Baltimore Ransomware Attack XP & Vistas Downfall
Baltimore ransomware attack due to Microsoft Win XP and Vista operating systems – it sounds like something from a tech thriller, right? But this wasn’t fiction. Outdated operating systems left Baltimore vulnerable, leading to a crippling ransomware attack that exposed the city’s digital weaknesses and the real-world consequences of neglecting security updates. This post dives into the details, exploring the vulnerabilities, the attack itself, and the crucial lessons learned.
We’ll unpack the technical aspects, the human impact, and the long-term implications of this significant cyber event.
The attack highlighted a critical issue: even major institutions can be crippled by outdated software. The reliance on Windows XP and Vista, long past their end-of-life support, created a gaping security hole that malicious actors exploited ruthlessly. We’ll examine the specific ransomware used, how it spread, and the devastating effects on essential city services. From disrupted emergency response to halted government operations, the impact was widespread and far-reaching.
Vulnerability of XP and Vista Systems
The Baltimore ransomware attack, while ultimately stemming from a poorly secured network, starkly highlighted the significant security vulnerabilities inherent in using outdated operating systems like Windows XP and Windows Vista. These systems, while functional at the time, lacked the crucial security features and regular updates that protect modern systems from sophisticated cyber threats. The reliance on these aging systems left the city vulnerable to exploitation.The core issue lies in the fundamental security architecture of XP and Vista.
These systems were developed in an era before many of the modern security threats we see today were prevalent. Consequently, they lack built-in defenses against many modern attack vectors. Furthermore, Microsoft’s extended support for these operating systems ended years ago, meaning no more security patches or updates were released, leaving them increasingly exposed.
Security Flaws in Windows XP and Vista
Windows XP and Vista suffered from a number of vulnerabilities that made them prime targets for ransomware. These included outdated encryption protocols, insufficient memory protection, and a lack of robust user account control features. Many exploits leveraged vulnerabilities in older versions of Internet Explorer and other applications that were not patched on these systems. The Baltimore attack likely exploited one or more of these vulnerabilities, allowing the attackers to gain initial access and then deploy ransomware.
The exact vulnerabilities remain confidential for security reasons.
Comparison with Modern Operating Systems
Modern operating systems like Windows 10 and 11, and macOS, incorporate significant advancements in security. These include features such as:
- Enhanced memory protection to prevent buffer overflows and other memory-related exploits.
- Robust user account control to limit the impact of malware and restrict unauthorized actions.
- Regular security updates and patches to address newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Improved sandboxing techniques to isolate potentially malicious processes.
- Advanced malware detection and prevention tools built directly into the operating system.
These features significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful ransomware attack. The difference in security between XP/Vista and modern systems is substantial, representing a significant evolution in operating system security architecture.
Microsoft’s Extended Support Timeline
Microsoft officially ended extended support for Windows XP in April 2014, and for Windows Vista in April 2017. This meant that no further security updates or patches were released after these dates. The risk to users running these systems increased exponentially after the end of support, as they became increasingly vulnerable to new threats. The Baltimore attack, occurring after the end of support for both operating systems, served as a stark reminder of the consequences of continued use of unsupported software.
The city’s reliance on these systems represents a failure of proactive IT management, leading to the significant disruption and financial losses associated with the ransomware attack.
The Baltimore Ransomware Attack: Baltimore Ransomware Attack Due To Microsoft Win Xp And Vista Operating Systems

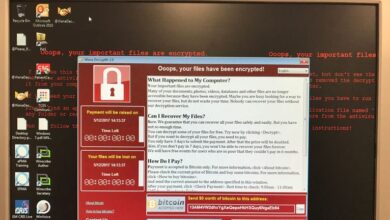
The May 2018 ransomware attack on the city of Baltimore serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in outdated technology and the devastating consequences of successful cyberattacks on critical infrastructure. This incident highlighted the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures, especially within governmental organizations. The attack, leveraging a relatively simple but effective ransomware variant, crippled essential city services and exposed the city to significant financial and reputational damage.
The RobbinHood Ransomware Variant
The Baltimore attack utilized a variant of the RobbinHood ransomware. This ransomware operated by encrypting files using AES-256 encryption, a strong encryption algorithm making decryption without the decryption key extremely difficult. The infection process involved the ransomware scanning for specific file types, encrypting them, and then appending the “.ROB!NHOOD” extension to the affected files. The attackers then demanded a ransom for the decryption key, effectively holding the city’s data hostage.
The strength of the encryption algorithm meant that manual decryption was practically impossible, forcing the city to consider paying the ransom.
Initial Infection Vector
The precise initial infection vector remains somewhat unclear, although evidence suggests that the attack leveraged EternalBlue, an exploit targeting a vulnerability in older versions of Microsoft Windows, specifically Windows XP and Windows Vista. This vulnerability, famously exploited by the WannaCry ransomware, allows attackers to remotely execute code on vulnerable systems. The city’s reliance on outdated systems, coupled with a potentially lack of sufficient patching and security updates, made them a prime target for this type of attack.
The attackers likely exploited this vulnerability to gain initial access to the network, from where they could then spread the ransomware to other systems.
Extent of the Damage
The attack severely impacted Baltimore’s IT infrastructure. Numerous city systems were affected, including those responsible for managing 911 calls, court records, and various other essential services. The encryption of critical data disrupted operations, leading to delays and inefficiencies across multiple city departments. While the precise amount of data compromised or encrypted is difficult to quantify definitively, reports suggest a significant portion of the city’s digital information was affected.
The disruption of services had a substantial impact on the daily lives of Baltimore citizens and the city’s ability to function effectively.
Ransom Demands
The attackers demanded a significant Bitcoin ransom, the exact amount of which varied according to reports. The city ultimately refused to pay the ransom, opting instead to invest resources in recovery and remediation efforts. This decision, while commendable from a security standpoint, significantly extended the recovery period and highlighted the substantial costs associated with responding to such an attack, even without paying the ransom.
The financial impact extended beyond direct costs, encompassing the lost productivity, the expense of hiring cybersecurity experts, and the potential for long-term reputational damage.
Impact and Response
The Baltimore ransomware attack, stemming from the city’s reliance on outdated Windows XP and Vista systems, had a significant and widespread impact on city services and operations. The attack crippled essential functions, highlighting the critical need for robust cybersecurity infrastructure and proactive patching strategies in public sector organizations. The city’s response, while ultimately successful in recovery, revealed areas needing improvement in incident response planning and execution.The immediate impact of the attack was a widespread disruption of critical city services.
Citizens experienced difficulties accessing essential government functions, leading to frustration and inconvenience. The financial consequences, both direct and indirect, were substantial, emphasizing the high cost of neglecting cybersecurity best practices.
Affected City Services and Duration of Disruption
The following table details the services affected by the ransomware attack and the length of time they were unavailable. Note that precise durations for some services were not publicly released, so the estimates provided represent a reasonable approximation based on available reporting.
| Service | Description | Duration of Outage | Recovery Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 311 Call Center | Citizen service request line for non-emergency issues. | Approximately 1 week | System restoration from backups, manual processing of urgent requests. |
| Parking Payment Systems | Online and kiosk-based parking payment systems. | Approximately 2 weeks | System rebuild and data recovery from backups, temporary manual payment options implemented. |
| Water Billing System | Online and in-person water bill payment and account management. | Approximately 10 days | System restoration from backups, temporary manual processing of payments. |
| Other Internal Systems | Various internal city government systems (exact details not publicly released). | Varies, ranging from several days to several weeks. | System restoration from backups, manual workarounds and alternative processes implemented. |
City’s Response to the Attack
Baltimore’s response involved a multi-faceted approach encompassing immediate containment, investigation, and recovery efforts. The city’s incident response team worked tirelessly to isolate the affected systems, prevent further spread of the ransomware, and restore critical services. This included collaborating with external cybersecurity experts and law enforcement agencies. The response, while ultimately successful, highlighted the need for more comprehensive and regularly tested incident response plans.
The lack of a robust disaster recovery plan significantly prolonged the recovery period.
Lessons Learned from the Baltimore Attack
The Baltimore ransomware attack served as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities of outdated technology and the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures. The experience underscored the need for robust security protocols, including:
- Regular Software Updates and Patching: The attack highlighted the critical need for prompt patching of vulnerabilities in operating systems and applications. Outdated systems like Windows XP and Vista were particularly vulnerable.
- Robust Backup and Recovery Strategies: Having frequent and secure backups of critical data is crucial for a swift recovery. Baltimore’s recovery was hampered by the inadequacy of its backup and recovery systems.
- Employee Security Awareness Training: Regular training for city employees on phishing and other social engineering tactics is essential to prevent future attacks. Many ransomware attacks begin with a successful phishing campaign.
- Comprehensive Incident Response Plan: A well-defined and regularly tested incident response plan is crucial for effective management of a ransomware attack or similar cybersecurity incident.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting the network can limit the impact of a breach, preventing the ransomware from spreading to other critical systems.
Financial Costs of the Attack
The exact financial cost of the Baltimore ransomware attack remains unclear, as the city did not disclose the ransom payment (if any). However, the costs included:
- Recovery Efforts: The cost of hiring cybersecurity experts, restoring systems, and addressing lost productivity was substantial.
- Lost Productivity: The disruption of city services resulted in significant lost productivity, impacting various city departments and potentially affecting revenue generation.
- Reputational Damage: The attack likely caused reputational damage to the city, potentially affecting its ability to attract investment and tourism.
While precise figures are unavailable, the total cost likely ran into millions of dollars, underscoring the high economic consequences of neglecting cybersecurity. Similar attacks on other municipalities have shown costs ranging from hundreds of thousands to tens of millions of dollars depending on the severity and duration of the disruption.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies

The Baltimore ransomware attack, stemming from outdated operating systems, serves as a stark reminder of the critical need for robust cybersecurity practices. Preventing future incidents requires a multi-layered approach encompassing technological safeguards, network architecture design, and comprehensive employee training. This section details key strategies for bolstering defenses against ransomware and similar threats.
Implementing effective prevention and mitigation strategies is paramount to safeguarding against ransomware attacks. This involves a combination of proactive measures, robust security architectures, and well-trained personnel. Failing to address any one of these areas significantly increases vulnerability.
Best Practices for Securing Computer Systems
Maintaining secure computer systems requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. Regular updates, strong passwords, and secure network configurations are foundational elements of a comprehensive security strategy. Neglecting these basics can leave systems vulnerable to exploitation.
- Timely Software Updates and Patching: This is arguably the single most important preventative measure. Outdated software contains known vulnerabilities that ransomware attackers actively exploit. Automatic updates should be enabled wherever possible, and manual patching should be performed promptly upon release of security updates.
- Strong and Unique Passwords: Employ strong, unique passwords for all accounts, including administrative accounts. Password managers can assist in securely managing complex passwords across multiple platforms.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password and a one-time code from a mobile app) to access accounts. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up critical data to an offline, secure location. This ensures data recovery in the event of a ransomware attack. The 3-2-1 backup rule (3 copies of data, on 2 different media types, with 1 copy offsite) is a widely accepted best practice.
- Antivirus and Antimalware Software: Utilize reputable antivirus and antimalware software and keep it updated. These tools can detect and prevent many ransomware threats.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users only the necessary access rights to perform their jobs. This limits the damage a compromised account can inflict.
- Network Security: Implement firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems to monitor and control network traffic.
Hypothetical Security Architecture for a City Government Network, Baltimore ransomware attack due to microsoft win xp and vista operating systems
A secure city government network requires a robust architecture designed for redundancy and resilience against attacks. This architecture should incorporate multiple layers of security to mitigate the impact of a successful breach.
A hypothetical architecture would include:
- Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments limits the impact of a breach. If one segment is compromised, the attacker’s access is restricted to that segment.
- Redundant Systems and Data Centers: Multiple servers and data centers provide failover capabilities in case of hardware failure or attack. This ensures continuous operation and data availability.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS monitor network traffic for malicious activity and can automatically block or alert on suspicious behavior.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regular security assessments identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network’s security posture.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: DLP tools monitor and control the movement of sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access or exfiltration.
- Robust Access Control Policies: Clearly defined access control policies ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data and systems.
Comparison of Security Solutions to Mitigate the Baltimore Attack
Several security solutions could have mitigated the Baltimore attack. The choice of solution depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the specific needs of the organization. A layered approach is often the most effective.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions monitor endpoints (computers, servers) for malicious activity. They can detect and respond to ransomware attacks in real-time, preventing encryption or limiting its impact. In the Baltimore case, EDR could have detected the initial infection and prevented widespread encryption.
- Network Segmentation: As mentioned previously, network segmentation would have limited the spread of the ransomware. If the infected systems were isolated, the attack would not have been able to propagate to other parts of the network.
- Microsegmentation: A more granular form of network segmentation, microsegmentation isolates individual applications or workloads, further limiting the impact of a breach. This provides even more robust protection than traditional network segmentation.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a centralized view of security events. This can help detect and respond to ransomware attacks more quickly.
Employee Training and Awareness
Employee training is a crucial element of a comprehensive ransomware defense strategy. Educated employees are less likely to fall victim to phishing attacks or other social engineering tactics used to deliver ransomware.
- Phishing Awareness Training: Educate employees on how to identify and avoid phishing emails and other social engineering attempts.
- Ransomware Recognition: Train employees to recognize the signs of a ransomware infection, such as unusual system behavior or encrypted files.
- Safe Browsing Practices: Teach employees safe browsing habits, including avoiding suspicious websites and downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Password Security Best Practices: Reinforce the importance of strong, unique passwords and the use of password managers.
- Reporting Procedures: Establish clear procedures for reporting suspected ransomware infections or security incidents.
- Regular Security Awareness Campaigns: Conduct regular security awareness campaigns to keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The Baltimore ransomware attack, stemming from outdated operating systems, raises complex legal and ethical questions for city officials and the broader cybersecurity landscape. Paying ransoms, while seemingly a pragmatic solution in the heat of the moment, has significant legal and ethical implications that must be carefully considered. The decision to pay or not pay is fraught with difficulties, impacting not only the immediate crisis but also setting precedents for future attacks.The legal ramifications of paying ransoms are multifaceted.
While not explicitly illegal in all jurisdictions, paying a ransom can be construed as aiding and abetting criminal activity, potentially leading to legal repercussions for the city. Furthermore, it emboldens cybercriminals, encouraging further attacks by demonstrating a willingness to pay. This creates a perverse incentive structure that undermines broader cybersecurity efforts.
Remember the Baltimore ransomware attack? Outdated systems, like the Windows XP and Vista machines they were running, made them a prime target. This highlights the urgent need for modern, secure systems, and that’s where the future of app development comes in; check out this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future to see how we can avoid similar disasters.
Ultimately, upgrading to secure, well-maintained software is the best defense against these kinds of attacks.
Legal Ramifications of Ransom Payments
Paying a ransom to cybercriminals often violates various laws and regulations, depending on the jurisdiction. In the United States, for instance, laws concerning money laundering and sanctions against terrorist organizations could be applicable, especially if the attackers are linked to such groups. Furthermore, internal policies and regulations within the city government might also prohibit ransom payments. The city could face legal challenges from citizens, businesses, or insurance companies due to negligence in maintaining secure systems and potentially contributing to financial losses incurred as a result of the attack.
These legal liabilities are magnified when considering the sensitive nature of the data potentially compromised, such as personal information or financial records. The potential for lawsuits related to data breaches, privacy violations, and the costs associated with recovery efforts are substantial.
Relevant Cybersecurity Laws and Regulations
Several laws and regulations address cybersecurity breaches and data protection. The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the US, for example, criminalizes unauthorized access to computer systems and the subsequent damage or theft of data. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare data and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for European citizens’ data are also critical considerations.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal penalties. The city’s legal team must thoroughly investigate whether any of these laws were violated during or before the attack.
Ethical Dilemmas Faced by City Officials
City officials faced a classic ethical dilemma: the immediate need to restore essential services versus the long-term consequences of paying a ransom. Paying the ransom might seem like the fastest way to regain control, but it encourages future attacks and could be seen as rewarding criminal behavior. Refusing to pay, on the other hand, risks prolonged disruption of essential services, potentially causing significant harm to citizens and businesses.
The decision involves balancing the immediate need to mitigate the crisis with the long-term implications for public safety, financial stability, and the city’s reputation. Transparency with the public about the decision-making process is also crucial to maintaining public trust.
Potential Legal Liabilities for the City
The city could face significant legal liabilities stemming from the ransomware attack. These liabilities include claims for negligence in maintaining adequate cybersecurity defenses, leading to the data breach. Failure to adequately secure systems and data could result in lawsuits from affected citizens, businesses, or even insurance companies. The city may also face legal repercussions for non-compliance with data protection regulations, potentially leading to significant fines and reputational damage.
The costs associated with data recovery, legal fees, and potential settlements could significantly impact the city’s budget. The potential for class-action lawsuits is a significant concern. The city’s legal team needs to proactively assess all potential liabilities and develop a comprehensive strategy for managing legal risks.
Final Conclusion
The Baltimore ransomware attack serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present threat of cybercrime and the critical importance of robust cybersecurity practices. Ignoring software updates and failing to invest in modern security infrastructure can have catastrophic consequences. While the city eventually recovered, the financial and reputational damage lingered. This event underscores the need for proactive security measures, employee training, and a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, not just for governments but for all organizations.
Let’s learn from Baltimore’s experience and strengthen our own digital defenses.
Commonly Asked Questions
What type of ransomware was used in the Baltimore attack?
While the specific variant isn’t always publicly disclosed for security reasons, it was a sophisticated ransomware capable of encrypting critical files and systems.
Did Baltimore pay the ransom?
This is a complex issue with no simple answer. The decision to pay a ransom is fraught with ethical and legal considerations, and the details surrounding Baltimore’s response are often debated.
How long did it take Baltimore to fully recover?
Full recovery took months, involving significant resources and a substantial investment in IT infrastructure upgrades and security improvements.
What are some common misconceptions about ransomware attacks?
Many believe ransomware is only a problem for large organizations. In reality, anyone can be a victim, from individuals to small businesses. Another misconception is that paying the ransom guarantees data recovery. This is not always true, and paying often emboldens attackers.