Can Ransomware Infect Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?
Can ransomware infect virtual desktop infrastructure? Absolutely. While VDI offers some inherent security advantages, it’s not immune to ransomware attacks. This isn’t some theoretical threat; we’re talking about real-world vulnerabilities that clever hackers actively exploit. Think of it like this: a well-designed fortress can still be breached if the guards are asleep at the wheel or the walls have weak points.
This post dives into the how, why, and most importantly, the
-how to prevent* a ransomware nightmare in your VDI environment.
We’ll explore common attack vectors, from phishing emails cleverly disguised as legitimate communications to compromised applications acting as Trojan horses. We’ll also examine the unique challenges of recovering from a ransomware attack in a virtualized environment compared to a traditional desktop setup. Get ready to bolster your VDI security – because prevention is always better than a painful, costly cure.
Vulnerabilities in VDI Environments
VDI environments, while offering many advantages, present a unique set of vulnerabilities that ransomware actors can exploit. Unlike traditional desktop environments, the virtualized nature of VDI introduces complexities in security management, increasing the potential attack surface. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for implementing robust security measures and mitigating the risk of ransomware attacks.VDI environments share many vulnerabilities with traditional desktop systems, but the virtualization layer introduces new attack vectors.
For instance, while a traditional desktop might be vulnerable to phishing emails leading to malware execution, a VDI environment could be compromised through vulnerabilities in the hypervisor, the management tools, or even misconfigurations in the network connecting the virtual desktops. The attack surface is broadened by the interconnectedness of virtual machines and the centralized management infrastructure.
Common VDI Vulnerabilities Exploitable by Ransomware
The centralized nature of VDI creates a single point of failure. A successful attack on the hypervisor or the management console could potentially compromise all virtual desktops simultaneously. Further, vulnerabilities in the underlying operating system of the virtual machines, outdated software, and weak or improperly configured access controls all represent significant risks. Unpatched applications within the virtual desktops themselves remain a prime target, just as they are in traditional environments.
Finally, inadequate network security, such as insufficient firewalls or intrusion detection systems, can leave the entire VDI infrastructure exposed.
Attack Vectors: Traditional Desktops vs. VDI
Traditional desktop ransomware attacks often rely on social engineering (phishing emails, malicious websites) to deliver malware directly to the endpoint. In VDI, the attack vector can be more diverse. Attackers could exploit vulnerabilities in the hypervisor, the VDI management platform, or the network infrastructure to gain access. They might target a single vulnerable virtual desktop, then leverage that access to move laterally across the network and infect other VMs, or even compromise the entire VDI infrastructure.
Another significant difference is the potential for a single compromised VM to impact many users simultaneously in a VDI environment, unlike in a traditional desktop setup where each machine is typically isolated.
Security Measures: Physical vs. Virtualized Environments
While many security best practices apply to both physical and virtualized environments (e.g., strong passwords, regular patching, anti-malware software), there are key differences in implementation and focus. In physical environments, the emphasis is often on individual endpoint security. In VDI, the focus shifts to securing the entire infrastructure – the hypervisor, the network, and the management tools. This requires a more holistic approach, including robust access control, regular security audits, and a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that specifically addresses the virtualized nature of the environment.
Consideration should also be given to the security of the storage infrastructure where the virtual machine images are housed.
Hypothetical Ransomware Attack Scenario Targeting a VDI System
Imagine a scenario where an attacker exploits a zero-day vulnerability in the hypervisor of a company’s VDI system. This grants them administrative access to the entire virtual infrastructure. They then deploy ransomware to all virtual desktops simultaneously, encrypting critical data across the organization. Because the VDI management console is compromised, the attacker can also potentially disable backups, hindering recovery efforts.
The company’s operations are crippled, and they face a significant financial loss and reputational damage due to data loss and downtime. This highlights the critical importance of robust security measures, including regular patching, penetration testing, and multi-factor authentication across all components of the VDI environment, as well as a well-defined incident response plan.
Ransomware Infection Methods in VDI

Ransomware attacks on Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) environments are a growing concern, leveraging vulnerabilities to spread rapidly and encrypt critical data. Understanding the various infection methods is crucial for implementing effective preventative measures. This section will delve into how ransomware infiltrates VDI environments and the techniques used for lateral movement and encryption.
Ransomware can spread within a VDI environment through several vectors, often exploiting existing vulnerabilities or leveraging human error. Lateral movement, the process of moving from an initially compromised system to other systems within the network, is a key element in the success of many ransomware attacks. Once a single virtual machine (VM) is infected, the malware can spread to others through shared resources, network connections, or vulnerabilities in the VDI management platform itself.
Ransomware Delivery Methods Targeting VDI
Several methods facilitate ransomware delivery into VDI environments. Phishing emails, often disguised as legitimate communications, remain a highly effective vector. These emails may contain malicious attachments, such as seemingly innocuous documents or executables, designed to initiate the infection process. Compromised applications, either through software vulnerabilities or malicious updates, can also serve as entry points. Once installed, these applications can silently execute ransomware payloads, encrypting data across the VDI environment.
Finally, vulnerabilities in the VDI hypervisor or underlying infrastructure can be exploited for direct ransomware deployment.
VM Encryption Techniques Used by Ransomware
Ransomware employs various techniques to encrypt virtual machines within a VDI environment. These techniques range from simple file encryption to more sophisticated methods targeting the entire VM’s disk image. Some ransomware strains leverage encryption algorithms that are computationally expensive to break, making data recovery difficult. Furthermore, sophisticated ransomware may employ techniques to evade detection by anti-malware software, further complicating remediation efforts.
The encryption process often involves targeting key system files and user data, rendering the VMs unusable until the ransom is paid.
Comparison of Security Controls Against Ransomware Attack Vectors in VDI
The following table compares the effectiveness of various security controls against common ransomware attack vectors in a VDI environment. Effectiveness is rated on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being the most effective. Note that the effectiveness of any control depends heavily on its proper implementation and ongoing maintenance.
| Security Control | Phishing Emails | Malicious Attachments | Compromised Applications | Vulnerable Hypervisor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security Awareness Training | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Antivirus/Antimalware Software | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Network Segmentation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Regular Patching | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Data Backup and Recovery | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
Impact of Ransomware on VDI
A successful ransomware attack on a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) can have devastating consequences, far exceeding the impact on a single compromised desktop. The interconnected nature of VDI and the potential for widespread infection makes it a particularly high-stakes target for cybercriminals. The ripple effect extends beyond immediate data loss, impacting business operations, financial stability, and user productivity in significant ways.The consequences of a ransomware attack on a VDI system are multifaceted and severe.
Data loss, a primary concern, can encompass critical business documents, customer information, financial records, and intellectual property. The disruption to business operations can be immediate and extensive, halting workflows, preventing access to essential applications, and ultimately impacting revenue generation. The financial impact includes not only the ransom itself (if paid), but also the costs associated with recovery efforts, including IT personnel time, data restoration, system rebuilds, legal fees, and potential regulatory fines.
Furthermore, the reputational damage caused by a data breach can be long-lasting and difficult to overcome.
Data Loss and Business Disruption
A ransomware attack on a VDI environment can lead to significant data loss, depending on the extent of the encryption and the backup strategy in place. If backups are inadequate or inaccessible, the loss of crucial data can cripple business operations. The disruption extends beyond simply accessing files; applications hosted within the VDI environment might become unusable, halting critical processes like order processing, customer service, and financial reporting.
Consider a hospital system relying on VDI for patient records and medical imaging – a ransomware attack could severely impact patient care and potentially endanger lives. The downtime associated with recovery efforts can lead to lost revenue and decreased productivity.
Yes, ransomware can absolutely infect virtual desktop infrastructures (VDIs), highlighting the need for robust security measures. Building secure and resilient applications is crucial, and that’s where understanding the evolving landscape of application development comes in, like exploring the possibilities discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , which can help create more secure apps.
Ultimately, protecting your VDI from ransomware requires a multi-layered approach, including strong patching and access controls.
Recovery Challenges in VDI Environments
Recovering from a ransomware attack in a VDI environment presents unique challenges compared to traditional desktop environments. The centralized nature of VDI means that a single vulnerability can compromise numerous virtual desktops simultaneously. Restoring individual virtual machines (VMs) can be a complex and time-consuming process, particularly in large-scale VDI deployments. The need to ensure data integrity and consistency across multiple VMs adds further complexity.
Moreover, the reliance on shared resources within the VDI infrastructure necessitates a thorough investigation to identify and eliminate any remaining malware before restoring systems to avoid re-infection. This is unlike a traditional desktop environment where individual machines can be addressed more independently.
Responding to a Ransomware Attack on VDI: A Step-by-Step Procedure, Can ransomware infect virtual desktop infrastructure
Responding effectively to a ransomware attack requires a well-defined incident response plan. This plan should be regularly tested and updated to reflect changes in the VDI environment. Here’s a suggested procedure:
- Isolate Infected Systems: Immediately disconnect affected VDI machines from the network to prevent further spread of the ransomware.
- Assess the Damage: Determine the extent of the infection, identifying which VMs are affected and the type of ransomware involved.
- Analyze the Attack Vector: Investigate how the ransomware gained access to the VDI environment to identify and patch vulnerabilities.
- Restore from Backups: If reliable backups are available, restore the affected VMs from a known clean backup point. Verify the integrity of the restored data.
- Remediate Infected Systems: If backups are unavailable or compromised, consider professional data recovery services. Thoroughly clean and sanitize all affected VMs to remove any remaining malware.
- Strengthen Security Measures: Implement enhanced security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, regular security patching, and advanced threat protection solutions.
- Post-Incident Review: Conduct a thorough post-incident review to identify lessons learned and improve the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
Impact on User Productivity and Business Operations
The impact of ransomware on user productivity and business operations within a VDI system can be substantial. Users lose access to their work environments, hindering their ability to complete tasks and meet deadlines. This disruption can lead to significant productivity losses, especially in industries with time-sensitive operations. For example, a financial institution facing a ransomware attack on its VDI might experience delays in trading, impacting profitability and potentially incurring regulatory penalties.
The overall impact extends beyond individual users, affecting team collaboration, project timelines, and the overall efficiency of business processes. The downtime required for recovery further exacerbates the impact on productivity and operational efficiency. The cost of lost productivity, coupled with the direct financial costs of the attack, can severely impact the bottom line.
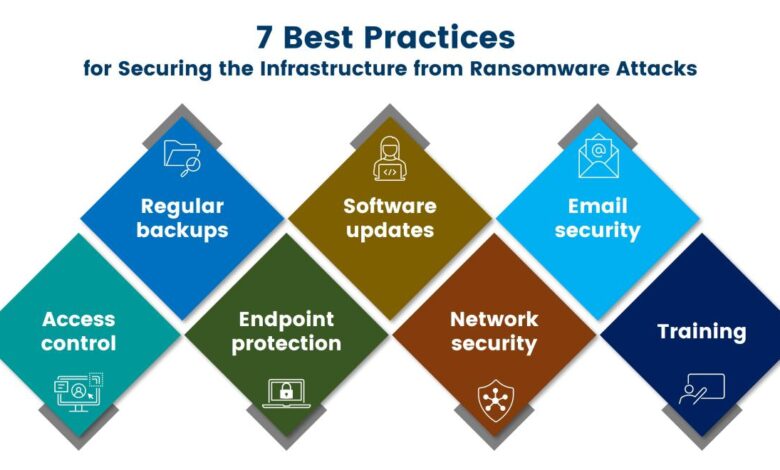
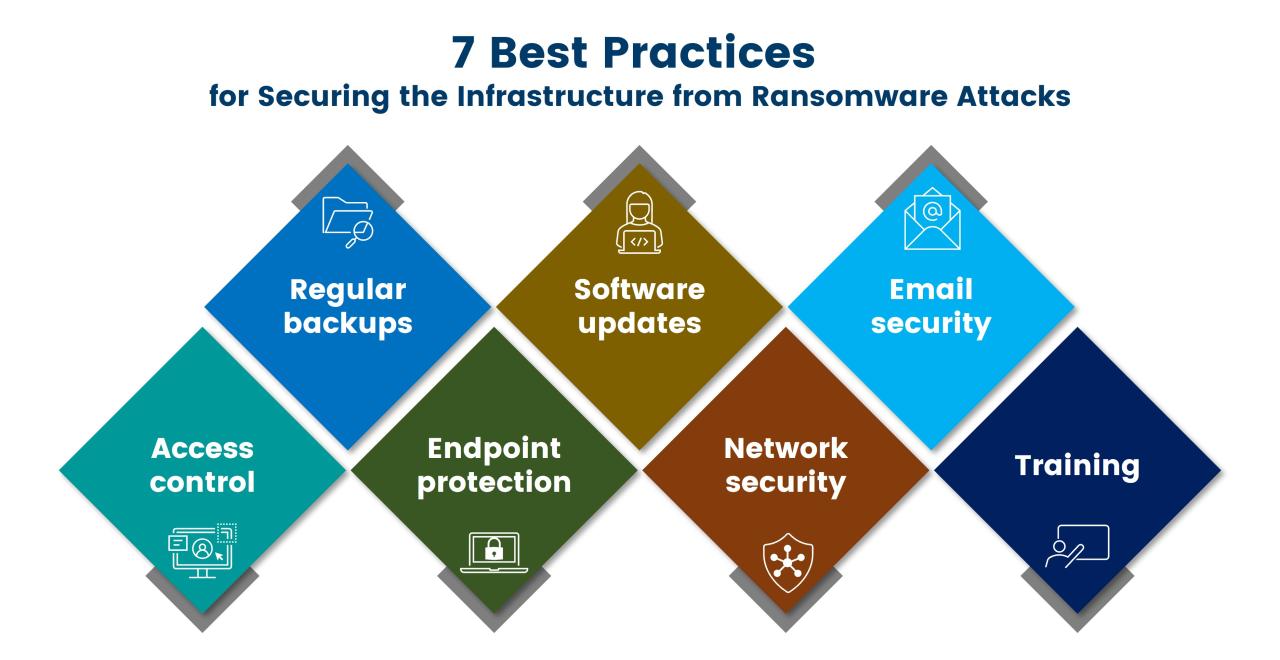
Security Best Practices for VDI

Protecting your Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) from ransomware requires a multi-layered approach encompassing robust security measures at every level. Ignoring even one aspect can leave your organization vulnerable to a devastating attack. This section Artikels crucial best practices to significantly reduce your ransomware risk.
A comprehensive VDI security strategy necessitates a combination of preventative measures, proactive monitoring, and rapid incident response capabilities. It’s not just about reacting to threats; it’s about creating a fortress that’s difficult for ransomware to penetrate in the first place.
Patch Management and Vulnerability Scanning
Regular patching is paramount. Outdated software is a prime target for ransomware exploits. Implement a robust patch management system that automatically updates all VDI components, including the hypervisor, operating systems, applications, and firmware. Regular vulnerability scanning should also be performed to identify and address any weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. This proactive approach significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the potential for successful ransomware infiltration.
Consider using automated vulnerability scanners that integrate with your patch management system for streamlined efficiency.
Access Control and Least Privilege
Restricting access to VDI resources is crucial. Implement the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary access rights to perform their tasks. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), should be enforced for all users. Regularly review and audit user access rights to ensure they remain appropriate and that no unnecessary permissions exist. Consider leveraging role-based access control (RBAC) to simplify management and enforce consistent security policies.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Regular backups are your last line of defense against ransomware. Implement a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy that includes frequent backups to an offline or air-gapped location. Test your recovery procedures regularly to ensure they are effective and that you can restore your data quickly in the event of a ransomware attack. Consider using immutable backups, which cannot be modified or deleted, to further protect against ransomware attacks.
The 3-2-1 backup rule (three copies of data, on two different media, with one copy offsite) is a good guideline to follow.
Network Segmentation and Isolation
Network segmentation is vital for containing the spread of ransomware. Isolate your VDI environment from other parts of your network to limit the impact of a successful attack. This prevents ransomware from spreading laterally to other critical systems. Implement firewalls and other network security controls to further restrict access to the VDI environment. Consider using micro-segmentation to further isolate individual virtual machines or applications within the VDI environment.
This granular approach significantly reduces the blast radius of a successful attack.
Endpoint Protection Solutions for VDI
Several endpoint protection solutions are specifically designed for VDI environments. These solutions offer advanced features like behavior-based detection, sandboxing, and machine learning to identify and prevent ransomware attacks. The effectiveness of each solution varies depending on its features and how well it’s integrated with your existing security infrastructure. Factors to consider when selecting a solution include its ability to handle the unique challenges of virtualized environments, its performance impact on VDI performance, and its ease of management.
Regularly evaluate and update your endpoint protection solution to ensure it remains effective against the latest ransomware threats.
Yes, ransomware can absolutely infect virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), highlighting the critical need for robust security measures. Understanding how to protect your VDI environment is crucial, and that involves strong cloud security posture management, like what’s discussed in this excellent article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management. Ultimately, securing your VDI against ransomware requires a multi-layered approach, including regular patching and strong access controls.
Security Recommendations for VDI Administrators
Preventing ransomware infections requires a proactive and diligent approach from VDI administrators. Here’s a list of crucial security recommendations:
- Implement and enforce a strong password policy.
- Regularly update and patch all VDI components.
- Use robust antivirus and anti-malware software.
- Enable application control to restrict the execution of unauthorized applications.
- Monitor user activity for suspicious behavior.
- Regularly back up all VDI data to an offline location.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Train users on ransomware awareness and prevention techniques.
- Develop and regularly test an incident response plan.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users.
Role of Hypervisor Security
The hypervisor sits at the heart of a VDI environment, acting as the foundational layer upon which virtual machines (VMs) reside. Its security posture, therefore, directly impacts the overall resilience of the VDI against ransomware attacks. A robust hypervisor security strategy is crucial in preventing ransomware from spreading laterally across VMs and disrupting operations. This involves not only securing the hypervisor itself but also leveraging its capabilities to enhance the security of the VMs it manages.The hypervisor’s role extends beyond simply providing virtualization; it acts as a critical control point, capable of enforcing security policies and isolating VMs from each other.
This isolation significantly limits the impact of a successful ransomware infection on a single VM, preventing it from cascading across the entire VDI infrastructure.
Hypervisor Security Features
Different hypervisors offer varying security features designed to mitigate ransomware threats. These features often overlap but have unique implementations and capabilities. Key features include enhanced memory protection, secure boot processes, and advanced VM isolation techniques. For instance, VMware vSphere offers features like vCenter Server Appliance security hardening, and VMware AppDefense, which provides runtime protection against malicious activities within VMs.
Microsoft Hyper-V integrates with Windows Defender ATP for enhanced threat detection and response, and utilizes features like Shielded VMs for enhanced isolation. Similarly, Citrix XenServer leverages its own security stack with features like secure boot and access control lists. The specific features and their effectiveness vary depending on the hypervisor vendor and version.
Hypervisor-Level Security Measures
Several hypervisor-level security measures can significantly enhance VDI resilience against ransomware. These measures focus on preventing the initial infection, limiting its spread, and enabling faster recovery. This includes implementing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms for accessing the hypervisor, regularly patching and updating the hypervisor software to address known vulnerabilities, and configuring robust logging and monitoring capabilities to detect suspicious activity.
Employing technologies like virtual machine introspection, which allows the hypervisor to monitor the activity within guest VMs for malicious behavior, is another crucial measure. Furthermore, the use of advanced memory protection techniques, such as memory encryption and integrity checks, helps prevent ransomware from modifying or encrypting critical system files.
Scenario: Preventing Ransomware Spread
Consider a scenario where a single VM in a VDI environment is compromised by ransomware. Without robust hypervisor security, the ransomware could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the hypervisor or leverage shared resources to spread to other VMs. However, with a properly secured hypervisor utilizing features like VM isolation and secure boot, the ransomware’s ability to move laterally is significantly curtailed.
The compromised VM remains isolated, its encrypted data contained, and the rest of the VDI environment remains operational. This isolation allows for a focused response to the infected VM, minimizing downtime and reducing the overall impact of the ransomware attack. The ability to quickly revert to a clean snapshot of the compromised VM further enhances recovery time. The hypervisor’s security features, therefore, become critical in limiting the blast radius of the ransomware infection and protecting the overall VDI environment.
Data Backup and Recovery in VDI
Protecting your virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) from ransomware requires a robust and well-tested backup and recovery strategy. This goes beyond simply backing up data; it involves understanding the unique challenges of VDI and implementing solutions that ensure business continuity in the face of a ransomware attack. A comprehensive plan accounts for the speed of recovery, the immutability of backups, and the overall security of the backup process itself.
A successful VDI backup and recovery strategy hinges on several key components, working in concert to provide a comprehensive defense against ransomware. The most critical elements include regular backups, offsite storage, immutable backups, and a well-defined recovery process. Failing to address any of these can significantly weaken your overall security posture and prolong recovery time in the event of a ransomware attack.
Offsite Backups and Immutable Storage
Offsite backups are crucial for mitigating the risk of data loss from physical disasters or ransomware attacks that compromise your on-site infrastructure. Storing backups in a geographically separate location ensures that even if your primary data center is compromised, you still have access to your data. This geographic separation is vital for preventing ransomware from encrypting your offsite backups.
Coupled with offsite storage, immutable storage is paramount. Immutable storage prevents backups from being modified or deleted, even by an administrator, making them resistant to ransomware attacks that attempt to encrypt or delete backups. This ensures that your recovery point is clean and unaffected by the attack. Consider using cloud-based storage solutions with versioning capabilities for this purpose, or dedicated immutable storage appliances.
Restoring Virtual Desktops and Data from Backups
The process of restoring virtual desktops and data after a ransomware attack involves several steps. First, identify the extent of the infection and isolate affected virtual machines. Next, restore the affected virtual machines from your most recent clean backup. This may involve restoring the entire virtual machine or only specific files and folders, depending on the backup strategy and the scope of the attack.
Finally, verify the integrity of the restored data and ensure that no ransomware remains on the system. This includes performing a thorough malware scan before bringing the restored VMs back online. A well-documented and tested recovery plan is critical for minimizing downtime and ensuring a smooth transition back to normal operations. Regular practice runs of the recovery plan are essential to ensure team familiarity and identify potential bottlenecks.
Comparison of Backup Technologies for VDI
Several backup technologies are suitable for VDI environments, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Traditional backup solutions, such as those using file-level or image-level backups, can be used but may be less efficient for VDI environments due to the overhead of managing many virtual machines. Snapshot-based backups, often integrated into the hypervisor, offer a fast and efficient way to create backups, but they may not provide the same level of protection against ransomware as immutable backups.
Cloud-based backup solutions provide offsite storage and often include features like immutable storage and versioning, but may be more expensive than on-premises solutions. The choice of technology depends on factors such as budget, recovery time objectives (RTOs), recovery point objectives (RPOs), and the overall security requirements of the organization. For example, a financial institution with stringent regulatory requirements might opt for a more robust and expensive solution with immutable storage and strong encryption, while a smaller organization might choose a more cost-effective solution with a longer RTO.
Conclusive Thoughts: Can Ransomware Infect Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
So, can ransomware infect your virtual desktop infrastructure? The short answer is a resounding yes. But the longer answer is far more empowering. By understanding the vulnerabilities, implementing robust security practices (from patching and access controls to ironclad backup strategies), and leveraging the inherent security features of your hypervisor, you can significantly reduce your risk. Don’t wait for a ransomware attack to become a crisis; proactively secure your VDI environment today.
Your peace of mind (and your data) will thank you for it.
FAQ Insights
What is the biggest difference between ransomware attacks on traditional desktops vs. VDI?
The biggest difference lies in the potential for lateral movement. In VDI, a compromised virtual desktop could potentially spread ransomware to other VMs if security isn’t properly segmented. Traditional desktops are usually more isolated.
How effective are traditional antivirus solutions in a VDI environment?
Traditional antivirus can be helpful, but they’re not a silver bullet. They need to be specifically designed or configured for VDI environments and often work best in conjunction with other security measures.
What about immutable backups? Are they really necessary?
Absolutely! Immutable backups are crucial because they cannot be modified or deleted, even by ransomware. This ensures you have a clean copy of your data to restore from, even if the ransomware has already encrypted your primary storage.
Can I rely solely on hypervisor-level security?
No. While hypervisor security offers a strong foundation, it should be considered one layer of a multi-layered security approach. It’s not a standalone solution for complete ransomware protection.





