Citrix Server Vulnerability Leads to Ransomware Attack
Citrix server vulnerability leads to ransomware attack – that’s a scary headline, isn’t it? But it’s a reality for many businesses. This post dives deep into how vulnerabilities in Citrix servers are being exploited by cybercriminals to deploy ransomware, leaving organizations facing crippling financial losses and operational disruptions. We’ll explore the common vulnerabilities, the attack methods used, the devastating impact, and most importantly, how to protect yourself.
We’ll cover everything from identifying potential weaknesses in your Citrix infrastructure to implementing robust security measures to prevent a ransomware attack. Think of this as your survival guide in the increasingly dangerous world of cyber threats. We’ll even look at real-world examples to illustrate the very real consequences of failing to secure your Citrix environment.
Citrix Server Vulnerabilities
Citrix servers, while offering powerful remote access capabilities, have unfortunately been a frequent target for cyberattacks due to a history of security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities, if left unpatched, can create significant entry points for malicious actors, leading to devastating consequences such as ransomware infections and data breaches. Understanding the common vulnerabilities and their potential impact is crucial for effective security posture management.
Citrix Server Vulnerability Types and Prevalence
Several types of vulnerabilities have plagued Citrix servers over the years, often stemming from flaws in their core components or misconfigurations. These range from authentication bypasses to remote code execution vulnerabilities, all potentially exploitable for malicious purposes. The prevalence of these vulnerabilities is unfortunately high, often due to delayed patching or inadequate security practices. Many organizations rely on Citrix for their remote access needs, making a large attack surface available to threat actors.
Specific Citrix Vulnerabilities and Their Impacts
A comprehensive understanding requires examining specific examples. The following table details some notable vulnerabilities, their descriptions, severity, and potential impacts. Note that this is not an exhaustive list, and new vulnerabilities are constantly being discovered and exploited.
| CVE Number | Vulnerability Description | Severity Level | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2019-19781 | Arbitrary file read vulnerability in Citrix ADC and Gateway. Attackers could potentially read sensitive files from the server. | Critical | Data breach, unauthorized access to sensitive information. |
| CVE-2020-8197 | Remote code execution vulnerability in Citrix ADC and Gateway. Successful exploitation allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the server. | Critical | Complete server compromise, ransomware deployment, data exfiltration. |
| CVE-2022-27518 | Authentication bypass vulnerability in Citrix Application Delivery Management (ADM). Attackers could gain unauthorized access without valid credentials. | High | Unauthorized access to administrative functions, potential for further exploitation. |
Note that the severity levels and potential impacts are based on common vulnerability scoring systems and industry best practices. The actual impact can vary depending on the specific environment and attacker capabilities. The consequences of successful exploitation can range from simple data breaches to complete system compromise and crippling ransomware attacks. Proactive patching and robust security measures are essential to mitigate these risks.
Attack Vectors
Ransomware groups are constantly seeking new ways to infiltrate systems and deploy their malicious payloads. Citrix servers, due to their widespread use and often complex configurations, have unfortunately become a prime target. Exploiting vulnerabilities in these servers provides attackers with a valuable foothold into an organization’s network, potentially leading to widespread data encryption and significant financial losses. Understanding the attack vectors used is crucial for effective mitigation and defense.The methods employed by ransomware actors to exploit Citrix vulnerabilities are diverse but often involve leveraging known security flaws to gain initial access.
Once inside, they move laterally across the network, escalating privileges, and ultimately deploying the ransomware. This process is often carefully orchestrated, using various tools and techniques to avoid detection and maximize their impact. The speed and efficiency with which these attacks can unfold underscore the importance of proactive security measures.
Citrix Vulnerability Exploitation Methods
Ransomware actors typically leverage publicly disclosed vulnerabilities or zero-day exploits to compromise Citrix servers. These vulnerabilities can range from authentication bypasses, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access, to remote code execution flaws, enabling them to run arbitrary code on the server. Once access is achieved, attackers often utilize various post-exploitation techniques to further their objectives.
Steps in a Typical Citrix-Based Ransomware Attack
This section Artikels the typical steps involved in a ransomware attack leveraging a Citrix vulnerability. Understanding this process helps security professionals anticipate and defend against such threats.
- Initial Compromise: The attack begins with the exploitation of a known vulnerability in the Citrix server, often through a publicly available exploit or a custom-developed zero-day exploit. This could involve sending a specially crafted request to the Citrix gateway, potentially exploiting a flaw in the authentication mechanism or a buffer overflow vulnerability.
- Privilege Escalation: After gaining initial access, attackers typically attempt to escalate their privileges to gain administrator-level access on the Citrix server. This allows them to access sensitive data and install additional malicious software.
- Lateral Movement: With administrator privileges, attackers can move laterally across the network, accessing other servers and workstations. This often involves using techniques such as pass-the-hash or exploiting other vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure.
- Data Exfiltration: Before deploying ransomware, attackers often exfiltrate sensitive data as a backup, to be used for extortion purposes even if the ransomware is removed or fails to encrypt data. This data could include financial records, customer information, or intellectual property.
- Ransomware Deployment: Once the attackers have achieved their objectives, they deploy the ransomware, encrypting sensitive files and demanding a ransom for their decryption.
- Extortion: The attackers demand a ransom, often threatening to release the exfiltrated data publicly if the ransom is not paid. They may provide a deadline and use various methods to communicate their demands.
Example Attack Scenario
Let’s imagine a scenario where a company’s Citrix server is vulnerable to a known authentication bypass flaw.
- A malicious actor discovers this vulnerability and crafts an exploit to gain unauthorized access to the Citrix server.
- Once inside, the actor uses readily available tools to escalate privileges to the administrator level.
- The actor then moves laterally, compromising a domain controller and gaining access to sensitive user credentials.
- Before encrypting files, the actor copies sensitive financial data to a remote server for later use in extortion.
- Finally, the actor deploys a sophisticated ransomware variant, encrypting files across the entire network.
- The actor demands a significant ransom in cryptocurrency, threatening to release the stolen financial data if the ransom is not paid within a specified timeframe.
Impact of a Successful Attack

A successful ransomware attack exploiting a Citrix server vulnerability can have devastating consequences for an organization, regardless of its size. The impact extends far beyond the immediate disruption of services; it can cripple operations, damage reputation, and lead to significant financial losses. The severity of the consequences, however, varies depending on the organization’s size, preparedness, and the specific nature of the attack.The immediate impact often involves data encryption, rendering critical systems and files inaccessible.
This can halt production, disrupt customer service, and prevent employees from performing their duties. Beyond the immediate operational standstill, there are long-term ramifications involving data recovery, legal repercussions, and the restoration of trust with customers and stakeholders. The financial burden encompasses not only the ransom payment (if paid), but also the costs associated with data recovery, system restoration, cybersecurity consulting, legal fees, and potential fines for regulatory non-compliance.
Furthermore, reputational damage can lead to a loss of customers, investors, and business opportunities.
Financial and Operational Impacts
The financial impact of a ransomware attack can be crippling. Direct costs include the ransom payment itself (which can range from thousands to millions of dollars), the cost of hiring cybersecurity experts to investigate and remediate the attack, and the expenses related to restoring data and systems. Indirect costs are equally significant and can include lost revenue due to business downtime, the cost of repairing damaged reputation, and potential legal and regulatory fines.
Operational impacts involve disruptions to daily business processes, decreased productivity, loss of customer trust, and potential damage to brand image. The disruption can cascade through the entire organization, affecting various departments and impacting the overall efficiency and profitability of the business. For example, a manufacturing company might experience production delays, leading to missed deadlines and lost contracts, while a financial institution might face regulatory scrutiny and fines for failing to protect sensitive customer data.
| Impact Category | Small Organization | Medium Organization | Large Organization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Impact | Potential business closure due to high ransom demands relative to revenue; significant loss of productivity and revenue; high cost of recovery relative to budget. | Significant loss of revenue; substantial costs for recovery, legal fees, and potential regulatory fines; potential impact on investor confidence. | High cost of recovery and remediation; significant loss of revenue and productivity; potential impact on stock price and investor relations; potential for large regulatory fines. |
| Operational Impact | Complete shutdown of operations; difficulty in recovering data and systems; loss of customer trust; potential for permanent business closure. | Significant disruption to operations; delays in project completion; loss of customer confidence; impact on employee morale and productivity. | Disruption to multiple departments and operations; potential for supply chain disruptions; loss of customer confidence; reputational damage; potential for long-term operational inefficiencies. |
| Reputational Impact | Loss of local customer base; damage to brand reputation within the community; difficulty attracting new customers. | Damage to brand reputation among wider customer base; loss of investor confidence; difficulty in attracting new clients. | Significant damage to brand reputation globally; loss of investor confidence; impact on stock price; difficulty attracting and retaining talent. |
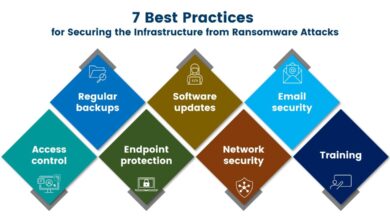
Mitigation Strategies
Protecting your Citrix environment from ransomware attacks stemming from vulnerabilities requires a multi-layered approach focusing on prevention and rapid response. Ignoring security best practices leaves your organization vulnerable to significant financial and reputational damage. A proactive strategy is far more cost-effective than reacting to a breach.Regular patching and updates are the bedrock of any effective security strategy. Failing to update your Citrix servers exposes them to known vulnerabilities that attackers actively exploit.
This isn’t just about installing patches; it’s about establishing a robust, automated patching process that ensures all systems are consistently up-to-date with the latest security fixes. Delays in patching can be disastrous, allowing attackers ample time to identify and exploit weaknesses.
Regular Patching and Updates
Implementing a robust patching strategy involves more than just downloading and installing updates. It requires a well-defined process, including testing patches in a non-production environment before deploying them to production systems. This minimizes the risk of unforeseen issues caused by patches. Automation tools can significantly streamline this process, scheduling updates during off-peak hours to minimize disruption. Furthermore, a comprehensive inventory of all Citrix servers and components is crucial for efficient patch management.
This allows for targeted updates, ensuring all vulnerable systems are addressed. Failing to adequately test patches before deployment can lead to system instability and service outages. Therefore, a phased rollout, monitoring for issues after each phase, is recommended.
Multi-Factor Authentication and Network Segmentation
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before accessing Citrix resources. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if attackers obtain credentials through phishing or other means. For instance, combining a password with a one-time code from an authenticator app makes it exponentially harder for attackers to gain access.
Network segmentation further enhances security by isolating sensitive Citrix servers from the rest of the network. This limits the impact of a successful breach, preventing attackers from easily moving laterally across the network to access other critical systems. If one segment is compromised, the damage is contained, preventing a widespread ransomware infection. For example, isolating the Citrix environment behind a firewall and restricting access only to authorized users and systems prevents attackers from accessing other critical systems, such as databases or file servers.
The recent Citrix server vulnerability leading to ransomware attacks highlights the critical need for robust security in enterprise systems. Building secure applications is paramount, and exploring modern development approaches like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future could help mitigate such risks. Ultimately, proactive security measures, combined with secure application development, are essential to prevent future Citrix-related breaches.
Proactive Security Measures
Implementing a comprehensive security strategy requires a proactive approach that goes beyond simply patching vulnerabilities. The following measures significantly enhance security and reduce the risk of a successful ransomware attack:
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regularly assess your Citrix environment for vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify potential security gaps.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Deploy IDS/IPS solutions to monitor network traffic for malicious activity and block suspicious connections. These systems provide real-time alerts and can help contain an attack before it spreads.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Use a SIEM system to centralize and analyze security logs from various sources. This allows for faster detection and response to security incidents.
- Employee Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and other common attack vectors. Regular training significantly reduces the likelihood of human error leading to a security breach.
- Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning: Maintain regular backups of your critical data and systems. Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of a ransomware attack. This includes offline backups, stored securely offsite, to prevent encryption from affecting your recovery efforts.
Case Studies
Learning from past incidents is crucial in cybersecurity. Examining real-world examples of ransomware attacks leveraging Citrix vulnerabilities helps us understand attack vectors and improve our defenses. The following case studies illustrate the severity and impact of such attacks.
Real-World Examples of Citrix-Related Ransomware Attacks, Citrix server vulnerability leads to ransomware attack
While specific details of many ransomware attacks involving Citrix vulnerabilities are often kept confidential for security reasons, we can analyze publicly available information to glean valuable insights. The following table summarizes three illustrative examples, although the actual number of incidents is likely much higher. Note that precise details about some attacks may be limited due to the sensitive nature of the information.
| Organization | Vulnerability Exploited | Attack Method | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Organization A – Name withheld due to confidentiality) | CVE-2019-19781 (Citrix NetScaler Gateway vulnerability) | Attackers exploited the vulnerability to gain initial access to the network. They then used lateral movement techniques to spread ransomware throughout the organization’s systems. This likely involved exploiting other vulnerabilities or using stolen credentials. | Significant data loss, operational disruption, and substantial financial costs associated with recovery, ransom payment (potentially), and legal repercussions. The exact ransom demand and whether it was paid remains undisclosed. |
| (Organization B – Name withheld due to confidentiality) | CVE-2018-0877 (Citrix StoreFront vulnerability) | The attackers leveraged the vulnerability in StoreFront to deploy malware onto the victim’s network. This malware then facilitated the deployment of ransomware across numerous endpoints. The attack likely involved exploiting other vulnerabilities to achieve full network compromise. | Significant downtime, data encryption, and potential data exfiltration. The organization experienced considerable financial losses due to business interruption and remediation efforts. Details on ransom payment are unavailable. |
| (Organization C – Name withheld due to confidentiality) | Multiple Citrix vulnerabilities (specific CVEs not publicly disclosed) | This attack involved a sophisticated multi-stage approach. Initial access was likely gained through a combination of vulnerabilities in Citrix products and phishing techniques. The attackers then established persistence and used various tools and techniques to spread ransomware throughout the network. | A widespread ransomware infection caused significant disruption to business operations, leading to substantial financial losses. The extent of data loss and whether a ransom was paid is not publicly available. |
Forensic Analysis: Citrix Server Vulnerability Leads To Ransomware Attack
Investigating a ransomware attack stemming from a Citrix vulnerability requires a methodical and comprehensive forensic approach. The goal is to identify the attack vector, the extent of the compromise, and the specific ransomware variant involved, all while preserving evidence for potential legal action. This process is crucial not only for recovering data but also for preventing future attacks.The forensic analysis of a Citrix-compromised system begins with securing the affected environment to prevent further data exfiltration or damage.
This involves isolating the compromised systems from the network and creating forensic images of hard drives and other storage devices. The analysis itself then proceeds in a series of well-defined steps.
Identifying Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) Related to Citrix
Identifying IOCs related to Citrix is paramount. These indicators can range from suspicious network activity to unusual log entries within the Citrix environment. For example, detecting unusual login attempts from unfamiliar IP addresses or the presence of unauthorized processes related to the Citrix server should raise immediate suspicion. Examining Citrix server logs for evidence of unauthorized access, unusual configurations, or the exploitation of known vulnerabilities is critical.
The recent Citrix server vulnerability leading to ransomware attacks highlights the urgent need for robust cloud security. Understanding and mitigating these risks is crucial, and solutions like those discussed in this excellent article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management are becoming increasingly vital. Ultimately, proactive security measures are the best defense against these devastating Citrix-related breaches.
Analyzing network traffic for connections to known command-and-control (C2) servers associated with ransomware groups is another key step. Furthermore, analyzing the registry for suspicious keys or values associated with the Citrix server and the ransomware can reveal crucial information about the attack. The presence of unusual files or processes, particularly those related to known ransomware strains, is also a strong indicator.
Data Recovery and System Restoration
Data recovery and system restoration following a ransomware attack are complex processes that depend heavily on the specific ransomware used and the extent of the encryption. The first step involves identifying the type of ransomware involved, which can be done by analyzing the ransom note and encrypted files. This helps determine the most effective recovery strategy. If backups are available and verified to be clean, restoring systems from these backups is the most efficient method.
However, if backups are unavailable or compromised, more advanced techniques may be necessary. These could include using specialized ransomware decryption tools (if available for the specific variant), attempting data recovery from shadow copies or other system recovery points, or employing professional data recovery services. Rebuilding affected systems from scratch, ensuring all software is updated and patched, is often necessary.
Post-recovery, a thorough security audit should be conducted to identify and address any remaining vulnerabilities.
Network Forensics
Network forensics play a vital role in understanding the attack’s scope and trajectory. Analyzing network logs and packet captures can reveal the attacker’s entry point, their activities within the network, and the exfiltration of data. This analysis can identify the source of the infection, the lateral movement within the network, and the communication channels used by the attackers.
For example, identifying suspicious traffic to and from external IP addresses, or unusual data transfers, are important clues. The investigation should include analyzing DNS logs to identify any suspicious domain name requests, and firewall logs to look for any unauthorized network access attempts.
Memory Forensics
Memory forensics provides insights into the attacker’s actions in real-time. Analyzing memory dumps from the compromised Citrix server can reveal active malware processes, network connections, and other artifacts left behind by the attackers. This can be particularly useful in identifying the specific techniques used by the attackers and in recovering data that might not be accessible through other methods.
For instance, memory analysis might uncover the encryption keys used by the ransomware, enabling data recovery. This technique requires specialized tools and expertise.
Legal and Regulatory Implications

A Citrix-related ransomware attack triggers a cascade of legal and regulatory ramifications for affected organizations. The severity of these implications depends on factors such as the volume of compromised data, the sensitivity of that data, the organization’s industry, and the effectiveness of its incident response. Failing to adequately address these legal obligations can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and even criminal prosecution.Organizations must navigate a complex web of laws and regulations designed to protect sensitive data.
These regulations often mandate specific actions in the event of a data breach, including notification requirements, data recovery strategies, and ongoing security improvements. Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines and legal action from both governmental agencies and private individuals.
Data Breach Notification Laws
Data breach notification laws vary significantly across jurisdictions, but generally require organizations to notify affected individuals and, in some cases, regulatory authorities within a specific timeframe following the discovery of a breach. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) impose stringent notification requirements, with specific details on the information that must be included in the notification.
The timeframe for notification can range from 24 to 72 hours, depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the breach. Failure to comply with these notification requirements can result in substantial penalties. For instance, under the GDPR, organizations can face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
Data Privacy Regulation Compliance
Complying with data privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is paramount after a Citrix-related ransomware attack. This involves conducting a thorough assessment of the compromised data to determine the extent of the breach and the individuals affected. This assessment must identify the type of data compromised (e.g., personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), financial data), the number of individuals affected, and the potential risks associated with the breach.
Based on this assessment, organizations must implement appropriate remediation measures, such as credit monitoring services for affected individuals, and enhance security measures to prevent future attacks. Detailed documentation of all actions taken during the incident response is crucial for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements.
Accountability and Liability
Organizations are accountable for the security of their systems and the data they hold. In the event of a Citrix-related ransomware attack, they may face legal action from affected individuals, regulatory bodies, and even business partners. Liability can extend to various parties, including the organization itself, its IT service providers, and even the developers of the vulnerable Citrix software.
This accountability underscores the importance of robust security practices, incident response plans, and comprehensive cybersecurity insurance to mitigate potential legal and financial consequences. Demonstrating a proactive approach to security, including regular security audits and vulnerability assessments, can help mitigate liability in the event of a breach. The organization’s response to the incident, including the speed and effectiveness of its remediation efforts, will be closely scrutinized by regulatory bodies and legal counsel.
Conclusion

The threat of ransomware attacks targeting Citrix vulnerabilities is real and ever-present. While the potential damage is significant, proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk. By understanding the common attack vectors, implementing strong security practices, and staying informed about the latest threats, you can significantly bolster your defenses. Remember, prevention is always better than cure – and in the world of cybersecurity, a cure can be incredibly expensive and painful.
Stay vigilant, stay updated, and stay secure!
Q&A
What are the common signs of a Citrix-related ransomware attack?
Unusual network activity, inaccessible applications, unusual login attempts, and ransomware notes demanding payment are all potential indicators.
How long does it typically take to recover from a Citrix ransomware attack?
Recovery time varies greatly depending on the severity of the attack, the size of the organization, and the availability of backups. It can range from days to weeks, or even longer.
Is my insurance likely to cover a Citrix ransomware attack?
Cybersecurity insurance coverage varies widely depending on your policy. It’s crucial to review your policy carefully to understand your coverage for ransomware attacks and the specific exclusions.
What is the role of regular patching in preventing Citrix ransomware attacks?
Regular patching is crucial. It addresses known vulnerabilities that attackers often exploit. Keeping your Citrix environment updated with the latest patches significantly reduces your attack surface.