A Surge in Smishing Cyber Attacks
A surge in smishing cyber attacks is terrifying, isn’t it? These sneaky text message scams are becoming increasingly sophisticated, preying on our trust and our reliance on our phones. From fake prize notifications to urgent bank alerts, the tactics are evolving rapidly, making it harder than ever to spot the fakes. This post dives deep into the world of smishing, exploring the methods used, the impact on victims, and most importantly, how to protect yourself.
We’ll examine the alarming statistics behind this rise in smishing, looking at the contributing factors like technological advancements and societal shifts in how we interact online. We’ll also uncover the social engineering tricks these criminals use to manipulate us, and explore the role of technology in making these attacks easier to launch. Get ready to learn how to identify and avoid these increasingly common threats.
Defining Smishing Attacks
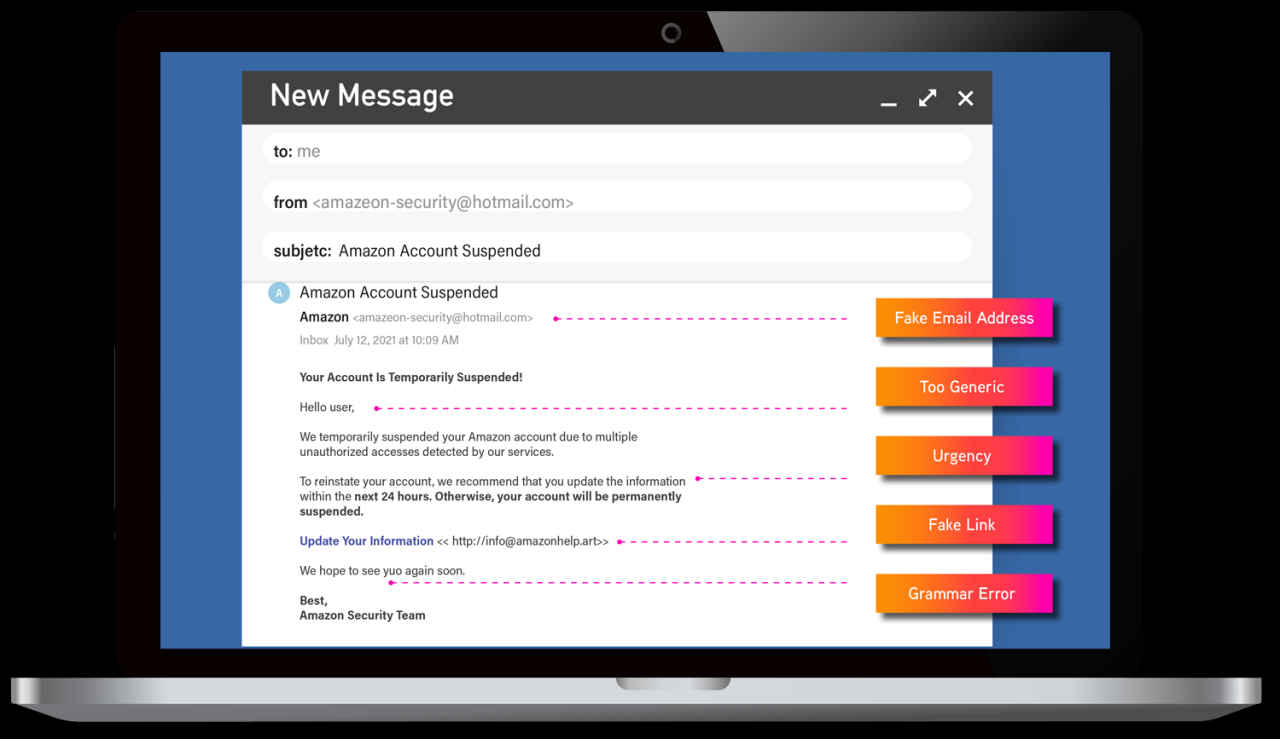
Smishing, a portmanteau of “SMS” and “phishing,” is a sophisticated form of cyberattack leveraging text messages to deceive individuals into divulging sensitive information or installing malware. Unlike traditional phishing emails, smishing exploits the immediacy and perceived trustworthiness associated with text messages, making it a particularly effective attack vector. The mechanics rely on social engineering principles, employing deceptive tactics to manipulate victims into taking action.Smishing attacks typically involve sending seemingly legitimate text messages from what appears to be a trusted source, such as a bank, government agency, or well-known company.
These messages often create a sense of urgency or fear, prompting the recipient to act quickly without critical thinking. The goal is to trick the victim into clicking a malicious link, downloading a harmful file, or revealing personal details like usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, or social security numbers.
Smishing Tactics and Phishing Lures
Smishing campaigns employ a variety of deceptive tactics to maximize their success rate. Messages often mimic official communications, using logos, branding, and language consistent with the purported sender. The urgency is frequently emphasized through phrases like “Urgent Action Required,” “Your Account Has Been Compromised,” or “You Have Won a Prize.” Variations in messaging include:
- Fake delivery notifications: Messages claiming a package is awaiting delivery and requiring immediate action to update shipping information or pay a fee.
- Account compromise alerts: Messages warning of suspicious activity on a bank account, requiring the victim to verify login credentials through a provided link.
- Government impersonation: Messages posing as government agencies, demanding payment of taxes or fines, threatening legal action if not responded to immediately.
- Lottery scams: Messages announcing a lottery win, requiring personal information to claim the prize.
These messages often include shortened URLs that mask the true destination, leading victims to malicious websites designed to steal their data or install malware onto their devices. The lures are carefully crafted to exploit common human vulnerabilities, such as fear, greed, and a desire for convenience.
Typical Targets of Smishing Campaigns
Smishing campaigns target a broad range of individuals, but certain demographics and vulnerabilities make some more susceptible than others. Elderly individuals, who may be less tech-savvy and more trusting, are frequently targeted. Similarly, those with limited digital literacy or those unfamiliar with security best practices are at increased risk. Furthermore, individuals who frequently use online banking or shopping services are prime targets, as their personal information is valuable to cybercriminals.
The attackers often leverage publicly available information to personalize their messages, increasing the likelihood of success. For example, a smishing message might include the victim’s name and partial address, creating a sense of legitimacy and encouraging a quicker response. A real-life example would be a message claiming a package is being held at a local post office, specifically mentioning the recipient’s street address.
The Recent Increase in Smishing Attacks
The number of smishing attacks, or phishing attacks conducted via SMS text messages, has experienced a dramatic upswing in recent years. This isn’t just anecdotal; we’re seeing a clear trend reflected in reports from major cybersecurity firms, highlighting a significant threat to individuals and businesses alike. Understanding the reasons behind this surge is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation.The increase in smishing attacks is a multifaceted problem stemming from both technological advancements and shifts in societal behavior.
Sophisticated techniques are making these attacks more convincing and harder to detect, while increased smartphone usage and reliance on mobile communication create a larger pool of potential victims. Moreover, the evolving tactics employed by cybercriminals are constantly adapting to bypass security measures.
Factors Contributing to the Rise of Smishing
Several key factors contribute to the recent surge in smishing attacks. Firstly, the widespread adoption of smartphones and mobile banking has created a fertile ground for these attacks. Criminals leverage the convenience and trust associated with mobile devices to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Secondly, the development of more sophisticated spoofing techniques allows attackers to convincingly mimic legitimate organizations, making it difficult for recipients to identify fraudulent messages.
For example, attackers can now easily mask their phone numbers to appear as if the message originates from a trusted bank or service provider. Finally, the relatively low barrier to entry for launching smishing campaigns makes it an attractive option for both individual hackers and organized crime groups. This accessibility contributes to the sheer volume of attacks we’re currently witnessing.
Comparison to Previous Years
Comparing the current smishing landscape to previous years reveals a significant shift in attack vectors and sophistication. While smishing attacks have existed for some time, their scale and effectiveness have dramatically increased. Reports from organizations like the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) show a consistent upward trend in the number of reported smishing incidents over the past few years.
For instance, the APWG’s data might show a 20% increase in reported smishing attacks in 2023 compared to 2022, and a 50% increase compared to
2021. (Note
These are hypothetical figures; actual data should be sourced from the APWG or similar reputable organizations). This increase is not merely due to better reporting; the sophistication of the attacks themselves has also improved, with criminals using more personalized messages and targeting specific demographics. Previously, smishing attacks were often crude and easily identifiable, but now they often leverage social engineering techniques to exploit human psychology and increase the likelihood of success.
Methods Used in Smishing Attacks
Smishing attacks, while relying on the same basic principle of phishing—deceiving the victim—employ a variety of methods to achieve their goals. These methods leverage technological advancements and sophisticated social engineering techniques to maximize their effectiveness and evade detection. Understanding these methods is crucial for individuals and organizations to protect themselves against these increasingly prevalent attacks.
The core of any successful smishing campaign lies in a carefully crafted message, designed to trigger an immediate response from the victim. This is often achieved through a combination of urgency, fear, or a sense of reward. Attackers skillfully manipulate these emotions to bypass critical thinking and prompt immediate action, such as clicking a link or revealing sensitive information.
Smishing Attack Methods and Their Effectiveness
Several methods are used to carry out smishing attacks, each with varying degrees of effectiveness and difficulty in detection. The following table compares some common techniques:
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Detection Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spoofed Sender ID | Attackers disguise the phone number or sender ID to appear as a legitimate entity (e.g., bank, government agency). | High – Creates a sense of trust and legitimacy. | Moderate – Sophisticated spoofing techniques can be difficult to detect. |
| Pretexting | Attackers create a believable scenario to justify their request for information, often involving urgency or a threat. For example, a message claiming your account has been compromised and needs immediate action. | High – Leverages emotional manipulation to bypass critical thinking. | High – The deceptive nature of the message makes detection challenging unless carefully scrutinized. |
| URL Shortening | Using shortened URLs masks the true destination of a link, making it difficult for victims to identify malicious websites. | Moderate – Makes the link appear less suspicious, but can be easily detected with URL expanders. | Low – Many tools are available to expand shortened URLs and reveal their destination. |
| Premium-Rate SMS | Victims are tricked into subscribing to premium-rate SMS services, resulting in unauthorized charges. | High – The financial impact is immediate and noticeable. | Moderate – Detecting this requires monitoring phone bills and recognizing unexpected charges. |
Social Engineering in Smishing Attacks
Social engineering plays a pivotal role in smishing attacks. Attackers leverage psychological principles to manipulate victims’ emotions and exploit their trust. They often create a sense of urgency or fear, using phrases like “Your account has been compromised” or “You have won a prize.” This pressure induces hasty actions, bypassing critical thinking processes. They also target specific demographics, tailoring their messages to resonate with the victim’s circumstances or beliefs.
For instance, a message impersonating a well-known charity could successfully target empathetic individuals.
Technology’s Role in Facilitating Smishing Attacks
Technology significantly facilitates smishing attacks. Automated tools allow attackers to send thousands of messages simultaneously, increasing the chances of successful attacks. Botnets, networks of compromised computers, provide the infrastructure for large-scale smishing campaigns, enabling attackers to mask their identities and distribute messages efficiently. The use of these technologies reduces the cost and effort required to launch a widespread attack, making smishing a highly effective and scalable cyber threat.
Impact and Consequences of Smishing Attacks: A Surge In Smishing Cyber Attacks
Smishing attacks, while seemingly small-scale, can have devastating consequences for both individuals and businesses. The financial losses, personal distress, and reputational damage caused by these attacks are significant and often far-reaching, impacting victims long after the initial compromise. Understanding the potential impact is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation strategies.The repercussions of a successful smishing attack extend beyond the immediate loss of funds.
Victims often experience a sense of violation and frustration, leading to emotional distress and a loss of trust in digital communications. For businesses, the consequences can be even more severe, potentially leading to financial ruin and legal action. The impact is multifaceted, encompassing financial losses, reputational damage, and legal ramifications.
Financial and Personal Consequences
Successful smishing attacks directly translate into financial losses for victims. Criminals can gain access to bank accounts, credit cards, and other financial information, leading to unauthorized transactions, identity theft, and significant debt. Beyond financial losses, victims often face considerable emotional distress, including anxiety, stress, and feelings of helplessness. The time and effort required to rectify the situation, including reporting the crime, canceling accounts, and disputing fraudulent charges, adds further burden.
In some cases, the impact can be so severe that it affects victims’ credit scores and overall financial stability for years to come.
Reputational Damage and Legal Repercussions
For businesses, a smishing attack can severely damage their reputation. If customer data is compromised, the company may face a loss of trust, negative publicity, and potential legal action. This reputational damage can translate into lost revenue, decreased customer loyalty, and difficulty attracting new clients. Legally, businesses can face fines and lawsuits from regulatory bodies and affected customers.
Depending on the severity of the breach and the applicable laws, the legal repercussions can be significant, potentially including hefty fines, settlements, and even criminal charges.
Examples of Smishing Impacts
The impact of smishing attacks varies greatly depending on the victim and the specific nature of the attack. Here are a few examples illustrating the wide-ranging consequences:
- An individual loses their life savings after falling victim to a convincing smishing campaign that redirects them to a fake banking website.
- A small business experiences a significant data breach, resulting in the theft of customer credit card information and subsequent legal action from affected customers.
- A large corporation suffers a reputational blow after a smishing attack exposes sensitive employee data, leading to a loss of investor confidence and decreased stock value.
- An individual’s identity is stolen after responding to a smishing message, resulting in the opening of fraudulent accounts and accumulation of significant debt.
- A person experiences significant emotional distress and anxiety after realizing they have been scammed through a smishing attack, leading to mental health challenges.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Smishing attacks are a growing threat, but proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk. By understanding the tactics used and implementing appropriate safeguards, both individuals and organizations can bolster their defenses against these malicious text messages. This section Artikels key strategies for prevention and mitigation.
A multi-layered approach is crucial for effective protection. This includes educating users about smishing techniques, implementing strong security measures on devices and networks, and establishing clear protocols for handling suspicious messages. Combining these elements creates a robust defense against smishing attacks.
Mobile Device Security Settings
Strengthening your mobile device’s security settings is a fundamental step in preventing smishing attacks. This involves enabling features designed to filter and block potentially harmful content. For example, activating built-in spam filters on your phone can significantly reduce the number of suspicious messages you receive. Regularly updating your operating system is also critical, as these updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by smishing campaigns.
Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to access your accounts even if they obtain your login credentials through a smishing attack. Finally, being cautious about downloading apps only from official app stores and regularly reviewing app permissions helps to prevent malicious software from gaining access to your personal information.
Effective Security Software
Employing robust security software on your mobile device provides an additional line of defense against smishing attacks. Many reputable security apps offer features such as real-time threat detection, phishing protection, and URL scanning. These features can identify and block suspicious links contained within smishing messages before you interact with them. Some security software also includes features that analyze the sender’s phone number and flag potentially malicious numbers based on known smishing campaigns.
Choosing a reputable security provider with a strong track record in mobile security is essential for effective protection. Examples include Lookout Mobile Security and Norton Mobile Security, but numerous others offer similar features.
Identifying and Responding to Suspicious Texts
Critical thinking and verification are paramount in dealing with potentially malicious text messages. Several key indicators can help identify a smishing attempt. For instance, messages with urgent requests, unexpected financial transactions, or threats are often red flags. Furthermore, messages containing generic greetings or requests for personal information, such as passwords or credit card details, should raise suspicion.
Seriously, the surge in smishing cyber attacks is terrifying! We need robust, secure apps to combat this, and that’s where learning about domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , becomes crucial. Developing secure, user-friendly apps is vital in protecting ourselves against these increasingly sophisticated phishing scams. It’s time to get serious about app security in the face of this rising threat.
Before clicking any links or replying to such messages, it’s crucial to independently verify the sender’s identity. This can be done by contacting the purported sender directly through a known legitimate phone number or email address, checking the sender’s website for contact information, or consulting official resources to confirm the legitimacy of any request. Never respond directly to suspicious texts, as this can inadvertently confirm your number as active and increase the likelihood of future attacks.
Report any suspicious text messages to your mobile carrier and the relevant authorities.
The Role of Mobile Carriers and Law Enforcement
The fight against smishing attacks requires a multi-pronged approach, with mobile carriers and law enforcement playing crucial roles. Their collaborative efforts are essential in mitigating the threat and holding perpetrators accountable. While individuals can take steps to protect themselves, systemic changes are needed to significantly reduce the prevalence of these attacks.Mobile carriers possess significant power in combating smishing due to their control over the mobile network infrastructure.
They are uniquely positioned to identify and block suspicious messages, implement advanced security protocols, and work with law enforcement to trace the origin of malicious SMS traffic. However, the effectiveness of their interventions depends heavily on their willingness to invest in and deploy robust anti-smishing technologies.
Mobile Carrier Responsibilities and Security Protocol Improvements
Mobile carriers have a responsibility to proactively protect their subscribers from smishing attacks. This includes investing in advanced technologies such as AI-powered spam filters capable of identifying and blocking suspicious messages based on content, sender information, and other contextual clues. Implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as stronger two-factor authentication (2FA) and enhanced SIM card security, can further deter attackers.
Improved collaboration between carriers to share threat intelligence and blacklist known malicious numbers is also crucial. For example, a system where carriers automatically share lists of identified smishing numbers across their networks would significantly reduce the effectiveness of these attacks. Furthermore, providing users with clear and concise information about smishing threats and how to report suspicious messages can empower users to take protective measures.
Law Enforcement Challenges in Investigating and Prosecuting Smishing Perpetrators
Investigating and prosecuting smishing perpetrators presents significant challenges for law enforcement. The perpetrators often operate internationally, making cross-border cooperation complex and time-consuming. Tracing the origin of smishing messages can be difficult due to the use of spoofed numbers and sophisticated techniques to mask the true sender. Furthermore, gathering sufficient evidence to secure convictions can be challenging, requiring expertise in digital forensics and international legal cooperation.
The relatively low penalties associated with smishing convictions in some jurisdictions also act as a deterrent to effective prosecution. For example, a case involving a large-scale smishing campaign might require collaboration between multiple law enforcement agencies across different countries to track down the perpetrators and gather sufficient evidence for prosecution. This often involves navigating different legal systems and overcoming language barriers.
Successful Initiatives in Mitigating Smishing Threats, A surge in smishing cyber attacks
Several initiatives highlight the potential for successful collaboration between mobile carriers and law enforcement. Some mobile carriers have implemented advanced AI-powered spam filtering systems that effectively block a significant percentage of smishing messages before they reach their intended recipients. Law enforcement agencies, in collaboration with mobile carriers, have successfully disrupted several large-scale smishing operations, leading to arrests and convictions.
These successes often involve the sharing of threat intelligence, coordinated investigations, and the development of joint strategies to combat smishing. For instance, a joint operation between a major mobile carrier and a national cybersecurity agency might involve analyzing suspicious SMS traffic patterns, identifying key perpetrators, and coordinating a takedown operation involving the seizure of servers and the arrest of individuals involved in the smishing campaign.
The success of such operations highlights the effectiveness of coordinated efforts in reducing the impact of smishing attacks.
Future Trends in Smishing Attacks
Smishing, like other forms of cybercrime, is constantly evolving. Attackers are relentlessly seeking new ways to bypass security measures and exploit vulnerabilities in our increasingly interconnected world. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for individuals and organizations to effectively protect themselves. The convergence of several technological advancements is fueling a new wave of sophisticated smishing campaigns, demanding a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity.The landscape of smishing attacks is poised for significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving attacker tactics.
We can expect to see a rise in more personalized and targeted attacks, leveraging vast amounts of data to craft highly convincing phishing messages. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) will play a crucial role in this evolution.
Increased Use of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are rapidly becoming integral to smishing campaigns. Attackers are using these technologies to automate the creation of convincing messages, personalize them to individual targets, and bypass spam filters more effectively. For example, AI can analyze vast datasets of personal information to craft incredibly realistic and tailored messages, increasing the likelihood of successful attacks. Furthermore, AI-powered tools can help attackers identify and exploit vulnerabilities in mobile operating systems and applications, allowing them to deliver malware more efficiently.
This automation also allows for a much larger scale of attacks than previously possible, making detection and response more challenging.
Exploitation of 5G and IoT Devices
The proliferation of 5G networks and the Internet of Things (IoT) presents new attack vectors for smishers. 5G’s increased speed and bandwidth can facilitate the rapid dissemination of smishing messages and the delivery of larger malware payloads. The sheer number of interconnected IoT devices, many of which lack robust security measures, creates a vast attack surface. Attackers could potentially compromise IoT devices to launch smishing attacks or use them as stepping stones to access more sensitive systems.
Imagine a scenario where a compromised smart home device is used to send smishing messages to the homeowner’s contacts, leveraging the established trust within their social circle.
Deepfakes and Synthetic Media
The increasing sophistication of deepfake technology poses a significant threat. Attackers could create realistic audio or video messages that appear to be from trusted individuals, such as family members or bank representatives, dramatically increasing the believability of smishing attempts. A deepfake video of a loved one urgently requesting money could be highly persuasive, making victims more likely to fall prey to the scam.
The challenge lies in developing reliable methods to detect and counter these sophisticated manipulations.
Challenges for the Cybersecurity Community
Addressing future smishing threats will require a multi-faceted approach. The constantly evolving nature of these attacks necessitates continuous adaptation and innovation in cybersecurity defenses. Keeping pace with the rapid advancements in AI and other technologies used by attackers is a significant challenge. Furthermore, effective collaboration between mobile carriers, law enforcement, and cybersecurity companies is vital to share threat intelligence and coordinate responses.
Educating the public about the latest smishing tactics and empowering them with the knowledge to identify and avoid these attacks remains a critical component of a comprehensive defense strategy. The scale of the problem, coupled with the constantly evolving methods, demands ongoing investment in research, development, and public awareness campaigns.
Closing Notes
Smishing attacks are a growing threat, but armed with knowledge, we can significantly reduce our vulnerability. Understanding the tactics used, staying vigilant about suspicious messages, and utilizing available security measures are crucial steps in protecting ourselves and our data. Remember, a little skepticism and a few extra seconds of verification can go a long way in preventing you from becoming the next victim.
Stay safe out there, and spread the word – awareness is our best defense against these digital thieves!
Answers to Common Questions
What’s the difference between smishing and phishing?
Phishing uses email, while smishing uses text messages (SMS) to trick you into revealing personal information.
Can I report a smishing attempt?
Yes! Report suspicious texts to your mobile carrier and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
What should I do if I think I’ve fallen victim to a smishing attack?
Immediately contact your bank and any other relevant institutions. Change your passwords and monitor your accounts closely.
Are there apps that can help protect me from smishing?
Yes, many security apps offer features to identify and block suspicious numbers and messages. Research reputable options and read reviews.





