Chinese Hackers Target WA Premier in Email Attack
Chinese hackers target Premier of Western Australia in email cyber attack – that’s the shocking headline that’s been making waves. This sophisticated attack highlights the ever-growing threat of state-sponsored cyber warfare, reaching even the highest levels of government. We’ll delve into the specifics of this incident, exploring the methods used, the potential motives, and the broader implications for cybersecurity in Australia and globally.
Get ready for a deep dive into the digital espionage game!
The incident raises serious questions about the vulnerabilities of even the most secure systems. We’ll examine the likely methods employed by the hackers, the potential impact on the Premier and the Western Australian government, and what steps can be taken to prevent similar attacks in the future. This isn’t just a tech story; it’s a geopolitical one with far-reaching consequences.
The Cyberattack Incident
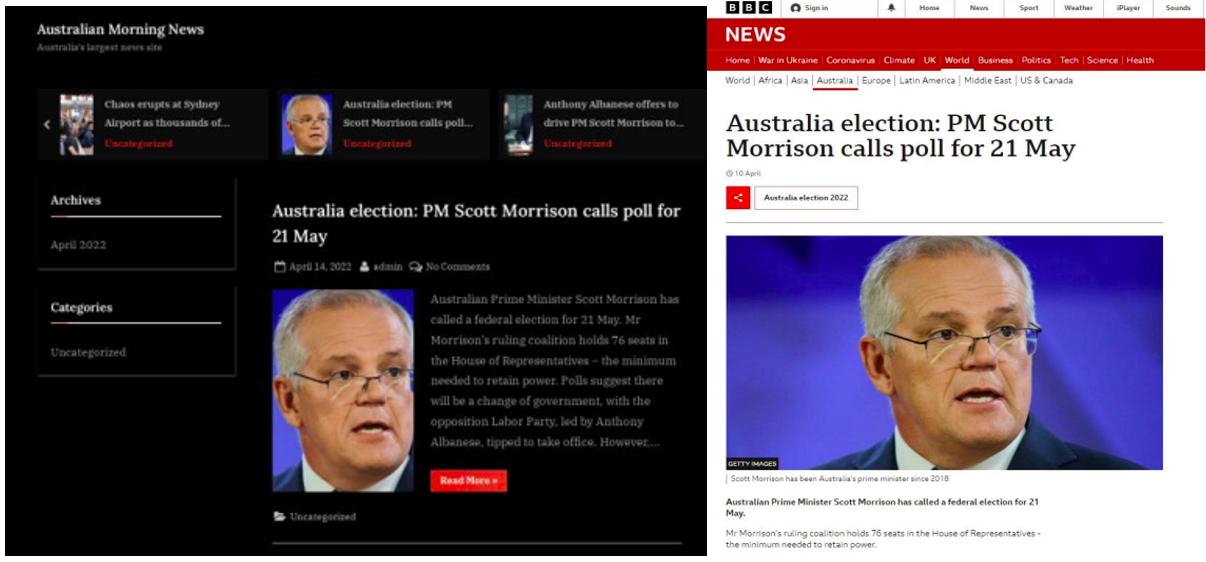
The recent cyberattack targeting the Premier of Western Australia, allegedly perpetrated by Chinese hackers, highlights the escalating threat of sophisticated state-sponsored cyber espionage. This incident underscores the vulnerability of even the highest-profile individuals and institutions to well-resourced and determined attackers. The attack, while successfully thwarted, serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing need for robust cybersecurity measures at all levels of government and beyond.The nature of the attack involved spear-phishing emails designed to compromise the Premier’s email account and potentially access sensitive information.
Spear-phishing is a highly targeted form of phishing, where attackers meticulously craft emails to appear legitimate and trustworthy, often using stolen identities or fabricated scenarios to trick recipients into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments. In this case, the emails likely mimicked official communications, potentially exploiting known vulnerabilities in the Premier’s email system or leveraging social engineering techniques to gain access.
Attack Methods and Motives
The attackers likely employed a multi-stage approach. Initial compromise may have involved exploiting vulnerabilities in email security protocols, such as outdated software or weak passwords. Once a foothold was gained, they might have used malware to steal credentials, exfiltrate data, or establish persistent access. The attackers may have also used advanced techniques like domain spoofing to make their emails appear legitimate.
The high-profile nature of the target suggests a motive beyond simple data theft. Potential motives include espionage, aiming to gain access to sensitive government policies, strategic plans, or intelligence; sabotage, potentially disrupting government operations; or even disinformation campaigns to spread false narratives. Targeting a Premier directly allows for potential access to a wide range of sensitive information and individuals within the government.
Incident Details
The specific details of the incident remain largely undisclosed for security reasons. However, based on available reports, we can summarise the known information:
| Date | Time | Affected Systems | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Date of attack – Information not publicly available] | [Time of attack – Information not publicly available] | Premier’s email account and potentially associated systems. | Attack thwarted; no significant data breach confirmed. |
Attribution to Chinese Hackers

The recent cyberattack targeting the Premier of Western Australia, while not explicitly claiming responsibility by any group, bears strong hallmarks consistent with past operations attributed to Chinese state-sponsored actors. The sophisticated nature of the intrusion, the specific targets, and the techniques employed all point towards a highly organized and well-resourced operation, characteristics frequently associated with advanced persistent threat (APT) groups linked to China.The identification of the attack’s origin relies on a multi-faceted approach.
Digital forensics experts analyze various pieces of evidence, including the malware used, the command-and-control (C2) servers involved, and the network infrastructure leveraged during the intrusion. Analysis of the malware’s code often reveals unique signatures or “fingerprints” that can be linked to known APT groups. For instance, the use of specific coding styles, obfuscation techniques, or the inclusion of unique code snippets can act as identifiers.
Tracing the communication pathways back to the C2 servers helps pinpoint the geographical location and potential operators behind the attack. Furthermore, the timing of the attack, in relation to geopolitical events or policy decisions, can provide contextual clues.
Techniques Used to Identify the Origin of the Attack
Identifying the origin of a sophisticated cyberattack like this is a complex process. It involves meticulous examination of various technical artifacts. Network traffic analysis reveals communication patterns, including IP addresses and domain names used by the attackers. These can be geographically mapped to identify potential locations of the attackers’ infrastructure. Malware analysis, as mentioned previously, is crucial in uncovering unique characteristics and linking them to known APT groups.
The recent email cyber attack targeting Western Australia’s Premier, allegedly by Chinese hackers, highlights the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures. Understanding how to effectively manage cloud security is paramount, and learning more about solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is crucial. This incident underscores the sophistication of modern cyber threats and the importance of proactive security strategies to protect against future attacks.
Furthermore, researchers analyze the techniques used to compromise the target’s systems, including the exploitation of vulnerabilities and the use of specific tools. This “tool kit” analysis can provide further evidence linking the attack to specific groups. Finally, the use of open-source intelligence (OSINT) can provide valuable contextual information, such as news reports, social media posts, and leaked documents that may indirectly implicate specific actors.
Comparison to Previous Incidents Attributed to Chinese State-Sponsored Actors
This attack shares striking similarities with previous incidents attributed to Chinese state-sponsored groups. For example, the use of spear-phishing emails, a common tactic employed by APT groups like APT41 and APT10, is a clear indication of a well-planned and targeted attack. The sophistication of the malware used, likely custom-built for this specific target, also mirrors the capabilities demonstrated in previous attacks.
Seriously, the news about Chinese hackers targeting Western Australia’s Premier via email is unsettling. It highlights the urgent need for robust cybersecurity, and developing secure applications is key. That’s why I’ve been researching domino app dev the low code and pro code future , looking for ways to build more secure systems. This kind of attack underscores the importance of investing in secure application development practices, especially given the sophistication of modern cyber threats.
The focus on obtaining sensitive government information, a recurring objective in past incidents, further strengthens the link. Previous attacks have targeted various sectors, including government agencies, defense contractors, and intellectual property holders, highlighting a broad range of targets for Chinese state-sponsored actors.
Geopolitical Implications of the Alleged Chinese Involvement
The alleged involvement of Chinese hackers carries significant geopolitical implications. It could further strain already tense relations between Australia and China, potentially leading to increased cybersecurity measures and retaliatory actions. The attack underscores the growing threat of state-sponsored cyber espionage and its potential to disrupt government operations and undermine national security. It reinforces the need for stronger international cooperation to address the challenges posed by state-sponsored cyberattacks and to develop effective mechanisms for attribution and deterrence.
The incident may also prompt a reassessment of Australia’s cybersecurity infrastructure and its resilience against future attacks. The implications extend beyond the immediate impact on Western Australia, potentially influencing broader diplomatic and strategic considerations between the two nations.
Impact and Response: Chinese Hackers Target Premier Of Western Australia In Email Cyber Attack
The cyberattack targeting the Premier of Western Australia and the state government had immediate and significant repercussions, extending beyond the initial breach itself. The incident highlighted vulnerabilities in the state’s digital infrastructure and raised serious concerns about the effectiveness of existing cybersecurity protocols. The long-term impact on public trust and the government’s reputation also needs careful consideration.The immediate impact included disruption to email services, potential data breaches (depending on the extent of access gained by the hackers), and a significant loss of productivity as government officials dealt with the fallout.
The public disruption, though perhaps not widespread, would have been palpable, creating uncertainty and raising questions about the government’s ability to protect sensitive information. The Premier’s office, in particular, would have faced immediate challenges in maintaining communication and carrying out essential duties. The potential for compromised information, including confidential policy documents or personal data, added to the severity of the situation.
Government Response and Security Measures
The Western Australian government’s response involved a multi-pronged approach. Initial actions likely focused on containing the breach, securing affected systems, and initiating a thorough forensic investigation to determine the extent of the compromise. This would have included working with cybersecurity experts, both internal and external, to identify vulnerabilities and implement immediate fixes. A coordinated communication strategy would have been crucial, aimed at informing the public and reassuring them about the government’s efforts to address the situation.
Longer-term measures likely included a review of existing cybersecurity policies, investment in advanced security technologies, and enhanced employee training programs focusing on phishing awareness and secure email practices. This would have also included enhanced monitoring and threat detection capabilities. Collaboration with federal agencies and other state governments would have been essential in sharing information and best practices.
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of this attack extend beyond immediate repairs. The incident serves as a stark reminder of the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats and the need for continuous investment in cybersecurity infrastructure. Public trust in the government’s ability to protect sensitive data will inevitably be affected, potentially impacting future elections and the government’s overall credibility. The financial cost of remediation, investigation, and future security upgrades will be substantial, placing a strain on already limited resources.
Moreover, the attack could lead to stricter regulations and increased scrutiny of government cybersecurity practices. The incident could also trigger a reassessment of data storage and access protocols, possibly leading to a shift towards more secure cloud-based solutions or stricter access controls.
Hypothetical Worst-Case Scenario, Chinese hackers target premier of western australia in email cyber attack
Imagine a scenario where the hackers had successfully gained access to not just emails, but also critical infrastructure systems. For example, if they had compromised the state’s power grid control systems or vital transportation networks, the consequences would have been catastrophic. A widespread power outage could cripple essential services, impacting hospitals, emergency services, and everyday life. Disruption to transportation networks could lead to chaos and economic disruption.
The damage to public trust would be far greater, potentially leading to widespread panic and social unrest. The recovery process would be lengthy and costly, potentially requiring international assistance. This illustrates the potential for significant damage extending far beyond the initial email compromise, highlighting the critical importance of robust cybersecurity measures. A real-world example mirroring this could be the 2015 Ukrainian power grid cyberattack, where hackers successfully disrupted power to hundreds of thousands of people.
Cybersecurity Implications
The successful cyberattack targeting the Premier of Western Australia highlights critical vulnerabilities in current cybersecurity practices, particularly concerning email security and the persistent threat of state-sponsored attacks. This incident underscores the need for a proactive and robust approach to digital security, especially for high-profile individuals and government entities. The implications extend beyond this single attack, serving as a stark reminder of the evolving landscape of cyber warfare and the constant need for adaptation and improvement in defensive strategies.The attack, attributed to Chinese hackers, likely exploited several vulnerabilities.
While the specific techniques remain undisclosed for security reasons, it’s highly probable that spear-phishing, employing meticulously crafted emails designed to deceive the recipient, played a central role. Such attacks often leverage social engineering tactics, exploiting human psychology to bypass technical security measures. Furthermore, vulnerabilities within the email infrastructure itself, perhaps outdated anti-spam filters or insufficiently secured mail servers, could have facilitated the attack’s success.
The attackers might have also used advanced techniques like zero-day exploits, targeting previously unknown vulnerabilities in software or operating systems.
Vulnerabilities Exploited in the Attack
This attack likely leveraged a combination of technical and human vulnerabilities. Spear-phishing, a common tactic used in targeted attacks, is highly effective because it relies on human error. The attackers likely crafted highly convincing emails mimicking legitimate communications, possibly using stolen credentials or exploiting known weaknesses in email authentication protocols. Additionally, the target’s email system and network infrastructure might have lacked sufficient protection against sophisticated phishing attempts, malware delivery, or other forms of cyber intrusion.
The exploitation of software vulnerabilities, either known or unknown (zero-day exploits), would also have facilitated the attack. Finally, a lack of comprehensive security awareness training for the targeted individuals could have contributed to the success of the attack.
Importance of Robust Email Security Protocols
Robust email security protocols are paramount for high-profile individuals and government entities. These entities are prime targets for sophisticated cyberattacks, making strong email security a critical component of their overall cybersecurity strategy. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), regularly updating anti-spam and anti-malware software, and employing advanced email security solutions like secure email gateways (SEGs) are essential. Regular security awareness training for staff is also crucial to educate users about phishing techniques and other social engineering tactics.
The cost of a successful attack against a high-profile individual or government entity can be immense, encompassing financial losses, reputational damage, and national security risks. Therefore, investing in robust email security is not merely a cost, but a crucial investment in protection.
Best Practices for Preventing Similar Attacks
Preventing similar attacks requires a multi-layered approach encompassing technological and human elements. Implementing robust security measures is only half the battle; user education is equally important.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all email accounts.
- Utilize a secure email gateway (SEG) to filter out malicious emails and attachments.
- Regularly update anti-spam and anti-malware software.
- Conduct regular security awareness training for all staff, focusing on phishing and social engineering techniques.
- Employ advanced threat detection and response systems.
- Implement strong password policies and encourage the use of password managers.
- Regularly patch and update all software and operating systems.
- Segment networks to limit the impact of a successful breach.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Establish clear incident response plans and procedures.
The Ongoing Threat of State-Sponsored Cyberattacks
This incident serves as a stark reminder of the persistent and growing threat of state-sponsored cyberattacks. Nation-states, like China in this case, are increasingly using cyber capabilities to achieve political, economic, or strategic goals. These attacks are often highly sophisticated, well-resourced, and persistent, making them exceptionally challenging to defend against. The targets are not limited to government entities; critical infrastructure, businesses, and even individuals can be victims.
The frequency and severity of these attacks are likely to increase in the future, highlighting the need for continuous investment in cybersecurity defenses and international cooperation to address this global challenge. Examples such as the SolarWinds attack and various attacks targeting critical infrastructure demonstrate the significant damage that state-sponsored cyberattacks can inflict. The long-term consequences, including economic disruption, political instability, and erosion of public trust, necessitate a proactive and coordinated global response.
International Relations
The alleged involvement of Chinese hackers in a cyberattack targeting the Premier of Western Australia has significant implications for international relations, potentially escalating tensions between Australia and China and further straining already fragile diplomatic ties. This incident highlights the growing challenge of attributing cyberattacks definitively and the difficulties in responding effectively within the framework of international law.The potential diplomatic fallout is considerable.
Australia, a staunch US ally, has increasingly voiced concerns about China’s assertive foreign policy and its growing cyber capabilities. A confirmed Chinese state-sponsored attack would likely trigger strong condemnation from Australia, potentially leading to sanctions, diplomatic expulsions, or further restrictions on Chinese investment and technological cooperation. Conversely, China would likely deny any involvement, potentially leading to a protracted period of diplomatic tension and mistrust.
The incident could also exacerbate existing anxieties among Australia’s regional allies regarding China’s cyber capabilities and intentions.
Comparison with Other Instances of Cyber Conflict
This incident shares similarities with other instances of alleged state-sponsored cyberattacks. The US has accused Russia and China of numerous cyber intrusions targeting critical infrastructure, government agencies, and private companies. The NotPetya attack in 2017, widely attributed to Russia, caused billions of dollars in damage globally. Similarly, China has been implicated in numerous intellectual property theft campaigns targeting Western businesses.
The key difference here, however, lies in the direct targeting of a high-profile political figure, escalating the potential for a significant diplomatic response. Unlike attacks on corporate entities where economic damage is the primary concern, this incident directly challenges national sovereignty and political stability. The response, therefore, is likely to be more politically charged than purely economically driven.
Visual Representation of Global State-Sponsored Cyberattacks
Imagine a world map. Each country is represented by a node, with the size of the node proportional to its perceived capability in state-sponsored cyber warfare. Larger nodes, such as the US, China, Russia, and Israel, would indicate more advanced capabilities. Lines connect the nodes, representing alleged cyberattacks. Thicker lines indicate more frequent or high-impact attacks.
The color of the lines could differentiate the type of attack (e.g., espionage, sabotage, disinformation). For example, a thick red line from a large Russian node to a smaller Ukrainian node could represent a significant disruptive attack. Multiple lines originating from a single node, such as China, could illustrate the breadth of their alleged activities. The map would visually demonstrate the global network of state-sponsored cyberattacks, highlighting key players and their targets, illustrating the complex and interconnected nature of this form of conflict.
The map would need to be updated regularly as the cyber landscape evolves and new information emerges, acknowledging the inherent uncertainties in attribution.
End of Discussion
The cyberattack targeting the Premier of Western Australia serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present threat of state-sponsored hacking. The incident underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures, not only within government but also across all sectors. While the full extent of the damage may not be immediately apparent, the long-term implications for public trust and international relations are significant.
This attack isn’t an isolated incident; it’s a wake-up call demanding a more proactive and collaborative approach to cybersecurity globally.
User Queries
What specific type of malware was used in the attack?
The exact type of malware hasn’t been publicly disclosed, but it likely involved sophisticated phishing techniques and potentially zero-day exploits to bypass security measures.
What was the immediate reaction of the Australian government?
The Australian government launched an immediate investigation, likely involving its cyber security agencies, and enhanced security protocols across relevant government systems.
How common are these types of attacks against high-profile individuals?
Attacks targeting high-profile individuals are unfortunately becoming increasingly common, as they often hold sensitive information and represent valuable targets for espionage or disruption.
What are the potential long-term consequences for Australia’s relationship with China?
The incident has the potential to further strain already tense relations between Australia and China, potentially leading to diplomatic fallout and increased scrutiny of Chinese activities within Australia.