Cyber Attack Forces Moodys to Downgrade Equifax
Cyber attack forces moodys to downgrade equifax – Cyber Attack Forces Moody’s to Downgrade Equifax sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story of corporate vulnerability and the ripple effects of a massive data breach. The 2017 Equifax hack wasn’t just a technological failure; it was a seismic event that shook the credit reporting industry to its core and exposed millions of individuals to identity theft.
This post delves into the details of the attack, Moody’s subsequent downgrade of Equifax’s credit rating, and the lasting impact on the company and consumers alike. We’ll explore the cybersecurity failures, the financial fallout, and the crucial lessons learned.
The sheer scale of the breach – impacting the personal information of nearly half of all US adults – was staggering. From Social Security numbers and addresses to driver’s license details, the stolen data was a goldmine for identity thieves. The immediate aftermath saw a flurry of lawsuits, regulatory investigations, and a dramatic plummet in Equifax’s stock price.
But the story doesn’t end there. Moody’s, a major credit rating agency, responded by downgrading Equifax’s credit rating, a move that further exacerbated the company’s financial woes and highlighted the long-term consequences of inadequate cybersecurity.
The Equifax Data Breach
The 2017 Equifax data breach remains a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in large-scale data storage and the devastating consequences of inadequate cybersecurity measures. This incident, one of the largest data breaches in history, exposed the personal information of millions and sent shockwaves through the financial and regulatory landscapes. Its impact continues to resonate today, shaping data protection policies and consumer awareness.The Equifax data breach timeline unfolds as a cautionary tale.
Timeline of the Equifax Data Breach
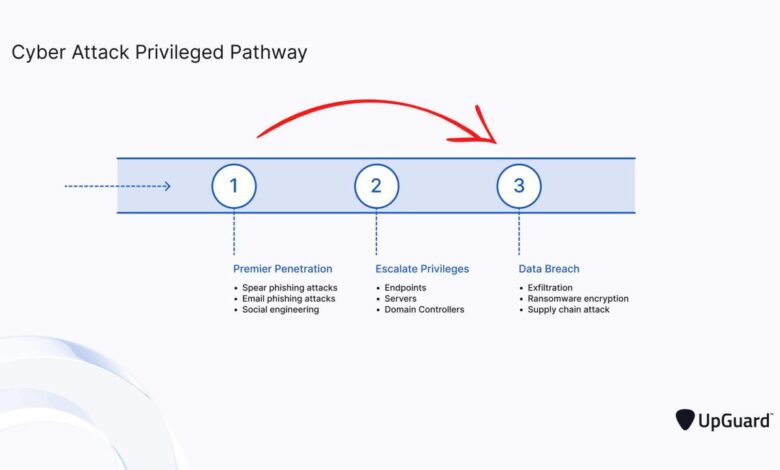
The breach, which went undetected for several months, began in mid-May 2017. Attackers exploited a known vulnerability in the Apache Struts framework, a widely used software component. Equifax discovered the breach on July 29th, 2017, but waited until September 7th to publicly announce it. This delay significantly exacerbated the damage, allowing the attackers ample time to exfiltrate sensitive data.
The company’s response was widely criticized for its slow pace and lack of transparency. The aftermath involved extensive investigations, lawsuits, regulatory fines, and a significant erosion of public trust. The vulnerability itself had been publicly disclosed in March 2017, highlighting the critical importance of prompt patching and security updates.
Data Compromised and Individuals Affected, Cyber attack forces moodys to downgrade equifax
The breach affected approximately 147 million individuals across the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada. The stolen data included highly sensitive personal information, such as names, Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, driver’s license numbers, and, in some cases, credit card numbers. This breadth of compromised information presented a significant risk of identity theft, fraud, and financial loss for those affected.
The sheer scale of the breach underscores the potential for widespread damage from a single security lapse.
Moody’s downgrading Equifax after that massive cyberattack really highlights the critical need for robust security. The incident underscores how vital it is to proactively manage cloud security risks, which is why understanding solutions like those discussed in this article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is so important. Ultimately, the Equifax breach serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of neglecting cybersecurity.
Financial and Reputational Consequences for Equifax
The financial repercussions for Equifax were substantial. The company faced billions of dollars in legal costs, regulatory fines, and compensation to affected individuals. Equifax’s reputation suffered immensely. The breach severely damaged consumer trust, leading to a decline in stock prices and a loss of business. The incident triggered significant regulatory scrutiny and fueled calls for stricter data protection laws and increased corporate accountability for data security.
The long-term consequences continue to be felt, impacting the company’s financial performance and its standing within the industry. The breach serves as a prime example of the high cost of inadequate cybersecurity practices.
Moody’s Downgrade Decision
The Equifax data breach of 2017, exposing the personal information of nearly 150 million people, had far-reaching consequences, extending beyond the immediate reputational damage and legal battles. One significant repercussion was Moody’s decision to downgrade Equifax’s credit rating, a move that reflected the substantial financial and operational risks the company faced in the aftermath of the attack. This downgrade signaled a significant loss of confidence in Equifax’s financial stability and its ability to manage risk effectively.Moody’s rationale for the downgrade stemmed from a multifaceted assessment of Equifax’s vulnerabilities and the potential long-term impact of the breach.
The agency considered not only the immediate costs associated with remediation, legal settlements, and regulatory fines, but also the longer-term implications for Equifax’s business model, customer relationships, and operational resilience. The potential for further reputational damage, decreased consumer trust, and increased regulatory scrutiny all played a role in Moody’s assessment. Furthermore, Moody’s evaluated the effectiveness of Equifax’s response to the breach, considering whether its actions were sufficient to mitigate future risks and restore confidence.
A slow or inadequate response could have further exacerbated the negative impact on the company’s creditworthiness.
Factors Considered in Moody’s Assessment
Moody’s considered several key factors when determining the extent of the downgrade. These included the magnitude of the data breach itself – the sheer number of individuals affected and the sensitive nature of the compromised information – representing a substantial reputational blow and a significant financial liability. The agency also evaluated the potential for future regulatory fines and legal settlements, which could significantly strain Equifax’s financial resources.
Moreover, the costs associated with enhancing cybersecurity infrastructure, improving data protection measures, and responding to customer inquiries were all factored into the assessment. Finally, Moody’s assessed the potential impact on Equifax’s future earnings and profitability, considering the possibility of lost business, decreased consumer trust, and increased operational expenses. The longer-term implications for the company’s competitive position and overall market value were also weighed heavily in the decision-making process.
Equifax Credit Rating Before and After Downgrade
| Rating Agency | Rating Before Downgrade | Date of Downgrade | Rating After Downgrade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moody’s | A3 | October 26, 2017 | Baa1 |
Impact of the Downgrade on Equifax
The Moody’s downgrade following the massive Equifax data breach sent shockwaves through the company, impacting its operations and financial standing significantly. The downgrade, a reflection of increased risk and diminished creditworthiness, had immediate and long-term consequences for Equifax’s business model and its ability to navigate the financial landscape. Understanding these ramifications is crucial to grasping the full extent of the breach’s impact.The immediate impact of the downgrade was a decline in Equifax’s stock price, reflecting investor concerns about the company’s future profitability and stability.
This loss of market value directly translated into reduced shareholder confidence and potentially hindered future investment opportunities. Furthermore, the downgrade made it more expensive for Equifax to borrow money, impacting its short-term liquidity and its ability to fund ongoing operations and future investments. The increased cost of capital limited the company’s capacity for expansion and strategic initiatives.
Short-Term Implications for Equifax’s Business Operations
The downgrade immediately increased the cost of borrowing for Equifax. This made it more expensive to manage day-to-day operations and invest in new technologies and services. The decreased credit rating also impacted client confidence. Some clients might have reconsidered their relationship with Equifax, fearing further reputational damage or increased risk. The company likely experienced increased scrutiny from regulators and faced heightened pressure to improve its security infrastructure and data protection measures.
This led to increased operational costs associated with remediation and enhanced security measures.
Long-Term Implications for Equifax’s Business Operations
The long-term consequences of the downgrade are potentially more severe. A lower credit rating can make it harder for Equifax to secure long-term financing for major projects or acquisitions. This could stifle growth and limit the company’s ability to compete effectively in the credit reporting industry. Sustained reputational damage could lead to a loss of market share as clients migrate to competitors perceived as more trustworthy.
The increased cost of capital could also impact profitability, making it more challenging for Equifax to maintain its competitive edge and investor confidence over the long term. The long-term effects could be compounded by increased regulatory oversight and potential legal liabilities stemming from the data breach.
Effects on Equifax’s Ability to Secure Loans and Financing
The Moody’s downgrade directly increased the interest rates Equifax would pay on any new loans or financing. Lenders are naturally risk-averse, and a lower credit rating signals increased risk. This meant Equifax had to pay a premium to borrow money, reducing its profitability and limiting its ability to invest in growth opportunities. The downgrade also reduced the amount of credit available to Equifax.
Lenders may have been less willing to provide large loans or lines of credit, restricting the company’s financial flexibility. This could have constrained Equifax’s ability to respond to market changes and invest in crucial upgrades to its systems and security infrastructure. For example, a planned expansion into a new market might have been delayed or cancelled entirely due to the difficulty and expense of securing necessary funding.
Strategies to Mitigate the Negative Impact of the Downgrade
To mitigate the negative effects of the downgrade, Equifax likely implemented several strategies. These might have included focusing on improving its cybersecurity infrastructure and data protection measures to regain client and investor confidence. Equifax probably increased transparency and communication with stakeholders, proactively addressing concerns and demonstrating a commitment to remediation. They likely engaged in robust investor relations to reassure investors about the company’s long-term viability and its plans for recovery.
Further, Equifax may have explored strategic partnerships or acquisitions to bolster its competitive position and enhance its technological capabilities. Finally, they likely implemented cost-cutting measures to improve profitability and demonstrate financial prudence to lenders and investors. These actions aimed at demonstrating a commitment to long-term stability and growth, gradually rebuilding its reputation and creditworthiness.
Cybersecurity Measures and their Effectiveness
The Equifax data breach exposed significant weaknesses in the company’s cybersecurity posture, highlighting the critical need for robust and proactive security measures. Analyzing Equifax’s pre- and post-breach security practices reveals a stark contrast, underscoring the importance of learning from past mistakes and implementing comprehensive security frameworks. The breach served as a harsh lesson, demonstrating that even large, established companies are vulnerable if their security protocols are inadequate.Equifax’s cybersecurity practices before the breach were demonstrably deficient.
Moody’s downgrading Equifax after that massive cyberattack really highlights the vulnerability of even the biggest companies. Building robust, secure systems is crucial, and that’s where understanding the future of app development comes in; check out this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future to see how we can improve security. Ultimately, the Equifax breach underscores the need for innovative and secure application development strategies to prevent future catastrophes.
Internal audits revealed a lack of sufficient patching of known vulnerabilities in Apache Struts, the open-source web application framework exploited by the attackers. This failure to implement timely updates allowed attackers to easily gain unauthorized access to the system. Furthermore, evidence suggests insufficient multi-factor authentication and a lack of robust intrusion detection and prevention systems. The company’s overall security culture seemingly lacked the urgency and proactive approach necessary to mitigate such risks.
In contrast, post-breach, Equifax invested heavily in improving its security infrastructure, including enhanced monitoring, more rigorous vulnerability management, and improved employee training. However, the damage had already been done, resulting in significant financial and reputational losses.
Vulnerabilities Exploited and Prevention Strategies
The attackers exploited a known vulnerability in the Apache Struts framework, specifically CVE-2017-5638. This vulnerability allowed attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code on the Equifax server. Prevention of this specific attack could have been achieved through prompt patching of the Apache Struts framework. Regular security audits and penetration testing would have also likely identified this vulnerability before exploitation.
Additionally, implementing a robust web application firewall (WAF) could have helped block malicious requests targeting this vulnerability. Beyond this specific vulnerability, the lack of multi-factor authentication allowed attackers to maintain access even after initial compromise. Implementing MFA would have significantly increased the difficulty for attackers to maintain persistence within the Equifax network. A more robust intrusion detection system (IDS) and intrusion prevention system (IPS) capable of identifying and blocking suspicious activity could have also limited the impact of the attack.
Finally, stronger access control policies and regular security awareness training for employees would have minimized the risk of human error contributing to the breach.
Recommended Best Practices for Data Security
The Equifax breach underscores the importance of a multi-layered approach to data security. The following best practices, if implemented, could have significantly reduced the likelihood and impact of the breach:
- Implement a robust vulnerability management program, including regular patching and updates of all software and systems.
- Employ a multi-layered security architecture, including firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and web application firewalls.
- Implement strong access control policies, including the principle of least privilege and robust authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Invest in comprehensive employee security awareness training to educate employees about phishing scams, social engineering attacks, and other security threats.
- Develop and maintain a comprehensive incident response plan to effectively manage and mitigate security incidents.
- Regularly back up critical data and ensure that backups are stored securely and are readily available for recovery in case of a breach.
- Comply with relevant data privacy regulations and industry best practices.
The Broader Implications of the Event
The Equifax data breach wasn’t just a massive security failure; it was a watershed moment, profoundly impacting consumer trust, reshaping the credit reporting industry, and sparking significant regulatory and legal action. The sheer scale of the breach – impacting nearly half the US population – exposed deep vulnerabilities within a system considered foundational to the American financial landscape. The long-term consequences continue to ripple through various sectors, underscoring the critical need for robust data protection measures.The breach significantly eroded public trust in Equifax and, by extension, the entire credit reporting industry.
Consumers became wary of sharing personal information online, leading to increased scrutiny of data handling practices across all sectors. The incident highlighted the inherent risks associated with centralized repositories of sensitive personal data and fueled the debate surrounding data privacy and security regulations. The lack of immediate transparency from Equifax further exacerbated public anger and distrust, leading to a decline in consumer confidence in the company’s ability to safeguard their data.
Regulatory and Legal Responses to the Breach
The Equifax breach triggered a wave of regulatory and legal actions. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) investigated Equifax’s security practices, ultimately settling with the company for $700 million. This settlement included provisions for improved data security measures and consumer redress. Several states also launched their own investigations and pursued legal action, resulting in further financial penalties and stricter regulatory requirements for credit reporting agencies.
Class-action lawsuits were filed on behalf of affected consumers, leading to settlements providing credit monitoring services and other forms of compensation. The effectiveness of these responses is still being assessed, as the long-term impact on data security practices within the industry remains to be seen. However, the sheer volume of legal and regulatory action clearly demonstrated a significant shift in the accountability expected of organizations handling sensitive consumer data.
The Importance of Robust Cybersecurity Measures
The Equifax breach served as a stark reminder of the critical importance of robust cybersecurity measures for organizations handling sensitive personal data. The breach exposed significant shortcomings in Equifax’s security infrastructure, including a failure to promptly patch known vulnerabilities. This highlighted the need for proactive security measures, including regular security audits, employee training on cybersecurity best practices, and the implementation of multi-layered security systems to protect against various types of cyberattacks.
The event underscored the need for organizations to adopt a risk-based approach to cybersecurity, prioritizing the protection of sensitive data and investing in advanced security technologies. The long-term costs associated with data breaches, including financial penalties, legal fees, reputational damage, and loss of consumer trust, far outweigh the costs of implementing robust security measures. The incident became a case study in the devastating consequences of neglecting cybersecurity best practices, prompting many organizations to reassess and strengthen their own security protocols.
Illustrative Example
Understanding the true scale of the Equifax data breach requires more than just numbers; it needs a visual representation that effectively conveys the human impact. Two visualizations would be particularly powerful in illustrating the severity of the situation.The first would focus on the sheer volume of compromised data and its implications for individuals. The second would chart the dramatic financial consequences for Equifax itself.
Data Breach Impact on Individuals
Imagine a bar chart. The X-axis represents categories of personal information compromised: names, addresses, Social Security numbers, driver’s license numbers, birthdates, and credit card numbers. The Y-axis represents the number of individuals affected by the breach for each data category. The bars would be strikingly tall, reflecting the massive number of individuals whose sensitive data was exposed. To add a further layer of impact, each bar could be color-coded according to the potential risk associated with each data type.
For example, Social Security numbers might be a deep red, indicating high risk of identity theft, while addresses might be a lighter orange, representing a lower, but still significant, risk. The overall message: a clear, visual representation of the extent of personal data exposure and the potential for identity theft and financial fraud for millions of people.
Equifax Stock Price Fluctuations
A line graph would effectively illustrate the volatility of Equifax’s stock price following the breach and subsequent Moody’s downgrade. The X-axis would represent time, spanning several months before the breach announcement, encompassing the announcement itself, the Moody’s downgrade, and continuing for several months afterward. The Y-axis would represent Equifax’s stock price. The line would show a relatively stable price before the breach announcement.
At the announcement, a sharp, dramatic drop would be clearly visible. A further dip would occur upon the Moody’s downgrade announcement. The subsequent months would show a slow, potentially uneven, recovery, but likely never reaching the pre-breach levels, illustrating the long-term financial consequences of the data breach for the company and its shareholders. This visual would clearly demonstrate the direct correlation between the cybersecurity incident, the loss of investor confidence, and the resulting impact on Equifax’s market valuation.
One could even overlay the graph with news headlines or dates of significant events related to the breach to further emphasize the timeline and impact.
Summary: Cyber Attack Forces Moodys To Downgrade Equifax
The Equifax data breach serves as a stark reminder of the critical importance of robust cybersecurity measures in today’s digital world. The consequences extended far beyond Equifax itself, impacting consumer trust, the credit reporting industry, and the broader regulatory landscape. While Equifax has implemented changes, the lasting effects of this breach underscore the need for constant vigilance and proactive security strategies across all organizations handling sensitive personal data.
The story of the Equifax hack isn’t just about a single company’s failure; it’s a cautionary tale for us all, highlighting the vulnerabilities we face and the steps we must take to protect ourselves in an increasingly interconnected world.
Query Resolution
What specific vulnerabilities were exploited in the Equifax breach?
Attackers exploited a known vulnerability in the Apache Struts framework, a widely used web application framework. Equifax failed to patch this vulnerability in a timely manner, leaving their systems open to attack.
Did Equifax executives face any consequences for the breach?
Yes, several Equifax executives resigned or were fired in the aftermath of the breach, and the company faced significant fines and legal settlements.
How did the breach affect consumers’ credit scores?
While the breach itself didn’t directly affect credit scores, the risk of identity theft increased significantly for affected individuals, potentially leading to negative impacts on their credit reports if fraudulent accounts were opened.
What long-term financial effects did the Moody’s downgrade have on Equifax?
The downgrade increased Equifax’s borrowing costs and made it more difficult to secure financing, impacting their ability to invest in future improvements and potentially hindering their long-term growth.





