Can Negotiations Yield Success in Ransomware Attacks?
Can negotiations yield success in ransomware attacks? This question is increasingly critical in our hyper-connected world. Ransomware attacks are becoming more sophisticated and frequent, leaving individuals and organizations scrambling for solutions. While paying a ransom seems like a simple fix, it’s a complex decision with significant ethical, legal, and financial implications. This post dives deep into the murky world of ransomware negotiations, exploring the strategies, pitfalls, and ultimately, the chances of a successful outcome.
We’ll examine successful and failed negotiations, analyze attacker motivations, and provide a framework for making informed decisions in the face of this growing threat.
We’ll explore the different types of ransomware, the factors influencing the decision to negotiate, and the critical role of a skilled negotiation team. We’ll also discuss the psychological aspects of dealing with cybercriminals, the importance of establishing clear goals, and the need for a robust post-negotiation plan. Through real-world examples and insightful analysis, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of whether negotiating with ransomware attackers is a viable strategy, and if so, how to approach it effectively.
The Nature of Ransomware Negotiations
Negotiating with ransomware attackers is a complex and ethically fraught decision. The potential for success, and the very act of negotiating, hinges on a multitude of factors, including the type of ransomware used, the attacker’s motivations, and the victim’s resources and risk tolerance. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating this precarious situation.Ransomware attacks vary significantly, impacting negotiation strategies accordingly.
Some attacks employ simple encryption, targeting individual users with relatively small ransom demands. Others involve sophisticated techniques like double extortion, where data is both encrypted and exfiltrated, creating leverage for the attackers. The more complex the attack, the more challenging and potentially costly the negotiation becomes. For example, a simple encryption attack targeting a home user might be resolved with a relatively small payment, while a large-scale attack against a hospital, involving sensitive patient data, might require extensive negotiation and potentially far higher sums.
The negotiation strategy must be tailored to the specific circumstances of the attack.
Types of Ransomware Attacks and Their Impact
The type of ransomware attack significantly influences the negotiation strategy. Crypto-ransomware, which encrypts files, is relatively straightforward, with negotiations focusing on the ransom amount and decryption key. However, ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) attacks, where attackers use a shared platform, introduce additional complexities. Negotiations might involve dealing with intermediaries, and the attackers may have less direct control over the encryption process.
Double extortion attacks, where data is both encrypted and exfiltrated, present the most difficult negotiation scenario. The threat of data leak adds immense pressure, often leading to higher ransom demands and more complex negotiations. The attackers might also demand a higher ransom to prevent the release of sensitive information on the dark web. Successful negotiations in these cases often involve a combination of ransom payment and a non-disclosure agreement to prevent data publication.
Conversely, unsuccessful negotiations can result in significant reputational damage and financial losses.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Negotiations
A successful negotiation might involve a company paying a ransom to regain access to critical data, securing a decryption key and an agreement to delete the stolen data. This outcome, while costly, prevents further disruption to business operations and protects sensitive information. Conversely, an unsuccessful negotiation could involve the refusal to pay a ransom, leading to irreversible data loss and significant financial consequences.
The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021 serves as a high-profile example where a ransom payment was made to restore operations. While controversial, the decision was deemed necessary to avoid significant disruptions to fuel supplies. In contrast, many smaller businesses that do not pay ransoms often face severe consequences, including business closure.
Factors Influencing the Decision to Negotiate
Several factors influence the decision to negotiate. These include the value of the encrypted data, the likelihood of successful recovery, the potential financial and reputational damage from a data breach, and the availability of insurance coverage. The potential legal implications of paying a ransom are also a significant consideration, as some jurisdictions view ransom payments as funding criminal activity.
Furthermore, paying a ransom might encourage future attacks, as it demonstrates the victim’s willingness to pay. Organizations must carefully weigh the risks and benefits before deciding to negotiate.
Negotiating Versus Not Negotiating, Can negotiations yield success in ransomware attacks
| Factor | Negotiating: Advantages | Negotiating: Disadvantages | Not Negotiating: Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Recovery | Potential for data recovery | May encourage future attacks; potential legal repercussions | Avoids funding criminal activity |
| Financial Impact | May minimize financial losses compared to data loss | High ransom costs | Lower immediate financial cost (but potential for greater long-term costs) |
| Reputational Impact | May mitigate reputational damage by preventing data leaks | Potential reputational damage associated with paying ransom | Avoids admitting vulnerability |
| Operational Impact | Faster restoration of operations | Delays in recovery if negotiations fail | Potential for longer downtime |
Identifying Negotiator Strengths and Weaknesses
Successful ransomware negotiations hinge on a skilled negotiator’s ability to leverage strengths while mitigating weaknesses. This involves understanding the psychological dynamics at play, employing effective tactics, and assembling a robust team. A failure in any of these areas can significantly compromise the chances of a positive outcome.Negotiating with cybercriminals demands a unique skillset, combining empathy, strategic thinking, and a firm understanding of the legal and technical aspects of the situation.
The process isn’t simply about exchanging money for data; it’s about managing risk, building trust (however fragile), and navigating a complex web of legal and ethical considerations. A well-defined strategy, coupled with an understanding of the attacker’s motivations, is crucial.
Effective Negotiation Tactics in Ransomware Incidents
Effective tactics often involve a measured approach that balances firmness with flexibility. For instance, a negotiator might initially offer a lower ransom than initially demanded, justifying the amount based on a thorough assessment of the data’s value and the potential damage from a leak. This approach demonstrates seriousness without immediately conceding to the attacker’s demands. Simultaneously, they might seek to establish a clear communication channel and timeline for payment and decryption.
In some cases, negotiators might offer to pay a smaller amount upfront as a “good faith” gesture, contingent upon a demonstration of the decryption capabilities. Crucially, all communications should be meticulously documented to protect the victim organization from potential legal ramifications. The ultimate goal is to de-escalate the situation and secure the data with minimal financial and reputational harm.
Psychological Aspects of Negotiating with Cybercriminals
Negotiating with cybercriminals requires an understanding of their psychology. They are often motivated by financial gain, but their behavior can also be influenced by factors such as ego, risk tolerance, and a desire for anonymity. A skilled negotiator will attempt to understand these motivations to tailor their approach. For example, building rapport, even with a malicious actor, can help to establish a degree of trust and encourage cooperation.
This doesn’t mean being overly friendly or compromising one’s position, but rather demonstrating respect and professionalism. Conversely, the negotiator must also be prepared for deception and manipulation. The cybercriminals may exaggerate their capabilities or threaten to leak data even if they have no intention of doing so. Maintaining a calm and controlled demeanor, even in the face of threats, is essential.
Importance of a Skilled Negotiation Team
A successful negotiation requires a multidisciplinary team. This team typically includes legal counsel to ensure compliance with regulations and to mitigate legal risks, cybersecurity experts to assess the technical aspects of the attack and verify decryption, public relations specialists to manage communication with stakeholders, and, of course, a lead negotiator with experience in crisis management and high-stakes negotiations. Each member brings a unique perspective and expertise, ensuring a comprehensive and effective response.
The team’s collaborative effort is crucial for coordinating actions, analyzing information, and making informed decisions under pressure. Clear communication and well-defined roles within the team are essential for success.
Potential Negotiation Pitfalls and Strategies to Avoid Them
Understanding potential pitfalls is critical for a successful negotiation. Failing to prepare adequately can lead to disastrous outcomes.
- Pitfall: Overpaying the ransom. Strategy: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to determine the actual value of the data and the potential cost of a data breach. Explore all other options, such as data recovery or alternative solutions, before resorting to payment.
- Pitfall: Lack of clear communication channels. Strategy: Establish a secure and reliable communication channel from the outset. Document all communications meticulously.
- Pitfall: Trusting the attacker’s promises without verification. Strategy: Demand proof of decryption capabilities before making any significant payments. Verify the decryption process independently.
- Pitfall: Failing to involve legal counsel. Strategy: Seek legal advice early in the process to understand legal implications and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Pitfall: Responding emotionally to threats. Strategy: Maintain a calm and professional demeanor throughout the negotiation. Avoid making rash decisions under pressure.
Assessing the Attacker’s Motivations
Understanding the motivations behind ransomware attackers is crucial for successful negotiation. It allows for a more strategic approach, potentially leading to a more favorable outcome and minimizing further damage. Different groups operate with varying levels of sophistication and goals, requiring a nuanced understanding of their individual drivers.
Ransomware attackers are primarily motivated by financial gain. The amount demanded often reflects the perceived value of the stolen data and the potential damage caused by its release or disruption of services. However, financial gain is not the sole motivator; some groups are also driven by ideological reasons, aiming to disrupt critical infrastructure or express political grievances. The level of sophistication of the attack and the attacker’s communication style can offer valuable clues about their motivations.
Key Motivators for Ransomware Attackers
Several factors influence a ransomware attacker’s willingness to negotiate. The most prominent is the potential financial reward. The size of the ransom demand is often calculated based on factors like the victim’s perceived ability to pay, the sensitivity of the data, and the attacker’s assessment of the likelihood of successful payment. Beyond monetary gain, some groups seek publicity and recognition for their exploits, while others may be driven by a desire to demonstrate their technical capabilities or affiliation with a larger criminal network.
Comparing Motivations Across Ransomware Groups
Different ransomware groups exhibit varying motivations. Some, like Conti, were known for their highly organized structure and focus on financially lucrative targets, often targeting large corporations. Their primary motivation was financial gain, with a clear business model centered around efficient extortion. In contrast, groups like REvil demonstrated a more opportunistic approach, sometimes targeting smaller organizations or individuals for relatively smaller ransoms.
Their motivations might have been a mix of financial gain and testing their capabilities. The level of communication, the sophistication of the attack, and the demands themselves can often point towards the group’s underlying goals. For example, groups motivated by ideology may include specific demands related to their political agenda, unlike financially motivated groups that focus solely on monetary compensation.
Determining Attacker Credibility and Trustworthiness
Assessing the credibility and trustworthiness of a ransomware attacker is challenging but essential. Previous behavior and reputation within the cybercriminal underworld play a significant role. Open-source intelligence (OSINT) gathering can reveal information about past attacks, ransom payment histories, and any associated online forums or communication channels. Analyzing their communication style, consistency of demands, and willingness to provide proof of data possession can help assess their trustworthiness.
A highly organized group with a history of successful negotiations might be more trustworthy than a less organized group with a history of failed attempts or inconsistent behavior. However, even seemingly trustworthy groups should be approached with caution, as their primary goal remains financial gain.
Assessing Attacker Motives: A Flowchart
A systematic approach is necessary to assess the attacker’s motives effectively. The following flowchart Artikels the key steps involved:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a “Start” box, followed by boxes representing steps like: 1. Gather Intelligence on the Attacker (OSINT, Dark Web forums), 2. Analyze Ransom Note and Communication Style, 3. Assess the Sophistication of the Attack, 4.
Evaluate Past Behavior and Reputation, 5. Identify Potential Motivations (Financial, Ideological, etc.), 6. Determine Credibility and Trustworthiness, and finally a “End” box. Arrows would connect these boxes to illustrate the sequential steps involved in the assessment process. The boxes would contain brief descriptions of the actions involved in each step.]
Developing a Negotiation Strategy

Ransomware negotiations are high-stakes affairs, demanding a carefully crafted strategy to maximize the chances of a successful outcome while minimizing potential harm. A well-defined plan, built on clear goals and a nuanced understanding of the attacker, is crucial for navigating these complex situations. Failing to develop a robust strategy can lead to escalating demands, prolonged downtime, and ultimately, a less favorable resolution.Effective negotiation hinges on a proactive and strategic approach, rather than reacting to the attacker’s demands.
This involves setting clear objectives, understanding your leverage, and employing appropriate negotiation tactics. The strategy should be adaptable, allowing for adjustments based on the attacker’s responses and the evolving situation.
Establishing Clear Negotiation Goals and Objectives
Before engaging in any negotiations, it’s imperative to define precise goals and objectives. These should go beyond simply recovering encrypted data. Consider factors like minimizing financial losses, limiting reputational damage, and preventing future attacks. For example, a hospital might prioritize restoring patient records and ensuring the continued functionality of critical systems over minimizing the ransom payment. A financial institution, on the other hand, might prioritize preventing data breaches and protecting sensitive customer information above all else.
These prioritized objectives will shape the negotiation strategy and determine acceptable compromises. Setting measurable objectives allows for a clear evaluation of the success of the negotiation process.
Negotiation Strategies: Collaborative and Competitive Approaches
The choice between collaborative and competitive negotiation strategies depends heavily on the specific circumstances. A collaborative approach emphasizes finding mutually beneficial solutions, fostering trust and cooperation. This might involve seeking common ground with the attacker, exploring alternative solutions to full payment, or focusing on information sharing to build a foundation for a resolution. However, a collaborative approach is not always feasible, particularly with sophisticated or malicious actors.In contrast, a competitive approach prioritizes securing the best possible outcome for the victim, even if it means adopting a more adversarial stance.
Negotiating with ransomware attackers is a risky gamble; success isn’t guaranteed. Building robust security systems, however, is a much surer bet, and that’s where understanding the evolving landscape of application development comes in. Check out this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future to see how improved app security can help mitigate future attacks, ultimately making negotiations less necessary.
This could involve leveraging legal threats, engaging law enforcement, or employing deception tactics. This approach demands careful execution, as it risks escalating the situation or damaging any potential for future collaboration. The choice between these strategies should be carefully weighed, considering the attacker’s profile, the potential risks and rewards, and the available resources. A hybrid approach, blending elements of both strategies, may also prove effective in certain scenarios.
Setting Boundaries and Maintaining a Firm Stance
Negotiations with ransomware attackers are often emotionally charged. It’s crucial to establish clear boundaries and maintain a firm stance throughout the process. This involves setting limits on what concessions will be made, refusing unreasonable demands, and adhering to a well-defined negotiation protocol. For example, refusing to pay an exorbitant ransom or provide additional sensitive information beyond what is absolutely necessary demonstrates resolve and can influence the attacker’s behavior.
Flexibility is important, but unwavering adherence to core principles prevents exploitation and maintains leverage. A firm stance, coupled with a clear understanding of the legal and ethical implications, protects the victim’s interests.
A Step-by-Step Plan for Conducting Ransomware Negotiations
A structured approach is essential for effective ransomware negotiations. The following plan provides a framework:
- Assess the Situation: Identify the type of ransomware, the extent of the data breach, and the attacker’s demands.
- Assemble a Negotiation Team: Include legal counsel, cybersecurity experts, and communication specialists.
- Establish Communication Channels: Use secure and encrypted communication methods to interact with the attacker.
- Gather Intelligence: Research the attacker’s past activities and identify their motivations.
- Develop a Negotiation Strategy: Choose a collaborative or competitive approach, or a hybrid strategy, based on the assessment of the situation.
- Set Clear Boundaries and Objectives: Define limits on concessions and prioritize objectives.
- Engage in Negotiations: Communicate with the attacker, making offers and counter-offers based on the established strategy.
- Document Everything: Maintain a detailed record of all communications and agreements.
- Verify the Decryption Process: Ensure the decryption key works as promised before making any final payments.
- Report the Incident: Notify relevant authorities and law enforcement agencies.
Post-Negotiation Considerations
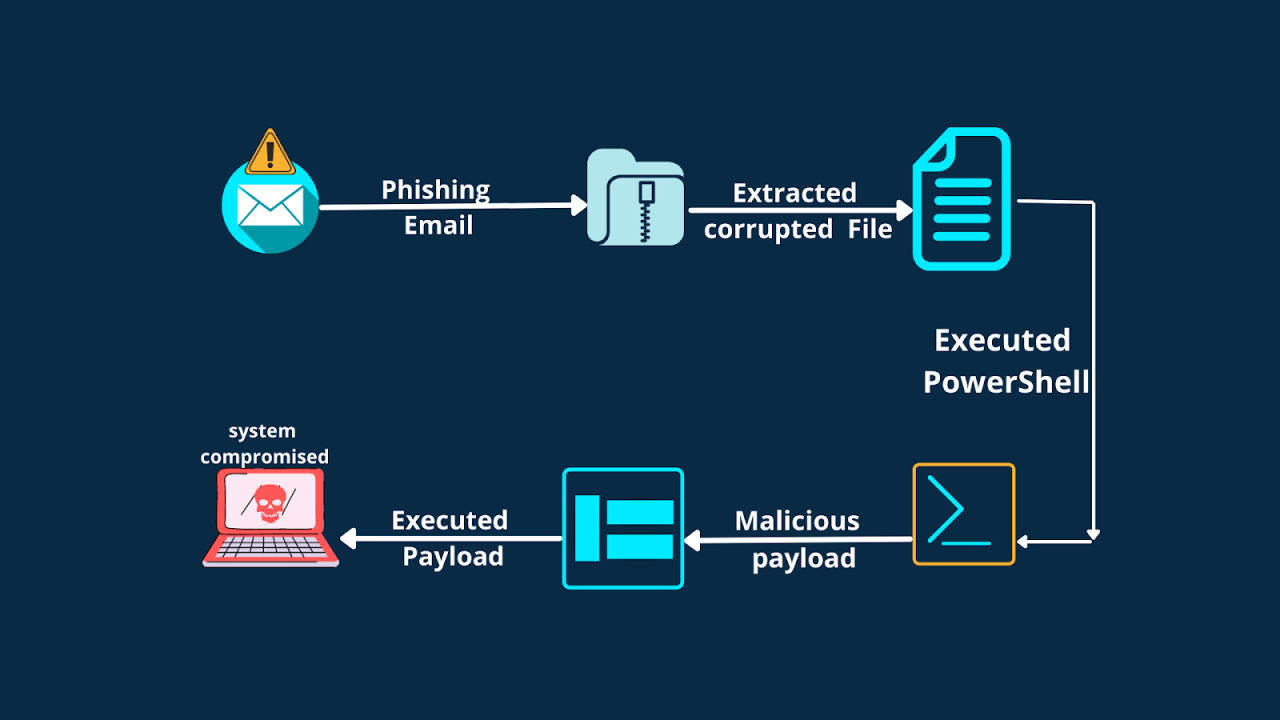
Negotiating a ransom payment doesn’t mark the end of the ransomware ordeal; it’s merely the beginning of a complex recovery process. Successful negotiation requires careful planning for the aftermath, encompassing technical restoration, legal considerations, and a thorough post-incident analysis to prevent future attacks. Ignoring these crucial post-negotiation steps can lead to prolonged downtime, significant financial losses, and lasting reputational damage.
Post-Incident Analysis and Lessons Learned
A comprehensive post-incident analysis is paramount. This involves meticulously documenting every step of the attack, from initial infection to the final payment and system restoration. This documentation should include details about the ransomware variant, the attack vector (e.g., phishing email, software vulnerability), the impact on systems and data, the negotiation process itself, and the effectiveness of existing security measures.
This detailed analysis allows for identifying vulnerabilities, improving security protocols, and developing more robust incident response plans. For example, a company might discover that a lack of multi-factor authentication allowed the initial breach, leading to the implementation of MFA across all systems post-incident. The analysis also helps in quantifying the financial losses incurred, including ransom payments, recovery costs, and potential business interruption costs.
System and Data Restoration
Restoring systems and data after a ransomware attack requires a methodical approach. This often involves engaging cybersecurity professionals specializing in data recovery. The process might include wiping affected systems and reinstalling operating systems and applications, restoring data from backups (if available and untainted), and verifying the integrity of recovered data. Prioritizing critical systems and data is essential. For instance, a hospital might prioritize restoring patient medical records before focusing on administrative systems.
The restoration process should be thoroughly tested to ensure all systems and data are functioning correctly and that the ransomware has been completely eradicated. This might involve running malware scans and penetration testing to identify any lingering vulnerabilities.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
Ransomware attacks and the subsequent negotiations often have significant legal and regulatory implications. Companies must comply with data breach notification laws, which vary by jurisdiction. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) requires businesses to notify California residents of data breaches. Furthermore, regulatory bodies like the FTC may investigate the incident, and failure to cooperate fully can result in hefty fines.
It’s crucial to engage legal counsel specializing in cybersecurity and data privacy to navigate these complexities and ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. This might involve conducting a legal risk assessment and developing a comprehensive legal response plan. Internal investigations might also be required to determine the extent of the breach and any potential liability.
Post-Negotiation Checklist
To ensure a smooth and effective post-negotiation process, it’s vital to create and follow a comprehensive checklist. This checklist should include:
- Securely destroy all copies of the ransom payment transaction records.
- Conduct a thorough forensic analysis of the compromised systems.
- Restore systems and data from clean backups, verifying data integrity.
- Implement enhanced security measures to prevent future attacks (e.g., multi-factor authentication, endpoint detection and response).
- Update security awareness training for employees.
- Notify affected parties (customers, partners, regulators) as required by law.
- Engage legal counsel to assess legal and regulatory implications.
- Document all actions taken during the incident response and recovery process.
- Conduct a post-incident review to identify areas for improvement.
- Review and update insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage for future incidents.
Illustrative Scenarios

Negotiating with ransomware attackers is a high-stakes gamble. Success hinges on a multitude of factors, from understanding the attacker’s motivations to possessing the right technical and legal expertise. Analyzing successful and unsuccessful negotiations provides valuable insights into best practices and potential pitfalls.
Successful Ransomware Negotiation: The Case of City Hospital
City Hospital, a small community hospital in rural Iowa, fell victim to a Ryuk ransomware attack. Their IT systems were crippled, impacting patient care, billing, and administrative functions. The attackers demanded a $500,000 ransom. The hospital’s crisis management team, comprised of the CEO, CIO, a cybersecurity consultant specializing in ransomware incidents, and a legal representative, decided to engage in negotiations.
They secured a forensic analysis of the attack to understand the extent of the damage and the capabilities of the attackers. This provided crucial leverage during negotiations. They also engaged with law enforcement, but made it clear to the attackers that they were cooperating with authorities. The negotiations were conducted through a secure communication channel established by the cybersecurity consultant, adhering to best practices to avoid detection and ensure privacy.
The hospital’s negotiators focused on building rapport, conveying their desperation, but also highlighting their financial constraints. They successfully negotiated the ransom down to $250,000, paid through a complex system of cryptocurrency transactions designed to make tracing difficult. Crucially, the attackers provided a decryption key that fully restored the hospital’s systems. The success was attributed to the hospital’s preparedness, their multi-disciplinary approach, their strategic use of information gathered from the forensic analysis, and their measured approach to negotiations.
They prioritized patient care throughout the process and maintained open communication with staff, patients, and regulators.
Failed Ransomware Negotiation: The Case of Global Manufacturing
Global Manufacturing, a large multinational corporation, experienced a devastating ransomware attack targeting their manufacturing control systems. The attackers demanded a $10 million ransom. The company’s initial response was chaotic. Internal disagreements between the IT department, the legal team, and the CEO hindered the decision-making process, delaying engagement with the attackers and leading to a delay in seeking expert assistance.
Negotiations, when they finally began, were poorly managed. The company’s representative, lacking experience in this area, made several critical errors. They initially refused to pay any ransom, adopting a hardline stance that alienated the attackers. They failed to establish a secure communication channel, leaving the negotiations vulnerable to eavesdropping and potentially increasing the risk of further attacks. The company also leaked information about their internal negotiations to the media, further undermining their position and potentially emboldening the attackers.
This resulted in the attackers increasing their ransom demands, ultimately refusing to cooperate even after a significant offer was made. The company suffered substantial financial losses and reputational damage. They lost critical production data, experienced significant downtime, and faced regulatory scrutiny. The failure was primarily due to a lack of preparedness, poor communication and coordination, and a poorly executed negotiation strategy.
Comparison of Scenarios
The contrasting outcomes highlight the critical importance of preparedness, a well-defined negotiation strategy, and effective communication. City Hospital’s success stemmed from their proactive approach, their expert team, and their strategic concessions, whereas Global Manufacturing’s failure resulted from internal conflicts, a lack of expertise, and poor communication. City Hospital’s measured approach, utilizing forensic analysis for leverage, allowed them to achieve a favorable outcome, while Global Manufacturing’s inflexible and poorly managed negotiations only exacerbated the situation.
The key difference lies in the level of preparation, the expertise of the negotiators, and the overall management of the crisis. A coordinated, informed response is essential to successful negotiation in ransomware attacks.
Final Review
Navigating the treacherous waters of ransomware negotiations requires careful planning, a cool head, and a deep understanding of the adversary. While there’s no guarantee of success, a well-structured approach, informed by a thorough assessment of the attacker’s motivations and a strong negotiation strategy, can significantly improve the odds. Remember, prevention is always the best cure, but understanding the negotiation landscape is crucial for mitigating the impact of a successful attack.
Ultimately, the decision to negotiate is a complex one, requiring a careful weighing of risks and potential benefits, and should be made in consultation with legal and cybersecurity professionals.
Answers to Common Questions: Can Negotiations Yield Success In Ransomware Attacks
What are the legal implications of paying a ransom?
Paying a ransom can have legal ramifications, varying by jurisdiction. Some countries consider it funding illegal activity, while others may have more lenient stances. Legal counsel is crucial to understand the specific legal risks involved.
Is it always advisable to involve law enforcement?
Involving law enforcement is generally recommended, as they can provide valuable expertise and potentially assist in tracing the attackers. However, timing is critical, and immediate notification might not always be feasible depending on the situation.
How can I prevent future ransomware attacks?
Proactive measures like regular software updates, strong passwords, employee training on phishing awareness, and robust data backups are essential for preventing future ransomware attacks.
What types of data are most commonly targeted by ransomware attacks?
Ransomware attackers often target sensitive data like financial records, customer information, intellectual property, and medical records, which can have significant consequences if compromised.