Comparing Competitors on G2 A Deep Dive
Comparing competitors on G2 is more than just glancing at star ratings; it’s about unearthing the real story behind the software. This post dives deep into how to effectively leverage G2’s data to analyze competitors, understand their strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately inform your own strategic decisions. We’ll explore G2’s features, data extraction techniques, and even how to visualize your findings for maximum impact.
From identifying key competitors within your specific niche to interpreting user reviews and sentiment, we’ll cover everything you need to make data-driven comparisons. Get ready to transform raw G2 data into actionable insights!
Understanding G2 Competitor Comparisons: Comparing Competitors On G2
G2 is a popular platform for software buyers to research and compare different products. Its competitor comparison features are a key element in helping users make informed decisions. Understanding how G2 presents this information is crucial for leveraging the platform effectively.G2 displays competitor comparisons in several ways, making it a versatile tool for product research. The platform offers side-by-side comparisons of key metrics, allowing users to quickly assess the strengths and weaknesses of different options.
This visual approach is highly effective in highlighting key differences. Additionally, G2 often presents data in the form of charts and graphs, providing a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding than simple numerical comparisons alone. Finally, users can filter and sort comparison results based on their specific requirements, enabling tailored evaluations.
Data Provided for Comparison
G2 provides a wealth of data to facilitate comprehensive competitor comparisons. This includes user ratings, which offer a general sense of user satisfaction. Detailed reviews offer qualitative insights into specific aspects of the software, such as ease of use, customer support, and overall value. Furthermore, G2 presents feature comparisons, highlighting which products offer specific functionalities. This allows users to determine if a particular software meets their specific needs.
Finally, G2 often incorporates data on pricing, deployment models, and other relevant aspects, enabling a holistic evaluation of the various options.
G2’s Scoring System and its Limitations, Comparing competitors on g2
G2 employs a proprietary scoring system to rank software products. This system aggregates various data points, including user ratings and reviews, to generate an overall score. While this provides a convenient summary, it’s crucial to understand its limitations. The scoring system may not equally weigh all factors, and the weighting scheme itself isn’t publicly disclosed. This lack of transparency can make it difficult to fully interpret the scores.
Furthermore, the scores are heavily influenced by the volume and nature of user reviews, meaning that products with fewer reviews might be unfairly disadvantaged. For example, a new product with excellent features but few reviews may have a lower score than an established product with many reviews, some of which are negative. Therefore, while G2’s scores provide a useful starting point, they should not be the sole basis for a purchasing decision.
A thorough review of individual reviews and feature comparisons is essential for a well-informed choice.
Identifying Key Competitors on G2
G2 is a powerful resource for understanding your market landscape and identifying key competitors. Effectively leveraging G2’s data requires a strategic approach to competitor identification, moving beyond simple searches to a more nuanced understanding of direct and indirect competition. This involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure a comprehensive and relevant comparison.Identifying the top competitors for a specific software category on G2 is straightforward.
Begin by navigating to the relevant software category on the G2 website. G2 typically presents a ranked list of products within each category, often based on user reviews and ratings. This initial list provides a strong starting point for identifying your primary competitors. Further refinement can be achieved by filtering the results based on specific features, pricing tiers, or target customer segments.
For example, if you’re selling project management software aimed at small businesses, you would filter the results to reflect those criteria, leading to a more precise set of competitors.
Identifying Direct and Indirect Competitors Using G2 Data
G2’s data allows for a clear distinction between direct and indirect competitors. Direct competitors offer essentially the same product or service as yours, targeting the same customer base. These are easily identified through the initial category ranking and filtering process described above. Indirect competitors, however, offer alternative solutions that address the same underlying customer needs, even if their products or services differ significantly.
Identifying indirect competitors requires a deeper dive into user reviews. By analyzing the reasons users choose specific products (or reject others), you can identify solutions that fulfill similar functions, even if they aren’t directly comparable in terms of features. For example, if you sell CRM software, an indirect competitor might be a marketing automation platform that provides similar customer relationship management capabilities, albeit in a different context.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Competitors for Comparison
Choosing the right competitors for a detailed comparison is crucial for generating meaningful insights. Several factors should inform this selection. First, consider market share. Focusing on major players ensures your comparison reflects the most relevant competitive landscape. Second, analyze product features and functionality.
Select competitors with overlapping features to enable a direct comparison of capabilities. Third, assess target audience overlap. Choose competitors that serve a similar customer base to ensure the comparison is relevant to your business strategy. Fourth, evaluate pricing and business models. Including competitors with diverse pricing structures provides a broader perspective on the market.
Finally, consider customer reviews and ratings. G2’s user reviews offer valuable insights into customer satisfaction and can reveal critical strengths and weaknesses of competing products. This holistic approach ensures a robust and insightful competitive analysis.
Data Extraction and Organization for Comparison
Gathering and organizing data from G2 for competitor analysis is crucial for a meaningful comparison. A well-structured approach ensures you’re comparing apples to apples, highlighting key differences and similarities effectively. This involves a strategic data extraction process followed by careful organization into a readily understandable format.
A systematic approach to data extraction is paramount for a fair and accurate comparison. This goes beyond simply browsing G2; it requires a defined process to ensure consistency and completeness. We’ll focus on identifying key data points, utilizing G2’s features to efficiently collect information, and establishing a clear organizational structure for the extracted data. This allows for easy comparison and insightful analysis.
Data Extraction Strategy
To effectively extract data from G2 for multiple competitors, develop a structured approach. First, create a spreadsheet or a database to store the information. Then, for each competitor, systematically gather data points such as overall ratings, number of reviews, pricing tiers (if available), key features mentioned in reviews and product descriptions, and specific customer feedback regarding those features. Remember to record the date of data extraction to track changes over time.
Competitor Data Table
Once the data is collected, organizing it into a clear and concise table is essential for effective comparison. The table below illustrates a possible structure, focusing on key aspects to facilitate analysis. Note that this is a sample; the specific data points will vary based on the products and services being compared.
| Competitor | Overall Rating | Pricing (Tier 1) | Key Feature 1 | Key Feature 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Competitor A | 4.5 | $100/month | Automated Reporting | Integrates with CRM X |
| Competitor B | 4.2 | $75/month | Customizable Dashboards | Integrates with CRM Y |
| Competitor C | 4.0 | $50/month | Basic Reporting | No CRM Integration |
Importance of Consistent Data Collection and Formatting
Consistent data collection and formatting are fundamental for drawing accurate conclusions. Inconsistent data leads to skewed comparisons and unreliable insights. For example, if you record pricing for one competitor in USD and another in EUR without converting, your comparison will be flawed. Similarly, using different scales for rating systems (e.g., 1-5 vs. 1-10) will distort the relative performance of the competitors.
Maintaining uniformity in data units, scales, and formats is essential for accurate and meaningful analysis.
Analyzing Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
G2’s wealth of user reviews provides a goldmine of information for understanding competitor strengths and weaknesses. By systematically analyzing this data, we can gain valuable insights into user perceptions, identify key differentiators, and ultimately inform our own strategic positioning. This analysis goes beyond simple feature comparisons; it delves into the emotional responses of users, revealing what truly resonates (or doesn’t) with their experiences.
The process involves meticulously reviewing both positive and negative feedback, identifying recurring themes, and ultimately extracting actionable intelligence. We’ll be looking for patterns that highlight what users value most about each competitor and, conversely, where they fall short. This will allow us to pinpoint each competitor’s unique selling propositions (USPs) and understand how they are perceived in the market.
Identifying Common Themes in Positive Reviews
Positive reviews often reveal a competitor’s key strengths and the features that drive user satisfaction. For example, if multiple reviews praise a competitor’s excellent customer support, this suggests a strong USP and a potential area where we might need to improve. Similarly, consistent praise for a specific feature (e.g., intuitive user interface, robust integrations) indicates a successful element of their product strategy.
By categorizing these positive themes, we can build a comprehensive picture of what makes each competitor appealing to its user base. This could include creating a table summarizing the frequency of positive mentions for key features or support aspects across all competitors. For instance, Competitor A might consistently receive praise for its ease of use, while Competitor B is lauded for its powerful reporting capabilities.
Identifying Common Themes in Negative Reviews
Analyzing negative reviews is equally crucial. Recurring negative comments highlight areas where competitors fall short. These often point to weaknesses in product functionality, customer service, or overall user experience. For example, consistent complaints about slow loading times or a confusing interface can signal critical areas for improvement within their product. Understanding these common complaints allows us to identify potential opportunities to differentiate our offering by addressing these unmet needs.
We might even find that some competitors are consistently criticized for aspects that our product excels in, highlighting a potential competitive advantage.
Highlighting Unique Selling Propositions (USPs) Using G2 Data
G2 data allows us to objectively quantify and illustrate each competitor’s USPs. By comparing the frequency and intensity of positive and negative feedback related to specific features, we can identify what truly sets each competitor apart. For instance, if Competitor C consistently receives rave reviews for its AI-powered features, while others lack this functionality or receive negative feedback for similar offerings, this clearly establishes a USP.
Similarly, a competitor with significantly higher ratings in customer support compared to others showcases a strong competitive advantage. By systematically documenting these findings, we can create a clear and concise comparison of each competitor’s unique strengths and weaknesses. This analysis will be instrumental in informing our own product development and marketing strategies.
Visualizing Competitor Comparisons
Data visualization is crucial for effectively communicating the findings of your G2 competitor analysis. A well-designed visual representation can quickly highlight key differences and trends, making it easier for stakeholders to understand the competitive landscape. This section focuses on creating effective visualizations to showcase your analysis results.
Radar Chart for Overall Performance
A radar chart, also known as a spider chart, provides an excellent overview of the relative strengths and weaknesses of each competitor across multiple metrics. Imagine a chart with each competitor represented by a separate polygon. Each axis represents a key G2 metric, such as user satisfaction, ease of use, or features. The distance of each polygon’s vertex from the center reflects the competitor’s score on that particular metric.
A larger distance indicates a higher score. This allows for a quick visual comparison of overall performance across all chosen metrics. For example, a competitor with a large polygon encompassing most of the chart space would represent a strong overall performer.
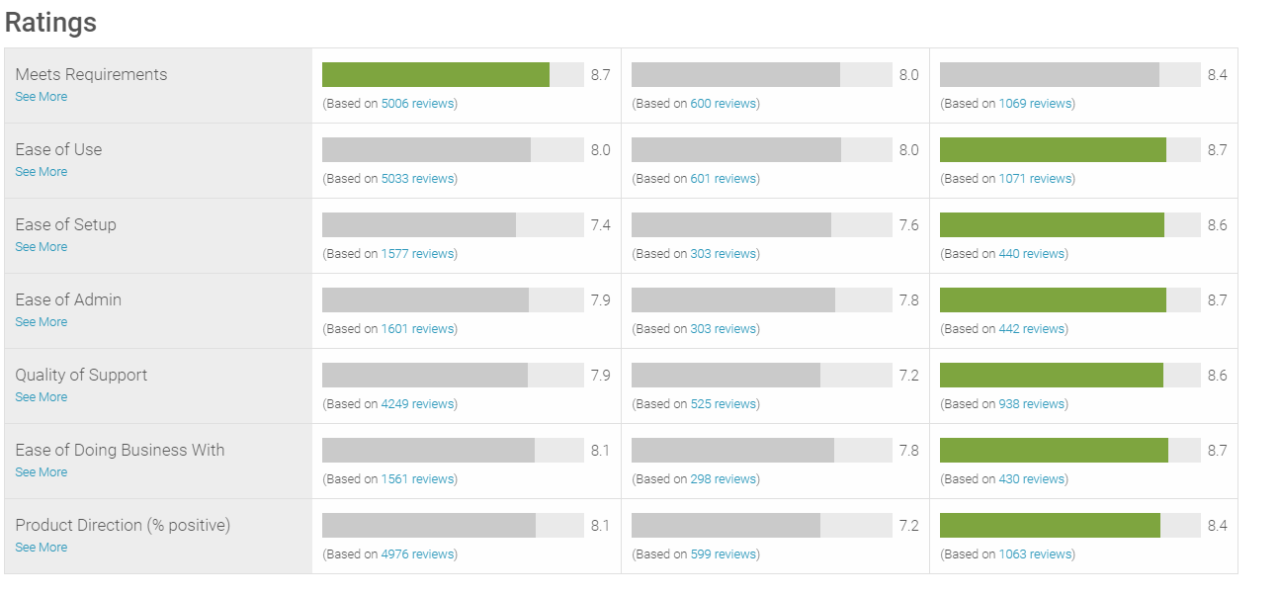
Bar Charts for Specific Metric Comparisons
Bar charts are ideal for comparing competitors on individual metrics. Each bar represents a competitor, and the height of the bar corresponds to their score on the selected metric. Grouping multiple bar charts together allows for a side-by-side comparison across various metrics. For instance, you could create separate bar charts for “Customer Satisfaction,” “Ease of Use,” and “Implementation.” This approach makes it easy to identify which competitor excels in each specific area.
A clear legend indicating the metrics and competitors is essential.
Presenting Findings Concisely
The goal is to present the visualized data in a clear and concise manner. Start by highlighting the key takeaways from the visualizations. For example, “Competitor A consistently outperforms its rivals in customer satisfaction, while Competitor B excels in ease of use.” Use concise language, avoiding technical jargon. Focus on the most significant differences and trends.
Support your observations with specific data points from the charts, such as “Competitor A boasts a 9.2 satisfaction rating, significantly higher than Competitor B’s 7.8.” Consider using annotations directly on the charts to emphasize key findings. Avoid overwhelming the audience with too much detail; instead, concentrate on the most important insights.
Considering User Reviews and Sentiment
Analyzing user reviews on G2 is crucial for a comprehensive competitor analysis. These reviews offer invaluable insights into the real-world experiences of customers, providing a nuanced perspective beyond the often-polished marketing materials. By understanding customer sentiment, you can identify areas where competitors excel or fall short, informing your own product development and marketing strategies.User reviews provide a rich source of qualitative data that complements the quantitative data available on G2.
They reveal the emotional responses of users, highlighting aspects of the product or service that resonate most strongly (positively or negatively). This sentiment analysis allows you to move beyond simple feature comparisons and understand the overall customer experience.
Categorizing User Reviews by Sentiment
Effective analysis requires a systematic approach to categorizing user reviews. A simple three-category system – positive, negative, and neutral – is often sufficient. Positive reviews express satisfaction and praise, negative reviews highlight dissatisfaction and problems, while neutral reviews offer balanced or factual observations without strong emotional connotations. Consider using analysis and sentiment scoring tools to automate this process for large datasets.
For example, words like “excellent,” “easy to use,” and “highly recommend” typically indicate positive sentiment, while words like “buggy,” “slow,” and “disappointing” suggest negative sentiment. Neutral reviews might contain words like “okay,” “functional,” or “adequate.”
Identifying Recurring Themes and Issues
Once reviews are categorized, the next step is to identify recurring themes and issues. This involves carefully reading through the reviews within each sentiment category, looking for patterns and commonalities. For instance, several negative reviews might consistently mention poor customer support, while positive reviews might frequently praise the user-friendliness of the interface. Tools that facilitate text analysis, such as topic modeling or word cloud generation, can help visualize these recurring themes.
For example, a word cloud generated from negative reviews might prominently feature words like “support,” “technical issues,” and “response time,” clearly indicating a major area for improvement for that competitor.
Final Conclusion
Mastering the art of competitive analysis on G2 empowers you to make informed decisions. By systematically collecting and analyzing data, understanding user sentiment, and visualizing your findings, you can gain a significant competitive advantage. Remember, it’s not just about the numbers – it’s about understanding the
-why* behind them. So, go forth and conquer the G2 landscape!
FAQ Guide
What if a competitor isn’t listed on G2?
This could mean they’re a newer player, focusing on a different market, or not actively managing their G2 presence. Consider alternative research methods like direct competitor websites or industry reports.
How do I handle biased reviews on G2?
Look for patterns and recurring themes across multiple reviews. Consider the overall sentiment and the reviewer’s profile to gauge credibility. Focus on the volume of reviews and the overall rating rather than individual outliers.
Can I automate data extraction from G2?
While G2 doesn’t offer a direct API for bulk data extraction, some web scraping tools might be able to assist. However, always check G2’s terms of service before employing such methods to avoid any violations.
