
Agenda Ransomware VMware & 17k Exchange Servers Under Attack
Agenda ransomware targeting vmware and 17k microsoft exchange servers vulnerable to cyber attacks – Agenda ransomware targeting VMware and 17,000 vulnerable Microsoft Exchange servers is a serious threat. This sophisticated malware is exploiting known vulnerabilities in both systems, leading to data encryption and significant disruption for businesses worldwide. We’ll dive into the specifics of how this ransomware operates, the vulnerabilities it exploits, and crucially, how you can protect yourself and your organization from falling victim.
This post will cover the technical aspects of the Agenda ransomware attacks, including its encryption methods and attack vectors. We’ll also examine the specific vulnerabilities in VMware and Microsoft Exchange servers that are being targeted, providing a clear understanding of how these attacks unfold. Finally, we’ll explore mitigation strategies, incident response planning, and the legal and regulatory implications of such breaches.
This is essential reading for anyone concerned about the security of their VMware and Exchange environments.
Agenda Ransomware Overview: Agenda Ransomware Targeting Vmware And 17k Microsoft Exchange Servers Vulnerable To Cyber Attacks
Agenda ransomware, a relatively new player in the cybercrime landscape, has quickly gained notoriety due to its sophisticated techniques and the significant impact of its attacks. While information remains somewhat limited compared to more established ransomware families, its targeting of vulnerable VMware environments and Microsoft Exchange servers highlights its potential for widespread damage. This overview will detail the known capabilities, attack vectors, and encryption methods employed by Agenda, offering a glimpse into its operational profile.
Agenda Ransomware Capabilities and Techniques
Agenda ransomware demonstrates advanced capabilities beyond simple file encryption. Reports suggest it employs techniques like lateral movement within compromised networks, potentially leveraging already-present vulnerabilities to expand its reach and encrypt a greater volume of data. This suggests a degree of automation and the use of sophisticated tools for reconnaissance and exploitation. The ransomware also often disables backups and shadow copies, further hindering recovery efforts.
The operators likely utilize a combination of automated and manual processes to maximize the impact of their attacks.
Agenda Ransomware Attack Vectors
The primary attack vectors for Agenda ransomware appear to be vulnerabilities in VMware vCenter Server and older, unpatched Microsoft Exchange servers. These vulnerabilities allow initial access to the network, from where the ransomware can spread. Phishing emails, exploiting known software vulnerabilities, and exploiting misconfigurations are also likely vectors, though less specifically documented in the case of Agenda. The focus on exploiting known, publicly disclosed vulnerabilities points to an opportunistic approach, targeting systems where patching and security updates have been neglected.
Agenda Ransomware Encryption Methods
While the precise encryption algorithm used by Agenda ransomware isn’t publicly available, the effects of its encryption are clearly devastating. It’s highly likely that Agenda employs strong, asymmetric encryption methods, making decryption without the decryption key extremely difficult, if not impossible. The ransomware likely appends a unique extension to encrypted files, further identifying them as victims of the attack.
The use of robust encryption is a common characteristic of successful ransomware strains, maximizing the pressure on victims to pay the ransom.
Timeline of Significant Agenda Ransomware Attacks
Precise timelines for Agenda ransomware attacks are difficult to obtain due to the nature of these incidents. However, reports indicate a rise in activity coinciding with the public disclosure of vulnerabilities in VMware and Microsoft Exchange products. The lack of publicly available detailed timelines reflects the secretive nature of ransomware operations and the reluctance of victims to publicize their compromises.
This underscores the importance of proactive security measures and rapid response capabilities.
Comparison of Agenda Ransomware to Other Prominent Strains
| Ransomware Name | Target Systems | Encryption Method | Notable Attacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agenda | VMware vCenter Server, Microsoft Exchange Servers, Windows Servers | Likely AES or similar strong encryption | Specific attacks remain largely undisclosed due to the sensitive nature of the incidents. |
| Ryuk | Windows Servers, Enterprise Networks | AES | Attacks against hospitals, municipalities, and other critical infrastructure. |
| REvil (Sodinokibi) | Various systems, targeting businesses | AES | High-profile attacks against numerous businesses, including those in the manufacturing and legal sectors. |
| LockBit | Various systems, targeting a wide range of organizations | AES | Known for its double extortion tactics (encryption and data leak threats). |
VMware Vulnerability Exploitation
Agenda ransomware, like many other strains, leverages vulnerabilities within VMware environments to gain a foothold and encrypt valuable data. This often involves exploiting weaknesses in the VMware vCenter Server, ESXi hypervisors, or even misconfigurations within the virtual infrastructure itself. Understanding these vulnerabilities and implementing robust security measures is crucial for protecting against such attacks.The exploitation methods used by Agenda ransomware against VMware are likely to involve known vulnerabilities in VMware products.
These could include unpatched security flaws allowing for remote code execution (RCE) or privilege escalation, enabling attackers to move laterally within the virtual environment and ultimately access and encrypt virtual machines. The ransomware might also target vulnerabilities in VMware tools installed within the guest operating systems, providing another avenue for infiltration and data encryption.
VMware Products and Versions Most Susceptible
Several VMware products have historically been targeted by ransomware operators. Older, unsupported versions of ESXi are particularly vulnerable due to the lack of security patches. Similarly, outdated versions of vCenter Server, which manages the entire VMware environment, present significant risks. Exploits often focus on vulnerabilities that allow attackers to gain initial access and then move laterally to other virtual machines.
For example, a successful exploit on a single ESXi host could provide access to all VMs hosted on that server. Furthermore, vulnerabilities in vRealize Automation, vSAN, and other VMware components can also be exploited to compromise the overall infrastructure.
Security Measures to Mitigate VMware Vulnerabilities
Effective mitigation strategies involve a multi-layered approach. Regular patching of all VMware components, including ESXi hosts, vCenter Server, and other management tools, is paramount. This ensures that known vulnerabilities are addressed promptly, reducing the attack surface. Implementing strong access controls, including role-based access control (RBAC), limits the potential damage from compromised accounts. Regular security audits and vulnerability scans help identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Furthermore, network segmentation isolates critical virtual machines from less secure parts of the network, hindering lateral movement by attackers. Finally, deploying a robust intrusion detection and prevention system (IDS/IPS) can help detect and block malicious activity.
Best Practices for Securing VMware Environments
Beyond regular patching and access control, several best practices contribute to a robust security posture. These include using strong, unique passwords for all administrative accounts and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Regular backups of virtual machines are essential, enabling recovery in the event of a ransomware attack. These backups should be stored offline or in an air-gapped environment to prevent them from being encrypted.
Regular security awareness training for administrators and users helps to mitigate human error, a common factor in many successful ransomware attacks. Finally, employing a comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) system provides centralized logging and monitoring capabilities, enabling quicker detection and response to security incidents.
Hypothetical Attack Scenario
Imagine a scenario where an attacker exploits a known vulnerability (e.g., a publicly disclosed RCE vulnerability) in an outdated ESXi host within a company’s VMware environment. This grants them initial access to the host. From there, they could leverage this access to move laterally to other VMs on the same host or even other hosts within the same vCenter Server domain.
They could then deploy Agenda ransomware, encrypting the data on multiple virtual machines containing sensitive business data, such as financial records, customer databases, and intellectual property. The attacker might exfiltrate a copy of the encrypted data before demanding a ransom for the decryption key. The lack of robust security measures, such as regular patching, multi-factor authentication, and offline backups, would significantly exacerbate the impact of the attack.
Microsoft Exchange Server Vulnerabilities
Agenda ransomware leveraged known vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange servers to gain initial access and subsequently encrypt victim data. These vulnerabilities, often exploited before patches were applied, allowed attackers to bypass standard security measures and execute malicious code with elevated privileges. Understanding these weaknesses is crucial for preventing similar attacks.
The specific vulnerabilities exploited by Agenda ransomware often overlapped with those targeted by other ransomware groups and malicious actors. These vulnerabilities frequently involved flaws in the Exchange server’s authentication mechanisms, allowing attackers to bypass authentication entirely or leverage stolen credentials to gain unauthorized access. One common entry point involved exploiting vulnerabilities in the Exchange Control Panel (ECP) or Outlook Web App (OWA) interfaces.
These interfaces, if improperly secured, could be manipulated to execute arbitrary code, granting attackers a foothold within the server’s environment.
Attack Process: From Initial Compromise to Data Encryption
The attack process typically began with the exploitation of a known vulnerability, often through automated scanning and exploitation tools. Once a vulnerability was successfully exploited, the attacker gained initial access to the Exchange server. This initial access might involve obtaining a shell or gaining control of a specific account with sufficient privileges. The attacker would then proceed to move laterally within the network, potentially compromising other servers and workstations.
This lateral movement often involved using techniques like pass-the-hash or exploiting additional vulnerabilities on other systems. Finally, once the attacker had established control and identified valuable data, the Agenda ransomware payload would be deployed and executed, resulting in the encryption of sensitive files. The encryption process often involved strong encryption algorithms, rendering the data inaccessible without the attacker’s decryption key.
Comparison with Other Known Vulnerabilities
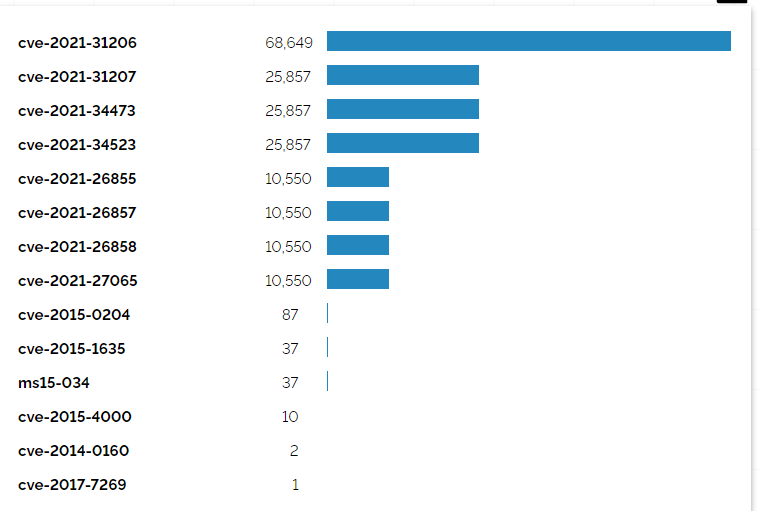
The vulnerabilities exploited by Agenda are similar to those exploited by other ransomware groups such as Conti and DarkSide. These often involve known and patched vulnerabilities that organizations failed to address in a timely manner. For example, the ProxyLogon vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-27065, CVE-2021-26857, CVE-2021-26858) were heavily exploited by various ransomware groups, including those that preceded Agenda. These vulnerabilities allowed attackers to authenticate to Exchange servers without valid credentials, bypassing critical security controls.
While the specific techniques and payloads might differ, the core principle of exploiting known vulnerabilities in unpatched systems remains consistent across various ransomware attacks. The similarities highlight the importance of maintaining up-to-date patching schedules and implementing robust security practices.
Security Patches and Updates
Regular patching is the most effective way to mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks targeting Exchange servers. The following patches and updates address many of the vulnerabilities commonly exploited:
The importance of timely patching cannot be overstated. Delayed patching significantly increases the risk of successful ransomware attacks and the subsequent data loss and financial repercussions.
- All cumulative updates released by Microsoft for Exchange Server.
- Security updates addressing ProxyLogon vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-27065, CVE-2021-26857, CVE-2021-26858).
- Updates addressing any vulnerabilities listed in Microsoft Security Advisories related to Exchange Server.
- Regular scans for known vulnerabilities using vulnerability scanners and penetration testing.
Impact and Mitigation Strategies

The Agenda ransomware attack, leveraging vulnerabilities in VMware and Microsoft Exchange servers, presents a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. The potential consequences extend far beyond simple data loss, impacting operations, finances, and reputation, potentially leading to long-term business instability. Understanding these impacts and implementing robust mitigation strategies is crucial for survival.The financial losses resulting from an Agenda ransomware attack can be substantial.
Direct costs include the ransom payment itself (if paid), costs associated with data recovery and system restoration, legal fees, and potential fines for regulatory non-compliance. Indirect costs are equally significant and include lost revenue due to business downtime, the cost of repairing damaged reputation, and the expense of hiring cybersecurity experts for incident response and remediation. Operational disruption can bring production to a standstill, impacting customer relationships and potentially leading to contract breaches.
Reputational damage can be equally devastating, eroding customer trust and making it difficult to attract new business. A successful attack can lead to a significant loss of competitive advantage and long-term financial instability.
Potential Impacts of an Agenda Ransomware Attack
An Agenda ransomware attack can significantly disrupt a business across multiple key areas. Financial losses can stem from ransom payments, data recovery expenses, lost revenue during downtime, and potential legal fees. Operational disruptions include halting production, impacting supply chains, and delaying projects. Reputational damage can lead to loss of customer trust, reduced market share, and difficulty attracting investors. Furthermore, the attack can result in legal and regulatory repercussions, including fines and penalties for data breaches.
For example, a mid-sized manufacturing company experiencing an Agenda attack might face millions of dollars in losses due to production downtime, lost orders, and the cost of restoring compromised systems. The reputational damage could lead to a significant decrease in customer loyalty and future sales.
Incident Response and Recovery Best Practices
Effective incident response is crucial in minimizing the impact of a ransomware attack. The first step is to contain the attack, isolating affected systems to prevent further spread. This involves disconnecting infected machines from the network and implementing network segmentation. Next, a thorough investigation is needed to determine the extent of the breach, identifying compromised data and systems.
Data recovery should be prioritized, utilizing backups if available. Following data recovery, system restoration is essential, ensuring all security vulnerabilities are addressed before restoring systems to their normal operational state. Finally, a post-incident review is necessary to identify weaknesses in security protocols and implement improvements to prevent future attacks. This process should be documented thoroughly, forming the basis for future incident response plans.
Creating a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan should be a living document, regularly reviewed and updated. It should clearly define roles and responsibilities for each team member during an incident. The plan should Artikel procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, recovering from, and learning from a security incident. It needs to include communication protocols for notifying stakeholders, including law enforcement if necessary. Regular training exercises are vital to ensure that the plan is understood and that team members are prepared to respond effectively.
The plan should also include a detailed inventory of critical systems and data, along with backup and recovery procedures. Finally, a post-incident review process should be built into the plan, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving threats. A well-defined plan significantly reduces response time and minimizes the impact of a ransomware attack.
The recent Agenda ransomware attacks targeting VMware and 17,000 vulnerable Microsoft Exchange servers highlight the urgent need for robust security solutions. Building secure and resilient applications is crucial, and that’s where exploring modern development approaches like those discussed in this insightful article on domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , becomes incredibly important. Ultimately, strengthening our application infrastructure is a key defense against threats like Agenda ransomware.
Preventative Measures for VMware and Microsoft Exchange Servers
A proactive approach to security is essential to prevent ransomware attacks. Implementing robust security measures for both VMware and Microsoft Exchange servers is paramount. The table below Artikels several key preventative measures:
| Security Measure | Description | Implementation Steps | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Patching | Applying the latest security patches to VMware and Exchange servers to address known vulnerabilities. | Establish a regular patching schedule; use automated patching tools where possible; thoroughly test patches in a staging environment before deploying to production. | High – significantly reduces the risk of exploitation of known vulnerabilities. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requiring multiple forms of authentication to access systems, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult. | Enable MFA for all administrative accounts and user accounts with access to sensitive data; utilize strong authentication methods like FIDO2 security keys. | High – significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. |
| Strong Passwords and Password Management | Implementing strong password policies and using a password manager to securely store and manage credentials. | Enforce complex password policies; regularly rotate passwords; utilize a password manager to generate and store strong, unique passwords for each account. | Medium – reduces the risk of brute-force attacks and credential stuffing. |
| Regular Backups | Creating regular backups of critical data and systems, allowing for quick recovery in case of a ransomware attack. | Implement a robust backup and recovery strategy; regularly test backups; store backups offline or in a secure cloud environment. | High – enables quick recovery and minimizes downtime in the event of a successful attack. |
| Network Segmentation | Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the impact of a breach. | Implement VLANs (Virtual LANs) to separate sensitive data and systems; use firewalls to control traffic flow between segments. | High – limits the spread of malware and reduces the impact of a successful attack. |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | Deploying IDS/IPS to monitor network traffic for malicious activity and block suspicious connections. | Deploy IDS/IPS solutions on critical network segments; configure alerts for suspicious activity; regularly review and update IDS/IPS rules. | Medium to High – provides early warning of potential attacks and can block malicious traffic. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Utilizing SIEM to collect, analyze, and correlate security logs from various sources to detect and respond to threats. | Implement a SIEM solution; configure alerts for suspicious activity; regularly review and analyze security logs. | High – provides centralized security monitoring and improves threat detection capabilities. |
Legal and Regulatory Implications

The aftermath of a ransomware attack like the one involving Agenda ransomware targeting VMware and Microsoft Exchange servers isn’t just about restoring systems; it’s also about navigating a complex legal and regulatory landscape. Organizations face significant legal and financial repercussions if they fail to comply with relevant regulations and demonstrate adequate security practices. This section Artikels the key legal and regulatory obligations organizations must meet following such an incident.Data breach notification laws vary considerably across jurisdictions, but they all share a common thread: timely disclosure to affected individuals and, in many cases, regulatory authorities.
The specific requirements regarding the timing and content of notifications are crucial and often dictated by the severity and scope of the breach. Failure to comply can result in substantial penalties.
Data Breach Notification Requirements
Organizations must adhere to specific notification timelines dictated by their location and the nature of the data compromised. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) have stringent notification requirements. The CCPA mandates notification within 45 days of discovering a breach, while GDPR often requires notification within 72 hours.
These notifications must clearly explain the nature of the breach, the types of data compromised, and the steps individuals can take to mitigate potential harm. Failure to provide adequate and timely notification can lead to significant fines and legal action. Consider the case of Equifax in 2017; their delayed notification of a massive data breach resulted in substantial fines and legal settlements.
Potential Fines and Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with data breach notification laws and broader cybersecurity regulations can result in severe financial penalties. Fines can range from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the severity of the breach, the number of affected individuals, and the jurisdiction involved. Beyond financial penalties, organizations may face reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and legal action from affected individuals.
For instance, GDPR violations can result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. The CCPA allows for private right of action, meaning individuals can sue companies for violations, adding another layer of potential financial liability.
Best Practices for Maintaining Compliance
Maintaining compliance requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. This includes implementing robust cybersecurity measures to prevent breaches, developing comprehensive incident response plans, conducting regular security assessments and penetration testing, and establishing a data breach notification process that aligns with all relevant regulations. Regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices and data protection is also crucial. Proactive monitoring of systems for suspicious activity can help detect and mitigate threats before they escalate into a full-blown ransomware attack.
Maintaining detailed records of security measures and incident response activities is vital for demonstrating compliance in the event of an investigation.
Legal Ramifications for Inadequate System Security, Agenda ransomware targeting vmware and 17k microsoft exchange servers vulnerable to cyber attacks
Organizations have a legal obligation to take reasonable steps to secure their systems and protect sensitive data. Failure to do so can expose them to legal liability, particularly in the event of a data breach. This liability can extend beyond data breach notification laws to include claims of negligence, breach of contract, and violation of other relevant regulations.
Courts may consider factors such as the organization’s size, industry, and the sophistication of the attack when determining liability. A lack of investment in adequate security measures, failure to patch known vulnerabilities, and inadequate employee training can all be used as evidence of negligence. The legal ramifications can include substantial financial penalties, reputational damage, and potential legal action from affected individuals and regulatory bodies.
End of Discussion
The Agenda ransomware attacks highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity practices. While the sophistication of this malware is concerning, understanding its methods and implementing appropriate preventative measures significantly reduces the risk of a successful attack. Staying up-to-date on security patches, regularly backing up data, and developing a comprehensive incident response plan are paramount. Remember, proactive security is far more effective and less costly than reactive recovery.
FAQ Section
What is the ransom typically demanded by Agenda ransomware?
The ransom amount varies depending on the size and sensitivity of the data encrypted. It’s often a significant sum, and paying the ransom doesn’t guarantee data recovery.
Are there any indicators of compromise (IOCs) associated with Agenda ransomware?
Yes, security researchers regularly publish IOCs, including specific file hashes, IP addresses, and domain names associated with Agenda ransomware. These can be used by security tools to detect and block malicious activity.
How long does it typically take to recover from an Agenda ransomware attack?
Recovery time depends on the extent of the damage, the availability of backups, and the resources dedicated to the recovery process. It can range from days to weeks or even months in severe cases.
What is the best way to report an Agenda ransomware attack?
Report the attack to law enforcement agencies (like the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center) and consider notifying relevant regulatory bodies, depending on your location and industry. Also, engage a cybersecurity incident response team for assistance.





