
Cost of Data Breaches in Different Countries
Cost of data breaches in different countries is a fascinating, and frankly, terrifying topic. We all know data breaches happen, but the sheer cost variation across the globe is eye-opening. From the impact of strict regulations like GDPR to the type of data stolen – financial records versus medical information – the financial fallout can vary wildly.
This post dives into the numbers, exploring the factors that make a data breach in one country exponentially more expensive than another.
We’ll be looking at regional averages, examining specific countries with the highest breach costs, and investigating how industry and company size influence the final bill. Think of it as a global crime scene investigation, except instead of solving a murder, we’re trying to understand the financial devastation left in the wake of a digital heist. Get ready to uncover some surprising – and alarming – statistics.
Introduction
Data breach costs represent the financial and reputational damage incurred by organizations following a successful cyberattack resulting in unauthorized access to sensitive data. These costs encompass both direct expenses, such as incident response, legal fees, and notification costs, and indirect expenses, including business disruption, loss of customers, and damage to brand reputation. The total cost can vary dramatically depending on a multitude of factors, making it challenging to arrive at a single global figure.
Understanding these variations is crucial for effective risk management and mitigation strategies.The variability of breach costs across nations stems from several key factors. These include differences in regulatory frameworks (e.g., GDPR in Europe vs. CCPA in California), the prevalence and sophistication of cybercrime, the average cost of labor for incident response teams, the level of insurance coverage available, and the cultural attitudes towards data privacy and security.
For example, a data breach impacting a company in a country with stringent data protection laws and high penalties for non-compliance will likely incur significantly higher costs than a similar breach in a country with less robust regulations. Furthermore, the size and type of organization impacted, as well as the nature and volume of data compromised, all play significant roles in determining the final cost.
Data Breach Cost Calculation Methodologies
Several methodologies exist for calculating the cost of a data breach. These often involve a combination of quantitative and qualitative assessments. One common approach is to utilize a cost-per-record methodology, estimating the cost based on the number of compromised records multiplied by a per-record cost. However, this approach is often criticized for its simplicity and lack of consideration for the complexities involved.
More sophisticated models take into account various factors such as the type of data breached (e.g., personally identifiable information, financial data), the severity of the breach, and the resulting business disruption. These advanced models often rely on data from surveys and reports conducted by cybersecurity firms, combining expert opinion with empirical data to provide a more comprehensive cost estimate.
For instance, the Ponemon Institute’s Cost of a Data Breach Report provides detailed analyses of breach costs across different industries and geographies, using a sophisticated methodology that considers numerous factors to generate a more accurate assessment than simple per-record calculations. These reports provide valuable insights into the trends and drivers of data breach costs globally.
Data Breach Cost Variations Across Countries
The cost of a data breach isn’t a fixed figure; it varies wildly depending on several factors, including the size of the organization, the type of data compromised, the speed of response, and—crucially—the location. Geographic location influences breach costs due to differing regulatory landscapes, legal frameworks, and the overall economic climate. Let’s delve into a regional analysis to understand these variations better.
The cost of data breaches varies wildly across countries, influenced by factors like regulations and industry. Building robust, secure applications is crucial, and that’s where learning about domino app dev the low code and pro code future becomes incredibly important. Investing in secure development practices, regardless of the chosen platform, ultimately mitigates the financial and reputational damage from a potential breach, saving businesses significant costs in the long run.
So, understanding these costs, globally, should drive our choices in application development.
Data breach costs are significantly impacted by factors like regulatory fines (GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California), legal fees, notification costs, and the potential loss of business and customer trust. These factors differ considerably across regions, leading to the observed variations in average breach costs.
Average Data Breach Costs in North America, Europe, and Asia
North America consistently reports higher average data breach costs compared to Europe and Asia. This is partly attributable to the higher costs of legal and regulatory compliance in North America, especially in the United States, where litigation is more common and potentially more expensive. Europe, while having stringent regulations like the GDPR, often sees lower average costs due to a more established framework for data protection and incident response.
Asia, on the other hand, shows a range of costs depending on the country and its level of regulatory development. More mature economies within Asia tend to have higher costs, while others may have lower costs due to less stringent regulations or underreporting of breaches.
Countries with the Highest Reported Average Data Breach Costs
Three countries consistently ranking among those with the highest average data breach costs are the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan. The high costs in the United States are largely due to the high number of class-action lawsuits, significant legal fees, and the complex regulatory landscape. The UK’s high costs are influenced by the GDPR’s hefty fines and the robust legal framework for data protection.
Japan’s high costs are often linked to the extensive reputational damage associated with data breaches and the stringent requirements for notification and remediation. These factors contribute to significant financial burdens for organizations experiencing breaches in these countries.
Average Data Breach Costs in Selected Countries
The following table summarizes the average cost of data breaches in several countries. Note that these figures can vary based on the methodology and data source used.
| Country | Average Cost (USD) | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 9.44 million | 2023 | IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report |
| United Kingdom | 4.42 million | 2023 | IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report |
| Japan | 3.77 million | 2023 | IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report |
| Germany | 3.22 million | 2023 | IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report |
| Australia | 3.15 million | 2023 | IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report |
Factors Influencing Data Breach Costs: Cost Of Data Breaches In Different Countries
The cost of a data breach isn’t a fixed number; it’s a complex equation with several variables influencing the final price tag. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses to accurately assess their risk and implement effective preventative measures. The impact can range from minor financial setbacks to crippling financial losses and reputational damage, depending on several key elements.
Regulatory Compliance Impact on Breach Costs
Stringent data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US, significantly impact the cost of data breaches. These regulations impose hefty fines for non-compliance and mandate specific procedures for handling breaches, including notification requirements and data subject rights. For example, a company failing to meet GDPR’s notification deadlines could face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
The cost of complying with these regulations, including conducting thorough data protection impact assessments, implementing robust security measures, and training employees, adds to the overall cost of a breach, even before considering potential fines. Furthermore, the cost of legal counsel specializing in data privacy is often substantial.
Data Type’s Influence on Breach Costs
The type of data compromised heavily influences the cost of a breach. Breaches involving sensitive personal information, such as financial data (credit card numbers, bank account details) or protected health information (PHI) under HIPAA, are significantly more expensive to remediate than breaches involving less sensitive data. This is due to the higher potential for identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage.
For example, a breach exposing PHI could trigger costly investigations by regulatory bodies, legal action from affected individuals, and extensive credit monitoring services for victims. The cost of notifying affected individuals, providing credit monitoring, and potentially offering compensation can quickly escalate the total cost.
Organizational Size and Type’s Role in Breach Costs
The size and type of organization also play a significant role in determining the cost of a data breach. Multinational corporations typically face higher costs due to their larger scale of operations, wider geographic reach, and greater volume of data. They may also have more complex IT infrastructure, increasing the difficulty and expense of identifying, containing, and remediating a breach.
Small businesses, on the other hand, often lack the resources and expertise to effectively respond to a breach, potentially leading to higher costs relative to their size. A small business might lack dedicated cybersecurity staff or the financial resources to engage external experts, leading to prolonged breach resolution and increased legal fees. For instance, a small business may struggle to meet regulatory notification requirements, leading to additional fines.
The recovery time can also be significantly longer for smaller organizations, resulting in lost revenue and business disruption.
The Impact of Industry on Data Breach Costs

Data breaches are costly, but the price tag varies wildly depending on the industry affected. Factors like the type of data compromised, regulatory requirements, and the industry’s inherent vulnerabilities all play a significant role. Understanding these industry-specific differences is crucial for effective risk management and cybersecurity planning.The average cost of a data breach isn’t uniform across sectors; some industries are far more vulnerable and face substantially higher financial and reputational damage than others.
This disparity highlights the need for tailored security strategies based on industry-specific risks.
Industries with the Highest Average Data Breach Costs
Three sectors consistently rank among the most expensive to recover from data breaches: healthcare, finance, and retail. These industries handle highly sensitive data, face stringent regulations, and often struggle with legacy systems that are more susceptible to attack. The consequences of a breach in these sectors can be devastating, leading to significant financial losses, legal penalties, and lasting damage to brand reputation.
Healthcare Industry Challenges
The healthcare industry faces unique challenges in managing data breaches. Protected Health Information (PHI) is highly valuable on the dark web, and breaches often involve large volumes of sensitive patient data, leading to substantial costs associated with notification, credit monitoring, and legal fees. Furthermore, the industry is subject to strict regulations like HIPAA in the US, with hefty fines for non-compliance.
- High cost of regulatory fines and legal fees due to HIPAA violations.
- Extensive costs associated with notifying affected individuals and providing credit monitoring services.
- Challenges in securing legacy systems and integrating new security technologies across diverse healthcare organizations.
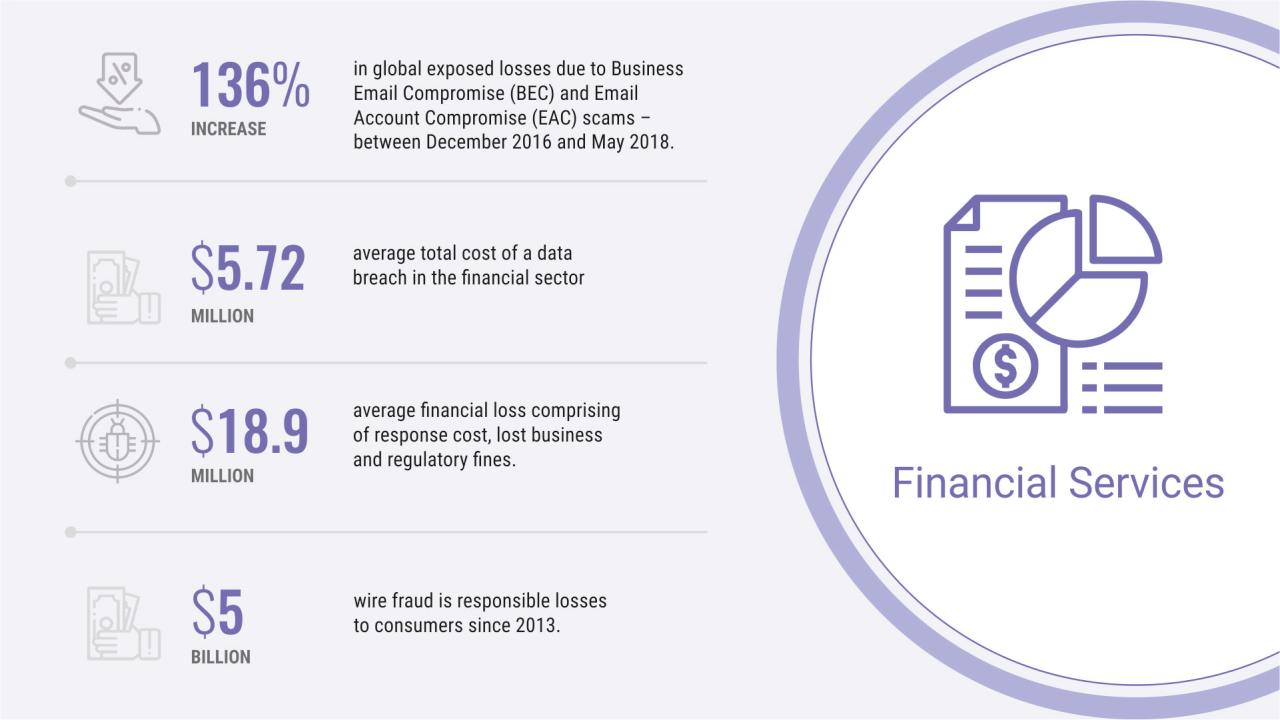
Financial Services Industry Challenges
Financial institutions handle vast amounts of sensitive financial data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. A data breach can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. The industry is also subject to strict regulations, such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California, adding to the cost of remediation. Moreover, the sophisticated nature of financial cyberattacks often necessitates expensive incident response and forensic investigations.
- Significant financial losses due to fraudulent transactions and theft of customer funds.
- High costs associated with regulatory fines and legal settlements related to data protection violations.
- The need for advanced security technologies and specialized expertise to combat sophisticated cyberattacks.
Retail Industry Challenges
The retail industry handles a large volume of customer data, including credit card information and personally identifiable information (PII). Breaches can lead to significant financial losses due to fraudulent transactions, chargebacks, and the costs of notifying affected customers and offering credit monitoring services. The reputational damage from a data breach can also significantly impact sales and customer loyalty.
The widespread use of point-of-sale (POS) systems, many of which are outdated and vulnerable, exacerbates the risk.
- High costs associated with customer notification, credit monitoring, and fraud investigation.
- Significant financial losses from fraudulent transactions and chargebacks.
- Reputational damage leading to decreased sales and customer loyalty.
Mitigation Strategies and Cost Reduction
Minimizing the financial fallout from data breaches requires a proactive and multi-layered approach. Effective mitigation strategies aren’t just about reacting to incidents; they’re about building a robust security posture that prevents breaches in the first place and limits the damage if one occurs. This involves a blend of preventative, detective, and responsive measures, each with its own cost-benefit analysis.
Preventative Measures
Preventative measures aim to stop breaches before they happen. Investing in these strategies upfront is significantly cheaper than dealing with the aftermath of a successful attack. The cost-benefit analysis here is clear: proactive spending prevents far greater losses down the line.
- Strong Access Controls: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), robust password policies, and regular access reviews significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. The cost involves implementing MFA systems and training employees, but the potential savings from preventing a breach far outweigh this initial investment. For example, a company might spend $10,000 on MFA implementation but avoid a potential $1 million breach cost.
- Employee Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe password practices is crucial. While training programs require an upfront investment in time and resources, they dramatically reduce the likelihood of human error leading to a breach. A well-designed program costing $5,000 per year could prevent breaches costing millions.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regularly assessing vulnerabilities in systems and applications identifies weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. The cost of these audits is relatively low compared to the potential cost of remediation after a breach is discovered. A yearly penetration test costing $20,000 could uncover and fix vulnerabilities that would otherwise lead to a far more expensive breach.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest makes it significantly harder for attackers to access and exploit the information even if a breach occurs. While encryption requires investment in software and hardware, the cost is minimal compared to the potential cost of data loss and regulatory fines. The cost of implementing encryption might be $50,000 but the potential cost of a data leak could be many times higher.
Detective Measures
Detective measures focus on identifying breaches that have already occurred. While they don’t prevent breaches, they help minimize the damage by enabling a faster response. The cost-benefit analysis here hinges on the speed and efficiency of detection, which directly impacts the extent of the damage.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS constantly monitors network traffic and systems for suspicious activity, alerting security teams to potential breaches in real-time. The cost of implementing and maintaining an IDPS is relatively low compared to the cost of a large-scale breach. A robust IDPS costing $10,000 annually can prevent significant data loss and reputational damage.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a centralized view of security events. This allows for faster identification and response to security incidents. The cost of a SIEM system, including implementation and maintenance, can be substantial, but the ability to quickly detect and respond to breaches makes it a worthwhile investment. A $50,000 SIEM system can drastically reduce the time to identify and contain a breach, minimizing its impact.
The cost of data breaches varies wildly across countries, influenced by factors like regulations and industry. Understanding these costs highlights the urgent need for robust security measures, and that’s where solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management become crucial. Investing in proactive security, like CSPM, can significantly mitigate these potentially devastating financial impacts, ultimately saving businesses from hefty breach-related expenses regardless of their location.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools monitor data movement within and outside an organization, identifying and preventing sensitive data from being exfiltrated. While the cost of DLP implementation can be significant, the potential savings from preventing data loss far outweigh the initial investment. A $30,000 DLP system can prevent the loss of sensitive customer data and avoid hefty fines.
Responsive Measures
Responsive measures are crucial for containing the damage after a breach has occurred. A swift and effective response can significantly reduce the long-term financial impact. The cost-benefit analysis focuses on minimizing the extent of the damage and the associated costs of recovery and remediation.
- Incident Response Plan: A well-defined incident response plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach. This plan should include procedures for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity. The cost of developing and maintaining an incident response plan is minimal compared to the cost of a poorly managed response to a breach. A comprehensive plan costing $5,000 can save millions by streamlining the response process.
- Forensic Investigation: Engaging a cybersecurity firm to conduct a forensic investigation after a breach helps determine the extent of the damage, identify the root cause, and gather evidence for legal and regulatory purposes. While forensic investigations can be expensive, the cost is often justified by the need to understand the breach and mitigate future risks. A forensic investigation might cost $50,000, but it provides critical information for remediation and future prevention.
- Notification and Communication: Promptly notifying affected individuals and regulatory bodies is crucial to managing the reputational and legal consequences of a breach. While notification can be costly, failure to comply with regulations can result in far greater penalties. The cost of notification and communication might be $20,000, but non-compliance can result in millions in fines.
Future Trends in Data Breach Costs

Predicting the future of data breach costs is a complex undertaking, influenced by a confluence of technological advancements, evolving threat landscapes, and increasingly stringent regulatory environments. While precise figures remain elusive, several key trends suggest a trajectory of escalating costs in the years to come. The interconnected nature of these factors means that understanding their individual impacts is crucial for effective risk management.The convergence of emerging technologies and expanding digital ecosystems will significantly impact the cost of data breaches.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies on Data Breach Costs
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing presents both opportunities and challenges in cybersecurity. AI-powered tools can enhance threat detection and response, potentially reducing breach costs. However, the increasing sophistication of AI-driven attacks, capable of bypassing traditional security measures, could simultaneously inflate breach costs. Similarly, the proliferation of IoT devices, while offering increased connectivity and automation, expands the attack surface, making organizations more vulnerable and increasing the potential scope and cost of a breach.
Consider the hypothetical scenario of a smart city infrastructure breach affecting traffic management systems, utilities, or emergency services; the resulting disruption and remediation costs would be significantly higher than a simple data breach targeting customer records. The complexity of interconnected systems increases the difficulty and expense of incident response and recovery. Cloud computing, while offering scalability and cost-effectiveness, introduces new vulnerabilities if not properly secured, potentially leading to larger-scale breaches with substantial financial repercussions.
Increasing Cybersecurity Threats and Evolving Attack Vectors
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), employing more sophisticated and targeted attacks. Ransomware attacks, for instance, are becoming increasingly prevalent and destructive, demanding higher ransoms and causing significant operational disruption. The rise of supply chain attacks, where attackers target a company’s vendors or partners to gain access to its systems, further complicates breach response and recovery efforts, resulting in higher costs.
Advanced persistent threats (APTs), characterized by long-term, stealthy attacks, are also becoming more common, often remaining undetected for extended periods, leading to more extensive data exfiltration and increased remediation costs. For example, a successful APT targeting a financial institution could lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory fines, far exceeding the cost of a typical ransomware attack.
The Impact of Stricter Regulations and Increased Penalties, Cost of data breaches in different countries
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter data protection regulations, such as the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California. These regulations mandate increased data security measures and impose hefty penalties for non-compliance. Failure to meet these regulatory requirements can result in substantial fines, legal fees, and reputational damage, significantly increasing the overall cost of a data breach. The increasing awareness of data privacy and the growing expectation of accountability from consumers and regulators are pushing organizations to invest more heavily in cybersecurity, though this investment may not fully offset the potential costs associated with a breach given the sophistication of modern attacks.
For example, a company found to be in violation of GDPR regulations could face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of its annual global turnover, a substantial financial burden.
Illustrative Example: The 2017 Equifax Data Breach
The 2017 Equifax data breach serves as a stark illustration of the devastating consequences and substantial costs associated with large-scale data breaches. This incident, affecting millions of individuals in the United States and impacting Equifax’s reputation and financial standing, provides a valuable case study for understanding the complexities of data breach costs.Equifax, one of the three major consumer credit reporting agencies in the US, experienced a massive data breach exposing the sensitive personal information of approximately 147 million people.
The breach, which went undetected for several months, involved the theft of names, Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, and, in some cases, driver’s license numbers. The immediate cost was substantial, including legal fees, regulatory fines, and the costs associated with credit monitoring services offered to affected consumers. However, the long-term financial and reputational damage proved even more significant.
Financial Costs of the Equifax Breach
The direct financial costs associated with the Equifax breach were staggering. Equifax incurred significant expenses related to investigating the breach, notifying affected individuals, providing credit monitoring services, and responding to numerous lawsuits. These costs totaled hundreds of millions of dollars. Furthermore, the company faced substantial regulatory fines from various government agencies, including the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), adding to the overall financial burden.
Beyond the direct financial costs, Equifax experienced a significant drop in its stock price, representing a substantial loss in shareholder value. The long-term impact on their business, including lost revenue and increased operational costs, further amplified the overall cost of the breach.
Factors Contributing to the High Cost
Several factors contributed to the exceptionally high cost of the Equifax data breach. Firstly, the sheer scale of the breach – impacting nearly half the US population – significantly increased the costs associated with notification, credit monitoring, and legal actions. Secondly, the nature of the stolen data – including highly sensitive personal information like Social Security numbers – amplified the potential for identity theft and fraud, leading to extensive costs for both Equifax and affected individuals.
Thirdly, the company’s delayed response to the breach and its initial attempts to downplay the severity of the situation exacerbated the damage and increased the costs associated with legal and regulatory scrutiny. Finally, the lack of robust cybersecurity measures and the failure to promptly patch known vulnerabilities in their systems played a crucial role in enabling the breach to occur and persist undetected for so long.
Long-Term Consequences
The Equifax data breach had far-reaching consequences for both the organization and the individuals affected. For Equifax, the breach resulted in significant reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and a long-term impact on its financial performance. The company faced intense public scrutiny, legal challenges, and ongoing regulatory oversight. For the affected individuals, the consequences included the risk of identity theft, financial losses, and considerable emotional distress.
Many individuals spent countless hours dealing with the aftermath of the breach, including contacting credit bureaus, freezing their credit reports, and monitoring their accounts for fraudulent activity. The long-term effects of this breach continue to impact individuals’ financial security and overall sense of well-being, underscoring the human cost of such incidents.
Concluding Remarks
So, there you have it: a whirlwind tour of the global cost of data breaches. The picture is complex, with regulations, industry type, and the sheer volume of data stolen all playing a significant role. While the numbers can be daunting, understanding the factors at play is crucial. By implementing proactive security measures and staying informed about evolving threats, businesses can significantly reduce their risk and mitigate the devastating financial consequences of a data breach.
Remember, prevention is always cheaper than the cure – especially when it comes to protecting your valuable data.
FAQ Insights
What is the average cost of a data breach globally?
There’s no single global average, as costs vary dramatically depending on factors discussed in this post. However, reports consistently show costs in the millions, even billions, for large-scale breaches.
Can small businesses afford to deal with data breaches?
Data breaches can cripple small businesses. While the initial costs might be lower than for larger corporations, the long-term reputational damage and potential legal fees can be devastating.
What’s the role of insurance in mitigating data breach costs?
Cybersecurity insurance can significantly reduce the financial burden of a data breach, covering expenses like legal fees, notification costs, and credit monitoring for affected individuals. However, coverage varies widely, so careful selection is crucial.
How long does it take to recover from a data breach?
Recovery time varies depending on the scale of the breach and the organization’s response. It can take months, or even years, to fully restore systems, repair reputation, and regain customer trust.





