Android Malware Draining Money From Bank Accounts
Android malware draining money in bank accounts – Android malware draining money from bank accounts is a serious threat, silently stealing from unsuspecting users. It’s not just a tech problem; it’s a real-world financial crisis impacting lives. This post dives into the scary reality of these malicious apps, exploring how they work, how to spot them, and, most importantly, how to protect yourself.
We’ll uncover the sneaky tactics used by these digital thieves, from cleverly disguised apps to sophisticated methods of bypassing security measures. We’ll also explore the various types of malware, their evolution, and the devastating consequences for victims. Get ready to arm yourself with the knowledge you need to safeguard your finances in the digital age.
Types of Android Malware Affecting Bank Accounts
Android malware continues to evolve, posing a significant threat to users’ financial security. These malicious applications can silently infiltrate devices, stealing sensitive banking information and draining accounts. Understanding the various types of malware and their methods is crucial for effective protection.
Five Common Types of Android Malware Targeting Bank Accounts
Several types of malware specialize in targeting banking applications and stealing financial data. Understanding their mechanisms is key to prevention.
- Banking Trojans: These are designed specifically to steal banking credentials and financial information. They often disguise themselves as legitimate apps, tricking users into installing them. Once installed, they can intercept login details, transaction information, and even one-time passwords (OTPs) sent via SMS. Data exfiltration usually occurs through command-and-control (C&C) servers controlled by the attackers.
- Spyware: Spyware aims to secretly monitor user activity, including their banking transactions. It can record keystrokes, capture screenshots, and log website visits. This information can be used to steal login credentials and track financial activities. Exfiltration methods are similar to banking Trojans, often using C&C servers.
- Fake Antivirus/Security Apps: These malicious apps masquerade as legitimate security software. They often display fake alerts about viruses or security threats, prompting users to grant them extensive permissions. Once granted, they can access banking apps and steal sensitive information. Data exfiltration usually happens through covert communication channels.
- Remote Access Trojans (RATs): RATs provide attackers with remote control over an infected device. This allows them to access all aspects of the device, including banking apps, and perform actions such as stealing data, installing other malware, and even monitoring calls and messages. Data exfiltration is directly controlled by the attacker through the remote access.
- SMS Trojans: These malware variants specifically target SMS messages, intercepting OTPs used for two-factor authentication (2FA). This allows attackers to bypass security measures and access bank accounts even if they have only partially compromised the user’s credentials. Stolen OTPs are directly used for unauthorized transactions.
Comparison of Banking Trojans and Spyware, Android malware draining money in bank accounts
While both banking Trojans and spyware can lead to financial theft, their primary functionalities differ. Banking Trojans directly target banking applications and aim to steal specific financial data. Spyware, on the other hand, takes a broader approach, monitoring various user activities, including banking transactions, to gather sensitive information. While spyware might not directly target banking apps, the data it collects can be easily used to compromise banking accounts.
Both utilize similar data exfiltration methods, often involving C&C servers.
Evolution of Android Malware Targeting Financial Institutions (Past Five Years)
The methods employed by Android malware targeting financial institutions have significantly evolved over the past five years. This evolution reflects the ongoing arms race between malware developers and security researchers.
| Malware Type | Year Emerged | Primary Method | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fake Banking Apps | 2019 | Deceptive App Stores, Social Engineering | Sophisticated UI mimicking legitimate banks; use of overlays |
| Advanced Banking Trojans (ABTs) | 2020 | Drive-by-downloads, phishing | Ability to bypass multi-factor authentication; sophisticated anti-analysis techniques |
| SMS-based Trojans | 2021 | Intercepting OTPs via Accessibility Services | Targeting specific banks; rapid exfiltration of funds |
| RATs with Banking Capabilities | 2022 | Exploiting vulnerabilities in Android OS | Remote control of device; data exfiltration, keylogging, screen recording |
| AI-powered Malware | 2023 | Adaptive techniques to evade detection | Dynamic code generation, self-mutation, polymorphic behavior |
Infection Vectors and User Vulnerability
Android banking malware, like other forms of mobile malware, relies on various methods to infiltrate devices and exploit user vulnerabilities. Understanding these methods and common user behaviors is crucial for effective prevention. This section will delve into the most prevalent infection vectors and highlight the risky behaviors that make users susceptible to these attacks.
The success of Android banking malware hinges on its ability to bypass security measures and gain access to sensitive financial data. This is achieved through a combination of sophisticated techniques and the exploitation of human error. The lines between legitimate and malicious applications can be incredibly blurred, making it difficult for even tech-savvy individuals to identify threats.
Prevalent Methods of Malware Distribution
Android banking malware is distributed through a variety of channels, often cleverly disguised to appear legitimate. Recognizing these methods is a critical first step in protecting yourself.
- Deceptive App Stores and Websites: Malicious apps are often disguised as legitimate applications and hosted on unofficial app stores or compromised websites. These sites may mimic the appearance of official app stores, tricking users into downloading infected apps.
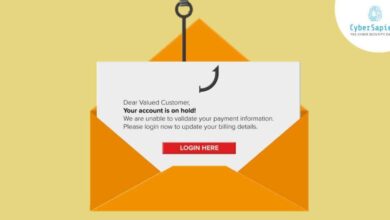
- SMS Phishing (Smishing): Users receive text messages containing links to malicious websites or attachments containing malware. These messages often create a sense of urgency or use social engineering tactics to manipulate users into clicking the link or opening the attachment.
- Drive-by Downloads: Visiting compromised websites can automatically download malware onto a device without the user’s explicit consent. This often happens when visiting sites with vulnerabilities or those containing malicious ads.
- Social Engineering: Attackers use social engineering techniques to trick users into installing malware. This might involve posing as a trusted source, such as a bank or tech support, to gain the user’s trust and convince them to install the malicious app.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Exploiting vulnerabilities in the Android operating system or other apps can allow attackers to install malware without user interaction. Regular updates are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Common User Behaviors Increasing Vulnerability
While sophisticated attack methods exist, many infections stem from simple user errors. Understanding these vulnerabilities can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
- Downloading Apps from Unofficial Sources: Downloading apps outside of the official Google Play Store significantly increases the risk of installing malware, as these apps often lack security checks.
- Ignoring Security Warnings: Dismissing security warnings or permissions requests from apps without carefully reviewing them can lead to malware installation. Always thoroughly examine what permissions an app is requesting.
- Clicking Suspicious Links: Clicking on links in unsolicited emails, text messages, or social media posts can lead to the download of malware or to phishing websites designed to steal credentials.
- Enabling Unknown Sources: Allowing installations from unknown sources (outside the official app store) weakens security and increases the chances of malware infection. This setting should only be enabled if absolutely necessary and with extreme caution.
- Failing to Update Software: Outdated software often contains vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Regularly updating the Android operating system and all apps is essential for security.
Hypothetical Scenario: Unknowing Malware Installation
Let’s imagine Sarah receives a text message appearing to be from her bank. The message states there’s a problem with her account and includes a link to “resolve” the issue. Intrigued and concerned, Sarah clicks the link.
- The Phishing Link: The link takes Sarah to a website that closely mimics her bank’s official website. It requests her login credentials, account number, and other sensitive information.
- Credential Theft: Unbeknownst to Sarah, this is a phishing website designed to steal her banking details. She enters her information, believing she’s interacting with her legitimate bank.
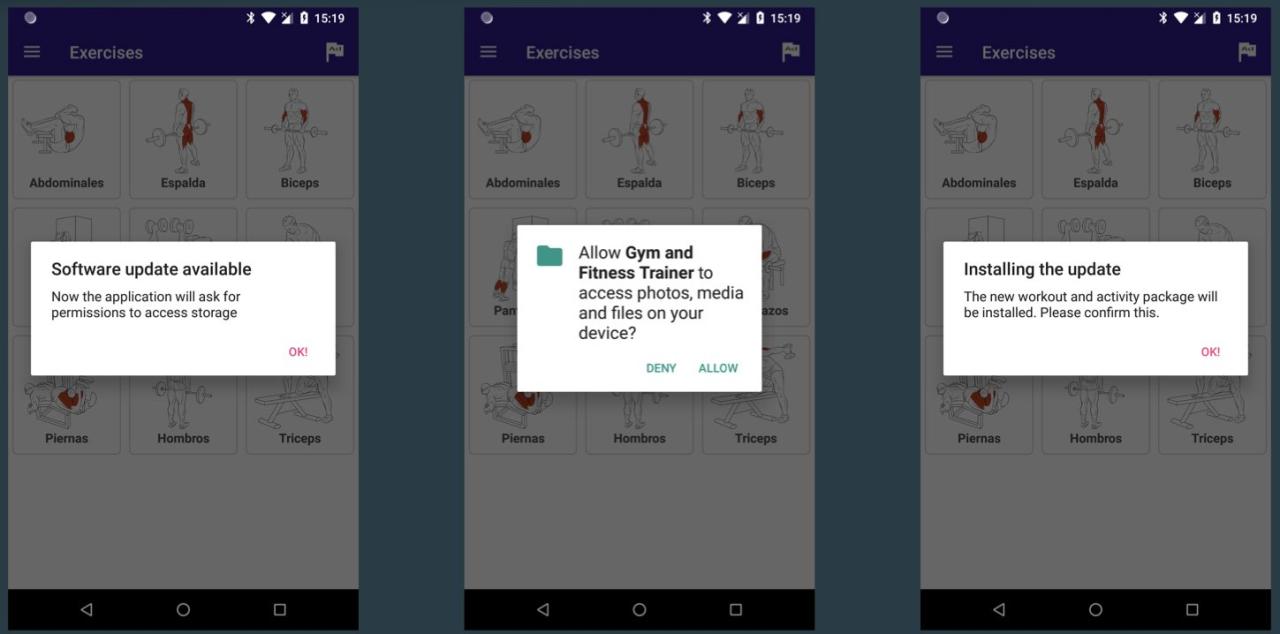
- Malware Download: While seemingly completing the “account verification,” the website secretly downloads a malicious app onto Sarah’s phone. This app is disguised as a security update or a necessary app for account access.
- Silent Installation: The malware installs itself in the background, often without any noticeable prompts or notifications.
- Data Theft: The malware begins to monitor Sarah’s banking activity, intercepting login credentials, transaction details, and other sensitive data, transferring this information to the attackers.
Malware Functionality and Data Theft Mechanisms
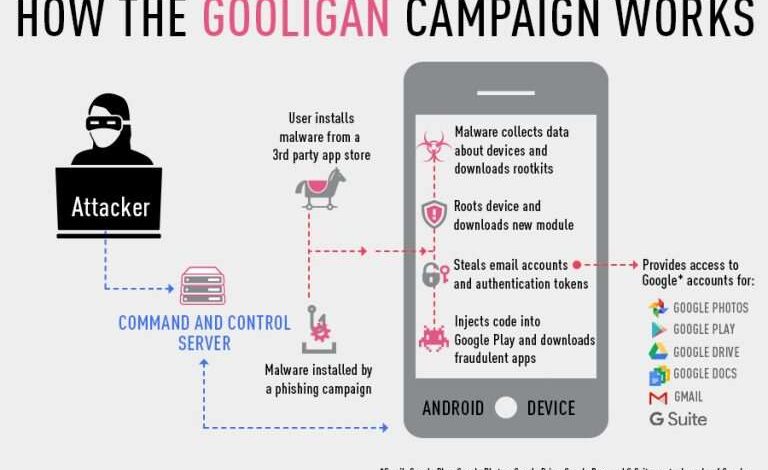
Android banking malware employs sophisticated techniques to steal financial information, often bypassing multiple layers of security. These malicious apps leverage various methods to gain access to sensitive data and transmit it to remote servers controlled by cybercriminals. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation.
The core functionality revolves around intercepting sensitive information and exfiltrating it without the user’s knowledge. This involves a combination of techniques to overcome device security measures and network protocols.
Credential Harvesting Techniques
Malware utilizes several methods to steal banking credentials. One common technique is overlay attacks, where a fake login screen is superimposed over the legitimate banking app. This deceptive overlay captures the user’s username and password as they log in, appearing authentic but sending the credentials to the attacker’s server instead. Another approach involves keylogging, where the malware records every keystroke the user makes, including passwords and sensitive information entered into banking apps.
Furthermore, some malware can directly inject code into banking apps to manipulate their behavior, allowing for the theft of credentials without requiring user interaction. For example, the malware could alter the app’s logic to automatically log in using stolen credentials or send the credentials directly to a command-and-control server.
SMS One-Time Password (OTP) Interception
Many banking apps utilize OTPs as an extra layer of security. Malware actively seeks to intercept these crucial codes. One method is to gain access to the device’s SMS messaging functionality. Once access is granted, the malware can read incoming messages containing OTPs and forward them to the attacker. Another technique is to utilize accessibility services, which provide access to a broad range of system functions, including the ability to read SMS messages.
Malicious apps can request these permissions under deceptive pretenses, making it difficult for users to identify the threat. For instance, an app disguised as a system optimization tool might request accessibility permissions, enabling it to intercept OTPs. The malware might then use a proxy server or other obfuscation techniques to hide its communication with the command-and-control server.
Data Exfiltration Process
The process of accessing and transmitting sensitive financial data involves several steps.
The following flowchart illustrates a typical data exfiltration process:
Flowchart: Data Exfiltration by Android Banking Malware
Step 1: Infection: The user downloads and installs the malicious app, often disguised as a legitimate application.
Step 2: Permission Acquisition: The malware requests and obtains necessary permissions (e.g., SMS access, accessibility services, storage access).
Step 3: Data Acquisition: The malware intercepts credentials, OTPs, and other sensitive data through keylogging, overlay attacks, or direct app manipulation.
Step 4: Data Encoding/Obfuscation: The stolen data is often encoded or obfuscated to avoid detection by security software.
Step 5: Data Transmission: The encoded data is transmitted to a remote command-and-control server using various methods, such as HTTP requests, encrypted connections, or data tunneling.
Step 6: Data Processing: The attacker receives the data, decrypts it, and uses it for fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized money transfers.
Seriously, the stories of Android malware silently stealing from bank accounts are terrifying. It highlights the urgent need for robust, secure mobile apps, which is why I’ve been diving into the world of app development lately, particularly exploring the exciting advancements discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future. Understanding these new development methods could help create safer, more secure apps and hopefully help prevent these kinds of financial heists.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies

Protecting your Android device from banking malware requires a multi-layered approach encompassing responsible app usage, proactive security measures, and regular updates. Ignoring these precautions can leave your financial information vulnerable to sophisticated attacks, resulting in significant financial losses and identity theft. Taking preventative steps is far more effective than dealing with the consequences of an infection.
By implementing the strategies Artikeld below, you significantly reduce the risk of your bank account being compromised by malicious software. Remember, vigilance and proactive security are your best defenses against these increasingly sophisticated threats.
Best Practices for Android Security
Several simple yet effective practices can dramatically reduce your risk of infection. These practices cover app acquisition, permission management, and system updates – all critical components of a robust security posture.
- Download apps only from official app stores: Stick to the Google Play Store. Third-party app stores often lack the security checks and vetting processes that Google employs, significantly increasing the risk of downloading malware-infected apps.
- Carefully review app permissions: Before installing any app, carefully review the permissions it requests. If an app requests access to your contacts, location, or financial information without a clear justification, it’s best to avoid installing it. Unnecessary permissions can be exploited by malicious actors.
- Keep your operating system and apps updated: Regularly update your Android operating system and all your apps. These updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities that malware could exploit.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your banking apps and other sensitive accounts. Even if your device is compromised, attackers will need access to your second authentication factor (like a code sent to your phone) to access your accounts.
- Be wary of phishing attempts: Never click on links or open attachments from unknown senders. Phishing attempts often try to trick you into revealing your banking credentials or downloading malware.
- Use strong and unique passwords: Choose strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts, especially your banking apps. Consider using a password manager to help you generate and manage strong passwords securely.
The Role of Security Software
Security software plays a crucial role in detecting and preventing Android banking malware. While proactive measures are essential, a robust security solution provides an additional layer of protection against sophisticated threats.
- Real-time malware scanning: Many security apps offer real-time scanning, constantly monitoring your device for malicious activity. This helps identify and neutralize threats before they can cause harm.
- App analysis and permission monitoring: These features analyze apps before installation, identifying potentially harmful permissions or behaviors. They can also alert you to suspicious app activity after installation.
- Anti-phishing protection: Security apps often include anti-phishing features that detect and block phishing websites and emails attempting to steal your credentials.
- Firewall: A firewall controls network traffic, blocking unauthorized connections that could be used to steal data or install malware.
- Regular updates: Just like your operating system and apps, your security software needs regular updates to remain effective against the latest threats. These updates add new threat signatures and improve detection capabilities.
Public Service Announcement: Protect Your Finances
This PSA aims to raise awareness about the dangers of Android banking malware. Clear and concise messaging, combined with compelling visuals, is key to effective communication.
Visual Description: The PSA would feature a split screen. One side shows a vibrant, healthy-looking plant symbolizing a secure and thriving financial life. The other side depicts the same plant wilting and dying, surrounded by menacing, dark digital tendrils representing malware. The wilting plant has a small, cracked smartphone at its base, visually connecting the malware to the device.
Text: “Don’t let malware drain your accounts! Protect your Android device with these simple steps: Download apps only from official stores, review app permissions carefully, and keep your software updated. Learn more at [website address – This would be added in the actual PSA, but not included here as requested].
Impact and Consequences

Android banking malware infections can have devastating financial and personal consequences for victims. The impact extends far beyond the immediate monetary loss, affecting credit scores, personal relationships, and overall sense of security. Understanding the full scope of these consequences is crucial for both individuals and law enforcement agencies.The financial losses incurred can range from relatively small amounts to life-altering sums depending on the malware, the victim’s financial situation, and the speed of detection and response.
For example, a victim might lose a few hundred dollars to a less sophisticated malware, while others could face the depletion of their entire life savings due to more advanced Trojans that gain persistent access to banking apps. Beyond direct financial losses, victims may also experience additional costs associated with restoring their accounts, repairing damaged credit, and seeking legal advice.
Financial Losses and Personal Impacts
Victims often experience significant financial hardship. The loss of funds can lead to difficulties paying bills, impacting credit scores negatively, and potentially causing serious stress and anxiety. Beyond the immediate financial impact, the emotional toll of being a victim of cybercrime is substantial. The violation of privacy and the feeling of helplessness can have long-lasting psychological effects.
In some cases, victims may even experience social isolation due to shame or embarrassment. Consider a scenario where a family loses their life savings intended for a child’s education – the financial loss is compounded by the emotional trauma and the shattered future plans.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Numerous legal and regulatory frameworks exist at national and international levels to address the growing problem of Android banking malware and financial crime. These frameworks vary in their scope and effectiveness but generally aim to criminalize the development, distribution, and use of such malware. Laws related to computer fraud and abuse, identity theft, and money laundering are often invoked in cases involving Android banking malware.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies like the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in the United States and similar agencies in other countries play a crucial role in monitoring suspicious financial activity and investigating financial crimes. International cooperation is also vital in tracking down perpetrators and recovering stolen funds, as many cybercrime operations span multiple jurisdictions.
Comparison of Malware Impacts
The impact of different types of Android banking malware on victims’ financial accounts varies considerably. Some malware might only steal small amounts of money, while others can cause significant damage. The type of data breached also differs, affecting the recovery process and the victim’s long-term vulnerability. The following table provides a simplified comparison, acknowledging that actual losses and recovery difficulties are highly variable and depend on numerous factors.
| Malware Type | Average Loss | Data Breached | Recovery Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fake Banking App | $500 – $2000 | Login credentials, account details | Moderate; requires account recovery procedures |
| Banking Trojan (e.g., Anubis) | $1000 – $10,000+ | Login credentials, transaction history, contact list, device information | High; potential for further fraudulent activities |
| Remote Access Trojan (RAT) | Variable, potentially unlimited | All data on the device, including banking information and personal files | Very High; requires extensive remediation and potential law enforcement involvement |
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, Android banking malware remains a significant concern. Understanding the methods employed by these malicious apps, coupled with proactive preventative measures, is crucial for protecting your financial well-being. Staying informed, practicing safe online habits, and utilizing robust security software are essential steps in mitigating the risks associated with this pervasive threat. Remember, vigilance is your best defense!
Essential Questionnaire: Android Malware Draining Money In Bank Accounts
What are the signs my phone is infected with banking malware?
Unusual app permissions requests, unexpected charges on your bank account, unexplained data usage, and slow performance are all red flags.
Can I recover my money if it’s stolen by banking malware?
Reporting the theft to your bank immediately is crucial. They may be able to reverse the transactions, but success isn’t guaranteed. You should also report the incident to law enforcement.
Is rooting my phone a risk factor for malware?
Yes, rooting your phone removes security measures, making it significantly more vulnerable to malware infections.
How often should I update my Android OS and apps?
Regularly! Updates often include security patches that protect against known vulnerabilities.