280M Indian Bank Accounts Exposed Online
Bank account details of about 280m indian citizens exposed on the web – Bank account details of about 280 million Indian citizens exposed on the web – that’s a headline that sent chills down my spine. This massive data breach represents a catastrophic failure of security, potentially impacting millions of lives and leaving a trail of financial ruin in its wake. We’re talking about a scale of vulnerability that’s almost incomprehensible, exposing personal banking information on a scale unseen before in India.
The implications are staggering, reaching far beyond mere financial loss; we’re talking about the erosion of trust, the potential for widespread identity theft, and the long-term consequences for individuals and the entire banking system.
The sheer volume of compromised data raises serious questions about the security protocols in place, the potential for insider threats, and the overall preparedness of Indian institutions to handle such a crisis. We need to delve into the source of this leak, understand the methods used to access this sensitive information, and explore the potential vulnerabilities exploited by the perpetrators.
Equally crucial is examining the response from the government and regulatory bodies, the steps being taken to mitigate the damage, and the measures banks are implementing to prevent future breaches. Ultimately, this event highlights the urgent need for increased public awareness about online security and the crucial steps individuals can take to protect themselves.
Data Breach Scope and Impact
The exposure of bank account details for an estimated 280 million Indian citizens represents a catastrophic data breach with potentially devastating consequences. The sheer scale of this breach necessitates a thorough understanding of its ramifications, encompassing the potential for widespread financial crimes, identity theft, and the disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations. The long-term effects on individuals and the nation’s financial stability are significant and far-reaching.The consequences of exposing this sensitive data are multifaceted and severe.
The leaked information could be used to perpetrate a wide range of financial crimes, leading to significant financial losses for individuals and potentially destabilizing the financial system. Furthermore, the potential for identity theft and the subsequent erosion of trust in digital banking services are substantial concerns.
Types of Financial Crimes
This data breach creates fertile ground for various financial crimes. Criminals could use the stolen information to directly access bank accounts, initiating unauthorized transactions like fund transfers and withdrawals. They might also use the data to create fraudulent loans or credit applications, leveraging the victims’ identities to obtain credit in their names. Phishing scams, where victims are tricked into revealing additional personal information, become far more effective with pre-existing knowledge of their bank details.
Furthermore, the data could be sold on the dark web, providing a steady stream of revenue for cybercriminals and escalating the risk for the affected individuals. The scale of this breach increases the likelihood of sophisticated, large-scale organized crime involvement.
Identity Theft and Fraud
The exposed bank account details, when combined with other potentially leaked personal information, provide a powerful toolkit for identity theft. Criminals can use this information to open new accounts, apply for loans, obtain credit cards, and even file fraudulent tax returns. The process of rectifying identity theft can be lengthy, costly, and emotionally draining for victims. The damage extends beyond financial losses; it can severely impact credit scores, employment prospects, and even access to essential services.
For example, a victim might find their ability to rent an apartment or obtain a loan significantly hampered due to fraudulent activity linked to their stolen identity.
Vulnerability Across Demographic Groups
The impact of this data breach will not be evenly distributed across the population. Elderly individuals, who may be less tech-savvy and more trusting, are particularly vulnerable to phishing scams and other forms of fraud. Low-income individuals, who may have limited financial resources to recover from losses, face a disproportionately severe impact. Those with limited digital literacy may struggle to identify and report fraudulent activities, further exacerbating their vulnerability.
Rural populations, with potentially less access to resources and support systems, could also experience significant difficulties in mitigating the consequences of this breach. This uneven impact highlights the urgent need for targeted support and resources for vulnerable groups.
Source and Nature of the Leak: Bank Account Details Of About 280m Indian Citizens Exposed On The Web
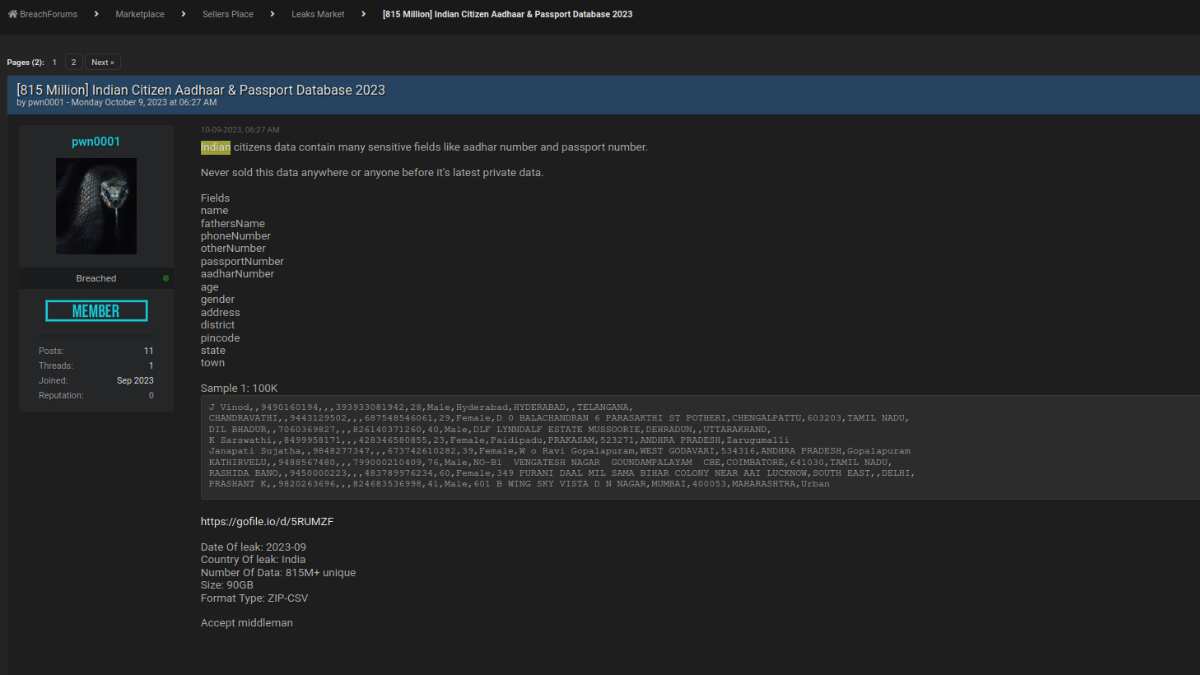
The exposure of the bank account details of an estimated 280 million Indian citizens represents a massive data breach, the scale of which demands a thorough investigation into its origins and methods. Understanding the source and nature of this leak is crucial not only for accountability but also for implementing preventative measures to avoid similar incidents in the future.
This analysis will explore potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors that may have been exploited.The sheer volume of data compromised suggests a breach originating from a centralized source, rather than numerous smaller, independent incidents. Several possibilities exist, each requiring a different approach to remediation and future security enhancements.
Potential Sources of the Data Breach, Bank account details of about 280m indian citizens exposed on the web
Several potential sources could explain the leak. A compromised database, either through a direct attack or an insider threat, is a highly probable scenario. Large databases containing sensitive customer information are prime targets for malicious actors, and even seemingly minor vulnerabilities can be exploited to gain access. Another possibility is a third-party vendor providing services to the bank or financial institutions involved.
Such vendors often handle sensitive data, and a breach within their systems could have far-reaching consequences. Finally, the possibility of a sophisticated social engineering attack, manipulating employees to divulge credentials or access sensitive information, cannot be discounted. The scale of the breach points to a likely sophisticated attack, possibly involving a combination of techniques.
Methods of Data Access and Extraction
The methods used to access and extract this sensitive information likely involved a combination of technical skills and social engineering. For a database compromise, attackers might have exploited known vulnerabilities like SQL injection flaws, insecure configurations, or weak passwords. They could have used automated tools to scan for vulnerabilities and then leverage those weaknesses to gain unauthorized access.
Once inside the system, they might have used various techniques to exfiltrate the data, including transferring it directly to a remote server or using compromised accounts to download it piecemeal. Social engineering, on the other hand, might have involved phishing emails or other deceptive tactics to gain access credentials from bank employees.
Technical Vulnerabilities Exploited
The precise technical vulnerabilities exploited remain unknown without a full forensic investigation. However, based on similar past breaches, we can speculate on potential weaknesses. Outdated software with unpatched security flaws, particularly in database management systems, is a common culprit. Weak or reused passwords, coupled with a lack of multi-factor authentication, could have facilitated unauthorized access. Insecure configurations of web servers or other network devices could have created entry points for attackers.
Furthermore, the lack of robust data encryption, both in transit and at rest, could have made the extracted data easily accessible and usable by the attackers. A failure to implement proper access control mechanisms could also have contributed to the breach.
Hypothetical Timeline of Events
A plausible timeline might begin with attackers identifying a vulnerable system, perhaps through automated vulnerability scanning. This could be followed by a period of reconnaissance, where they map the network and identify potential entry points. Subsequently, they would exploit the identified vulnerability, gaining unauthorized access to the database. Data exfiltration would then occur, possibly over a period of time to avoid detection.
Finally, the data would be disseminated, perhaps through sale on the dark web or other illicit channels. The discovery of the breach might have been triggered by an internal security audit, a tip-off, or the appearance of the data on the dark web. The exact timeline and specifics would require a thorough investigation by cybersecurity professionals.
Government and Regulatory Response
The exposure of the bank account details of an estimated 280 million Indian citizens represents a catastrophic data breach, demanding a swift and comprehensive response from the Indian government and its regulatory bodies. The scale of this breach necessitates a multi-pronged approach involving investigations, legal action, and preventative measures to protect citizens and rebuild public trust. Failure to act decisively could severely damage India’s reputation as a reliable digital economy and erode public confidence in financial institutions.The expected response will likely involve several key agencies.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), responsible for regulating financial institutions, will be central to the investigation, potentially issuing fines and directives to affected banks. The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) will likely coordinate the overall government response, potentially collaborating with law enforcement agencies like the Cyber Crime Investigation Cell to identify and prosecute those responsible. The Data Protection Board of India, once fully functional, will also play a crucial role in enforcing data protection laws and investigating the breach.
Expected Actions of Indian Government and Regulatory Bodies
The government’s response will likely include investigations to determine the source and extent of the leak, identifying the responsible parties and holding them accountable. This will involve scrutinizing the security practices of the affected banks and potentially other involved entities. Simultaneously, measures to mitigate the impact on affected citizens will be implemented, potentially including credit monitoring services, fraud alerts, and public awareness campaigns.
Furthermore, the government may revise data protection regulations and strengthen cybersecurity frameworks to prevent similar incidents in the future. Examples of potential actions include issuing stricter guidelines on data storage and security, mandating regular security audits, and increasing penalties for non-compliance. A public inquiry may also be launched to assess the systemic failures that led to the breach.
Past Responses to Similar Data Breaches in India and Other Countries
India has seen several significant data breaches in the past, though none on this scale. The Aadhaar data breach of 2018, for example, led to increased scrutiny of biometric data security and prompted calls for stronger data protection laws. Internationally, the Equifax breach in 2017 resulted in significant fines and regulatory action, highlighting the potential for severe consequences for companies that fail to protect sensitive data.
The response to these breaches varied, but generally involved investigations, regulatory penalties, and measures to improve data security. However, the scale of this current breach necessitates a response that goes beyond past actions.
Comparison of Legal Frameworks
India’s legal framework regarding data protection is still evolving, with the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019, undergoing revisions. While the bill aims to provide comprehensive data protection, its implementation and effectiveness remain to be seen. Compared to jurisdictions with more mature data protection laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), India’s current legal framework may lack the same level of enforcement power and citizen protection.
The GDPR, for example, includes stringent requirements for data security and imposes substantial fines for non-compliance. The outcome of this breach will likely influence the final shape and enforcement of India’s data protection laws.
Potential Plan of Action for Government Agencies
A comprehensive plan of action should include immediate steps to mitigate the immediate impact on citizens, followed by longer-term measures to prevent future breaches. Immediate actions could include: (1) Establishing a dedicated task force to investigate the breach; (2) Issuing public advisories to citizens on how to protect themselves from fraud; (3) Collaborating with banks to provide credit monitoring and fraud prevention services to affected individuals; and (4) Launching a public awareness campaign on cybersecurity best practices.
Longer-term measures should focus on strengthening data protection laws, improving cybersecurity infrastructure, and increasing penalties for non-compliance. This could include: (1) Expediting the enactment and implementation of a robust data protection law; (2) Mandating regular security audits for financial institutions and other data handlers; (3) Investing in cybersecurity infrastructure and training; and (4) Creating a national cybersecurity strategy that addresses the unique challenges faced by India’s digital economy.
This coordinated and decisive response is crucial to rebuilding public trust and preventing future incidents of this magnitude.
Impact on the Banking Sector
The exposure of the bank account details of an estimated 280 million Indian citizens represents a catastrophic breach of trust and poses significant challenges for the Indian banking sector. The ramifications extend far beyond immediate financial losses, impacting reputation, customer confidence, and the overall stability of the financial system. The scale of this data leak necessitates a multifaceted response, encompassing immediate remediation efforts, long-term security enhancements, and a robust strategy for regaining public trust.The sheer volume of compromised data presents a massive threat to the reputation of the banks involved.
A loss of public confidence could lead to a decline in customer deposits, impacting liquidity and profitability. The potential for widespread fraud, identity theft, and financial losses further exacerbates this reputational risk. The negative publicity surrounding such a large-scale data breach can severely damage a bank’s brand image, potentially impacting its ability to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
This damage is not easily repaired, and the long-term effects could be profound.
Financial Implications for Banks
The financial burden on affected banks will be substantial. The costs associated with remediation will include expenses related to investigating the breach, notifying affected customers, providing credit monitoring services, and implementing enhanced security measures. Legal fees, regulatory fines, and potential compensation payouts to affected customers will further add to these costs. The cost of enhancing cybersecurity infrastructure and training employees in data security best practices will also represent a significant long-term investment.
For example, a bank might need to invest in advanced threat detection systems, implement multi-factor authentication, and conduct regular security audits, all of which come with significant financial implications. The potential for class-action lawsuits adds another layer of unpredictable financial risk. The overall financial impact could run into billions of rupees, depending on the extent of the damage and the legal repercussions.
Measures to Improve Data Security
To prevent future breaches, Indian banks need to adopt a comprehensive approach to data security. This includes implementing robust security protocols, investing in advanced technologies, and providing comprehensive training to employees. Specific measures could involve transitioning to more secure authentication methods like biometric authentication or hardware security keys, encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest, and regularly conducting penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify and address security weaknesses.
Banks should also invest in advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying and responding to sophisticated cyberattacks in real time. Furthermore, a strong emphasis on employee training is crucial, focusing on secure coding practices, phishing awareness, and the importance of adhering to data security policies. Regular security audits, conducted by independent third-party experts, are essential to ensure that security measures are effective and up-to-date.
Communicating with Affected Customers and Regaining Public Trust
A transparent and empathetic communication strategy is paramount for regaining public trust. Banks should promptly notify affected customers about the breach, clearly outlining the nature of the compromised data and the steps being taken to mitigate the risk. Providing affected customers with free credit monitoring services and identity theft protection is crucial. Regular updates on the ongoing investigation and remediation efforts should be communicated to maintain transparency.
Public statements acknowledging the seriousness of the breach and expressing sincere apologies for the inconvenience caused are essential for demonstrating accountability. Active engagement with customers through various channels, such as dedicated helplines, email updates, and social media, will demonstrate a commitment to addressing their concerns. A proactive approach, demonstrating a commitment to improving data security and preventing future breaches, will be crucial in rebuilding public confidence.
Transparency, empathy, and a demonstrable commitment to security are key to restoring trust.
Public Awareness and Education
The recent data breach affecting the bank account details of millions of Indian citizens underscores the critical need for enhanced public awareness regarding online security and data protection. This isn’t just about technical jargon; it’s about empowering individuals to safeguard their hard-earned money and personal information. A proactive and comprehensive public awareness campaign is essential to mitigate future risks and help victims of this breach.This section Artikels steps individuals can take to protect themselves, resources available to those affected, and methods to identify and avoid common online scams.
Understanding these preventative measures is crucial for building a more secure digital landscape.
Protecting Yourself from Financial Fraud After a Data Breach
Following a data breach like this, proactive measures are crucial to minimize the risk of financial fraud. This includes regularly monitoring bank accounts and credit reports for unauthorized activity, promptly reporting any suspicious transactions, and strengthening online security practices. Ignoring these steps could lead to significant financial losses.
Resources for Victims of Identity Theft and Financial Fraud
Victims of identity theft and financial fraud have access to various resources that can provide support and guidance during this difficult time. These resources range from government agencies and consumer protection organizations to specialized credit reporting agencies and legal aid services. Knowing where to turn for help is a critical step in recovering from such incidents. For example, the Indian government’s National Cyber Security Coordination Centre (NCSCC) provides valuable information and assistance.
Furthermore, credit bureaus like CIBIL and Experian offer tools and services to monitor credit reports and address potential fraud.
Identifying Phishing Attempts and Online Scams Targeting Personal Financial Data
Phishing and other online scams are increasingly sophisticated, making it vital to understand how to identify and avoid them. These scams often exploit the fear and uncertainty following a data breach. Recognizing suspicious emails, websites, or messages can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these attacks.
- Suspicious Emails and Messages: Look for poorly written emails with grammatical errors, generic greetings, urgent requests for personal information, and links to unfamiliar websites. Legitimate financial institutions rarely ask for sensitive information via email or text message.
- Unfamiliar Websites: Check the website’s URL carefully. Look for misspellings or unusual characters. Legitimate banking websites typically use secure connections (HTTPS) and have a padlock icon in the address bar.
- Unexpected Phone Calls: Be wary of unsolicited calls from individuals claiming to be from your bank or other financial institutions. Never provide personal information over the phone unless you initiated the call and can verify the caller’s identity independently.
- Requests for Personal Information: Legitimate institutions rarely ask for all your personal information in one go. Be suspicious if a request seems too broad or unnecessary.
- Unusual Account Activity: Regularly check your bank statements and credit reports for any unauthorized transactions. Report any suspicious activity immediately to your bank.
Technological Solutions and Prevention
The massive data breach affecting 280 million Indian citizens highlights a critical need for robust technological safeguards within the banking sector. Preventing future incidents requires a multi-layered approach incorporating advanced security measures, stringent data protection protocols, and a commitment to continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices. This section will explore specific technological solutions and best practices that can significantly mitigate the risk of similar breaches.
Implementing effective technological solutions requires a holistic strategy encompassing several key areas. This includes strengthening network security, employing robust data encryption techniques, and implementing rigorous access control measures. Furthermore, regular security audits and penetration testing are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. The proactive adoption of these technologies and practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of future data breaches.
Encryption and Data Anonymization
Encryption is paramount in protecting sensitive data. Strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, should be used to encrypt data both in transit (while being transmitted over networks) and at rest (while stored on servers or databases). Data anonymization techniques, such as data masking and pseudonymization, can further enhance security by removing or replacing personally identifiable information (PII) with surrogate values, making the data less valuable to attackers even if a breach occurs.
For example, instead of storing a customer’s full name, a unique identifier could be used, linked to the anonymized data in a separate, highly secured database. This approach minimizes the impact of a potential breach by rendering the exposed data largely useless to malicious actors.
Cybersecurity Technologies Comparison
Several cybersecurity technologies can be effectively deployed to prevent and detect data breaches. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) monitor network traffic for malicious activity, while firewalls control network access, blocking unauthorized connections. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network without authorization. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources to detect and respond to security incidents.
The choice of technology depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization, but a layered approach utilizing multiple technologies is generally recommended for optimal protection. For instance, a bank might use a combination of firewalls, IDPS, DLP, and SIEM systems, along with regular penetration testing, to create a robust security posture.
The news about the exposure of bank account details for around 280 million Indian citizens is terrifying. This massive data breach highlights the urgent need for robust security measures, and it makes me wonder about the future of app development. Learning more about secure application building, like what’s discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , seems crucial now more than ever, especially considering the scale of this vulnerability and the potential for future breaches.
We need better solutions to protect sensitive data like this.
Best Practices for Data Security in the Financial Sector
Implementing robust data security practices is essential for protecting sensitive financial information. The following table Artikels some key best practices:
| Best Practice | Description | Implementation Example | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Security Audits | Periodic assessments of security controls to identify vulnerabilities. | Hiring a third-party security auditor to conduct annual penetration testing. | Early detection of vulnerabilities and proactive mitigation of risks. |
| Strong Access Control | Restricting access to sensitive data based on the principle of least privilege. | Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to grant users only the necessary permissions. | Reduced risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. |
| Employee Security Training | Educating employees about security threats and best practices. | Conducting regular phishing simulations and awareness training programs. | Improved employee awareness and reduced risk of social engineering attacks. |
| Incident Response Plan | A documented plan for handling security incidents, including data breaches. | Developing a comprehensive incident response plan that Artikels procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery. | Faster and more effective response to security incidents, minimizing the impact of breaches. |
Outcome Summary
The exposure of 280 million Indian citizens’ bank account details is a wake-up call, a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in our increasingly digital world. While the immediate focus is on mitigating the damage and assisting affected individuals, this incident underscores the critical need for comprehensive reforms in data security practices across the Indian banking sector and beyond.
We need stronger regulations, improved technological safeguards, and a significant increase in public awareness about online security threats. Only through a multi-pronged approach – encompassing technological solutions, robust regulatory frameworks, and responsible individual behavior – can we hope to prevent such catastrophic breaches from happening again. The long road to recovery begins now, and it’s a journey we must all undertake together.
Expert Answers
What types of financial crimes are likely to result from this breach?
Identity theft, fraudulent transactions, loan applications, account takeovers, and phishing scams are all major concerns.
How can I tell if my bank account has been compromised?
Monitor your accounts regularly for unauthorized transactions. Check your credit report for any suspicious activity. Be wary of unexpected communication from your bank.
What should I do if I suspect my information has been compromised?
Contact your bank immediately. Change your passwords and online banking security questions. Report the incident to the authorities.
What long-term effects might this breach have?
Erosion of public trust in banks, increased regulatory scrutiny, and potential long-term financial damage for victims are all possibilities.