundamental weakness in the mobile network infrastructure.Simjacker leverages vulnerabilities within the SS7 (Signaling System No. 7) protocol, the backbone of global telecommunications.
SS7, while crucial for connecting calls and text messages, contains inherent security flaws that Simjacker ruthlessly exploited. Instead of directly targeting the phone’s operating system or applications, Simjacker manipulated SS7 signaling to send malicious commands directly to the SIM card itself. This bypassed traditional security measures focused on the phone’s software.
Simjacker’s Mechanism
The core of Simjacker’s attack lies in its ability to send malicious commands to a victim’s SIM card using SS7. These commands, crafted specifically to exploit weaknesses in the SIM card’s firmware, could trigger a range of actions, from retrieving location data to intercepting calls and messages. Crucially, the victim remained completely unaware of the attack. The attacker didn’t need access to the phone itself or even the phone number; only access to the SS7 network was required.
This highlights the critical need for enhanced security measures within the SS7 protocol itself, as well as robust SIM card firmware.
Susceptible SIM Cards
A wide range of SIM cards were vulnerable to Simjacker attacks. The vulnerability wasn’t tied to a specific manufacturer or operating system. Instead, it exploited weaknesses in the SIM card’s firmware, which is the low-level software that controls the SIM card’s functionality. Older SIM cards, lacking robust security features, were particularly susceptible. Even modern SIM cards, depending on their firmware version and security implementations, could potentially be vulnerable.
The attack targeted the SIM card’s ability to process commands from the network, making almost any SIM card potentially vulnerable, depending on its security level and how it handled incoming SS7 messages.
Stages of a Simjacker Attack
A Simjacker attack typically unfolds in several stages. First, the attacker gains unauthorized access to the SS7 network. This access could be achieved through various means, potentially exploiting vulnerabilities within the network infrastructure itself. Second, the attacker identifies a target SIM card. Third, the attacker crafts and sends malicious commands to the target SIM card via the SS7 network.
These commands are designed to exploit vulnerabilities in the SIM card’s firmware. Fourth, the SIM card executes these malicious commands, unknowingly providing the attacker with access to the victim’s data and communication capabilities. Finally, the attacker collects the desired information or carries out the intended actions, such as location tracking or call interception, often without leaving any trace on the victim’s device.
Comparison of Simjacker to Other Mobile Vulnerabilities
The following table compares Simjacker to other common mobile security vulnerabilities:
| Vulnerability Type | Attack Vector | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simjacker | SS7 network exploitation | Location tracking, call interception, SMS interception, data theft | SS7 network security improvements, secure SIM card firmware |
| SMS Phishing | Malicious SMS messages | Credential theft, malware installation | User education, robust anti-phishing measures |
| Malware | Infected apps, websites, email attachments | Data theft, device control, financial fraud | Antivirus software, secure app stores, cautious online behavior |
| Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack | Compromised Wi-Fi networks, rogue base stations | Data interception, credential theft | Use of VPNs, secure Wi-Fi networks, strong passwords |
Impact and Consequences of Simjacker: A Synopsis Of Simjacker Mobile Security Vulnerability
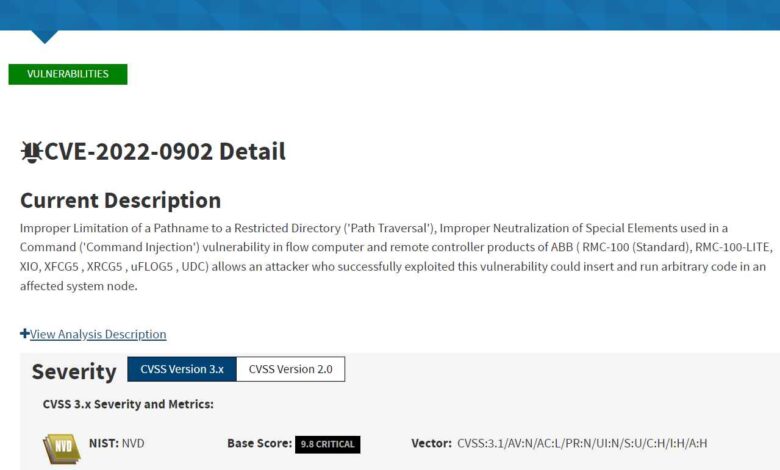
Simjacker, unlike many other vulnerabilities, doesn’t require user interaction or sophisticated phishing techniques. Its insidious nature lies in its ability to remotely exploit a weakness in the SS7 protocol, allowing attackers to silently infiltrate a victim’s mobile device and extract sensitive information or even control its functions. The consequences, therefore, are far-reaching and potentially devastating for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.The potential ramifications of a successful Simjacker attack are significant and varied, depending on the attacker’s goals and the victim’s profile.
The vulnerability’s ability to bypass traditional security measures makes it particularly dangerous. Understanding the diverse impacts is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Impact on Individuals
A successful Simjacker attack could allow an attacker to gain complete control over a victim’s mobile phone. This means accessing personal data like contact lists, messages, photos, location data, and even banking details. Furthermore, attackers could intercept calls and messages, impersonate the victim, or even remotely activate the phone’s microphone and camera for surveillance. The loss of privacy and the potential for financial fraud, identity theft, and emotional distress are considerable.
Simjacker, a terrifying mobile security vulnerability, allows attackers to remotely control your phone via SIM card commands. Building robust security measures requires innovative app development, and that’s where exploring the potential of domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , becomes crucial. Understanding this development approach could help us better defend against sophisticated threats like Simjacker in the future.
Ultimately, mitigating such vulnerabilities necessitates a multi-pronged approach, including improved app security.
Imagine your private conversations being listened to, your bank account emptied, or your identity stolen – all without your knowledge or consent. This level of intrusion is deeply unsettling and can have long-lasting consequences.
Impact on Businesses and Organizations
For businesses, the consequences of a Simjacker attack can be even more severe. Compromised employee phones could lead to the theft of confidential company data, intellectual property, and trade secrets. This could result in significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal repercussions. Furthermore, if a Simjacker attack targets a company’s critical infrastructure, the disruption could be catastrophic, potentially leading to operational downtime and significant financial losses.
For example, imagine a scenario where an attacker uses Simjacker to disable communication systems within a power plant or a hospital. The potential for widespread disruption and damage is clear.
Privacy Implications of Simjacker, A synopsis of simjacker mobile security vulnerability
Simjacker represents a significant threat to personal privacy. The ability to remotely access a victim’s location data, communications, and other personal information without their knowledge or consent is a blatant violation of privacy. The scale of data compromised is potentially vast, as attackers could access everything stored on the victim’s device and even monitor their activity in real-time.
The long-term implications of such pervasive surveillance are alarming, especially considering the potential for misuse of this data for blackmail, stalking, or other malicious purposes. This highlights the urgent need for robust security measures and greater awareness of the potential threats to personal privacy in the digital age.
Real-World Scenarios Demonstrating the Effects of Simjacker
While specific, publicly documented cases of large-scale Simjacker attacks are relatively rare due to the covert nature of the exploit, the potential for such attacks is undeniably real. We can draw parallels to similar vulnerabilities exploited in the past, such as the widespread use of SS7 flaws for tracking individuals’ locations or intercepting communications. The potential impact is the same: complete compromise of personal data, financial accounts, and communication channels.
Imagine a scenario where a journalist’s phone is compromised, leading to the interception of sensitive sources and the exposure of confidential information. Or consider a business executive whose financial transactions are monitored and manipulated, leading to significant financial loss. These illustrate the real-world potential for devastation.
Potential Damages Categorized by Severity
The potential damages from a Simjacker attack can be categorized as follows:
This list demonstrates the broad range of potential harm. The severity depends on the attacker’s goals and the victim’s profile.
| Severity | Damage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Unauthorized access to contact list | Exposure of personal contacts |
| Medium | Financial fraud through interception of banking details | Unauthorized transactions, account depletion |
| High | Complete compromise of a business’s communication systems | Operational downtime, significant financial losses, reputational damage |
Technical Aspects of Simjacker

Simjacker wasn’t just another vulnerability; it was a sophisticated attack leveraging weaknesses in the SS7 protocol, a foundational part of the global telecommunications infrastructure. Understanding its technical intricacies reveals the gravity of its potential impact and the ingenuity (and unfortunately, malicious intent) behind its creation. This section delves into the specific protocols exploited, the steps involved in an attack, the types of actions possible, and the necessary network infrastructure.
SS7 Signaling Protocols Exploited by Simjacker
Simjacker cleverly exploited several SS7 (Signaling System No. 7) messages, specifically focusing on those designed for legitimate mobile network operations. These include the “Send SMS” and “Read SMS” messages, but also more subtly, the “Mobile Equipment Identity” (IMEI) request and “Location Information” messages. By manipulating these messages, the attackers could surreptitiously interact with a victim’s SIM card without their knowledge or consent.
The attack hinges on the fact that SS7, while powerful, lacks robust authentication and authorization mechanisms in many implementations, allowing malicious actors to inject commands and receive sensitive data.
Technical Steps Involved in a Simjacker Attack
A Simjacker attack unfolds in several stages. First, the attacker identifies a target and obtains their IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity). Next, they use this IMSI to interact with the SS7 network, exploiting vulnerabilities to send malicious commands to the victim’s SIM card. These commands, typically crafted as seemingly legitimate SS7 messages, instruct the SIM card to execute specific actions.
Finally, the attacker receives the response from the SIM card, potentially containing sensitive information or confirming successful command execution. The entire process happens without the victim’s knowledge or interaction.
Types of Actions Executed Remotely via Simjacker
The range of actions remotely executable through Simjacker is disturbingly broad. This includes the ability to surreptitiously read SMS messages, potentially revealing sensitive information such as one-time passwords (OTPs) for banking or other services. Furthermore, Simjacker can remotely retrieve the victim’s location data, allowing for real-time tracking. Critically, the attacker can also execute commands that could potentially lead to the installation of malware or compromise the victim’s device, offering a potential springboard for more intrusive attacks.
Network Infrastructure Required for a Simjacker Attack
A successful Simjacker attack requires access to the SS7 network. This typically involves compromising or leveraging weaknesses within a telecommunications provider’s infrastructure or through partnerships with malicious actors who possess such access. The attacker needs to be able to send and receive SS7 messages to and from the victim’s mobile network operator. This isn’t easily achieved, highlighting the sophistication and specialized knowledge required for this type of attack.
It also emphasizes the systemic vulnerabilities within the global telecommunications network.
Diagram Illustrating the Flow of a Simjacker Attack
Imagine a diagram showing three main sections: The Attacker, the Mobile Network, and the Victim.The Attacker’s section shows a computer connected to a server. This server is connected to a gateway which has access to the SS7 network.The Mobile Network section displays various interconnected nodes representing elements of the mobile network infrastructure, including the Home Location Register (HLR), the Visitor Location Register (VLR), and the Mobile Switching Center (MSC).The Victim section depicts a smartphone with a SIM card.The attack flow is as follows: The attacker sends malicious SS7 messages (e.g., “Send SMS” or “Read SMS”) via their server and gateway to the SS7 network.
These messages are routed through the MSC and VLR to the victim’s SIM card. The SIM card executes the commands, sending the requested data (e.g., SMS content, location data) back through the network to the attacker’s server. The entire process is covert, occurring outside the awareness of the victim and their mobile operator. The diagram visually emphasizes the attacker’s ability to bypass typical security measures by directly interacting with the SIM card via the vulnerable SS7 network.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Simjacker, while a sophisticated attack, isn’t insurmountable. A multi-pronged approach involving individual vigilance, organizational security upgrades, and carrier-level improvements is crucial for effective mitigation. This section Artikels practical steps at each level to minimize vulnerability.Protecting yourself and your organization from Simjacker requires a layered security approach, encompassing both proactive measures and reactive responses. Understanding the attack vector – exploitation of SS7 vulnerabilities – is key to developing effective countermeasures.
Individual Mitigation Strategies
Individuals can significantly reduce their risk by being proactive about their mobile security. This includes staying informed about the latest threats, regularly updating software, and being cautious about suspicious messages or calls. While complete protection is impossible, these steps dramatically reduce the likelihood of a successful Simjacker attack.
Organizational Preventative Measures
For organizations, a comprehensive security strategy is essential. This goes beyond simply updating software; it involves implementing robust mobile device management (MDM) systems, enforcing strong password policies, and conducting regular security audits. Employee training on recognizing and reporting suspicious activity is also paramount. Consider implementing network segmentation to limit the impact of a potential breach.
Mobile Carrier Security Enhancements
Mobile carriers play a critical role in mitigating Simjacker. They need to invest in upgrading their SS7 infrastructure to incorporate modern security protocols and implement stricter authentication measures. This includes actively monitoring for suspicious SS7 activity and collaborating with security researchers to identify and address vulnerabilities promptly. Proactive patching and regular security assessments are also crucial.
The Role of Software Updates
Software updates are fundamental to mitigating Simjacker. These updates often include patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by the attack. Keeping your operating system, mobile apps, and network equipment up-to-date is crucial. Regular updates plug security holes, reducing the attack surface and making it harder for attackers to exploit weaknesses. Enable automatic updates whenever possible to ensure you’re always running the latest, most secure versions.
Best Practices for Securing Mobile Devices
The following best practices summarize the key actions to take for robust mobile security against Simjacker and similar threats:
- Keep your operating system and apps updated.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible.
- Be wary of suspicious links, messages, and calls.
- Install reputable anti-malware software.
- Regularly back up your data.
- Report suspicious activity to your mobile carrier and relevant authorities.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for enhanced privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Simjacker, a sophisticated attack leveraging SS7 vulnerabilities, raises significant legal and ethical concerns, impacting individuals, businesses, and national security. The potential for widespread abuse necessitates a thorough examination of the legal ramifications and ethical responsibilities surrounding its development, deployment, and mitigation.
Legal Ramifications of Malicious Simjacker Use
The legal consequences of using Simjacker for malicious purposes vary depending on jurisdiction and the specific actions undertaken. In many countries, unauthorized access to a person’s mobile phone, interception of communications, and theft of personal data are serious criminal offenses, potentially leading to hefty fines and imprisonment. For example, actions such as tracking a person’s location without their consent, intercepting their calls and messages, or stealing financial information using Simjacker would likely fall under existing laws prohibiting hacking, fraud, and invasion of privacy.
The severity of the punishment would depend on factors such as the scale of the attack, the nature of the data compromised, and the intent of the perpetrator. Civil lawsuits for damages could also be filed by victims.
Ethical Concerns Related to Simjacker Development and Deployment
The development and deployment of Simjacker raise serious ethical concerns. The technology’s potential for misuse to violate an individual’s privacy, security, and autonomy is undeniable. Even if developed for legitimate security research purposes, the potential for the technology to fall into the wrong hands is a significant ethical risk. Researchers have a responsibility to carefully consider the potential for misuse and to implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and deployment.
The lack of transparency around the technology’s capabilities and the potential for its use in mass surveillance operations further exacerbate these ethical concerns.
Responsibilities of Mobile Carriers Regarding Simjacker Vulnerabilities
Mobile carriers bear a significant responsibility in mitigating Simjacker vulnerabilities. They are custodians of vast amounts of sensitive user data and have a duty to protect their customers’ privacy and security. This includes proactively identifying and patching vulnerabilities in their networks, implementing robust security protocols to prevent Simjacker attacks, and providing timely notification to users about potential threats. Failure to do so could expose them to legal liability for damages incurred by users as a result of Simjacker attacks.
Furthermore, carriers have an ethical obligation to prioritize the security and privacy of their customers above all else.
Legal Frameworks Surrounding Simjacker in Different Countries
Legal frameworks addressing Simjacker-related activities vary considerably across countries. Some nations have robust laws protecting data privacy and prohibiting unauthorized access to communication networks, while others lack comprehensive legislation in this area. This disparity creates challenges in prosecuting perpetrators and ensuring consistent protection for victims across borders. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) provides a high level of protection for personal data, while other jurisdictions may have less stringent regulations.
This inconsistency necessitates a harmonized international approach to address the legal challenges posed by Simjacker.
International Cooperation in Addressing Simjacker Threats
International cooperation is crucial in effectively addressing Simjacker threats. The transnational nature of cybercrime necessitates collaboration between law enforcement agencies, intelligence services, and telecommunications companies across borders. Sharing information about attacks, vulnerabilities, and best practices is essential to developing effective mitigation strategies. International agreements and treaties can help establish a common legal framework and facilitate the extradition of perpetrators.
The lack of effective international cooperation could allow malicious actors to exploit jurisdictional differences and evade prosecution, undermining efforts to protect individuals and national security.
Conclusive Thoughts
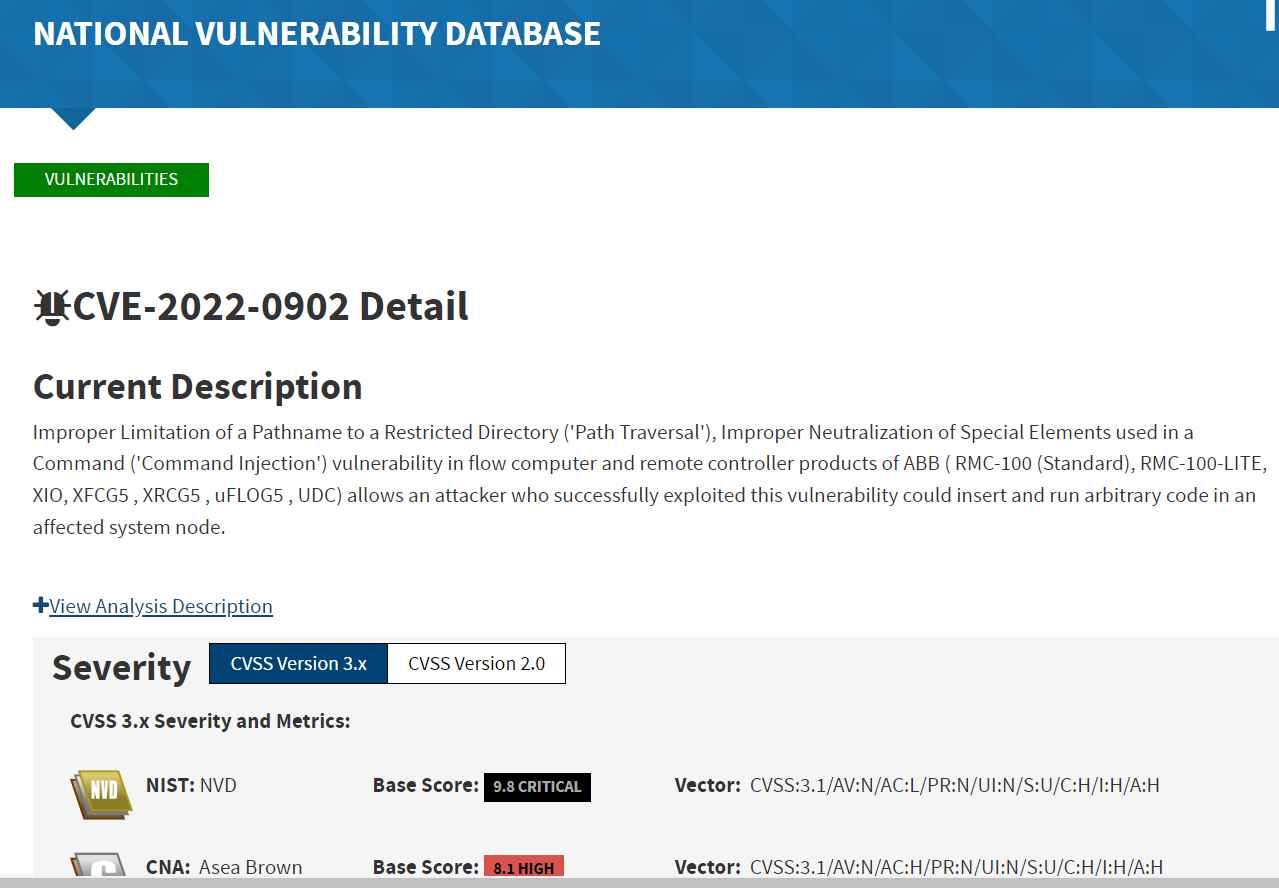
Simjacker serves as a stark reminder that our mobile devices, while incredibly convenient, are not impenetrable fortresses. Understanding the mechanics of this sophisticated attack is crucial for both individuals and organizations. While complete elimination of such threats is unlikely, implementing proactive security measures, staying updated on software patches, and advocating for stronger network security protocols are essential steps in mitigating the risk.
The fight against sophisticated attacks like Simjacker is an ongoing battle, but with awareness and vigilance, we can significantly reduce our vulnerability.
FAQ Explained
What types of data can Simjacker access?
Simjacker can access a wide range of data, including call logs, text messages, location data, and even activate the microphone or camera remotely.
Can I tell if my phone has been compromised by Simjacker?
Unfortunately, detecting Simjacker is difficult as it operates silently. Unusual battery drain, unexpected calls or texts, and a general feeling that your phone is behaving strangely could be indicators, but there’s no foolproof way to know for certain without specialized forensic analysis.
Are there any legal repercussions for using Simjacker?
Yes, absolutely. Using Simjacker for malicious purposes is illegal and carries severe penalties, including hefty fines and imprisonment, depending on the jurisdiction and the extent of the damage caused.
How often are SS7 vulnerabilities patched?
The frequency of SS7 vulnerability patching varies depending on the specific vulnerability and the involved telecom providers. However, ongoing efforts are being made by telecom companies and security researchers to identify and address these weaknesses.