Beware of This IRS Email Scam Loaded with Ransomware
Beware of this IRS email scam loaded with ransomware! These sneaky phishing attempts are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it harder to spot the red flags. Think you’re safe? Think again. This isn’t your grandpappy’s email scam; we’re talking ransomware, folks – the kind that locks up your precious files and demands a ransom for their release. This post dives deep into how these scams work, how to identify them, and what steps to take if you’ve fallen victim.
Let’s get started!
The IRS will
-never* contact you via email demanding immediate payment or threatening legal action. These scams use convincing subject lines, official-looking logos, and even spoofed email addresses to trick you. They often include malicious attachments or links that unleash ransomware onto your computer, encrypting your files and demanding a hefty payment for their decryption. The consequences can be devastating, leading to financial losses, data breaches, and significant disruptions to your life.
Understanding the tactics used is the first step to protecting yourself.
Understanding the Scam Email
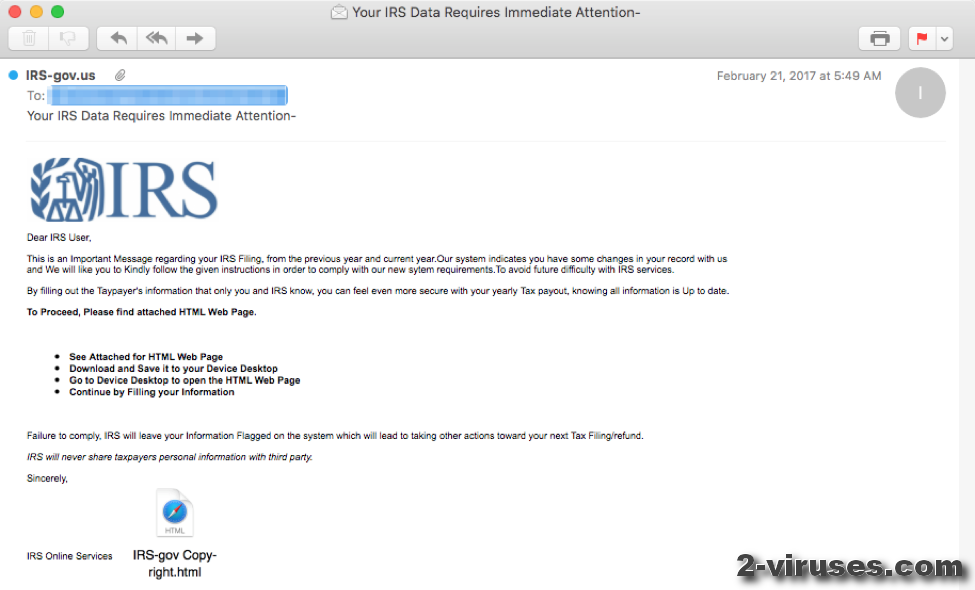
IRS phishing emails are a serious threat, designed to trick you into revealing sensitive personal and financial information or installing malware. These scams leverage fear and urgency to pressure victims into acting quickly without thinking critically. Understanding their common characteristics is crucial for effective protection.These emails often mimic official IRS communications, employing various deceptive tactics to gain your trust.
They typically prey on people’s anxieties surrounding tax obligations, using threats of legal action or financial penalties to create a sense of panic. This pressure often overrides critical thinking, leading victims to fall prey to the scam.
Typical Characteristics of IRS Phishing Emails
Phishing emails pretending to be from the IRS share several key traits. They often contain poor grammar and spelling errors, a common sign of fraudulent activity. The sender’s email address might appear legitimate at first glance, but closer inspection often reveals inconsistencies or suspicious domains. The emails frequently use generic greetings like “Dear Taxpayer” instead of your name, a clear indication of a mass-sent campaign.
They may include a sense of urgency, demanding immediate action or threatening severe consequences for inaction. Finally, they often contain links or attachments that lead to malicious websites or download ransomware.
Tactics Used to Appear Legitimate
These emails employ several tactics to enhance their credibility. They might include the official IRS logo or seal, attempting to visually legitimize the message. The email body often uses official-sounding language, referencing IRS regulations and procedures. They may even include seemingly legitimate details, such as a reference number or a specific tax year. However, these details are often fabricated or subtly altered to appear plausible but ultimately false.
The use of government-sounding email addresses, such as those ending in “.gov” (though often spoofed), contributes to the deception.
Examples of Subject Lines and Email Body Content
Subject lines often convey a sense of urgency and threat. Examples include: “Urgent Tax Notice,” “Immediate Action Required,” “IRS Legal Action,” or “Your Tax Refund is Delayed.” The email body typically claims some sort of tax issue, such as an unpaid tax bill, an error in your return, or an unexpected refund. They might threaten penalties, wage garnishment, or even arrest if you don’t respond immediately.
The body will almost always contain a link or attachment, often disguised as an official IRS form or document, designed to steal your information or install malware. For example, a body might state: “We have identified discrepancies in your tax return for the 2022 tax year. Please click here to resolve this issue immediately to avoid further penalties.”
Comparison of Legitimate and Scam IRS Communication Methods
| Communication Method | Legitimate IRS | Scam IRS Email |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Contact | Usually by mail; may use phone for complex cases | Always via email; often unsolicited |
| Personalization | Uses your full name and specific tax information | Uses generic greetings like “Dear Taxpayer” |
| Language | Clear, concise, and professional | May contain grammatical errors and informal language |
| Call to Action | Requests you visit the IRS website or call a specified number | Demands immediate action via a suspicious link or attachment |
The Ransomware Payload: Beware Of This Irs Email Scam Loaded With Ransomware

Ransomware is a malicious software designed to encrypt a victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. This isn’t just about inconvenience; it’s about the potential loss of crucial data and the significant financial and reputational damage that can follow. Understanding how ransomware operates is key to protecting yourself.Ransomware works by using strong encryption algorithms to scramble files, making them unreadable without the decryption key held by the attackers.
The encryption process is typically very fast and affects a large number of files simultaneously. Once encrypted, files are often renamed with extensions indicating the ransomware family, such as “.crypt”, “.locked”, or similar. The attackers then display a ransom note, usually detailing the amount of ransom demanded (often in cryptocurrency) and instructions on how to pay. Failure to pay often leads to the threat of permanent data loss, or the release of the encrypted data to the dark web.
Data Targeted by Ransomware
Ransomware attacks target a wide variety of data. The most valuable data is prioritized. This includes financial records, customer databases, intellectual property, medical records, and personal files. Essentially, any data that holds significant value to the victim is a prime target. The impact of a ransomware attack on an organization can range from minor disruption to complete business shutdown, depending on the criticality of the compromised data.
For example, a hospital losing access to patient medical records could face severe consequences, while a small business losing financial records could face bankruptcy.
Ransomware Delivery Methods
While email attachments remain a common delivery method, ransomware is increasingly spread through other vectors. These include malicious websites, compromised software, removable media (like infected USB drives), software vulnerabilities (exploiting security flaws in applications), and even through remote desktop protocol (RDP) attacks targeting poorly secured servers. Sophisticated ransomware campaigns often leverage a combination of techniques to maximize their success rate.
For instance, a phishing email might lure a victim to a malicious website, which then exploits a vulnerability to install the ransomware.
Encryption Techniques and Decryption Difficulty
Ransomware employs sophisticated encryption algorithms, often asymmetric encryption, to secure the files. Asymmetric encryption uses two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The attackers use the public key to encrypt the victim’s files and keep the private key for themselves. This makes decryption incredibly difficult without the private key. The strength of the encryption algorithms, coupled with the potential for the attackers to delete the private key after receiving the ransom, means that decryption is not always possible, even with specialized decryption tools.
In some cases, paying the ransom doesn’t guarantee decryption either; attackers might not provide the decryption key, or the provided key might not work correctly. The difficulty lies not just in the strength of the algorithm but also in the attackers’ ability to maintain control and anonymity.
Identifying and Avoiding the Scam
The IRS will never demand immediate payment via email, text, or social media. Understanding this fundamental truth is your first line of defense against these sophisticated phishing attempts. These scams leverage fear and urgency to pressure you into acting rashly, often before you have a chance to critically assess the communication. Let’s explore how to spot these fraudulent emails and protect yourself.Identifying suspicious emails from the IRS requires a keen eye and a healthy dose of skepticism.
Don’t fall prey to pressure tactics; instead, take your time to verify the sender’s legitimacy. Remember, the IRS prioritizes secure communication channels, not unsolicited emails demanding immediate action.
IRS Email Red Flags
A checklist of red flags can help you quickly assess the legitimacy of an email. The presence of even one red flag should raise significant concerns. Never click links or open attachments from suspicious emails.
- Generic Greetings: Emails from the IRS will usually address you by your full name, not a generic greeting like “Dear Sir/Madam” or “Valued Customer.”
- Threats and Demands: Legitimate IRS communications are professional and informative, not threatening or demanding immediate payment.
- Suspicious Links and Attachments: Hover your mouse over links to see the actual URL. Avoid clicking links that look suspicious or lead to unfamiliar websites. Never open attachments from unknown senders.
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: Official IRS communications are written professionally and free of grammatical errors.
- Unusual Email Addresses: The IRS uses official government email addresses, not free email services like Gmail or Yahoo.
- Requests for Personal Information: The IRS will not ask for sensitive information like your Social Security number, bank account details, or passwords via email.
- Sense of Urgency: Creating a false sense of urgency is a common tactic used in phishing emails. Legitimate communications provide ample time to respond.
Reporting a Suspected IRS Phishing Email
If you suspect you’ve received a phishing email impersonating the IRS, reporting it is crucial. This helps protect others from falling victim to the same scam.
- Forward the email: Forward the entire email (including headers) to [email protected].
- Delete the email: After forwarding, immediately delete the email from your inbox to prevent accidental clicks.
- Change your passwords: If you clicked on a link or opened an attachment, change your passwords immediately for all your online accounts.
- Monitor your accounts: Regularly check your bank and credit card statements for any unauthorized activity.
- Contact the IRS directly: If you are concerned about your tax situation, contact the IRS through official channels, such as their website or phone number, to verify the legitimacy of any communication.
Analyzing Email Headers
Email headers contain valuable information about the email’s origin and journey. Examining these headers can reveal suspicious elements. For example, a header might show the email originated from an IP address known for malicious activity or a non-IRS domain.
Example: A suspicious email header might show an “Received:” line indicating the email passed through several obscure servers before reaching your inbox, suggesting a possible attempt to mask its origin. Another red flag would be a “From:” address that doesn’t match the purported sender’s official IRS domain.
Post-Exposure Actions
Discovering you’ve interacted with a malicious email can be unsettling, but swift action significantly improves your chances of minimizing damage. This section details the crucial steps to take immediately after suspecting a ransomware infection. Remember, speed is of the essence.Immediate actions are critical to contain the spread of ransomware and limit the extent of data compromise. Delaying these steps can lead to irreversible data loss and significant financial repercussions.
Reporting the Incident
Reporting the incident is vital for several reasons. First, it allows law enforcement agencies to track the perpetrators and potentially disrupt their operations. Second, it helps security researchers understand the evolving tactics of ransomware groups, leading to better defenses in the future. Finally, reporting can trigger investigations that may lead to the recovery of some of your data.
You should report the incident to both the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). These agencies have dedicated resources to handle cybercrime reports and can provide valuable guidance. Be prepared to provide detailed information about the email, the ransomware, and any actions you’ve taken.
Data Recovery and System Restoration
Data recovery and system restoration after a ransomware attack can be complex and challenging. The success rate depends on several factors, including the type of ransomware, the level of encryption, and the extent of the infection. If you have regular backups stored offline (on a separate, physically unconnected device), this is your best bet for recovery. Restore your system from a known clean backup point, ensuring the backup is not also infected.
If you don’t have offline backups, professional data recovery services may be necessary. These services utilize specialized tools and techniques to try to decrypt your files or recover data from corrupted storage. However, this is often an expensive endeavor, and there’s no guarantee of success. In some cases, the ransomware may have permanently damaged your data beyond recovery.
Seriously, folks, those IRS email scams are vicious – ransomware is no joke! It’s a good reminder to be vigilant about phishing attempts. Meanwhile, I’ve been diving into the world of app development, exploring the exciting possibilities discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , which is a fascinating contrast to the malicious code behind those scams.
So, stay safe online and keep your eyes peeled for those dodgy emails!
Disconnecting Infected Systems
Immediately disconnect the infected system from the network, both wired and wireless. This prevents the ransomware from spreading to other devices on your network, protecting other computers and data. This isolation step is crucial before attempting any recovery or remediation actions. If the infected system is a server, the consequences of inaction can be far more extensive, affecting many users and causing significant disruption.
System and Data Backup Strategy
A robust backup strategy is the first line of defense against ransomware. This includes regular backups of all critical data, stored offline and in multiple locations. Employ the 3-2-1 backup rule: maintain three copies of your data, on two different media, with one copy stored offsite. This approach minimizes the risk of complete data loss, even in the event of a catastrophic failure or ransomware attack.
Consider using cloud-based backup services, but ensure they offer strong security features to prevent unauthorized access. Regular testing of your backup and recovery processes is also vital to ensure they function correctly when needed.
Flowchart Illustrating Actions After Ransomware Infection
The following describes a flowchart illustrating the steps to take. Imagine a diagram with boxes and arrows. The first box would be “Suspect Ransomware Infection?”. If yes, an arrow points to “Disconnect from Network”. Then, “Backup Exists?”.
If yes, an arrow points to “Restore from Backup”. If no, an arrow points to “Contact Data Recovery Specialist”. From both “Restore from Backup” and “Contact Data Recovery Specialist”, arrows point to “Report to Authorities (IC3 and CISA)”. Finally, an arrow from “Report to Authorities” points to “Review Security Practices”. This visual representation helps guide users through the necessary steps in a clear and concise manner.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Protecting yourself from ransomware attacks like the IRS email scam requires a multi-layered approach focusing on proactive measures and robust security practices. This isn’t just about reacting to threats; it’s about building a strong defense to prevent them from ever taking hold. By combining technological safeguards with responsible online behavior, you significantly reduce your vulnerability.
Email Security Best Practices
Implementing strong email security measures is crucial. This includes being vigilant about suspicious emails, never clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown senders, and regularly reviewing your email filters to ensure they are effectively blocking spam and phishing attempts. Consider enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) for your email account, adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Training yourself to spot phishing attempts—look for grammatical errors, unusual sender addresses, and urgent requests for personal information—is equally vital. Remember, legitimate organizations rarely demand immediate payment or sensitive data via email.
Safe Internet Browsing Habits
Safe internet browsing complements strong email security. Avoid visiting untrusted websites or clicking on links from unknown sources. Keep your browser and its plugins updated, as outdated software often contains vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit. Use strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts and consider using a password manager to help you manage them effectively. Be cautious about downloading software from unofficial sources; stick to reputable app stores and websites.
Regularly clear your browsing history and cookies to minimize your digital footprint and reduce the risk of tracking.
Security Software and Tools
Employing robust security software is a cornerstone of a comprehensive security strategy. A reputable antivirus program with real-time protection can detect and remove malware, including ransomware. Consider adding a firewall to monitor and control network traffic, preventing unauthorized access to your system. A web filter can help block access to malicious websites and phishing attempts. Many security suites combine these features into a single package, offering a convenient and effective solution.
Examples of such software include Norton 360, McAfee Total Protection, and Bitdefender Total Security. These programs regularly update their virus definitions and security protocols, ensuring continued protection against emerging threats.
Software Updates and Patching
Regularly updating your software is paramount. Operating systems, applications, and browsers frequently release patches to address security vulnerabilities. These updates often fix bugs and flaws that ransomware and other malware can exploit. Enable automatic updates whenever possible to ensure your systems are always running the latest, most secure versions. Failing to update your software leaves your systems vulnerable to attacks, negating the effectiveness of other security measures.
Regularly check for updates on all your devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets.
Comprehensive Security Plan for Individuals and Small Businesses
A comprehensive security plan should encompass all aspects of digital security. For individuals, this involves practicing safe browsing habits, using strong passwords, regularly updating software, and employing robust security software. For small businesses, this expands to include employee training on security awareness, implementing access control measures, and regularly backing up data to a secure, offsite location. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Develop an incident response plan outlining steps to take in the event of a ransomware attack, including contacting IT professionals and law enforcement if necessary. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of a successful attack and facilitates a swift recovery.
Legal and Financial Implications
Falling victim to an IRS email scam containing ransomware can have severe legal and financial repercussions. The consequences extend beyond the immediate loss of data and money, impacting your credit, reputation, and potentially leading to legal battles. Understanding these implications is crucial for both recovery and prevention.The financial impact of such a scam can be devastating. Direct losses include the ransom itself, the cost of data recovery services (if successful), and expenses incurred in notifying affected parties, like customers or clients, if your business was compromised.
Indirect costs include lost productivity, potential business disruption, legal fees for pursuing legal action against perpetrators (if feasible), and the cost of credit monitoring and identity theft protection. Moreover, reputational damage can lead to lost business opportunities and difficulty securing future contracts. The legal implications involve potential violations of data protection laws like GDPR or CCPA if personal or sensitive data was compromised, leading to fines and lawsuits.
Potential Legal Consequences
Victims of ransomware attacks, especially those involving fraudulent IRS emails, might face legal repercussions stemming from data breaches. If the attack results in the unauthorized release of personal information belonging to employees, clients, or other individuals, the victim organization could face lawsuits for negligence or failure to protect sensitive data. This is particularly relevant under regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, which impose strict requirements on data security and breach notification.
Non-compliance can result in significant fines. Furthermore, if the organization is found to have acted recklessly or knowingly disregarded security best practices, it could face criminal charges in some jurisdictions. Individuals may also face legal action if they were involved in fraudulent activities related to the scam, even unknowingly.
Financial Implications of Ransomware Attacks
The financial burden of a ransomware attack extends far beyond the ransom payment itself. Data recovery can be extremely expensive, especially if professional services are required. Legal fees for handling breach notifications, responding to lawsuits, or pursuing legal action against attackers can also quickly accumulate. Beyond direct costs, there are indirect losses to consider. Lost productivity due to system downtime, the cost of replacing damaged hardware or software, and potential business disruption can severely impact profitability.
The long-term impact on reputation and customer trust can lead to lost business opportunities, decreased revenue, and ultimately, financial instability. In some cases, businesses may even face bankruptcy. For example, a small business might not survive the financial fallout from a ransomware attack that demands a substantial ransom and disrupts operations for an extended period.
Resources for Victims
Several organizations offer assistance to victims of ransomware attacks. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) is a valuable resource for reporting cybercrimes and receiving guidance. The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) in the UK and similar agencies in other countries provide valuable information and support. Additionally, various cybersecurity firms specialize in incident response and data recovery.
Seeking legal counsel from a lawyer experienced in data breach and cybersecurity law is highly recommended to understand your rights and options. They can advise on compliance with data protection regulations and represent you in legal proceedings if necessary.
Potential Financial Losses Associated with a Ransomware Attack, Beware of this irs email scam loaded with ransomware
The financial impact of a ransomware attack can be significant and multifaceted. It’s essential to consider the various potential losses:
- Ransom payment
- Data recovery costs
- Legal fees
- Cost of incident response services
- Lost productivity and revenue
- Cost of system repairs and replacements
- Cost of credit monitoring and identity theft protection
- Reputational damage and loss of business
- Regulatory fines for non-compliance
- Potential litigation costs
Ending Remarks
So, the bottom line? Don’t fall for these IRS email scams! Staying vigilant is your best defense. Learn to spot the red flags, be cautious of unexpected emails, and always verify communication through official IRS channels. Remember, your data is valuable, and protecting it is your responsibility. If you’ve already been targeted, don’t panic – follow the steps Artikeld in this post to mitigate the damage and report the incident.
Stay safe, stay informed, and stay ransomware-free!
Popular Questions
What should I do if I accidentally opened a suspicious email?
Immediately disconnect from the internet, run a full virus scan, and change your passwords. Contact your IT professional or a cybersecurity expert for assistance.
Can I recover my files if they’ve been encrypted by ransomware?
Data recovery is possible, but it’s often complex and costly. Professional data recovery services may be needed. Do NOT pay the ransom, as there’s no guarantee you’ll get your files back.
How can I report an IRS phishing email?
Forward the email to [email protected]. You can also report it to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at reportfraud.ftc.gov.
Are there any free tools to help detect and remove ransomware?
Several reputable antivirus programs offer free scans and malware removal tools. However, professional assistance may be necessary for complex infections.