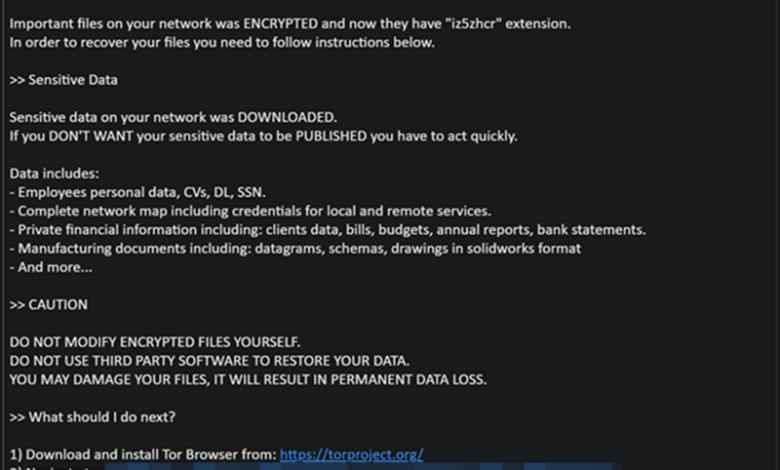
Cicada Linked to AlphV Ransomware Says Report
Cicada linked to alphv ransomware says report – Cicada linked to AlphV ransomware says report – Whoa, that’s a headline that grabbed
-my* attention! This isn’t your typical ransomware story; we’re diving into a complex web of malware, sophisticated attacks, and a potentially game-changing connection between two seemingly disparate threats. Prepare for a deep dive into the world of cybercrime, where the lines between different attacks blur and the stakes are incredibly high.
The report alleges a surprising link between the Cicada malware and the notorious AlphV ransomware operation. This connection raises serious questions about the scale and sophistication of these cybercriminal groups, and the potential for even more devastating attacks in the future. We’ll explore the technical details of both Cicada and AlphV, examining their attack methods, targets, and the evidence suggesting a collaboration.
We’ll also look at the potential impact of this link and discuss strategies for mitigating the risks these threats pose.
Cicada Malware’s Technical Analysis: Cicada Linked To Alphv Ransomware Says Report
The recent reports linking the Cicada malware to the ALPHV ransomware operation highlight a concerning evolution in advanced persistent threat (APT) tactics. Understanding Cicada’s technical capabilities is crucial for effective mitigation and defense against future attacks. This analysis delves into the malware’s functionalities, infiltration methods, and comparative analysis with other ransomware families.
Cicada Malware Functionalities
Cicada is a sophisticated piece of malware demonstrating a multi-stage infection process. Its core functionality centers around data exfiltration and encryption, typical of ransomware operations. However, Cicada’s capabilities extend beyond simple encryption; it employs techniques for persistence, privilege escalation, and evasion of security tools. The malware actively seeks sensitive data, including intellectual property, financial records, and personally identifiable information (PII), before encrypting it.
Furthermore, Cicada exhibits strong anti-analysis capabilities, making reverse engineering and malware analysis challenging.
Cicada Infiltration Methods
Initial access vectors for Cicada infections remain under investigation, but evidence suggests a combination of spear-phishing campaigns targeting specific organizations and potential exploitation of known vulnerabilities in widely used software. The malware likely leverages social engineering techniques to trick users into opening malicious attachments or clicking on compromised links. Once inside the network, Cicada utilizes lateral movement techniques to spread to other systems, potentially establishing a foothold within critical infrastructure.
The use of compromised credentials and legitimate administrative tools further aids its propagation.
Comparison with Other Ransomware Families
Compared to other prominent ransomware families like Ryuk or Conti, Cicada displays a more targeted approach, focusing on specific high-value targets rather than indiscriminate mass attacks. While sharing similar goals of data encryption and extortion, Cicada’s technical sophistication and advanced evasion techniques differentiate it. Unlike some ransomware families that rely heavily on readily available exploit kits, Cicada appears to utilize more customized and targeted exploits, suggesting a higher level of expertise and resources behind its development.
The level of persistence and stealth displayed by Cicada also surpasses many other ransomware strains.
Cicada Encryption Algorithms
The precise encryption algorithms employed by Cicada are not publicly available due to ongoing investigation and the malware’s anti-analysis capabilities. However, based on observed behavior, it is likely that Cicada uses strong, asymmetric encryption algorithms to encrypt sensitive data, making decryption without the decryption key extremely difficult, if not impossible. The use of strong encryption is a common characteristic among sophisticated ransomware operations, aiming to maximize the impact of the attack and increase the likelihood of successful extortion.
So, the news about the Cicada threat actor being linked to AlphV ransomware is pretty wild, right? It makes you think about the vulnerabilities in our systems, and how crucial robust security is. Building secure applications is key, which is why I’ve been diving into the world of domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , lately – learning how to create more secure and efficient apps.
Hopefully, advancements in app development can help us stay ahead of threats like Cicada and AlphV.
Hypothetical Cicada Infection Pathway
A hypothetical network diagram illustrating a Cicada infection pathway would begin with a spear-phishing email containing a malicious attachment. Upon execution, the malware establishes persistence, potentially through registry modifications or scheduled tasks. It then proceeds with lateral movement, utilizing techniques like pass-the-hash or exploiting known vulnerabilities in network services to access other systems. Once the malware identifies high-value targets, it exfiltrates sensitive data before encrypting files on targeted machines.
Finally, a ransom note is displayed, demanding payment for decryption and the return of stolen data. This process would involve multiple stages, requiring the malware to evade detection at each step. The diagram would visually represent this multi-stage attack, highlighting the various techniques used by the malware to achieve its objectives.
AlphV Ransomware’s Operational Methods

AlphV, also known as BlackCat, is a sophisticated ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation that has significantly impacted various organizations globally. Its operational methods are characterized by advanced techniques, aggressive ransom demands, and a focus on high-value targets. Understanding these methods is crucial for effective prevention and response strategies.AlphV’s success stems from a combination of factors, including its use of advanced evasion techniques, its ability to quickly encrypt large volumes of data, and its effective extortion tactics.
This analysis delves into the key aspects of AlphV’s operational methodology.
Ransom Negotiation Tactics
AlphV operators typically engage in direct negotiations with victims, often using encrypted communication channels to maintain anonymity and security. They often present a tiered pricing structure, with the ransom amount increasing if the victim delays payment or attempts to recover data independently. The operators are known for their aggressive approach, often threatening to publicly release stolen data if the ransom isn’t paid promptly.
They may also leverage leaked internal communications to pressure victims into compliance. The negotiations are often highly personalized, reflecting detailed knowledge of the victim’s operations and the sensitivity of the stolen data.
Typical Targets of AlphV Ransomware Attacks
AlphV attacks predominantly target large enterprises and organizations across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. These organizations often possess valuable intellectual property, sensitive customer data, and critical operational systems, making them attractive targets for high-value ransom demands. The attackers meticulously select their victims, focusing on those with a high likelihood of paying the ransom due to the potential impact of data loss or operational disruption.
Infrastructure Used for Command and Control
AlphV employs a decentralized command-and-control (C2) infrastructure, making it more resilient to takedown attempts. This infrastructure often utilizes a combination of techniques, including encrypted communication channels, multiple servers located in different jurisdictions, and anonymization services. This layered approach makes tracing the operators and disrupting their operations significantly challenging. The use of multiple, rapidly shifting infrastructure components contributes to the difficulty in tracking and disrupting their activities.
Examples of Ransom Demands
While precise ransom amounts vary depending on the size and sensitivity of the targeted organization, reports indicate that AlphV demands often range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars in cryptocurrency. In some cases, the ransom demand is directly tied to the estimated financial losses the victim would incur from data loss or business disruption. The payment is typically demanded in untraceable cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, further complicating law enforcement efforts.
Timeline of Notable AlphV Attacks and Their Impact
Tracking specific AlphV attacks with confirmed attribution is difficult due to the group’s operational security. However, numerous reports highlight attacks on various organizations across different sectors, resulting in significant data breaches, operational disruptions, and substantial financial losses. The impact extends beyond the immediate financial consequences, including reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and legal repercussions. While specific dates and victim names are often kept confidential for security reasons, the overall trend shows a steady increase in the frequency and sophistication of AlphV attacks over time.
The Reported Link Between Cicada and AlphV
The recent reports alleging a connection between the Cicada advanced persistent threat (APT) group and the AlphV (also known as BlackCat) ransomware operation have sent ripples through the cybersecurity community. While the specifics remain somewhat shrouded in mystery, the implications of such a link are significant, suggesting a potential evolution in the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of both actors.
This analysis will delve into the nature of this reported connection, examining the evidence presented and the methodologies employed to establish attribution.The nature of the reported connection between Cicada and AlphV centers around shared infrastructure, overlapping techniques, and potential personnel links. The reports, while not publicly releasing all their evidence due to ongoing investigations, suggest a convergence of activities that points towards a collaborative effort or, at the very least, a significant degree of operational overlap.
This isn’t a simple case of one group directly controlling the other; rather, the evidence suggests a more complex relationship, possibly involving shared resources or a coordinated effort between the groups.
Evidence Linking Cicada and AlphV, Cicada linked to alphv ransomware says report
The evidence cited in the reports linking Cicada and AlphV is multifaceted and relies on a combination of technical analysis and intelligence gathering. Key elements include the discovery of shared infrastructure, such as command-and-control (C2) servers and data exfiltration channels, used by both actors. Furthermore, similarities in the malware’s code, particularly in obfuscation techniques and specific functionalities, are noted.
Finally, some reports hint at potential overlaps in personnel or operational patterns, although these details are often kept confidential due to the sensitive nature of the intelligence. The precise details of the evidence remain largely undisclosed to protect ongoing investigations and operational security.
Attribution Methodologies
The attribution methodologies used in the report likely involved a combination of techniques. Technical analysis of the malware samples, network traffic analysis to identify shared infrastructure and communication patterns, and intelligence gathering from various sources (human intelligence, open-source intelligence, and signals intelligence) were probably all employed. The process of attributing malicious cyber activity to specific actors is complex and requires a high degree of certainty, relying on multiple lines of evidence converging to point towards a specific group.
The level of confidence in the attribution will vary depending on the available evidence and the rigor of the analysis.
Comparison of Cicada and AlphV
The following table summarizes the key similarities and differences between Cicada and AlphV based on publicly available information and the reported findings:
| Characteristic | Cicada | AlphV | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Espionage, data theft | Ransomware deployment, data extortion | Different primary goals, but potential for overlap in data exfiltration |
| Target Profile | Government entities, critical infrastructure | Broad range of organizations, prioritizing high-value targets | Cicada is more focused, while AlphV has a wider target base. |
| Modus Operandi | Sophisticated APT techniques, stealthy operations | Aggressive ransomware attacks, public data leaks | Contrasting approaches, yet potential collaboration on data acquisition. |
| Geographic Focus | Primarily East Asia | Global reach | Different primary regions of operation, though potential for collaboration to expand reach. |
Potential Motivations Behind a Link
Several potential motivations could explain a link between Cicada and AlphV. One possibility is a strategic partnership, where Cicada provides initial access and intelligence gathering, paving the way for AlphV to deploy ransomware. This would allow AlphV to target high-value organizations with a higher likelihood of success, while Cicada benefits from the financial gains generated by the ransomware attacks.
Another possibility is a more opportunistic relationship, where both groups independently exploit shared infrastructure or leverage similar techniques without explicit collaboration. Finally, it’s possible that some individuals with expertise in both espionage and ransomware operations are involved in both groups, creating an overlap in capabilities and methods. The exact nature of the relationship remains a subject of ongoing investigation.
Impact and Mitigation Strategies
The convergence of the Cicada advanced persistent threat (APT) group and the AlphV ransomware operation presents a significant threat to organizations globally. Understanding the potential consequences of a successful attack, and implementing robust mitigation strategies, is crucial for minimizing damage and ensuring business continuity. The financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruption can be devastating, far exceeding the immediate ransom demand.The financial impact of a successful Cicada/AlphV attack extends beyond the ransom payment itself.
Data breaches can lead to significant legal fees, regulatory fines (like GDPR penalties), and the cost of restoring systems and data. The loss of intellectual property, customer data, and operational downtime can cripple businesses, leading to lost revenue and decreased market share. Reputational damage can be equally devastating, impacting customer trust, investor confidence, and overall brand value. A single high-profile attack can severely damage an organization’s reputation, potentially leading to long-term financial consequences.
For example, the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017 caused billions of dollars in damages across multiple industries, highlighting the catastrophic potential of such events.
Financial and Reputational Damage from Cicada/AlphV Attacks
The combined threat of Cicada’s sophisticated espionage capabilities and AlphV’s destructive ransomware capabilities creates a uniquely dangerous scenario. Cicada’s initial intrusion could remain undetected for extended periods, allowing AlphV to encrypt critical data and systems, maximizing the damage. The resulting financial losses could include: direct ransom payments; costs associated with data recovery and system restoration; legal and regulatory fines; loss of revenue due to downtime; and the expense of public relations and reputation management.
Reputational damage could manifest as loss of customer trust, damage to brand image, decreased investor confidence, and difficulty attracting and retaining talent. The long-term consequences can be substantial, impacting an organization’s ability to compete and thrive. Consider the impact on a healthcare provider, for example, whose patient data is compromised – the reputational and legal repercussions would be severe.
Successful Mitigation Strategies Against Similar Ransomware
Several successful mitigation strategies have proven effective against ransomware attacks similar to AlphV. These include implementing robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all systems and accounts, regularly patching and updating software to address known vulnerabilities, and employing a comprehensive endpoint detection and response (EDR) solution to detect and respond to malicious activity in real-time. Furthermore, regular backups of critical data, stored offline and in a geographically separate location, are crucial for data recovery in the event of an attack.
These backups should be tested regularly to ensure their integrity and recoverability. Finally, employing a security information and event management (SIEM) system can help organizations monitor security events, detect anomalies, and respond to threats more effectively. The successful mitigation of the WannaCry ransomware attack in some organizations can be attributed to the timely application of security patches, illustrating the importance of proactive security measures.
Best Practices for Ransomware Protection
Organizations should prioritize a multi-layered approach to ransomware protection. This involves:
- Regularly updating software and operating systems to patch vulnerabilities.
- Implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Regularly backing up critical data to offline and geographically diverse locations.
- Using endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to monitor and respond to threats.
- Employing a security information and event management (SIEM) system for centralized security monitoring.
- Educating employees about ransomware threats and phishing techniques.
- Implementing network segmentation to limit the impact of a breach.
- Regularly testing and validating backup and recovery procedures.
- Developing an incident response plan to guide actions in the event of an attack.
Security Awareness Training Program
A comprehensive security awareness training program is vital in mitigating ransomware attacks. The program should focus on educating employees about:
- Recognizing and avoiding phishing emails and malicious attachments.
- Understanding the risks of clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Practicing good password hygiene, including using strong, unique passwords and enabling MFA.
- Reporting suspicious activity to the IT department immediately.
- Understanding the organization’s ransomware response plan and their role in it.
The program should include interactive modules, simulated phishing attacks, and regular refresher training to reinforce key concepts and keep employees informed about evolving threats. Regular testing and reinforcement of these principles are key to maintaining a high level of awareness and reducing the risk of human error, a common entry point for ransomware attacks.
The Role of Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity in today’s complex cyber landscape. Ransomware attacks, like the suspected link between Cicada malware and the AlphV ransomware, highlight the critical role threat intelligence plays in proactive security. Without it, organizations are essentially fighting blind, reacting to attacks instead of preventing them. Understanding the threat landscape, identifying vulnerabilities, and anticipating attacks are all key components of a robust security posture.Threat intelligence empowers organizations to move beyond reactive security measures.
By leveraging insights into attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), organizations can proactively identify and mitigate risks before they become full-blown incidents. This proactive approach significantly reduces the impact of successful attacks, minimizing downtime and financial losses. It also allows for the development of more effective security controls tailored to specific threats.
Threat Intelligence and Risk Mitigation
Effective threat intelligence directly translates into improved risk mitigation strategies. By analyzing threat data, organizations can identify their most vulnerable systems and prioritize remediation efforts. This might involve patching known vulnerabilities, strengthening access controls, or implementing advanced security technologies like intrusion detection and prevention systems. Furthermore, threat intelligence enables the development of more realistic and effective incident response plans, ensuring a faster and more efficient recovery process in the event of an attack.
So, the news about the Cicada group being linked to the ALPHV ransomware is pretty wild, right? It highlights just how sophisticated these attacks are becoming. Understanding how to mitigate this kind of threat requires robust security measures, and that’s where solutions like those discussed in this article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management become crucial.
Ultimately, improving cloud security is key to combating these advanced ransomware groups like Cicada.
Developing and Implementing a Threat Intelligence Program
Building a robust threat intelligence program involves several key steps. First, organizations need to define their scope and objectives, identifying the specific threats they are most concerned about. This includes identifying potential sources of threat intelligence, such as open-source intelligence (OSINT), commercial threat feeds, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. Next, a process for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating intelligence needs to be established.
This involves creating a team with the necessary skills and expertise, and defining clear workflows for handling threat information. Finally, the program needs to be continuously evaluated and improved based on its effectiveness and the evolving threat landscape. Regular testing and updates are crucial to maintaining its relevance.
Hypothetical Threat Intelligence Report: Cicada/AlphV
Subject: Potential Link Between Cicada Malware and AlphV Ransomware OperationsThreat Actors: Cicada APT group, AlphV Ransomware operatorsObserved Activities: Evidence suggests Cicada may be leveraging its access and capabilities to facilitate AlphV ransomware deployments. This includes initial access through spear-phishing or exploitation of vulnerabilities, followed by lateral movement and data exfiltration prior to ransomware deployment.Technical Indicators of Compromise (TIOCs): [List of specific IOCs would be included here, such as specific malware hashes, IP addresses, domain names, and file paths].Impact: Successful attacks could lead to significant data breaches, operational disruption, and financial losses. The potential for reputational damage is also considerable.Mitigation Strategies: Enhanced endpoint detection and response (EDR), regular security awareness training, robust network segmentation, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are recommended. Proactive threat hunting based on the provided TIOCs is also crucial.
Applying Threat Intelligence Data
Interpreting and applying threat intelligence involves a multi-faceted approach. The hypothetical report above provides a framework. Organizations should cross-reference the TIOCs with their own security logs and network traffic to identify potential compromises. Threat intelligence should also inform security awareness training programs, highlighting the specific tactics used by Cicada and AlphV to help employees identify and report suspicious activities.
Finally, the identified mitigation strategies should be prioritized and implemented to reduce the organization’s attack surface and enhance its overall resilience. Continuous monitoring and analysis are essential to ensure the effectiveness of these measures.
Closing Summary
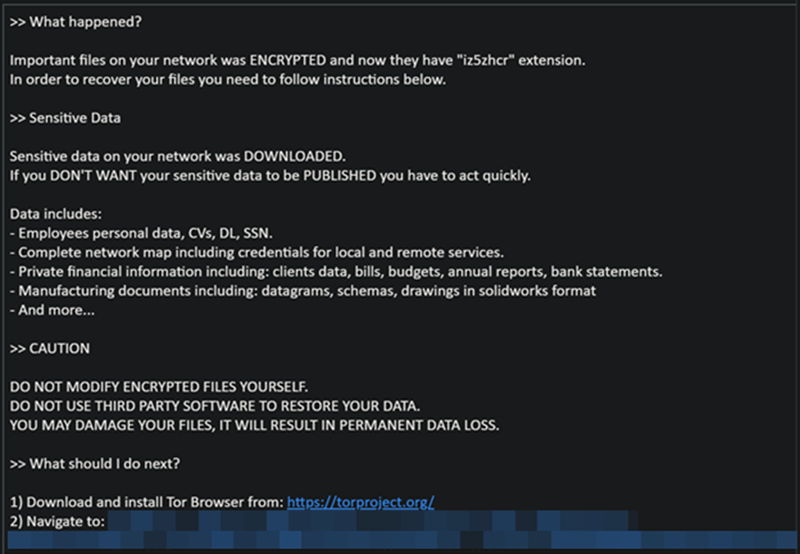
The alleged link between Cicada and AlphV ransomware paints a concerning picture of the evolving cyber threat landscape. The sophistication and potential for widespread damage highlighted in this report should serve as a wake-up call for individuals and organizations alike. Strengthening cybersecurity defenses, staying informed about emerging threats, and investing in robust threat intelligence are no longer optional – they’re essential for survival in this increasingly dangerous digital world.
The fight against ransomware is far from over, and understanding the connections between different threats is key to winning the battle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes AlphV ransomware particularly dangerous?
AlphV is known for its aggressive tactics, targeting large organizations with significant data exfiltration and high ransom demands. Their operational security is also quite advanced, making them difficult to track and disrupt.
How does Cicada malware infiltrate systems?
The exact methods used by Cicada are still under investigation, but initial reports suggest sophisticated phishing campaigns and potential exploitation of software vulnerabilities.
What is the potential impact of a combined Cicada/AlphV attack?
A combined attack could result in significant data loss, financial losses from ransom payments, reputational damage, and operational disruption for affected organizations.
Are there any indicators of compromise (IOCs) associated with Cicada?
Specific IOCs are usually kept confidential by security researchers to avoid alerting threat actors. However, reputable security firms often release general information on tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).





