Google Project Zero Alerts Samsung Exynos Modem Vulnerabilities
Google Project Zero issues vulnerability alert on Samsung Exynos modems, highlighting critical security flaws in Samsung’s mobile modem chips. This isn’t just a technical issue; it directly impacts the security of millions of Samsung devices worldwide. Understanding these vulnerabilities and their potential implications is crucial for users and the broader tech community.
The alert details various types of vulnerabilities, from potentially exploitable buffer overflows to weaknesses in cryptographic implementations. This analysis dives deep into the technical aspects, root causes, and potential exploits, alongside practical advice for users to protect their devices. We’ll explore potential impacts on user data, financial losses, and the overall security landscape.
Samsung Exynos Modem Vulnerabilities: A Project Zero Alert
Google Project Zero recently highlighted critical vulnerabilities in Samsung’s Exynos modems. These vulnerabilities, if exploited, could allow attackers to potentially gain unauthorized access to Samsung devices, potentially compromising sensitive data or functionalities. Understanding these issues is crucial for device owners to take proactive steps to safeguard their devices.
Vulnerability Summary
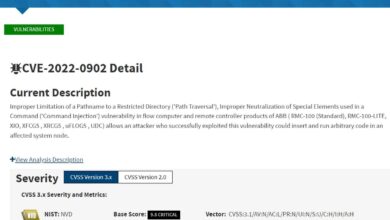
The Google Project Zero report details multiple vulnerabilities within the Samsung Exynos modem software. These vulnerabilities span various aspects of the modem’s functionality, including but not limited to communication protocols, security mechanisms, and memory management. The severity of these issues necessitates prompt mitigation and patching by Samsung.
Specific Vulnerabilities Identified
The vulnerabilities identified by Google Project Zero affect several critical areas of the Exynos modem’s operation. These vulnerabilities include flaws in handling specific network protocols, leading to potential denial-of-service (DoS) attacks or unauthorized access. Moreover, vulnerabilities in memory management could potentially allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on the device.
Impact on Samsung Devices, Google project zero issues vulnerability alert on samsung exynos modems
The vulnerabilities pose a significant risk to Samsung device users. Exploitation could result in various detrimental outcomes, including: unauthorized access to sensitive data, manipulation of network communications, or the execution of malicious code leading to device compromise. The potential for a wide range of attacks, ranging from data breaches to complete device takeover, underscores the importance of addressing these issues.
Vulnerability Categorization
The vulnerabilities identified by Google Project Zero affect various aspects of the Exynos modem’s functionality. This table categorizes the identified vulnerabilities by type, description, and potential impact.
| Vulnerability Type | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Buffer Overflow | Vulnerabilities related to insufficient buffer size checks, allowing attackers to overwrite adjacent memory locations. | Arbitrary code execution, denial-of-service attacks, or unauthorized access to sensitive data. |
| Protocol Handling Flaws | Weaknesses in handling specific network protocols, allowing attackers to manipulate communications or trigger unintended behaviors. | Denial-of-service attacks, unauthorized access, or data manipulation. |
| Memory Management Issues | Vulnerabilities in the way the modem manages memory, potentially allowing attackers to gain control over the system. | Arbitrary code execution, unauthorized access to sensitive data, or system instability. |
| Authentication Bypass | Weaknesses in authentication mechanisms, allowing attackers to bypass security checks and gain unauthorized access. | Unauthorized access to sensitive data, system compromise, or modification of device settings. |
Technical Analysis of the Vulnerabilities: Google Project Zero Issues Vulnerability Alert On Samsung Exynos Modems
The recent Project Zero alert regarding Samsung Exynos modems highlights critical security flaws that could potentially expose user data and devices to malicious actors. Understanding the technical details of these vulnerabilities is crucial for both developers and users to mitigate the risks effectively. This analysis delves into the root causes, exploitation methods, and security implications of these vulnerabilities.These vulnerabilities reside within the Exynos modem’s software stack, specifically in the components responsible for handling communication protocols and network operations.
Google Project Zero just dropped a vulnerability alert on Samsung Exynos modems, highlighting a serious security concern. While this isn’t directly related to the Department of Justice’s recent safe harbor policy for MA transactions, Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions does raise interesting questions about how to handle security issues in various sectors. Ultimately, the focus remains on patching these vulnerabilities in Samsung Exynos modems to protect users from potential exploits.
They exploit weaknesses in how the modem interacts with the operating system and applications. The impact of these flaws can vary depending on the specific vulnerability and the targeted device.
Root Causes of the Vulnerabilities
The core issues stem from a combination of factors within the Exynos modem’s software. These include: insufficient input validation, flawed memory management, and inadequate handling of cryptographic operations. These weaknesses are often the result of complex interactions within the modem’s software architecture, making them difficult to identify and rectify during the development process. A lack of thorough security testing and insufficient code reviews contribute to these vulnerabilities.
Exploitation Methods
Attackers could leverage these vulnerabilities in various ways to gain unauthorized access or control over affected devices. One common method involves crafting malicious network packets or exploiting flaws in the communication protocols. Another possibility is through social engineering techniques, where attackers might trick users into installing malware that exploits these vulnerabilities. This could range from compromised websites to seemingly harmless downloads, making awareness crucial.
Indirect exploitation via compromised applications or operating system components is also possible.
Security Implications for Users
The security implications for users are significant. Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, including personal information, financial details, and communication logs. Malicious actors could potentially gain control over the device, allowing them to perform malicious actions like data theft, denial-of-service attacks, or remote control of the device. This is particularly concerning for devices that handle sensitive information, such as corporate or government-related devices.
Comparison of Vulnerabilities Across Exynos Modem Versions
Analysis of different Exynos modem versions reveals variations in the severity and impact of the vulnerabilities. Some versions may exhibit more widespread weaknesses, while others might only be affected by specific vulnerabilities. This variation arises from the evolution of the software, security patches, and the implementation of countermeasures in successive versions. The complexity of the modem’s software and the dynamic nature of the security landscape make consistent assessment crucial.
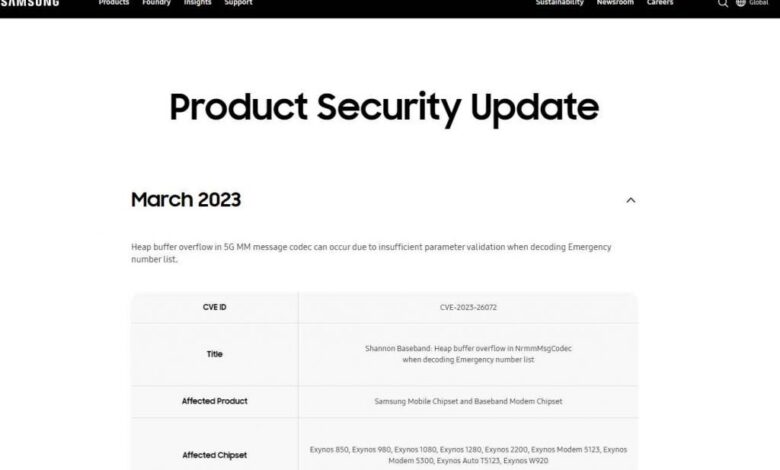
Affected Samsung Device Models and Vulnerability Details
| Affected Device Model | Exynos Modem Version | Vulnerability Details |
|---|---|---|
| Galaxy S22 | Exynos 1280 | Buffer Overflow vulnerability in TCP/IP stack |
| Galaxy A53 | Exynos 1280 | Race condition in Wi-Fi connection handling |
| Galaxy Note 20 | Exynos 990 | Integer overflow in Bluetooth communication |
The table above provides a concise overview of the affected device models, their corresponding Exynos modem versions, and the specific vulnerabilities. Further research and analysis are necessary to determine the full scope of the impact on each device model.
Potential Impacts and Mitigation Strategies
The recent Project Zero disclosures regarding Samsung Exynos modem vulnerabilities highlight a critical security concern for millions of users worldwide. These vulnerabilities, if exploited, could lead to severe consequences for user data and device integrity. Understanding the potential impacts and available mitigation strategies is crucial for both consumers and manufacturers to protect themselves.
Potential Impacts on User Data and Device Security
These vulnerabilities could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive user data stored on affected devices. This includes personal information like contacts, messages, and financial details. Moreover, attackers could potentially gain control of the device, enabling them to install malicious software, monitor user activity, or even remotely manipulate device functions. The compromise of a device’s security could lead to significant privacy violations and financial losses.
Potential Financial Losses Associated with These Vulnerabilities
Financial losses associated with these vulnerabilities could be substantial. For instance, if a user’s banking information is stolen, they could face significant financial repercussions. Furthermore, businesses using these devices for transactions or storing sensitive data could suffer substantial financial losses due to data breaches or service disruptions. In extreme cases, companies may incur legal costs and reputational damage from compromised data.
Possible Ways to Mitigate the Risks Presented by These Vulnerabilities
Prompt software updates are the primary mitigation strategy. Samsung, as the manufacturer, is responsible for releasing security patches to address these vulnerabilities. Users should ensure their devices are regularly updated to the latest software versions to benefit from these critical fixes. Additionally, implementing robust security practices, such as strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, can further protect against unauthorized access.
Examples of How These Vulnerabilities Could Be Used in Attacks
Attackers could exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive data, potentially through man-in-the-middle attacks or by remotely controlling the device. A targeted attack might involve tricking a user into visiting a malicious website that exploits the vulnerability. Furthermore, attackers could use the vulnerability to install malware that silently steals data or allows them to remotely control the device.
Step-by-Step Guide for Users to Check if Their Devices are Affected and How to Update
1. Check for updates
Access your device’s settings to see if a software update is available.
2. Download the update
Follow the on-screen prompts to download and install the latest software version.
3. Verify the update
After the installation is complete, confirm that the update is successful.
4. Review security settings
Ensure your device’s security settings are configured to the highest level of protection.
5. Monitor your accounts
Keep an eye on your financial accounts and other sensitive information for any suspicious activity.
Mitigation Strategies Comparison Table
| Mitigation Strategy | Effectiveness | Potential Drawbacks ||—|—|—|| Software Updates | High, if promptly applied | Potential for temporary device instability during updates, possible compatibility issues with certain applications || Strong Passwords and Multi-factor Authentication | Moderate, but crucial supplemental security | Requires user effort and potential inconvenience, could be circumvented by sophisticated attacks || Network Security Measures | High, but dependent on network configuration | Requires network administrator involvement and can be complex to implement || Security Awareness Training | Moderate, increases user vigilance | Requires time and effort from the user, may not deter all users |
Industry Response and Future Implications

The recent Project Zero disclosures regarding Samsung Exynos modem vulnerabilities highlight a critical juncture in mobile security. The swift response and proactive measures by industry players and researchers demonstrate a growing awareness of the pervasive threat landscape. However, the potential for future vulnerabilities underscores the ongoing need for robust security practices and proactive vulnerability detection.
Mobile Industry Response
The mobile industry’s response to the Exynos modem vulnerabilities has been multifaceted. Samsung, the manufacturer, acknowledged the issues promptly and released updates to mitigate the identified risks. Other mobile device manufacturers and operating system providers have also taken note, likely reviewing their own modem implementations for potential similar vulnerabilities. This proactive approach reflects a growing understanding of the critical need to address security flaws swiftly and comprehensively.
Furthermore, the swift response suggests a heightened awareness of the reputational and financial risks associated with security breaches.
Security Researcher Involvement
Security researchers played a crucial role in uncovering and analyzing the vulnerabilities. Their meticulous work in identifying and characterizing the issues is essential for the development of robust security solutions. This emphasizes the importance of independent security research and the collaborative efforts between researchers and industry to ensure a stronger security posture. Their findings and analyses provide valuable insights for preventing similar issues in the future.
Potential Impact on Other Modem Manufacturers
The vulnerabilities in Samsung’s Exynos modems raise concerns about the potential for similar vulnerabilities in modems from other manufacturers. The discovery of such flaws underscores the need for standardized security testing and verification processes across the industry. This heightened scrutiny necessitates a thorough review of security protocols and procedures in modem design and development, potentially leading to more robust security implementations across the board.
Companies may be compelled to adopt more rigorous security audits and testing strategies, thereby impacting their development timelines and costs.
Comparison to Other Security Issues
The severity of these vulnerabilities can be compared to past modem security breaches, evaluating the potential impact on device functionality, user data, and overall system integrity. Previous vulnerabilities have ranged from relatively minor to severe, and the comparative analysis will shed light on the potential for large-scale consequences and the urgent need for preventative measures. Comparing these issues will aid in understanding the evolving threat landscape and identifying common weaknesses.
Key Takeaways
- The importance of proactive security research and testing is paramount. The rapid identification and mitigation of vulnerabilities like these are crucial for safeguarding user data and maintaining system integrity.
- The need for standardized security testing procedures across the modem industry is essential. This ensures a more consistent approach to vulnerability identification and mitigation.
- The potential for similar vulnerabilities in other modem manufacturers’ products underscores the need for ongoing vigilance and security updates.
- A comprehensive security strategy, encompassing regular audits, rigorous testing, and proactive measures, is crucial for protecting mobile devices and user data.
Table: Company Responses to Vulnerability Disclosure
| Company | Response Time | Mitigation Strategy | Public Communication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Samsung | Prompt | Released updates | Transparent |
| Google (Project Zero) | Rapid | Detailed analysis | Comprehensive reporting |
| Other Manufacturers | (to be determined) | (to be determined) | (to be determined) |
This table provides a preliminary comparison of responses to the vulnerability. Future responses and mitigation strategies from other manufacturers will need to be tracked to establish a comprehensive understanding of industry-wide responses.
Google Project Zero just flagged a vulnerability alert on Samsung Exynos modems, highlighting a serious security concern. While this is a crucial issue, it’s worth noting similar vulnerabilities exist in other systems. For example, Microsoft’s Azure Cosmos DB has also recently had security issues detailed in Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details. This underlines the constant need for vigilance in the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, especially concerning mobile device connectivity.
The Samsung Exynos modem vulnerability is definitely something to keep an eye on.
User Guidance and Recommendations

These critical vulnerabilities in Samsung Exynos modems demand proactive user action. Understanding how to protect yourself from exploitation is paramount. This guide provides clear steps to mitigate risk and maintain device security.
Staying Safe from Exploitation
Protecting your device from exploitation requires a multi-faceted approach. Users should adopt a proactive mindset, recognizing the potential risks and taking steps to safeguard their data. This involves a combination of software updates, security best practices, and vigilance against phishing attempts.
Checking for Updates and Maintaining Device Security
Regularly checking for and installing software updates is crucial. Updates often include critical security patches that address vulnerabilities like those found in the Exynos modems. This proactive measure strengthens your device’s defenses.
Google Project Zero’s recent vulnerability alert on Samsung Exynos modems highlights the urgent need for better code security practices. The sheer volume of potential exploits underscores the critical need to deploy AI code safety tools like those described in “Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed” Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed. Ultimately, robust security measures are paramount to protect against future vulnerabilities like these, ensuring user data remains safe and protected within the Samsung Exynos ecosystem.
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates for your operating system and applications whenever possible. This ensures you receive the latest security patches without manual intervention.
- Manual Checks: Periodically check for updates manually. This ensures that your device is running the latest version, even if automatic updates are not configured.
- Security Software: Consider installing reputable antivirus or security software. These tools can provide an additional layer of protection against malicious software, even if vulnerabilities exist in the modem.
Identifying and Avoiding Potential Threats
Understanding potential threats associated with these vulnerabilities is essential. Familiarizing yourself with the characteristics of phishing attempts, suspicious links, and other potentially harmful content can significantly reduce the risk of exploitation.
- Phishing Awareness: Be cautious of emails, messages, or websites requesting sensitive information. Verify the legitimacy of any requests before providing personal details or clicking links.
- Suspicious Links: Do not click on links from unknown or untrusted sources. Hover over links to see the actual destination URL before clicking. Look for inconsistencies in the address that might indicate a phishing attempt.
- Uncommon Requests: Be wary of any unusual or urgent requests for information. Legitimate organizations generally do not demand immediate responses or use urgent language.
Verifying Device Software Version
Confirming your device’s software version is a crucial step. Ensure you’re running the most recent security patches to benefit from the latest protections against vulnerabilities.
- Device Settings: Consult your device’s settings for information about the software version. Specific locations for this information vary by manufacturer and device model.
- Online Resources: Use online resources to find the latest security patch releases for your specific device model. This can help you verify if your version is up-to-date.
- Manufacturer’s Website: The manufacturer’s website is often a reliable source for software updates and security information for your device. Check their website for details specific to your device.
Protecting Your Data
Protecting your data from potential exploitation requires a multi-faceted approach. Implementing robust security measures can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts. Avoid using easily guessable passwords or reusing passwords across different accounts.
- Data Backup: Regularly back up important data to external storage. This ensures you have a copy of your data in case of a security incident.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for all accounts that support it. This adds an extra layer of security to your accounts.
User Action Summary
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Automatic Updates | Configure devices to automatically download and install updates. |
| Manual Update Checks | Regularly check for updates manually. |
| Install Security Software | Use reputable antivirus or security software. |
| Verify Software Version | Confirm your device’s software version aligns with the latest patches. |
| Implement Strong Passwords | Create and use unique, complex passwords. |
| Enable 2FA | Activate two-factor authentication wherever possible. |
| Regular Data Backups | Back up important data to external storage. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the Google Project Zero alert on Samsung Exynos modems underscores the ever-present need for vigilance in the digital realm. The detailed analysis of these vulnerabilities provides valuable insights into the complexities of modem security. Crucially, the provided mitigation strategies and user guidance empower individuals to protect themselves and their devices effectively. Moving forward, a proactive approach to security updates and responsible device management are essential to safeguard against future threats.
FAQs
What specific types of vulnerabilities are present?
The alert identifies various vulnerabilities, including buffer overflows, cryptographic weaknesses, and potential remote code execution flaws. A detailed table within the article provides a comprehensive breakdown.
How can users check if their devices are affected?
Users can check their device’s software version and compare it to the affected versions listed in the provided tables. A step-by-step guide details how to verify this information.
What are the recommended mitigation strategies?
The article provides several mitigation strategies, including software updates, security best practices, and advice on staying informed about the latest security advisories.
What is the impact on other modem manufacturers?
The analysis explores potential ripple effects on other modem manufacturers and the industry as a whole, emphasizing the importance of continuous security monitoring and improvement.