5 Best Practices for Creating an Effective CSIRT
5 best practices for creating an effective computer security incident response team csirt – 5 Best Practices for Creating an Effective Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) – that’s a mouthful, right? But it’s crucial. In today’s digital landscape, a well-oiled CSIRT isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s a necessity. Think of it as your company’s digital SWAT team, ready to spring into action when cyber threats strike. This post dives into five key strategies to build a CSIRT that’s not only effective but also prepared for anything the digital world throws its way.
We’ll cover everything from defining roles and responsibilities to implementing cutting-edge tools and fostering continuous improvement. Get ready to beef up your organization’s cybersecurity defenses!
Building a robust CSIRT involves more than just throwing a bunch of tech-savvy people together. It requires careful planning, clear communication, and a commitment to ongoing learning. We’ll explore how to define roles and responsibilities, establish clear incident response procedures, implement effective communication strategies, utilize advanced security tools, and foster a culture of continuous improvement and training. By the end of this post, you’ll have a solid foundation for creating a CSIRT that can effectively protect your organization from cyber threats.
Establishing Incident Response Procedures: 5 Best Practices For Creating An Effective Computer Security Incident Response Team Csirt
A well-defined incident response plan is the backbone of any effective CSIRT. Without clear, documented procedures, your team will struggle to react efficiently and consistently to security breaches. This section Artikels the crucial steps involved in creating and maintaining such a plan, emphasizing practical application and regular testing.
A robust incident response plan follows a structured lifecycle, enabling a systematic approach to handling security incidents. This lifecycle guides the team through each phase, ensuring no critical steps are missed and minimizing the impact of the incident.
The Incident Response Lifecycle
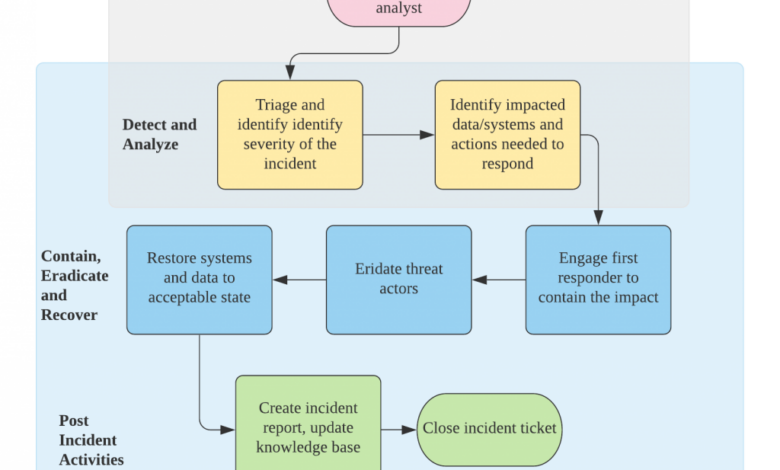
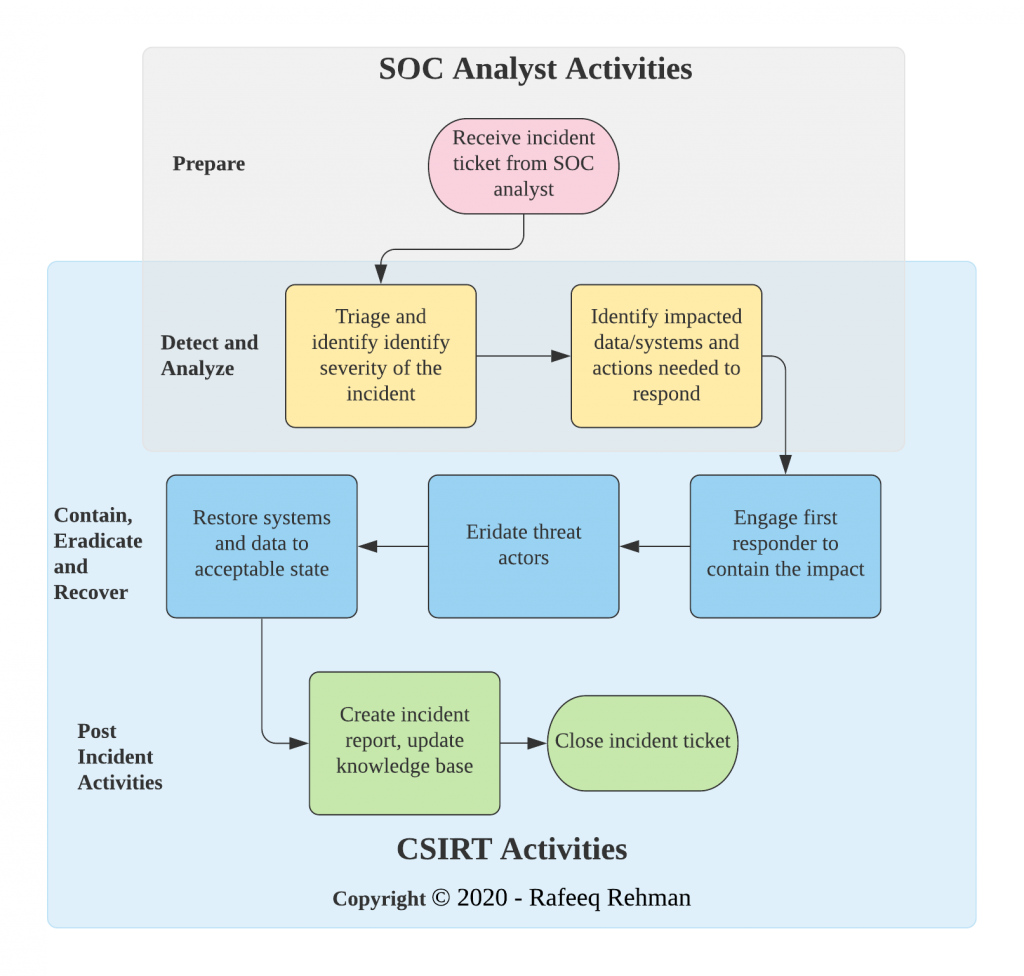
The incident response lifecycle typically involves six key phases: Preparation, Identification, Containment, Eradication, Recovery, and Lessons Learned. Each phase is critical, and a well-defined process for each is essential for effective incident response.
A clear understanding of each phase’s responsibilities and procedures is vital. This involves not only defining the steps but also assigning roles and responsibilities to specific team members.
- Preparation: This phase involves proactive measures takenbefore* an incident occurs. It includes developing the incident response plan itself, establishing communication protocols, defining roles and responsibilities, and creating a list of essential contact information (internal and external). It also involves establishing a secure communication channel for use during an incident.
- Checklist: Develop the incident response plan, define roles and responsibilities, establish communication protocols, identify key stakeholders, create a list of essential contact information, secure a dedicated communication channel, conduct regular training and awareness sessions, establish data backup and recovery procedures.
- Identification: This is the phase where the security incident is detected. This might involve alerts from security information and event management (SIEM) systems, reports from users, or external notifications. The goal is to quickly assess the situation and determine the nature and scope of the incident.
- Checklist: Gather initial information, analyze security logs, assess the potential impact, determine the type of incident, initiate the incident response plan, notify appropriate stakeholders.
- Containment: Once an incident is identified, the priority shifts to limiting its impact. This might involve isolating affected systems, blocking malicious network traffic, or preventing further data compromise. Speed and decisiveness are critical in this phase.
- Checklist: Isolate affected systems, block malicious traffic, prevent data exfiltration, secure evidence, limit access to affected resources, implement temporary security controls.
- Eradication: This involves removing the root cause of the incident. This might involve removing malware, patching vulnerabilities, or disabling compromised accounts. Thoroughness is crucial to prevent recurrence.
- Checklist: Remove malware, patch vulnerabilities, disable compromised accounts, restore system integrity, reconfigure security settings, conduct forensic analysis.
- Recovery: This involves restoring systems and data to their operational state. This might involve restoring from backups, reinstalling software, and reconfiguring systems. The goal is to return to normal operations as quickly and securely as possible.
- Checklist: Restore systems from backups, reinstall software, reconfigure systems, test system functionality, verify data integrity, update security configurations.
- Lessons Learned: After the incident is resolved, it’s crucial to review the response process. This involves identifying areas for improvement and updating the incident response plan to reflect the lessons learned. This continuous improvement cycle is essential for strengthening your organization’s security posture.
- Checklist: Document the incident response process, identify areas for improvement, update the incident response plan, conduct post-incident review meeting, share lessons learned with relevant teams, implement preventive measures.
Documenting Incident Response Procedures
Clear, concise, and easily accessible documentation is paramount. The documentation should include step-by-step instructions for each phase of the lifecycle, contact information for key personnel, and diagrams illustrating system architecture and data flows. Regular updates are crucial to reflect changes in technology and organizational structure. Using a version control system ensures that everyone is working with the most up-to-date version of the plan.
Setting up a killer CSIRT involves clear roles, regular training, and documented procedures. But even the best response plan needs adaptable technology, which is why understanding the potential of modern development approaches like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future is crucial. This knowledge helps build robust, secure systems that minimize vulnerabilities and streamline incident response, making your CSIRT even more effective.
Conducting Drills and Simulations
Regular drills and simulations are essential to test the effectiveness of the incident response plan and identify weaknesses. These exercises should involve different types of incidents, varying in scope and complexity. Post-incident reviews should be conducted to identify areas for improvement. For example, a simulation could involve a phishing attack scenario, testing the team’s ability to identify and respond to such an incident.
Another simulation might involve a ransomware attack, testing the team’s ability to contain the spread of malware and restore data from backups. These exercises can help identify bottlenecks and improve the team’s coordination and efficiency.
Implementing Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication is the lifeblood of a successful CSIRT. During a security incident, timely and accurate information flow is crucial for minimizing damage, containing the breach, and ensuring a swift recovery. A well-defined communication strategy ensures everyone involved – from internal teams to external stakeholders – is kept informed and coordinated, preventing confusion and enhancing the overall response effectiveness.The speed and accuracy of communication directly impact the severity and duration of a security incident.
Delays in informing relevant parties can lead to a wider breach, increased financial losses, and reputational damage. Conversely, clear and concise communication empowers teams to act decisively and efficiently, mitigating the impact of the attack.
Communication Channels for Different Stakeholders
Choosing the right communication channel is paramount. Different stakeholders require different levels of detail and communication preferences. A generic email blast isn’t suitable for all situations.
Internal teams often benefit from real-time communication platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams, allowing for quick updates and collaborative problem-solving. Management might prefer more formal updates via email or scheduled briefings, focusing on the high-level impact and the CSIRT’s response strategy. External partners, such as vendors or service providers, require clear and concise communication regarding the incident’s impact on their systems and the steps being taken to address it.
Finally, law enforcement communication requires strict adherence to legal and regulatory guidelines, often involving secure channels and formal reporting mechanisms.
Effective Communication Templates
Standardized communication templates streamline the process and ensure consistency in messaging. These templates should be pre-prepared and easily accessible to CSIRT members.
For incident notifications, a template could include: date and time of the incident, a brief description of the event, the affected systems or data, the current status of the incident, and initial actions taken. Regular updates should follow, providing details on the ongoing investigation, containment efforts, and recovery progress. These updates can leverage the same template, updating the relevant sections with the latest information.
A final report summarizing the incident, root cause analysis, and remediation steps should also utilize a standardized template for clarity and archiving purposes. Consider using a ticketing system to track communication and ensure accountability.
Communication Plan
A well-defined communication plan Artikels the process for notifying relevant parties and keeping them updated throughout the incident response lifecycle. This plan should specify communication channels, escalation procedures, and responsibilities for each stakeholder.
The plan should detail who is responsible for communicating with which stakeholders, the frequency of updates, and the content of those updates. For example, a designated spokesperson might be responsible for communicating with the media and public relations, while a technical lead updates internal teams on the technical aspects of the incident. Regular drills and simulations can test the effectiveness of the communication plan and identify areas for improvement.
The plan should also address crisis communication scenarios, including pre-approved messaging for potential public announcements.
Utilizing Advanced Tools and Technologies
A robust CSIRT relies heavily on advanced tools and technologies to effectively detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents. These tools provide the necessary automation, visibility, and intelligence to streamline the incident response process and minimize damage. Without them, a CSIRT would be significantly hampered in its ability to handle the complexities of modern cyber threats.The selection and integration of these tools is crucial for optimizing the CSIRT’s performance.
Careful consideration must be given to the specific needs and resources of the organization. A small organization may find a simpler, more integrated solution sufficient, while a large enterprise might require a more complex, multi-layered system.
Advanced Security Tools and Technologies
Several advanced security tools and technologies significantly enhance a CSIRT’s effectiveness. These tools offer diverse functionalities, from threat detection and analysis to automated response and incident orchestration. Proper integration of these tools creates a powerful and efficient security posture.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources across the network, providing a centralized view of security events. This enables faster detection of suspicious activities and facilitates incident investigation.
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): SOAR platforms automate repetitive tasks involved in incident response, such as threat hunting, malware analysis, and containment. This frees up CSIRT members to focus on more complex issues, improving efficiency and response time.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: These platforms aggregate threat intelligence from various sources, including open-source intelligence (OSINT), commercial feeds, and internal sources. This provides valuable context for analyzing incidents and predicting future threats.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide deep visibility into endpoint activity, enabling the detection of malware and other malicious activities on individual devices. This is crucial for containing breaches and investigating their root causes.
- Vulnerability Scanners: Regularly scanning systems for vulnerabilities is critical for proactive security. Vulnerability scanners identify weaknesses that attackers could exploit, allowing the CSIRT to prioritize patching and remediation efforts.
Comparison of Incident Response Platforms
Choosing the right incident response platform is critical. The following table compares some key features of different platforms:
| Platform | Strengths | Weaknesses | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Splunk | Comprehensive SIEM capabilities, extensive customization options, strong community support | Can be complex to implement and manage, high cost | High |
| IBM QRadar | User-friendly interface, robust threat intelligence integration, good scalability | Can be expensive, some features require additional modules | High |
| LogRhythm | Strong security analytics, good automation capabilities, relatively easy to use | Can be resource-intensive, limited customization options compared to Splunk | Medium-High |
| AlienVault OSSIM | Open-source option, cost-effective, good for smaller organizations | Limited features compared to commercial solutions, requires more technical expertise | Low |
Integrating Security Tools for Automated Responses
Integrating security tools is essential for automated responses. For example, a SIEM can automatically trigger an alert when it detects suspicious activity. This alert can then automatically initiate a workflow in a SOAR platform, which might involve isolating infected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, and launching a malware analysis. This automated response significantly reduces the time it takes to contain an incident and minimizes the impact.
Such automation is particularly crucial in large-scale attacks where manual response would be too slow and inefficient.
Utilizing Threat Intelligence Feeds for Proactive Mitigation
Threat intelligence feeds provide valuable insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities. By subscribing to reputable threat intelligence feeds, a CSIRT can proactively identify and mitigate potential risks. For example, if a feed reports a new zero-day vulnerability affecting a specific software version, the CSIRT can immediately prioritize patching affected systems, preventing exploitation before an attack occurs. This proactive approach significantly reduces the organization’s attack surface and minimizes the likelihood of successful attacks.
Regular analysis of threat intelligence data is vital for maintaining a strong security posture.
Fostering Continuous Improvement and Training
A truly effective CSIRT isn’t a static entity; it’s a dynamic team that constantly adapts to the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. Continuous improvement and robust training are not just beneficial additions, they are absolutely essential for maintaining a high level of preparedness and responsiveness. Regularly assessing performance, updating skills, and refining processes are vital for ensuring the CSIRT’s continued success in mitigating and responding to security incidents.The cornerstone of a thriving CSIRT is a commitment to continuous learning and development.
This involves a multifaceted approach encompassing formal training, practical exercises, and post-incident analysis, all aimed at enhancing individual and team capabilities. By proactively addressing skill gaps and incorporating lessons learned, the CSIRT can significantly improve its efficiency and effectiveness in handling future incidents.
CSIRT Member Training Programs
A comprehensive training program should be developed and regularly updated to cover a wide range of technical and non-technical skills. This includes hands-on training with incident response tools, simulations of real-world scenarios, and workshops on communication, collaboration, and legal considerations. For example, a training module might focus on advanced malware analysis techniques, while another might cover effective communication protocols during a crisis.
Regular refresher courses and specialized training on emerging threats, such as ransomware or AI-driven attacks, are also crucial. The training should also incorporate ethical considerations and legal compliance aspects related to incident response.
Post-Incident Reviews and Lessons Learned, 5 best practices for creating an effective computer security incident response team csirt
Post-incident reviews (PIRs) are critical for identifying areas for improvement within the CSIRT’s processes and response strategies. These reviews should be conducted following every significant incident, involving all CSIRT members and relevant stakeholders. A structured approach, such as using a standardized PIR template, ensures consistent analysis and documentation. The PIR process should identify both successes and shortcomings, focusing on areas such as incident detection time, containment effectiveness, communication clarity, and overall response time.
For instance, a PIR might reveal that the initial detection of a particular attack was delayed due to a lack of sufficient monitoring tools, leading to a longer containment time.
Documenting Lessons Learned and Updating Response Plans
The findings from PIRs should be meticulously documented and used to update the CSIRT’s incident response plans and procedures. A centralized repository, accessible to all team members, should store these documents. This repository could be a wiki, a shared document, or a dedicated incident management system. These lessons learned should not be treated as mere historical records; they should be actively integrated into training materials and future response strategies.
For example, if a PIR reveals a weakness in a particular security control, the CSIRT can use this information to improve the control, update its documentation, and incorporate the improvement into future training exercises.
Regularly Updating CSIRT Procedures and Technologies
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new attack vectors and techniques emerging regularly. The CSIRT must proactively adapt to these changes by regularly reviewing and updating its procedures and technologies. This includes staying abreast of the latest security threats and vulnerabilities, adopting new security tools and technologies, and updating its incident response plans to reflect best practices.
For instance, the CSIRT might need to update its procedures to handle new types of ransomware or incorporate new threat intelligence feeds into its monitoring systems. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing can also identify weaknesses in existing systems and help to improve the overall security posture.
Summary
So, there you have it – five essential best practices for building a rock-solid CSIRT. Remember, a strong CSIRT isn’t just about technology; it’s about people, processes, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By following these practices, you can significantly reduce your organization’s vulnerability to cyberattacks and build a team capable of handling any incident with confidence and efficiency. Don’t wait for a crisis to hit – start building your dream team today!
Questions and Answers
What’s the difference between a CSIRT and a SOC?
While both deal with security, a Security Operations Center (SOC) monitors for threats proactively, while a CSIRT responds to incidents
-after* they occur. Think of the SOC as preventative medicine and the CSIRT as emergency response.
How often should we conduct CSIRT drills?
Regular drills are vital! Aim for at least quarterly simulations, varying scenarios each time to test different aspects of your response plan. The frequency should depend on your risk tolerance and industry regulations.
What are some common mistakes in CSIRT creation?
Common mistakes include poorly defined roles, lack of communication protocols, inadequate training, and insufficient budget allocation. Thorough planning and clear communication are key to avoiding these pitfalls.
How do I get buy-in from leadership for CSIRT investment?
Highlight the potential financial losses from a major security breach. Quantify the benefits of a CSIRT – faster incident response, reduced downtime, and improved compliance. A strong business case is essential.