Beware of This Phishing Microsoft Teams Email
Beware of this phishing Microsoft Teams email! These sneaky scams are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it harder to spot the fakes. They often mimic legitimate messages, using familiar logos and subject lines to trick you into clicking malicious links or downloading harmful attachments. Understanding the tactics used in these attacks is crucial to protecting yourself and your data.
This post will equip you with the knowledge to identify and avoid these dangerous emails.
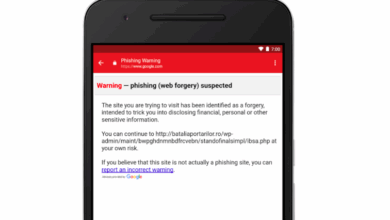
Phishing emails disguised as Microsoft Teams messages are a growing threat. They employ various techniques, from creating a sense of urgency with subject lines like “Urgent Meeting Request” to using slightly altered email addresses that look almost identical to legitimate ones. These emails often contain malicious links leading to websites designed to steal your login credentials or infect your computer with malware.
We’ll explore how to identify these red flags and what steps to take if you suspect you’ve received a phishing email.
Identifying Phishing Attempts in Microsoft Teams Emails: Beware Of This Phishing Microsoft Teams Email
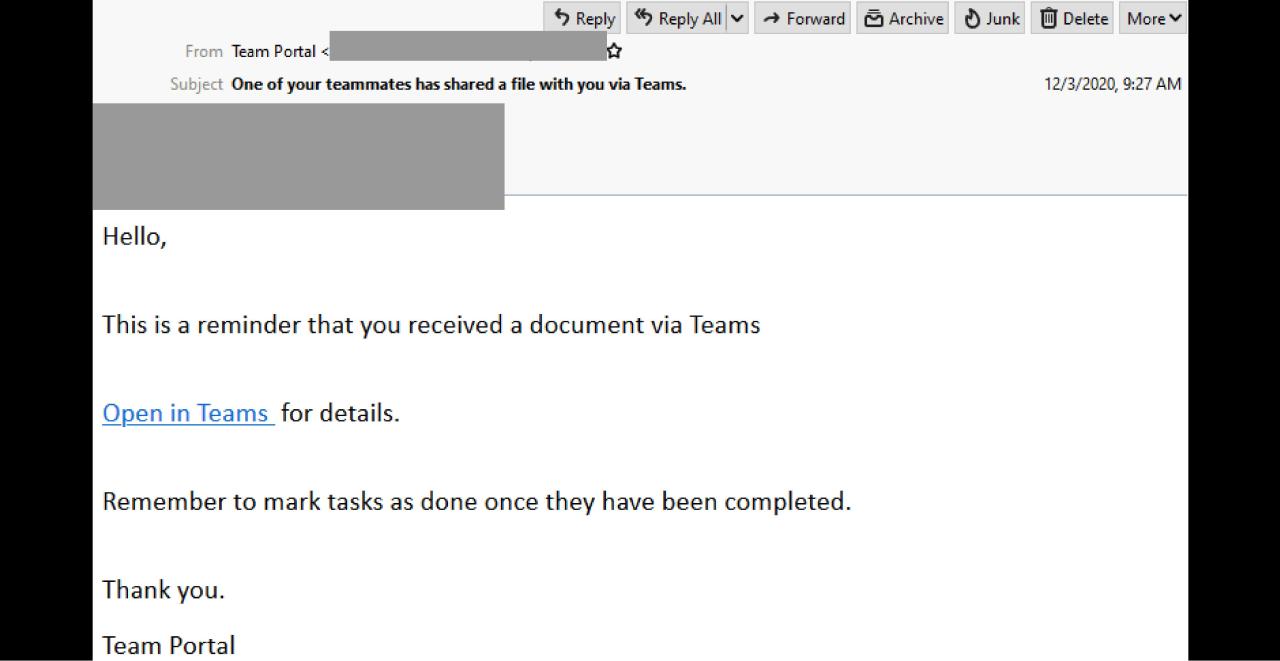
Phishing attacks targeting Microsoft Teams users are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Understanding the common tactics employed by phishers is crucial to protecting yourself and your organization from these threats. These attacks often leverage the familiarity and trust associated with the platform to trick users into divulging sensitive information or installing malware.
Phishing emails disguised as Microsoft Teams messages often share several key characteristics. Recognizing these patterns can significantly improve your ability to spot and avoid these scams.
Deceptive Subject Lines and Sender Addresses
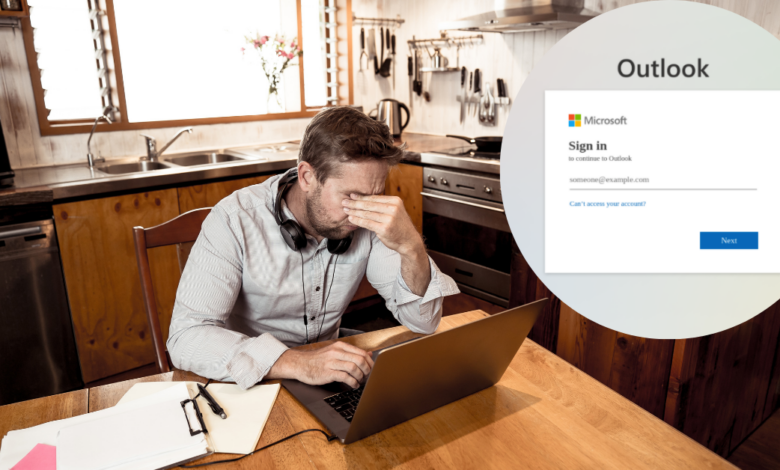
Phishing emails frequently employ subject lines designed to create a sense of urgency or importance, mimicking legitimate Microsoft Teams notifications. Examples include: “Urgent: Action Required – Microsoft Teams Account Update,” “You have a new Teams message from [familiar name/department],” or “Microsoft Teams Security Alert.” The sender address is often subtly altered to appear legitimate at first glance, possibly using a similar-looking domain name or even slightly misspellings the official Microsoft Teams domain.
For instance, instead of `teams.microsoft.com`, a phisher might use `teams-microsoft.com` or a domain that includes extra characters or numbers. They might also use a name that resembles a colleague or a trusted source.
Creating a Sense of Urgency or Fear
Phishing emails frequently exploit a sense of urgency or fear to pressure recipients into acting quickly without thinking critically. Common tactics include: threatening account suspension, warning of security breaches, claiming immediate action is needed to prevent data loss, or promising a significant reward. These messages often contain alarming language and time-sensitive deadlines to bypass rational thought processes. For example, a message might state, “Your account will be suspended in 24 hours unless you verify your information immediately,” or “Your Microsoft Teams account has been compromised; click here to secure it now!”
Verifying the Authenticity of a Microsoft Teams Email
Several methods exist to verify the authenticity of a suspected phishing email. First, carefully examine the sender’s email address. Look for subtle differences in spelling or domain names. Hovering over links before clicking them will reveal the actual URL destination, allowing you to verify it’s a legitimate Microsoft Teams address. Secondly, never click links or open attachments from unknown or suspicious senders.
If you’re unsure, contact the purported sender directly through a known and trusted communication channel (not the email itself) to confirm the message’s legitimacy. Finally, Microsoft provides several resources and tools to report phishing emails and learn more about identifying scams. Reporting suspected phishing emails helps protect others and assists Microsoft in combating these attacks.
Analyzing the Email Content for Red Flags
Spotting a phishing email disguised as a Microsoft Teams message requires a keen eye for detail. Don’t just glance at the subject line; carefully examine the entire email for inconsistencies and suspicious elements that betray its true nature. Even a seemingly minor detail could be a critical indicator of a malicious attempt.The email’s content is often the most revealing aspect.
Phishing emails frequently contain subtle clues that expose their fraudulent intentions. By learning to recognize these red flags, you can significantly improve your ability to identify and avoid becoming a victim.
Suspicious Links and Attachments
Malicious links and attachments are common hallmarks of phishing emails. These links often redirect you to fake login pages or download malware onto your computer. Hovering your mouse over a link (without clicking) will usually display the actual URL in a tooltip. If the URL looks suspicious or doesn’t match the expected Microsoft Teams domain (e.g., it contains unusual characters or doesn’t end in “.com” or “.net”), it’s a major red flag.
Similarly, avoid opening any attachments unless you are absolutely certain of their source and legitimacy. Unknown file types (.exe, .scr, etc.) should be treated with extreme caution. For example, an email claiming to be from your team leader but containing a “.zip” file with an unfamiliar name should raise immediate suspicion.
Grammatical Errors and Inconsistencies
Phishing emails are often written by individuals who are not native English speakers or who are simply trying to quickly create convincing messages. As a result, they often contain grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inconsistencies in writing style. These errors can be subtle, such as incorrect punctuation or awkward phrasing, but they can be a significant indicator of a fraudulent email.
For example, a legitimate Microsoft Teams email would likely be written in a professional and consistent tone, while a phishing email might contain sentences like, “Your account has been compromised. Click here to verify your password immediatly!” Note the spelling error in “immediately”.
Requests for Sensitive Information
Legitimate Microsoft Teams communications will rarely, if ever, ask for your password, credit card details, or other sensitive personal information via email. If an email requests such information, it’s almost certainly a phishing attempt. Microsoft will never ask for your password through email. They may ask you to change your password through the official website, but never directly via email.
Similarly, any request for credit card information within a Teams email should be treated with extreme suspicion. Remember, legitimate companies have secure systems for handling such sensitive data, and they will never ask for it through an insecure email.
Comparison of Legitimate and Phishing Emails
| Feature | Legitimate Email | Phishing Email | Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sender Address | Valid Microsoft Teams address (@teams.microsoft.com or similar) | Suspicious or generic address | Check the sender’s email address carefully. |
| Grammar and Spelling | Correct grammar and spelling | Grammatical errors and spelling mistakes | Look for inconsistencies in writing style. |
| Links and Attachments | Links point to official Microsoft Teams domains | Links redirect to suspicious websites or contain malicious attachments | Hover over links to check the URL; avoid opening unknown attachments. |
| Request for Information | No request for passwords, credit card details, or other sensitive information | Requests sensitive information | Legitimate companies rarely ask for such information via email. |
Understanding the Phishing Techniques Employed
Phishing attacks targeting Microsoft Teams users rely heavily on social engineering, manipulating users into believing the email is legitimate and prompting them to take action, such as clicking a malicious link or downloading a harmful attachment. These attacks leverage the familiarity and trust users have in the Microsoft Teams platform to their advantage. Understanding the tactics employed is crucial to effective defense.The success of these phishing campaigns hinges on the ability of the attackers to convincingly mimic legitimate Microsoft Teams communications.
They exploit psychological vulnerabilities, creating a sense of urgency, fear, or curiosity to encourage immediate action without critical thinking. This often bypasses the more cautious security measures individuals might otherwise employ.
Seriously, folks, watch out for those phishing emails pretending to be from Microsoft Teams – they’re getting sneakier! It’s a good reminder that robust security is crucial, and that’s why I’ve been diving into the world of application development lately, particularly exploring the exciting advancements discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future.
Learning about secure app development is vital in combating these threats, so stay vigilant and keep your security software updated to protect yourself from these Microsoft Teams scams.
Social Engineering Tactics in Microsoft Teams Phishing, Beware of this phishing microsoft teams email
Attackers use a variety of social engineering techniques. A common tactic is creating a sense of urgency, often using subject lines like “Urgent Meeting Request” or “Important Account Notification.” They might impersonate a known colleague, supervisor, or even a seemingly official Microsoft Teams account, crafting emails that appear to originate from within the organization’s communication network. This familiarity lowers the recipient’s guard, making them more susceptible to the deception.
Another strategy is to prey on curiosity, using vague or intriguing subject lines to entice the user to open the email and click the embedded link. The ultimate goal is always to bypass critical thinking and elicit a quick, impulsive response.
Types of Microsoft Teams Phishing Attacks
Several types of phishing attacks target Microsoft Teams users. One common approach involves sending emails that appear to be notifications about account issues, requiring the user to update their password or verify their account details through a malicious link. Another involves mimicking legitimate meeting invitations, leading users to a compromised website or downloading malware disguised as a meeting application.
A third type leverages the file-sharing capabilities of Teams, sending emails containing malicious attachments that, once opened, infect the user’s system. These attacks vary in their approach, but they all share the common goal of gaining unauthorized access to sensitive information or compromising the user’s device.
Common Lures in Microsoft Teams Phishing Emails
Understanding the common lures used in these phishing emails is essential for identifying and avoiding them. Here are some examples:
- Urgent meeting requests with unusual time constraints or unexpected attendees.
- Important account notifications requiring immediate action to prevent account suspension or loss of access.
- Suspicious login attempts or password reset requests originating from unknown locations.
- Notifications about shared files or documents that don’t align with expected activity.
- Requests to download or update software or applications that appear to be from Microsoft or Teams.
- Emails containing attachments with unexpected file types or unusual names.
- Messages promising significant financial rewards or other incentives in exchange for personal information.
Illustrating the Dangers of Phishing Emails
Phishing emails, disguised as legitimate communications, pose a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. The seemingly innocuous click of a link or the opening of an attachment can unleash a cascade of damaging consequences, ranging from minor inconvenience to catastrophic data breaches and financial losses. Understanding these potential dangers is crucial for effective protection.The consequences of interacting with malicious content in phishing emails are far-reaching and severe.
Clicking a malicious link can redirect you to a fake website designed to steal your login credentials, credit card information, or other sensitive data. Opening an infected attachment can install malware on your computer, allowing attackers to remotely access your system, steal your data, or even use your computer to launch attacks against others. This malware can range from simple keyloggers that record your keystrokes to sophisticated ransomware that encrypts your files and demands a ransom for their release.
Potential Damage to Personal and Organizational Data
The damage caused by successful phishing attacks can be devastating. For individuals, this can include identity theft, financial loss through fraudulent transactions, and the compromise of personal information like addresses, social security numbers, and medical records. The emotional distress and time spent rectifying the damage can also be significant. Organizations face even greater risks, including data breaches that expose customer information, intellectual property theft, reputational damage, and hefty fines for non-compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR.
A single successful phishing attack can cost an organization millions of dollars in recovery costs, lost productivity, and legal fees. For example, the 2017 Equifax data breach, attributed in part to a phishing attack, resulted in the exposure of personal information for over 147 million people and cost the company billions of dollars in fines and settlements.
Steps to Take if You Suspect a Phishing Email
If you suspect you’ve received a phishing email, it’s crucial to act swiftly and cautiously. First, do not click any links or open any attachments. Instead, carefully examine the email for red flags, such as poor grammar, inconsistencies in sender information, urgent or threatening language, and unusual requests for personal information. Then, delete the email immediately. It’s also advisable to run a malware scan on your computer to ensure no malicious software has been installed.
Finally, change your passwords for any accounts mentioned in the email, or any accounts you suspect might be compromised.
Reporting a Suspected Phishing Email
Reporting suspected phishing emails is a crucial step in protecting yourself and others. Most organizations have dedicated security teams or email reporting mechanisms. Forward the email to your organization’s security team or IT department, clearly indicating your suspicion. If you received the email outside of your work context, you can report it to the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) or your internet service provider.
These organizations collect and analyze phishing reports to identify and disrupt phishing campaigns. Providing details like the email sender, subject line, and any links or attachments included will aid in the investigation and help prevent others from falling victim to the same attack.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
Protecting yourself from phishing attacks requires a multi-layered approach encompassing individual awareness, robust security settings, and proactive organizational measures. This isn’t just about clicking the right buttons; it’s about cultivating a security-conscious mindset and implementing practical strategies to minimize risk. By combining these elements, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to sophisticated phishing schemes.
Effective phishing prevention involves a blend of technical safeguards and user education. While technology can block many attempts, human error remains a significant weakness. Therefore, empowering users with the knowledge and skills to identify and avoid phishing attempts is crucial for a truly effective defense. This includes understanding how phishing works, recognizing common red flags, and knowing the appropriate response when faced with a suspicious email.
Best Practices for Identifying and Avoiding Phishing Emails
Several key practices can significantly improve your ability to spot and avoid phishing emails. These practices should be regularly reviewed and reinforced to maintain a high level of vigilance.
- Verify the sender’s email address: Carefully examine the sender’s email address for inconsistencies. Phishing emails often use addresses that closely mimic legitimate ones but contain subtle differences (e.g., an extra character or a slightly altered domain name).
- Hover over links before clicking: Before clicking any link, hover your mouse over it to see the actual URL displayed in the status bar. This allows you to verify that the link leads to the expected website and not a malicious one.
- Check for grammatical errors and poor formatting: Legitimate organizations typically use professional language and formatting. Phishing emails often contain grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and unprofessional formatting.
- Be wary of urgent requests: Phishing emails often create a sense of urgency, pressuring you to act quickly without thinking. Legitimate requests rarely demand immediate action.
- Never open attachments from unknown senders: Attachments can contain malware that can infect your computer. Only open attachments from senders you trust and expect.
- Report suspicious emails: If you receive a suspicious email, report it to your IT department or the appropriate authorities. Many email providers have reporting mechanisms built-in.
Configuring Microsoft Teams Settings to Enhance Security
Microsoft Teams offers several security settings that can be configured to enhance protection against phishing attempts. Proper configuration of these settings is vital in mitigating risk.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code from your phone, in addition to your password. This makes it significantly harder for phishers to access your account even if they obtain your password.
- Review and manage connected apps: Regularly review the apps connected to your Microsoft Teams account and remove any that you don’t recognize or no longer use. Malicious apps can be used to gain unauthorized access to your account.
- Enable email verification: Configure Teams to require email verification for all new users and guest accounts. This helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of compromised accounts.
- Utilize Teams’ built-in reporting mechanisms: Report any suspicious messages or activities within Teams using the platform’s reporting tools. This helps Microsoft identify and address potential threats.
Educating Users About Phishing Awareness
A comprehensive user education program is essential for building a strong defense against phishing attacks. This program should be ongoing and cover various aspects of phishing awareness.
- Conduct regular training sessions: Organize regular training sessions using interactive methods like quizzes, simulations, and real-world examples to reinforce learning.
- Develop and distribute awareness materials: Create easily digestible materials, such as infographics, videos, and short guides, to explain phishing techniques and best practices. Make these materials readily accessible to all users.
- Implement phishing simulations: Conduct periodic simulated phishing attacks to assess user awareness and identify vulnerabilities. This provides valuable feedback and allows for targeted training.
- Establish clear reporting procedures: Clearly define the process for reporting suspicious emails and ensure that users feel comfortable reporting such incidents without fear of retribution.
- Promote open communication: Encourage users to ask questions and seek clarification if they are unsure about the authenticity of an email or message.
The Importance of Regular Security Training and Awareness Programs
Ongoing security training and awareness programs are not a one-time event; they are a continuous process crucial for maintaining a strong security posture. Regular reinforcement of key concepts is vital to combat evolving phishing techniques.
For example, a company that only provides initial phishing awareness training might find its employees increasingly vulnerable as new phishing tactics emerge. Regular refresher courses, incorporating updated information on current threats and best practices, are necessary to maintain a high level of security awareness. This continuous learning approach helps employees stay ahead of the curve and adapt to the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.
Companies should consider integrating security awareness training into their ongoing professional development programs to ensure that employees receive consistent and updated information.
Closing Notes
In short, staying vigilant against phishing emails, particularly those masquerading as Microsoft Teams messages, is paramount. By understanding the common tactics used, learning to spot the red flags, and following best practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to these scams. Remember, it’s always better to be cautious and verify the authenticity of any suspicious email before clicking any links or opening attachments.
Your digital security depends on it!
Commonly Asked Questions
What should I do if I think I’ve already clicked a malicious link?
Immediately change your Microsoft Teams password and any other passwords that might be compromised. Run a malware scan on your computer and contact your IT department or security team to report the incident.
How can I report a suspected phishing email?
Most organizations have a dedicated email address or system for reporting phishing attempts. Check your company’s internal resources. You can also report it to the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG).
Are there any browser extensions that can help detect phishing emails?
Yes, several browser extensions are designed to identify phishing websites and warn you before you click a potentially harmful link. Research reputable options and read reviews before installing any.
What if the phishing email looks almost identical to a legitimate Microsoft Teams email?
Even if it looks very similar, always hover over links to check the actual URL before clicking. Look for grammatical errors or inconsistencies in the email’s text. Contact the sender directly through a known legitimate channel (not the email itself) to confirm the message’s authenticity.