Airbus Bags Contract to Protect EU Institutions
Airbus bags contract to protect EU institutions against cyber threats – that headline alone grabbed my attention! It’s a huge deal, really. We’re talking about one of the world’s leading aerospace companies stepping up to safeguard the digital infrastructure of the entire European Union. Think about the implications – the sheer volume of sensitive data, the potential targets for malicious actors, the devastating consequences of a successful breach.
This contract isn’t just about lines of code; it’s about protecting the very heart of European governance.
This partnership between Airbus and the EU represents a significant investment in cybersecurity, signaling a growing recognition of the ever-evolving threat landscape. The contract covers a broad range of services, from threat detection and response to vulnerability management and incident handling. Airbus brings decades of experience in securing sensitive systems, and their involvement promises a significant upgrade to the EU’s overall cybersecurity posture.
We’ll delve into the specifics of the contract, Airbus’s capabilities, and the critical vulnerabilities it aims to address. Buckle up, it’s going to be an interesting ride!
Contract Overview
The Airbus contract for cybersecurity protection of EU institutions represents a significant investment in bolstering the digital defenses of the European Union. While the exact financial details are often kept confidential for competitive reasons, the contract’s scope and ambition are publicly acknowledged as substantial. This contract focuses on providing a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity services, aiming to proactively mitigate a wide range of threats facing EU institutions.The contract encompasses a broad spectrum of services designed to protect EU institutions from various cyberattacks.
This includes threat detection and response capabilities, vulnerability management, security awareness training for staff, and the implementation and maintenance of robust security infrastructure. Airbus likely leverages its expertise in advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance the effectiveness of these services. The contract also likely incorporates regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify weaknesses and proactively address potential vulnerabilities.
Scope of Services Provided
The services offered under the Airbus contract extend beyond basic cybersecurity measures. It likely involves continuous monitoring of EU networks and systems for suspicious activity, rapid incident response capabilities to contain and mitigate the impact of successful attacks, and comprehensive forensics analysis to determine the root cause of incidents and prevent future occurrences. Furthermore, the contract likely includes the development and implementation of custom security solutions tailored to the specific needs and vulnerabilities of different EU institutions.
This approach allows for a more nuanced and effective defense strategy compared to a one-size-fits-all approach.
Cyber Threats Addressed by the Contract
The contract aims to mitigate a wide array of cyber threats, including but not limited to: advanced persistent threats (APTs), ransomware attacks, phishing campaigns, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, data breaches, and insider threats. The sophistication of these threats requires a multi-layered defense strategy, which is likely a key element of the Airbus contract. For example, the contract might include measures to detect and prevent APT attacks, which are often characterized by their stealthy nature and long-term persistence within a target’s network.
Similarly, robust defenses against ransomware, a significant threat to data integrity and operational continuity, are crucial components of the contract.
So Airbus just landed a huge contract to beef up EU cybersecurity, which got me thinking about how vital robust systems are. Building those systems efficiently is key, and that’s where the speed and flexibility of domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes into play. Imagine the possibilities for rapid deployment of security patches and upgrades – critical for protecting EU institutions from evolving cyber threats like the ones Airbus is now combating.
Comparison to Previous Contracts, Airbus bags contract to protect eu institutions against cyber threats
Direct comparison to previous cybersecurity contracts awarded to other companies is challenging due to the confidential nature of such agreements. However, we can infer that the Airbus contract likely reflects a trend towards more comprehensive and proactive cybersecurity solutions. Previous contracts might have focused more on reactive measures, such as incident response, while the Airbus contract likely emphasizes proactive threat hunting and prevention.
The use of advanced technologies and AI-powered solutions in the Airbus contract also suggests a move towards more sophisticated and adaptive cybersecurity strategies compared to previous contracts which may have relied more heavily on traditional security methods. The scale of the contract itself likely reflects the increasing awareness of the importance of robust cybersecurity for EU institutions in the face of evolving and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Airbus’s Cybersecurity Capabilities
Airbus isn’t just known for its aircraft; it’s a significant player in the global cybersecurity landscape, boasting extensive experience protecting critical infrastructure and government entities. Their expertise extends beyond aviation, encompassing a wide range of sectors requiring robust and reliable security solutions. This contract with EU institutions leverages this established competence to fortify their digital defenses against sophisticated cyber threats.Airbus’s cybersecurity division offers a comprehensive suite of services, from threat intelligence and vulnerability management to incident response and security consulting.
Their approach is characterized by a deep understanding of the specific challenges faced by government organizations, including the need for high levels of security, compliance with stringent regulations, and the protection of sensitive data.
Airbus’s Government Cybersecurity Experience
Airbus has a proven track record of delivering successful cybersecurity projects for government institutions worldwide. For example, they’ve worked with national defense agencies on securing critical communication networks and protecting sensitive data from cyber espionage. Their projects often involve complex, multi-layered security architectures designed to withstand advanced persistent threats (APTs). Another example involves collaboration with a major European nation’s electoral commission to secure voting systems and prevent interference.
These successes demonstrate Airbus’s ability to adapt their solutions to diverse environments and regulatory landscapes.
Airbus’s Technologies and Methodologies
This contract will utilize a multi-faceted approach incorporating cutting-edge technologies and proven methodologies. Airbus will leverage its expertise in threat intelligence to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks. This includes advanced analytics to detect anomalies and predict potential attacks. Their security information and event management (SIEM) systems will provide real-time monitoring and incident response capabilities. Furthermore, Airbus will implement robust security protocols and access controls to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Their approach emphasizes a layered defense strategy, combining preventative measures with detection and response capabilities. This includes the use of advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) technologies to identify and neutralize malware.
Comparison of Airbus’s Capabilities with Other Major Cybersecurity Firms
The following table compares Airbus’s cybersecurity capabilities with those of other leading firms. Note that this comparison is a high-level overview and specific capabilities can vary significantly based on individual projects and client needs.
| Company | Key Technologies | Experience | Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airbus | SIEM, EDR, Threat Intelligence, Vulnerability Management, Incident Response, Cloud Security | Extensive experience securing government and critical infrastructure systems globally | ISO 27001, ISO 9001, various national security clearances (specifics vary by country and project) |
| Lockheed Martin | Cybersecurity consulting, threat intelligence, incident response, system hardening | Long history of working with government agencies on national security projects | ISO 27001, various government certifications and clearances |
| Northrop Grumman | Network security, data protection, cloud security, threat intelligence | Significant experience in government and defense sectors | ISO 27001, various government certifications and clearances |
| Palantir | Big data analytics, threat intelligence platforms, predictive policing | Experience working with government agencies on large-scale data analysis and threat detection | Various industry and government certifications (specifics may vary) |
EU Institutions’ Cybersecurity Needs
The European Union’s institutions are increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure, making them prime targets for sophisticated cyberattacks. Protecting these institutions is paramount to maintaining the integrity of EU policies, operations, and citizen trust. The scale and complexity of the threat landscape necessitate a robust and proactive cybersecurity strategy, addressing both immediate vulnerabilities and emerging threats.The consequences of successful cyberattacks against EU institutions can be severe, ranging from data breaches and financial losses to disruptions in essential services and damage to international relations.
Compromised systems could lead to the release of sensitive information, undermining public trust and potentially jeopardizing ongoing negotiations or policy decisions. The economic impact, including the cost of remediation, recovery, and reputational damage, could be substantial. Furthermore, successful attacks could embolden malicious actors, encouraging further attacks against the EU and its member states.
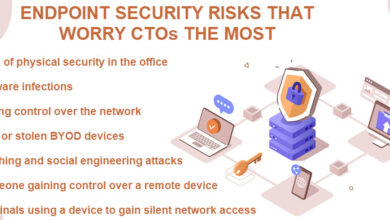
Critical Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities Faced by EU Institutions
EU institutions face a multitude of cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Outdated systems and a lack of standardized security protocols across different agencies represent significant weaknesses. Human error, such as phishing scams and weak password management, remains a common entry point for attackers. The increasing reliance on cloud services introduces new challenges, requiring robust security measures to protect data and applications in the cloud environment.
Furthermore, the interconnected nature of EU networks means that a breach in one system could potentially compromise others. The sheer volume of data handled by EU institutions also makes them an attractive target for data exfiltration.
Potential Consequences of Successful Cyberattacks
A successful cyberattack against an EU institution could have far-reaching consequences. Data breaches could expose sensitive information, such as personal data of citizens or confidential policy documents. This could lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage. Disruption of essential services, such as online voting systems or financial transactions, could severely impact citizens and the functioning of the EU.
Attacks could also cripple critical infrastructure, causing widespread disruption. Furthermore, successful attacks could undermine the EU’s credibility and its ability to effectively address global challenges. The economic costs associated with recovery, investigation, and remediation could be significant, diverting resources from other crucial areas.
Examples of Recent Cyberattacks Targeting Government Entities in Europe
Several recent cyberattacks highlight the real and present danger facing European government entities. For example, the 2020 SolarWinds attack, while not solely targeting EU institutions, affected numerous governments worldwide, demonstrating the potential for widespread damage from supply chain compromises. Numerous other attacks against various national governments in Europe have been reported, often involving ransomware or data exfiltration, underscoring the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures.
Specific details about these attacks are often kept confidential for national security reasons, but the frequency and sophistication of these incidents underscore the severity of the threat.
Significant Cyber Threats to EU Institutions
The following list Artikels some of the most significant cyber threats facing EU institutions:
- Ransomware attacks: These attacks encrypt data and demand a ransom for its release, potentially causing significant disruption and financial losses.
- Phishing and social engineering: These attacks exploit human error to gain access to systems and data.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): These sophisticated attacks involve long-term infiltration and data exfiltration, often by state-sponsored actors.
- Supply chain attacks: These attacks compromise software or hardware suppliers to gain access to multiple targets.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: These attacks overwhelm systems, making them unavailable to legitimate users.
- Data breaches: These attacks result in the unauthorized access and theft of sensitive data.
Contract Implementation and Management
This section details the phased rollout and ongoing management of the Airbus cybersecurity contract for EU institutions. The plan emphasizes a collaborative approach, ensuring seamless integration with existing EU security infrastructure and minimizing disruption to ongoing operations. Regular performance monitoring and robust incident response mechanisms are central to the contract’s success.
The contract’s implementation will proceed in a structured, phased manner, prioritizing the most critical systems and data first. This approach allows for iterative testing and refinement, minimizing risk and maximizing the effectiveness of the deployed security solutions. The phased implementation also facilitates ongoing feedback and adjustment, ensuring the solution remains adaptable to evolving threats.
Implementation Phases
The contract implementation is divided into three distinct phases: Phase 1 focuses on assessment and planning, Phase 2 on system deployment and integration, and Phase 3 on ongoing monitoring and optimization. Each phase has clearly defined deliverables and milestones to ensure accountability and timely progress.
Phase 1 involves a comprehensive security assessment of the EU institutions’ IT infrastructure, identifying vulnerabilities and prioritizing remediation efforts. This phase will also include the development of detailed implementation plans and the establishment of communication protocols. Phase 2 focuses on the deployment and integration of Airbus’s cybersecurity solutions, including the installation of necessary hardware and software, configuration, and testing.
Finally, Phase 3 involves ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and optimization of the deployed systems, as well as regular security updates and vulnerability patching. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving threats.
Contract Performance Monitoring and Management
Airbus will employ a multi-faceted approach to monitor and manage the contract’s performance. This includes regular progress reports, key performance indicator (KPI) tracking, and periodic audits. The KPIs will focus on metrics such as the number of security incidents detected and resolved, the time taken to resolve incidents, and the overall effectiveness of the implemented security measures.
Regular progress meetings will be held with EU representatives to review progress, address challenges, and ensure alignment with the contract objectives. These meetings will involve detailed discussions of the KPIs and any deviations from the agreed-upon timelines or performance targets. Independent audits will be conducted periodically to verify the effectiveness of the implemented security solutions and to identify areas for improvement.
These audits will be conducted by an independent third-party organization to ensure objectivity and impartiality. The results of these audits will be shared with both Airbus and the EU institutions.
Security Incident Reporting and Response
A comprehensive incident reporting and response plan is a critical component of the contract. Airbus will establish a dedicated 24/7 security operations center (SOC) to monitor the EU institutions’ networks and systems for any suspicious activity. Any detected security incidents will be immediately reported to the relevant EU authorities, along with a detailed analysis of the incident and recommended remediation steps.
The incident response plan Artikels clear procedures for escalation, communication, and remediation. It includes detailed steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. Regular simulations and drills will be conducted to test the effectiveness of the incident response plan and to ensure that all stakeholders are adequately prepared to respond to real-world security incidents. These simulations will incorporate various types of cyberattacks, such as phishing campaigns, malware infections, and denial-of-service attacks, to ensure a comprehensive and realistic test of the plan’s effectiveness.
The plan will be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving threats and best practices.
Contract Management Process Flowchart
The following describes a flowchart illustrating the contract’s management process. The process begins with the initiation phase, encompassing contract signing and initial planning. This is followed by the implementation phase, including system deployment and integration. Ongoing monitoring and performance evaluation form the core of the operational phase. Finally, the contract concludes with a final review and report.
The process is iterative, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation to changing needs and circumstances. The flowchart would visually represent these phases with clear transitions and feedback loops, highlighting key decision points and deliverables at each stage. For example, a box might represent “Security Incident Detected,” leading to a decision diamond (“Incident Contained?”), branching to remediation or escalation procedures.
Each phase would have associated documents and milestones clearly defined in the flowchart.
Impact and Future Implications

This Airbus contract marks a significant step forward for EU cybersecurity, promising to bolster the resilience of its institutions against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. The long-term effects will ripple through various sectors, influencing not only the immediate beneficiaries but also shaping the broader European cybersecurity landscape and the nature of public-private partnerships in this critical area.The enhanced cybersecurity posture resulting from this contract will likely manifest in several key ways.
Improved threat detection and response capabilities, coupled with more robust preventative measures, should reduce the frequency and severity of successful cyberattacks against EU institutions. This, in turn, will contribute to greater public trust and confidence in the digital security of vital governmental processes and data. The increased expertise and resources deployed will also enable a more proactive approach to cybersecurity, allowing for more effective mitigation of emerging threats.
Strengthened EU Cybersecurity Market
The Airbus contract represents a substantial injection of resources into the European cybersecurity market. It will stimulate demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions and services, fostering innovation and competition amongst European cybersecurity firms. This increased demand could lead to the creation of new jobs, the development of more sophisticated technologies, and a general strengthening of the European cybersecurity industry’s competitive position globally.
Similar large-scale contracts awarded to other European cybersecurity companies could create a positive feedback loop, further boosting the sector’s growth and capabilities. For example, the success of this Airbus contract could encourage other EU institutions and member states to invest more heavily in domestic cybersecurity providers, promoting a more self-reliant and secure digital infrastructure within the EU.
Evolution of Public-Private Cybersecurity Partnerships
This contract serves as a compelling case study for future public-private partnerships in cybersecurity. It showcases the potential benefits of collaborative efforts between government bodies and private sector expertise. Successful implementation will likely lead to increased confidence in the viability and effectiveness of such partnerships, encouraging further collaboration on complex cybersecurity challenges. The contract’s structure, including its terms and conditions, could serve as a template for future agreements, facilitating more efficient and effective partnerships.
Lessons learned from this contract’s implementation, both successes and challenges, will be invaluable in shaping future collaborative projects, leading to more streamlined processes and better outcomes. For instance, clear communication channels and well-defined responsibilities, established through this contract, can be replicated in future agreements, ensuring a more efficient allocation of resources and a clear understanding of roles and expectations.
Influence on Future Cybersecurity Standards and Regulations
The experience gained through the implementation of this contract will undoubtedly inform the development of future EU cybersecurity standards and regulations. The practical application of existing regulations and the identification of any gaps or shortcomings will provide valuable feedback for policymakers. This, in turn, could lead to improvements in existing legislation or the creation of new regulations better suited to the evolving cybersecurity landscape.
For example, the contract’s focus on specific threat vectors and vulnerabilities could influence the design of future cybersecurity standards, ensuring that these standards are more relevant and effective in addressing real-world threats. The data collected during the contract’s execution, regarding the types of attacks encountered and the effectiveness of different mitigation strategies, could also inform future policy decisions, leading to more targeted and effective cybersecurity regulations.
The contract could also contribute to the development of EU-wide cybersecurity certification schemes, enhancing trust and transparency in the cybersecurity market.
Illustrative Example
Let’s imagine a sophisticated, multi-pronged cyberattack targeting the European Commission’s servers. This isn’t a far-fetched scenario; similar attacks have been attempted against various governmental bodies worldwide. This hypothetical attack highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures, precisely the kind provided by the Airbus contract.The attack begins with a spear-phishing campaign targeting high-level Commission officials. These emails, seemingly from legitimate sources, contain malicious attachments or links.
Successful compromise of even a single account could provide the attackers with a foothold within the network. This initial breach could then be exploited to gain access to other systems through lateral movement techniques.
Attack Progression and Methods
The attackers, after gaining initial access, deploy a variety of malicious tools. They might use custom malware designed to bypass existing security software, potentially employing techniques like polymorphic code to evade detection. Simultaneously, a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is launched against the Commission’s public-facing websites, overwhelming their servers and disrupting access for citizens and staff. This diversionary tactic allows the attackers to operate more covertly within the internal network.
Data exfiltration, focusing on sensitive documents and personal information, is carried out using covert channels and encrypted communication protocols.
Mitigation and Response Using Airbus Services
The Airbus contract, with its comprehensive cybersecurity services, could have significantly mitigated the impact of this attack. Their advanced threat detection capabilities would likely have identified the initial spear-phishing attempts and blocked malicious emails before they reached their targets. Furthermore, their intrusion detection and prevention systems would have detected the lateral movement within the network and the deployment of malware, alerting security personnel to the ongoing attack.
Airbus’s incident response team could have swiftly contained the breach, limiting the damage and preventing further data exfiltration. Their expertise in DDoS mitigation would have neutralized the attack against the public-facing websites, maintaining service availability.
Potential Damage and Lessons Learned
The potential damage from this attack could have been catastrophic. The loss of sensitive data, including personal information and confidential policy documents, would have had serious consequences, leading to reputational damage, legal repercussions, and significant financial losses. Disruption of essential services could have hampered the Commission’s ability to function effectively.
The hypothetical scenario underscores the critical need for proactive and robust cybersecurity measures. Investing in advanced threat detection, prevention, and response capabilities is not merely an expense; it’s an essential investment in the security and stability of EU institutions. The Airbus contract, with its comprehensive suite of services, provides a crucial layer of protection against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Closure

The Airbus contract to bolster EU cybersecurity is more than just a business deal; it’s a statement. It reflects the urgent need for robust defenses against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. While the specifics of the contract’s implementation remain to be seen, its very existence offers a glimmer of hope in the face of ever-present digital threats. The collaboration between private industry and government is a crucial step towards a more secure digital future for Europe.
This is a story that will continue to unfold, and I, for one, will be watching closely.
Detailed FAQs: Airbus Bags Contract To Protect Eu Institutions Against Cyber Threats
What specific technologies will Airbus utilize?
While the exact technologies aren’t publicly detailed, we can expect a blend of advanced threat detection, incident response, vulnerability management, and potentially AI-powered security solutions.
How long is the contract for?
The contract’s duration hasn’t been officially released. It’s likely a multi-year agreement given the complexity of the undertaking.
What happens if a breach occurs despite the contract?
The contract will likely include detailed incident response plans, outlining responsibilities and procedures for addressing any security breaches. Liability and remediation strategies would also be defined.
How much did the contract cost?
The financial details of the contract are generally kept confidential for competitive and security reasons.