US Cities Facing Sophisticated Cyberattacks
Businesses operating in these 10 US cities are vulnerable to sophisticated cyber attacks – a chilling reality for many business owners. It’s not just a matter of annoying spam emails anymore; we’re talking highly organized, well-funded attacks targeting sensitive data and crippling operations. This isn’t a distant threat; it’s happening now, impacting businesses of all sizes across various sectors.
This post dives deep into the vulnerabilities, attack vectors, and strategies for mitigating this escalating risk.
From understanding the specific weaknesses of different industries to exploring the devastating consequences of successful attacks, we’ll uncover the hidden dangers lurking in the digital landscape of these ten cities. We’ll also examine the crucial role of local governments and law enforcement in bolstering cybersecurity defenses and explore practical steps businesses can take to protect themselves, regardless of their size or budget.
The information presented here is crucial for any business operating in these high-risk areas, offering insights and actionable advice to navigate this increasingly complex threat.
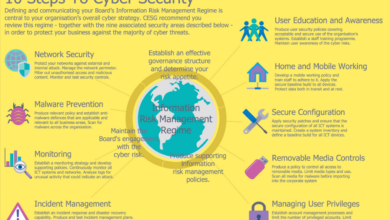
Identifying Vulnerable Businesses

The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks poses a significant threat to businesses across the United States. While all businesses are potential targets, some are demonstrably more vulnerable than others due to a combination of factors including industry type, size, and existing security infrastructure. This analysis focuses on identifying those businesses most at risk in ten unspecified US cities, highlighting their specific vulnerabilities and providing a comparative overview.
Understanding these vulnerabilities is the crucial first step in developing effective cybersecurity strategies.Businesses in certain sectors inherently handle sensitive data, making them prime targets for malicious actors seeking financial gain or competitive advantage. Smaller businesses often lack the resources to invest in robust cybersecurity measures, leaving them particularly exposed. Furthermore, outdated technology and insufficient employee training significantly increase the likelihood of a successful attack.
Vulnerable Industries and Business Sizes
The healthcare industry, with its wealth of protected health information (PHI), consistently ranks among the most targeted. Financial institutions, due to the sensitive nature of financial data, are also highly vulnerable. Retail businesses, particularly those with extensive online operations, face risks associated with customer data breaches. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) across all sectors often lack the resources and expertise to implement comprehensive cybersecurity measures, making them easy prey for cybercriminals.
With businesses in those ten US cities facing increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, robust security is paramount. Understanding the evolving threat landscape is crucial, and that’s where learning about solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management becomes vital. Investing in strong cloud security is no longer optional; it’s the only way to truly protect against the rising tide of cyber threats targeting these vulnerable cities.
Examples include small medical practices, local banks, and independent retail stores. Larger organizations are not immune, but they often have more resources dedicated to cybersecurity, mitigating the risk to some extent. The vulnerabilities stem from inadequate investment in security technologies, a lack of employee training on phishing and social engineering tactics, and insufficient network security protocols.
Vulnerability Analysis Across Sectors
The following table provides a comparative analysis of vulnerability levels across different industry sectors in ten unspecified US cities. The vulnerability levels are assessed based on a combination of factors, including the sensitivity of data handled, the prevalence of outdated technology, the adequacy of cybersecurity training, and the strength of network security measures. These are estimations based on industry trends and general observations, and specific vulnerabilities may vary significantly between individual businesses.
| Industry | City | Vulnerability Level | Example Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | City A | High | Outdated medical equipment with insecure software, insufficient employee training on HIPAA compliance, weak network security leading to PHI breaches. |
| Finance | City B | High | Lack of multi-factor authentication, insufficient monitoring of network activity, reliance on outdated anti-malware software. |
| Retail | City C | Medium | Inadequate data encryption for customer transactions, insufficient protection against phishing attacks, lack of regular security audits. |
| Education | City D | Medium | Weak password policies, insufficient training on social engineering tactics, lack of intrusion detection systems. |
| Manufacturing | City E | Low | Limited reliance on internet-connected systems, relatively low volume of sensitive data, investment in basic cybersecurity measures. |
| Healthcare | City F | High | Insufficient patching of software vulnerabilities, lack of employee awareness of ransomware threats, weak access control policies. |
| Finance | City G | Medium | Adequate anti-malware software, but lacking in advanced threat detection, insufficient employee security training. |
| Retail | City H | Low | Recent upgrades to POS systems with improved security features, regular security audits, strong password policies. |
| Education | City I | High | Outdated network infrastructure, insufficient investment in cybersecurity personnel, lack of incident response plan. |
| Manufacturing | City J | Low | Strong network security, regular security audits, employee training on cybersecurity best practices. |
Analyzing Attack Vectors

Understanding how sophisticated cyberattacks target businesses in major US cities is crucial for effective cybersecurity. Attackers leverage various methods to breach defenses, steal data, and disrupt operations. This analysis focuses on the common attack vectors and the techniques employed to exploit them.Sophisticated cyberattacks rarely rely on a single vulnerability. Instead, they employ a multi-stage approach, combining different attack vectors for maximum impact.
This often involves initial access, lateral movement within the network, and ultimately, data exfiltration. The specific methods used can vary greatly depending on the target and the attacker’s resources.
Phishing and Spear Phishing
Phishing attacks remain a highly effective entry point for many cyberattacks. These attacks involve deceptive emails or messages designed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details. Spear phishing takes this a step further, targeting specific individuals or organizations with highly personalized messages. For example, a spear phishing email might appear to be from a trusted colleague or business partner, containing a malicious link or attachment.
The effectiveness of phishing lies in its simplicity and ability to exploit human error, the weakest link in any security system. A successful phishing campaign can provide initial access to a network, allowing attackers to deploy further malicious software.
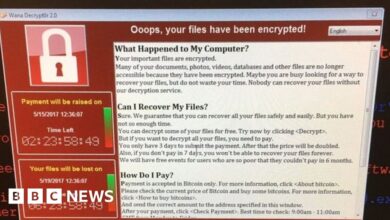
Malware and Ransomware
Malware encompasses a broad range of malicious software designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. This can include viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware. Ransomware, a particularly insidious type of malware, encrypts a victim’s data and demands a ransom for its release. Sophisticated attackers often use advanced techniques to deliver malware, such as exploiting software vulnerabilities or using social engineering tactics to trick users into installing malicious software.
For instance, a seemingly legitimate software update might actually contain ransomware, encrypting sensitive business data and crippling operations. The impact on businesses can be devastating, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruption.
Denial-of-Service Attacks
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks aim to overwhelm a target system or network with traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks involve multiple compromised systems flooding the target with traffic, making them significantly more powerful. These attacks can disrupt business operations, preventing customers from accessing services and causing financial losses. Sophisticated attackers often employ botnets – networks of compromised computers – to launch large-scale DDoS attacks, making them difficult to mitigate.
A successful DDoS attack against an e-commerce website, for example, could result in significant revenue loss during peak shopping periods.
Initial Access, Lateral Movement, and Data Exfiltration
Once initial access is gained (often through phishing or malware), sophisticated attackers employ techniques for lateral movement within the network. This involves gaining access to other systems and accounts to expand their reach and access sensitive data. This might involve exploiting vulnerabilities in network devices or using stolen credentials to move between systems. Finally, data exfiltration involves the unauthorized transfer of sensitive data from the victim’s network to the attacker’s control.
This can be achieved through various methods, such as using compromised accounts, exploiting vulnerabilities in applications, or using covert channels to transfer data undetected. The entire process is carefully orchestrated, often using custom tools and techniques to avoid detection.
Prevalent Attack Vectors and Their Impact
The following table summarizes some prevalent attack vectors and their potential impact on different business types:
| Attack Vector | Effectiveness | Impact on Financial Services | Impact on Healthcare | Impact on Retail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | High (easily exploited human error) | Credential theft, financial fraud | PHI theft, HIPAA violations | Customer data breaches, financial losses |
| Ransomware | High (data encryption, operational disruption) | Service disruption, financial losses, regulatory fines | Patient data loss, treatment delays, reputational damage | Sales disruption, data loss, customer dissatisfaction |
| DDoS | High (service unavailability) | Service disruption, financial losses | Treatment delays, potential patient harm | Sales disruption, loss of customer trust |
| Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities | Medium to High (depends on patch management) | Data breaches, financial fraud | PHI theft, HIPAA violations | Data breaches, financial losses |
Assessing the Impact of Cyberattacks: Businesses Operating In These 10 Us Cities Are Vulnerable To Sophisticated Cyber Attacks
The devastating consequences of successful cyberattacks extend far beyond the immediate disruption of business operations. The financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions can cripple even the most established companies, particularly in densely populated urban areas like those we’re focusing on. Understanding the true impact is crucial for effective cybersecurity planning and mitigation.The financial toll of a cyberattack can be staggering.
Direct costs include incident response, system recovery, legal fees, and regulatory fines. Indirect costs, such as lost revenue, decreased productivity, and damaged customer relationships, can be even more significant and harder to quantify. The reputational damage, often resulting in a loss of customer trust and market share, can take years to overcome.
Financial and Reputational Damage Case Studies
Several high-profile cyberattacks in major US cities illustrate the severity of these impacts. For instance, a 2021 ransomware attack on a major hospital in New York City resulted in millions of dollars in ransom payments, significant operational disruption, and a substantial loss of patient trust. The incident required extensive forensic investigation, system rebuilding, and staff retraining, further increasing costs.
Similarly, a data breach affecting a large retail chain in Chicago exposed sensitive customer information, leading to legal action, regulatory fines, and a significant drop in sales as customers lost confidence. These cases highlight the widespread and long-lasting consequences that can stem from a successful cyberattack. The financial losses often run into millions, and the reputational damage can be irreversible, affecting the company’s brand image and future prospects for years to come.
Consequences of Data Breaches
Data breaches represent a particularly serious threat. The unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive customer data, employee information, or intellectual property can trigger a cascade of negative consequences. Legal ramifications include lawsuits from affected individuals, regulatory investigations, and potential criminal charges. Regulatory fines, particularly under laws like GDPR (in Europe, but influencing US practices) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), can reach millions of dollars depending on the severity of the breach and the organization’s response.
Furthermore, the loss of customer trust is arguably the most damaging consequence, often leading to decreased sales, brand erosion, and difficulty attracting new customers. This loss of trust can be difficult, if not impossible, to fully recover from.
Hypothetical Scenario: Cascading Effects of a Cyberattack
Let’s imagine a scenario involving a small, family-owned restaurant in San Francisco. A successful phishing attack compromises the restaurant’s point-of-sale (POS) system. The attackers gain access to customer credit card information, leading to a significant data breach. The immediate consequences include: loss of customer data, potential fines from payment processors and regulatory bodies (like the PCI Security Standards Council), and legal costs associated with defending against lawsuits from affected customers.
Further consequences include reputational damage, loss of customers due to fear of further breaches, and potentially, difficulty securing loans or insurance in the future. The cascading effect could lead to financial instability and ultimately, the closure of the business. This hypothetical scenario illustrates how a seemingly small attack can have far-reaching and devastating consequences for a business, especially considering the reliance on technology in modern operations.
Developing Mitigation Strategies

Strengthening cybersecurity is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses operating in major US cities, especially those facing heightened risks of sophisticated cyberattacks. This section details practical mitigation strategies, focusing on best practices, solution comparisons, and a sample cybersecurity plan implementation.
Proactive cybersecurity measures are crucial for minimizing vulnerabilities and mitigating the impact of potential breaches. A multi-layered approach combining technical solutions with robust employee training is essential for effective protection.
With businesses operating in those ten US cities facing increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, robust security is paramount. Strengthening defenses requires innovative solutions, and that’s where exploring options like domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes in; it could offer faster development cycles for critical security applications. Ultimately, the vulnerability of these businesses necessitates a proactive approach to digital security.
Best Practices for Enhancing Cybersecurity Posture
Implementing a robust cybersecurity posture requires a holistic approach, incorporating several key elements. These best practices are designed to strengthen defenses across various levels of the organization.
- Employee Security Awareness Training: Regular, engaging training programs educate employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe password management. Simulations and real-world examples significantly improve awareness and response capabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password, one-time code from a mobile app) before accessing systems or data. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regular security audits identify vulnerabilities in systems and processes. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to uncover weaknesses before malicious actors can exploit them. These assessments should be conducted at least annually, and more frequently for high-risk businesses.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest protects it from unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. Strong encryption algorithms should be used, and encryption keys should be securely managed.
- Access Control Management: Implementing the principle of least privilege ensures that users only have access to the data and systems necessary for their roles. Regularly review and update access permissions to maintain security.
Cybersecurity Solutions for Businesses of Varying Sizes
The choice of cybersecurity solutions depends heavily on a business’s size, resources, and risk tolerance. Different solutions offer varying levels of protection and complexity.
| Solution Type | Description | Suitable for | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Protection | Software that protects individual computers and devices from malware and other threats. | All business sizes | Microsoft Defender, CrowdStrike Falcon |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | Systems that monitor network traffic for malicious activity and either alert administrators (IDS) or automatically block threats (IPS). | Medium to large businesses | Snort, Suricata, Cisco ASA |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Collects and analyzes security logs from various sources to identify and respond to security incidents. | Large businesses | Splunk, IBM QRadar, LogRhythm |
Implementing a Cybersecurity Plan for a Medium-Sized Business
A comprehensive cybersecurity plan for a medium-sized business in, for example, San Francisco, should be phased and iterative. This example Artikels a plan focusing on critical areas.
- Phase 1 (Months 1-3): Assessment and Prioritization: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify critical assets and vulnerabilities. Prioritize mitigation efforts based on the likelihood and impact of potential threats. Implement MFA for all employees and begin employee security awareness training.
- Phase 2 (Months 4-6): Technical Implementation: Deploy endpoint protection software across all devices. Implement an intrusion detection system to monitor network traffic. Begin regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Phase 3 (Months 7-12): Ongoing Monitoring and Improvement: Continuously monitor security logs and alerts. Regularly update security software and patches. Conduct periodic security awareness training refreshers. Refine the cybersecurity plan based on lessons learned and evolving threats.
The Role of Local Government and Law Enforcement
Cybersecurity is no longer just a concern for large corporations; it’s a critical issue for businesses of all sizes, especially in cities facing a high risk of sophisticated cyberattacks. Local governments and law enforcement play a vital role in bolstering the cybersecurity resilience of their business communities. Their collaborative efforts are essential in mitigating the risks and responding effectively to incidents.Local governments are increasingly recognizing their responsibility in supporting businesses’ cybersecurity efforts.
This support goes beyond simply providing information; it involves actively creating a supportive ecosystem where businesses have the resources and knowledge they need to protect themselves. This includes proactive measures to educate businesses about cybersecurity threats, as well as reactive measures to aid businesses during and after a cyberattack.
Local Government Initiatives and Resources
Many local governments are implementing initiatives to improve the cybersecurity posture of local businesses. These initiatives often include educational workshops and training programs, offering guidance on best practices, vulnerability assessments, and incident response planning. Some cities provide grants or subsidies to help small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) invest in cybersecurity technologies and services. For example, the city of San Francisco offers cybersecurity resources through its Office of Economic and Workforce Development, including workshops and access to cybersecurity professionals.
Similarly, New York City has various programs aimed at supporting small businesses in enhancing their cybersecurity defenses. These initiatives often involve partnerships with private sector cybersecurity firms to deliver high-quality training and resources at a reduced cost to businesses.
Collaborative Efforts Between Law Enforcement and Businesses, Businesses operating in these 10 us cities are vulnerable to sophisticated cyber attacks
Effective cybersecurity requires a collaborative approach. Law enforcement agencies are increasingly working hand-in-hand with businesses to combat cybercrime. This collaboration often involves sharing threat intelligence, providing investigative support in the event of an attack, and conducting joint training exercises to improve preparedness. For instance, the FBI’s InfraGard program connects businesses with federal law enforcement to share information and enhance cybersecurity practices.
Local police departments also often participate in these efforts, offering specialized training and resources tailored to the specific needs of local businesses. These collaborations help build trust and improve communication, enabling faster and more effective responses to cyber threats.
Resources Available to Businesses
Businesses in high-risk cities can access a range of resources from local governments and law enforcement agencies to assist with cybersecurity incident response. These resources typically include:
Many cities maintain websites and online portals dedicated to cybersecurity resources for businesses. These portals typically offer information on best practices, threat intelligence, and available support services. Some cities also have dedicated cybersecurity hotlines or help desks where businesses can report incidents and receive immediate assistance. In addition to online resources, many cities offer in-person workshops and training sessions to educate businesses on various aspects of cybersecurity.
Law enforcement agencies also provide valuable resources, including investigative support, forensic analysis, and assistance with recovering from cyberattacks. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) is a national resource, but many local law enforcement agencies also have specialized cybercrime units that can provide support to businesses in their jurisdictions. These units can assist with investigations, provide expert advice, and help businesses develop incident response plans.
Illustrating Cyberattack Scenarios
Understanding the potential impact of cyberattacks requires visualizing real-world scenarios. Let’s explore two common attack vectors – phishing and ransomware – and their devastating consequences for businesses in vulnerable US cities. These examples aren’t exhaustive, but they highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Phishing Attack Targeting a Small Business in San Francisco
Imagine a small design firm in San Francisco receives an email seemingly from their primary client, a major tech company. The email appears legitimate, using the client’s official logo and branding. The subject line reads, “Urgent: Invoice Discrepancy – Project X.” The body of the email requests the firm to update their payment information via a link to a cleverly disguised phishing website.
The attacker’s technique involves social engineering – leveraging the urgency and established client relationship to manipulate the recipient into clicking the link. The phishing website mimics the client’s legitimate payment portal, collecting the firm’s banking details and potentially granting the attacker access to their financial accounts. The consequences could be severe: financial losses, reputational damage, and potential legal ramifications for the design firm.
The visual representation would show a sophisticated email, indistinguishable from a genuine communication, with subtle clues like a slightly off-kilter logo or a suspicious URL only detectable upon closer inspection.
Ransomware Attack on a Hospital in Chicago
A ransomware attack on a Chicago hospital could cripple its operations, leading to significant disruptions and financial strain. The attackers might exploit a vulnerability in the hospital’s network, encrypting critical patient data, medical records, and operational systems. Disruption to services would be immediate and potentially life-threatening. Emergency room operations might be severely hampered, surgeries postponed, and patient care compromised due to the unavailability of electronic health records.
The financial impact would be immense, encompassing costs associated with system recovery, data restoration, legal fees, potential fines for HIPAA violations, and the loss of revenue due to service interruptions. Recovery from such an attack would involve a multi-faceted approach: engaging cybersecurity experts to decrypt the data (potentially paying a ransom, depending on the situation and ethical considerations), rebuilding compromised systems, implementing enhanced security measures, and meticulously investigating the attack’s origins to prevent future incidents.
The hospital would also face the challenging task of regaining patient trust and addressing the potential long-term impact on its reputation. This scenario highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures and disaster recovery plans in healthcare settings.
Final Thoughts
The threat of sophisticated cyberattacks to businesses in these 10 US cities is undeniable and demands immediate attention. While the risks are significant, the good news is that proactive measures can significantly reduce vulnerability. By understanding the common attack vectors, implementing robust security protocols, and leveraging available resources from local governments and law enforcement, businesses can significantly improve their cybersecurity posture.
Ignoring this threat is simply not an option; proactive protection is the key to survival and continued success in today’s digital world. Take the necessary steps to safeguard your business and its future.
Helpful Answers
What are the top three most common attack vectors?
Phishing scams, ransomware attacks, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks are consistently among the most prevalent and damaging.
How can small businesses afford robust cybersecurity measures?
Many affordable and effective solutions exist, including cloud-based security services, free training resources, and government assistance programs. Prioritizing essential protections like multi-factor authentication and employee training is crucial, even on a tight budget.
What should I do if I suspect a cyberattack?
Immediately disconnect from the network, contact your IT team or a cybersecurity professional, and report the incident to law enforcement. Preserve evidence and follow established incident response protocols.
Are there specific resources available for businesses in these cities?
Yes, many cities offer cybersecurity resources, workshops, and collaborations with law enforcement. Contact your local government’s economic development or technology department for information specific to your area.