
Britain Watchdog Fines Equifax £658,000 for EternalBlue Breach
Britain watchdog 658000 fine on equifax and nsa eternal blue cyber threat – Britain Watchdog Fines Equifax £658,000 for EternalBlue Breach – that headline alone screams cybersecurity drama! Remember the massive Equifax data breach? Well, the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) just slapped them with a hefty fine, highlighting the devastating consequences of failing to protect sensitive data. This wasn’t just any breach; it involved the infamous EternalBlue exploit, a vulnerability famously linked to the NSA.
Let’s dive into the details of this significant case and explore the implications for data security worldwide.
This post unpacks the ICO’s decision, explaining the circumstances leading to the £658,000 penalty, the role of the EternalBlue exploit, and Equifax’s response (or lack thereof). We’ll also discuss the broader implications for data protection and cybersecurity, examining the lessons learned and best practices for preventing similar breaches in the future. Get ready for a deep dive into the world of data breaches and the crucial need for robust cybersecurity measures!
The UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) Fine

The UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) levied a substantial fine on Equifax in 2021, highlighting the significant consequences of failing to adequately protect personal data. This penalty underscores the ICO’s commitment to enforcing data protection regulations and holding organizations accountable for breaches.
Circumstances Surrounding the £658,000 Fine
The ICO’s investigation into Equifax followed a data breach affecting approximately 400,000 UK citizens. The breach, discovered in July 2017, involved the exposure of sensitive personal information, including names, addresses, dates of birth, and driver’s licence numbers. The ICO determined that Equifax failed to implement appropriate security measures to protect this data, leading to the significant breach. The investigation focused on Equifax’s failure to address known vulnerabilities in its systems and its inadequate response to the breach itself.
Data Breaches Leading to the Penalty
The primary cause of the data breach was Equifax’s failure to patch a known vulnerability in its systems, specifically the Apache Struts vulnerability. This allowed unauthorized access to the company’s servers, resulting in the exfiltration of personal data. The ICO also criticized Equifax’s lack of robust security protocols, insufficient staff training, and inadequate incident response planning. The failure to implement and maintain appropriate security measures, coupled with a slow and inadequate response to the breach, were key factors contributing to the severity of the fine.
Calculation of the Fine and Relevant Legislation
The £658,000 fine was calculated in accordance with the UK’s Data Protection Act 2018, which allows for substantial fines for organizations that fail to comply with data protection regulations. The ICO considered the scale of the breach, the number of individuals affected, the severity of the data compromised, and Equifax’s failure to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures. The fine reflects the seriousness of the breach and serves as a deterrent to other organizations.
While the exact calculation methodology isn’t publicly available in detail, the ICO’s decision Artikeld the factors considered in determining the appropriate penalty. The legislation allows for fines up to £17.5 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. In Equifax’s case, the fine was significantly lower, likely reflecting mitigating factors considered by the ICO.
Comparison to Other ICO Fines for Data Breaches
The £658,000 fine, while substantial, falls below some of the largest fines levied by the ICO for data breaches. For instance, British Airways received a £20 million fine for a data breach affecting hundreds of thousands of customers, and Marriott International was fined £99.2 million for a data breach impacting millions of guests. The disparity in fines reflects the varying circumstances of each breach, including the number of individuals affected, the sensitivity of the data compromised, and the organization’s response to the breach.
However, the Equifax fine serves as a significant example of the ICO’s commitment to holding organizations accountable for data protection failures.
Hypothetical ICO Press Release Announcing the Decision
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
ICO Fines Equifax £658,000 for Data Breach Affecting 400,000 UK Citizens
The UK’s hefty £658,000 fine on Equifax for their role in the NSA’s EternalBlue cyber threat highlights the critical need for robust security. Building secure applications is paramount, and that’s where understanding the evolving landscape of application development comes in, like exploring the exciting possibilities discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future.
Ultimately, strong security practices, regardless of development methodology, remain essential to prevent future breaches like the Equifax incident.
London, [Date] – The Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) today announced a monetary penalty notice (MPN) of £658,000 against Equifax Limited for serious breaches of the UK’s data protection law. The ICO’s investigation found that Equifax failed to take adequate measures to secure personal data, resulting in a data breach affecting approximately 400,000 individuals. The breach exposed sensitive personal information including names, addresses, and dates of birth. The ICO found that Equifax failed to implement appropriate security measures and did not adequately respond to the breach. The fine reflects the seriousness of the breach and the ICO’s commitment to holding organizations accountable for protecting personal data.
“Organisations must take responsibility for protecting personal data. Equifax’s failure to implement basic security measures and respond appropriately to the breach is unacceptable. This penalty should serve as a warning to other organisations that failing to protect personal data will have serious consequences.” – Information Commissioner, [Name]
The EternalBlue Exploit and its Impact
The Equifax data breach of 2017, resulting in the exposure of sensitive personal information for millions of individuals, serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of unpatched vulnerabilities. A critical factor in this breach was the exploitation of the EternalBlue exploit, a piece of malware leveraging a previously unknown vulnerability in Microsoft’s Windows operating systems. Understanding EternalBlue’s role is crucial to grasping the scale and severity of the Equifax incident.The EternalBlue exploit leveraged a vulnerability (MS17-010) in the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, a core component of Windows used for file sharing and network communication.
This specific vulnerability allowed attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code on affected systems without requiring user interaction. In essence, it provided a backdoor into vulnerable machines, enabling attackers to gain complete control. The exploit, initially developed by the NSA, was leaked online, making it readily available to malicious actors. This accessibility greatly increased the threat landscape, as cybercriminals could easily weaponize EternalBlue to target organizations with outdated systems.
EternalBlue’s Exploitation Method in the Equifax Breach
The attackers used EternalBlue to gain initial access to Equifax’s systems. Once inside, they moved laterally, exploiting additional vulnerabilities and gaining access to sensitive databases. The attackers were able to leverage the initial access provided by EternalBlue to escalate their privileges and ultimately access the databases containing personal information. This highlights the importance of not only patching known vulnerabilities but also implementing robust network segmentation and access control measures to limit the impact of successful breaches.
Systems and Data Affected by EternalBlue at Equifax
The EternalBlue exploit allowed attackers to compromise Equifax servers holding sensitive personal information, including names, Social Security numbers, addresses, and driver’s license numbers. The exact number of affected systems remains undisclosed, but the scale of the breach involved the compromise of databases containing data for approximately 147 million individuals. The impact extended beyond individual consumers to include the broader financial system, due to the potential for identity theft and fraud.
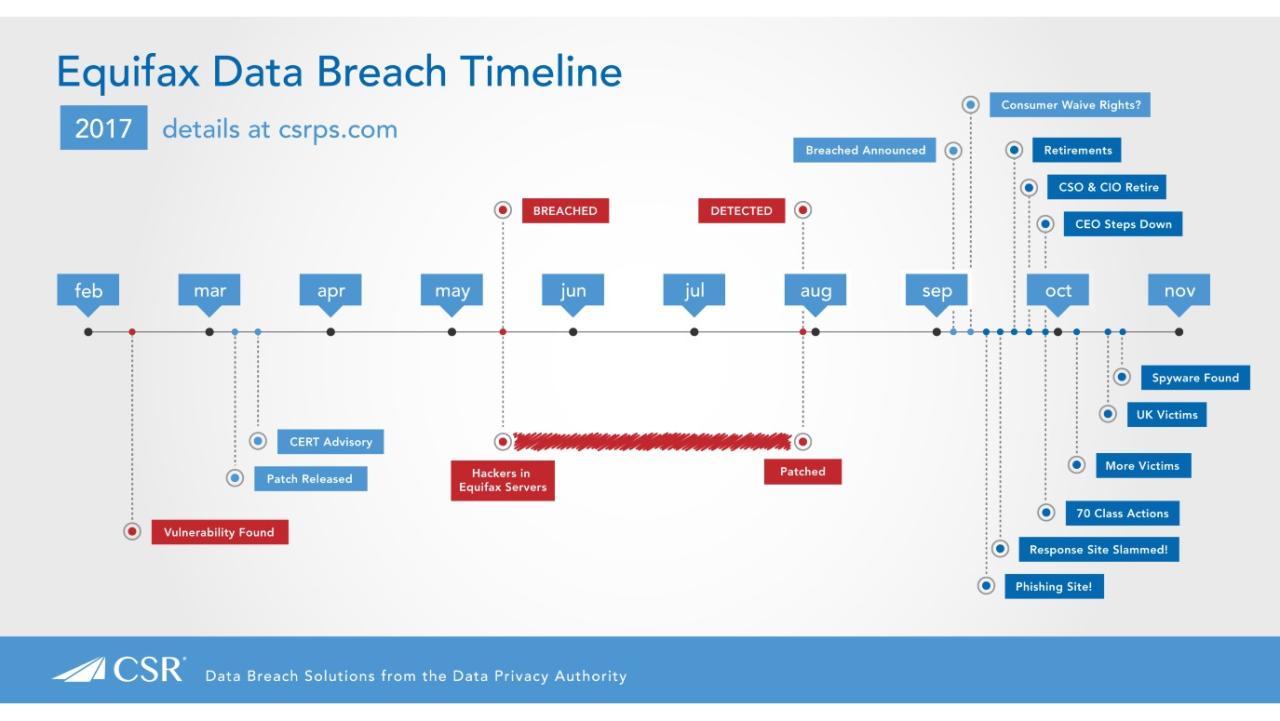
Timeline of the Equifax Breach
While the precise dates remain partially obscured due to the investigation, the timeline of the Equifax breach, as understood from public reports, indicates that the initial compromise via EternalBlue occurred in mid-May 2017. The breach went undetected for several weeks, with the company only discovering the intrusion in July 2017. The delay in discovery allowed the attackers ample time to exfiltrate vast amounts of data.
The public disclosure of the breach occurred in September 2017, triggering widespread concern and legal repercussions.
Key Characteristics of EternalBlue and its Impact on Equifax
| Vulnerability | Exploitation Method | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS17-010 (SMB vulnerability) | Remote code execution via SMB protocol | Initial system compromise, data exfiltration, widespread identity theft | Patching systems, network segmentation, intrusion detection systems |
Equifax’s Response and Remediation Efforts
Equifax’s response to the 2017 data breach, which exposed the personal information of nearly 148 million people, was widely criticized for its slowness, lack of transparency, and perceived inadequacy. The company’s initial actions, or rather, inactions, significantly exacerbated the situation and ultimately contributed to the severity of the damage. This section will examine Equifax’s response, its remediation efforts, and how its actions compared to industry best practices.Equifax’s initial response to the discovery of the breach in July 2017 was far from swift or decisive.
The company waited several weeks before publicly disclosing the breach, a delay that allowed the attackers more time to potentially exploit the compromised data and hampered efforts to mitigate the damage. Furthermore, initial communications with affected individuals were unclear and lacked crucial information. This lack of transparency fueled public anger and distrust.
Timeline of Equifax’s Actions Following the Breach Discovery
The following timeline highlights key events in Equifax’s response to the data breach:
- July 2017: Equifax discovers the data breach. Internal investigation begins.
- September 7, 2017: Equifax publicly discloses the breach.
- September 2017: Equifax establishes a website and hotline for affected consumers to access credit monitoring services.
- October 2017: Equifax faces intense congressional scrutiny and multiple lawsuits.
- January 2018: The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) files a complaint against Equifax.
- July 2018: Equifax agrees to a $700 million settlement with the FTC, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), and 48 states.
This timeline illustrates the significant delay between the discovery of the breach and the public disclosure. This delay allowed for potential further exploitation of the stolen data and significantly damaged the company’s reputation.
The £658,000 fine levied on Equifax by the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office for their failure to protect customer data following the NSA’s EternalBlue exploit highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity. This incident underscores why proactive measures are essential, and understanding solutions like those offered by Bitglass, as detailed in this excellent article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management , is crucial.
Ultimately, preventing breaches, like the one Equifax suffered, requires a multi-layered approach to security, emphasizing cloud security posture management.
Equifax’s Remediation Efforts and Security Improvements
Following the breach, Equifax claimed to have implemented various security improvements. These included enhancing its vulnerability management program, investing in advanced threat detection technologies, and improving its employee training on cybersecurity best practices. However, the effectiveness of these measures remains a subject of debate, particularly given the severity of the original breach and the subsequent criticism.
Comparison to Industry Best Practices
Equifax’s response fell short of industry best practices in several key areas. Rapid and transparent disclosure of data breaches is considered a crucial element in minimizing damage and maintaining public trust. Equifax’s delayed disclosure and initial lack of transparency violated this principle. Furthermore, the company’s seemingly inadequate security measures prior to the breach demonstrate a failure to meet industry standards for data protection.
Proactive vulnerability management, robust security testing, and employee training are all critical components of a strong cybersecurity posture, and Equifax’s apparent shortcomings in these areas directly contributed to the scale of the breach.
Equifax’s Actions and the Severity of the Breach, Britain watchdog 658000 fine on equifax and nsa eternal blue cyber threat
Equifax’s delayed response and inadequate security measures significantly amplified the severity of the breach. The prolonged period between the discovery of the breach and its public disclosure allowed the attackers to potentially exfiltrate more data and potentially conduct further malicious activities. The lack of transparency eroded public trust and led to widespread anxiety among affected individuals. The financial and reputational damage to Equifax was substantial, highlighting the significant costs associated with failing to adequately address data security and respond effectively to a breach.
The settlement demonstrates the substantial legal and financial consequences that can result from inadequate response to a data breach.
Data Protection and Cybersecurity Implications
The Equifax breach, resulting in the exposure of sensitive personal data for millions of individuals, serves as a stark reminder of the critical importance of robust data protection and cybersecurity measures. The incident highlighted significant vulnerabilities in Equifax’s systems and processes, underscoring the devastating consequences of inadequate security protocols for both organizations and consumers. The £658,000 fine levied by the UK’s ICO, while substantial, only scratches the surface of the broader ramifications of this breach.The Equifax data breach had far-reaching implications, extending beyond the immediate financial losses and reputational damage suffered by the company.
The exposure of personal information, including Social Security numbers, addresses, and driver’s license numbers, put countless individuals at risk of identity theft, fraud, and other forms of financial and personal harm. This breach also eroded public trust in Equifax and the broader credit reporting industry, highlighting the need for increased transparency and accountability in data handling practices. The use of the EternalBlue exploit, a known vulnerability, further emphasizes the importance of proactive patching and vulnerability management.
Lessons Learned from the Equifax Breach
The Equifax case provides several crucial lessons for organizations handling sensitive data. Firstly, the delay in disclosing the breach amplified its impact. Swift and transparent communication with affected individuals and regulatory bodies is paramount. Secondly, the failure to promptly patch known vulnerabilities, such as EternalBlue, demonstrates the critical need for proactive vulnerability management and a robust patching strategy.
Finally, the lack of adequate security monitoring and incident response capabilities hampered Equifax’s ability to detect and contain the breach effectively. These shortcomings underscore the need for comprehensive security architectures that incorporate multiple layers of defense, including intrusion detection systems, security information and event management (SIEM) tools, and regular security audits.
Robust Cybersecurity Measures for Organizations Handling Sensitive Data
Organizations handling sensitive data must implement a multi-layered security approach encompassing various technical and non-technical measures. This includes strong access controls, data encryption both in transit and at rest, regular security awareness training for employees, and robust incident response plans. Investing in advanced threat detection and response technologies, such as threat intelligence platforms and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) tools, is also crucial.
Furthermore, regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments are essential to identify and address security weaknesses proactively. The adoption of a zero-trust security model, which assumes no implicit trust, and verifies every user and device before granting access, is becoming increasingly important. Finally, adherence to relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is non-negotiable.
Best Practices for Preventing and Responding to Cyberattacks
Preventing and responding to cyberattacks requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. This includes implementing strong password policies, enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regularly updating software and firmware. Regular security awareness training for employees is vital to reduce the risk of phishing attacks and other social engineering techniques. Developing and regularly testing incident response plans is crucial to minimize the impact of a successful breach.
This includes establishing clear communication protocols, defining roles and responsibilities, and outlining procedures for data recovery and containment. Organizations should also invest in robust security monitoring and logging capabilities to detect and respond to threats quickly.
Recommendations for Enhancing Data Security Posture
The following recommendations can help organizations significantly enhance their data security posture:
- Implement a comprehensive vulnerability management program, including regular patching and security assessments.
- Enforce strong access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all systems and applications.
- Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
- Conduct regular security awareness training for all employees.
- Develop and regularly test incident response plans.
- Invest in robust security monitoring and logging capabilities.
- Adopt a zero-trust security model.
- Comply with all relevant data protection regulations.
- Regularly review and update security policies and procedures.
- Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify and address security weaknesses.
The Role of the National Security Agency (NSA): Britain Watchdog 658000 Fine On Equifax And Nsa Eternal Blue Cyber Threat

The alleged involvement of the National Security Agency (NSA) in the 2017 Equifax data breach, through the EternalBlue exploit, remains a highly controversial topic. The situation highlights the complex interplay between national security interests, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and the ethical responsibilities of government agencies. Understanding the NSA’s alleged role requires examining the exploit itself, the agency’s response, and the broader implications for data protection and international relations.The NSA’s alleged role centers on the development and subsequent leak of EternalBlue, a powerful exploit targeting a vulnerability in Microsoft’s Windows operating systems.
Reports suggest that the NSA developed EternalBlue as a cyber weapon, utilizing it for intelligence gathering purposes. However, the exploit was later leaked by the Shadow Brokers, a mysterious hacking group, making it readily available to other malicious actors. This leak is alleged to have facilitated the Equifax breach, where cybercriminals exploited the vulnerability to gain access to sensitive personal data of millions of individuals.
The EternalBlue Exploit and the Equifax Breach
EternalBlue’s effectiveness stemmed from its ability to exploit a critical vulnerability (MS17-010) in older versions of Microsoft Windows. This vulnerability allowed remote code execution, granting attackers complete control over affected systems. Critically, the vulnerability was known to the NSA prior to its public disclosure. The failure to patch the vulnerability or otherwise mitigate its risk, coupled with the subsequent leak of the exploit, arguably contributed to the devastating Equifax breach, where hackers exploited this vulnerability to gain access to the company’s systems and exfiltrate sensitive customer data.
The scale of the breach underscored the severe consequences of both the vulnerability itself and the unauthorized release of the exploit.
Ethical and Legal Implications of NSA Involvement
The alleged NSA involvement raises significant ethical and legal questions. The development and use of cyber weapons, even for intelligence gathering, involves inherent risks. The potential for unintended consequences, such as the leak and subsequent misuse of such weapons, necessitates a rigorous ethical framework for their development, deployment, and control. The lack of transparency surrounding the NSA’s handling of the EternalBlue vulnerability further complicates the ethical picture.
Legal implications include potential liability for damages resulting from the misuse of the exploit, as well as scrutiny under laws related to data protection and cybersecurity. The incident sparked considerable debate about the appropriate balance between national security and the protection of civilian data.
Controversy Surrounding the Release of EternalBlue
The release of EternalBlue by the Shadow Brokers sparked intense controversy. The leak exposed a previously unknown vulnerability, leaving millions of systems vulnerable to attack. The speed and scale of subsequent attacks highlighted the critical need for rapid patching and improved cybersecurity practices. The controversy also extended to the NSA’s alleged role in creating the exploit and the potential failure to adequately secure it, leading to widespread criticism of the agency’s cybersecurity practices and oversight.
The lack of proactive measures to prevent the exploit’s dissemination further fuelled the controversy.
Comparison of NSA Response to Similar Situations
While the NSA’s response to the EternalBlue leak and its consequences is a subject of intense debate and analysis, comparisons to its response to similar situations involving vulnerabilities are difficult due to the inherent secrecy surrounding such operations. However, the incident brought into sharp focus the need for a more robust and transparent approach to vulnerability management within the agency, along with a clearer framework for addressing the ethical implications of developing and deploying cyber weapons.
The incident spurred discussions about improved information sharing practices between government agencies and the private sector to improve overall cybersecurity.
Impact of NSA Actions on National Security and International Relations
The NSA’s actions, both in developing EternalBlue and in its handling of the vulnerability, had a significant impact on national security and international relations. The leak damaged the reputation of the United States and its intelligence agencies, raising concerns about the potential for misuse of such capabilities. Furthermore, the incident heightened tensions in the realm of cybersecurity, underscoring the potential for offensive cyber capabilities to backfire and create unforeseen risks.
The global implications underscored the need for international cooperation in addressing cybersecurity threats and establishing norms of responsible state behavior in cyberspace.
Conclusion
The Equifax breach, and the subsequent £658,000 fine levied by the ICO, serves as a stark reminder of the high stakes involved in data security. The use of the EternalBlue exploit underscores the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats and the critical need for proactive security measures. While the fine is a significant step, the real takeaway should be a renewed focus on robust cybersecurity practices, transparent incident response, and a commitment to protecting sensitive data.
Let this case serve as a cautionary tale for businesses of all sizes – failing to prioritize data security is simply not an option.
FAQ Insights
What exactly is the EternalBlue exploit?
EternalBlue is a computer worm that exploits a vulnerability in older versions of Microsoft’s Windows operating system. It allows attackers to remotely access and control affected computers.
How did the NSA get involved?
The NSA allegedly developed the EternalBlue exploit as a tool for its own cyber operations. The exploit later leaked online, making it available to malicious actors.
What could Equifax have done differently?
Equifax could have implemented stronger security measures, including patching known vulnerabilities promptly and investing in more robust intrusion detection systems.
What are the long-term consequences for Equifax?
Beyond the financial penalty, Equifax faces reputational damage and potential legal action from affected individuals. The breach could also lead to stricter regulatory scrutiny.





