Biden Cyber Attacks Threaten National Security
Cyber attacks are grave risks to national security says US President Joe Biden, and his statement underscores a chilling reality: we live in a world increasingly vulnerable to digital warfare. From crippling infrastructure attacks to the theft of sensitive government data, the potential consequences are staggering. This isn’t just a tech problem; it’s a national security crisis demanding immediate and comprehensive action.
We’ll explore the various threats, the government’s response, and the crucial role of the private sector in bolstering our defenses.
President Biden’s warning isn’t just hyperbole; it’s a reflection of escalating cyber threats from state-sponsored actors, organized crime, and even lone wolves. The interconnected nature of our digital world means a successful attack in one sector can have cascading effects across the entire economy and society. Understanding these vulnerabilities is the first step towards mitigating the risk and building a more resilient digital future.
Biden’s Statement on Cyberattacks and National Security
President Biden’s recent statement highlighting the grave risk of cyberattacks to national security underscores a growing concern within the US government and globally. His assertion that preparations have been made and the issue addressed, while reassuring, also suggests the ongoing and evolving nature of this threat. Understanding the context of this statement requires examining the geopolitical landscape and the specific types of cyberattacks posing the most significant danger.
Geopolitical Context of Biden’s Statement
Biden’s statement arrives amidst heightened geopolitical tensions, particularly with nation-states actively employing cyber warfare as a tool of influence and aggression. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, for example, has seen a significant increase in cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure and government systems in both Ukraine and allied nations. This context emphasizes the need for robust cybersecurity measures and international cooperation to mitigate these threats.
Furthermore, the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, coupled with the blurring lines between state-sponsored and criminal actors, complicates the attribution and response efforts. The rise of ransomware attacks, often originating from criminal organizations but potentially facilitated by nation-states, adds another layer of complexity.
Types of Cyberattacks Affecting National Security
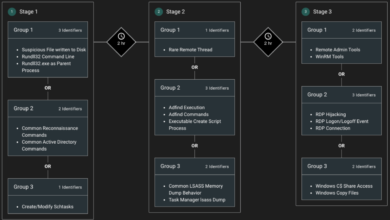
President Biden’s remarks likely encompass a wide range of cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure, government agencies, and private sector entities with national security implications. These include, but are not limited to, data breaches aimed at stealing sensitive information (such as defense secrets or intellectual property), disruptive attacks that cripple essential services (like power grids or financial systems), and disinformation campaigns that sow discord and undermine public trust.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), characterized by long-term, stealthy intrusions by sophisticated actors, also pose a significant and ongoing challenge. The use of malware, phishing campaigns, and exploitation of vulnerabilities in software and hardware are common attack vectors.
Examples of Past Cyberattacks Impacting National Security
Several past cyberattacks have demonstrably impacted national security. The NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, attributed to Russia, caused billions of dollars in damages globally, significantly disrupting businesses and government operations. The SolarWinds attack in 2020, where malicious code was inserted into widely used software, compromised numerous government agencies and private companies, demonstrating the potential for widespread and devastating breaches. The Stuxnet worm, discovered in 2010, targeted Iranian nuclear facilities, showcasing the potential of cyberattacks to disrupt critical infrastructure related to national security.
These examples highlight the diverse range and devastating consequences of such attacks.
Impact of Cyberattacks Across Sectors
| Cyberattack Type | Energy Sector Impact | Financial Sector Impact | Defense Sector Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware | Disruption of power generation and distribution, potential blackouts | System outages, financial losses, data breaches exposing customer information | Compromise of sensitive data, disruption of military operations |
| Data Breach | Theft of intellectual property, operational secrets | Theft of customer data, financial fraud | Exposure of classified information, compromise of defense systems |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) | Disruption of grid operations, impacting power supply | Website outages, disruption of online banking services | Interruption of communication and command systems |
| Supply Chain Attack | Compromise of critical infrastructure components | Disruption of financial transactions | Compromise of defense systems through compromised suppliers |
National Security Threats Posed by Cyberattacks
President Biden’s recent statements highlight the increasingly grave threat cyberattacks pose to national security. These attacks aren’t just about stolen data; they represent a direct assault on the foundations of our nation’s infrastructure and its ability to function effectively. The potential for widespread disruption and damage is immense, demanding a robust and proactive national response.Cyberattacks can compromise critical infrastructure in numerous ways, significantly impacting national security.
The interconnected nature of modern systems creates a cascading effect where a single breach can trigger widespread failures.
Compromise of Critical Infrastructure
A successful cyberattack against a power grid, for instance, could cause widespread blackouts, crippling essential services like hospitals, transportation, and communication networks. Similarly, attacks on water treatment facilities could contaminate drinking water supplies, posing a serious public health risk. Attacks on financial institutions could destabilize the economy, while attacks on transportation systems could disrupt the flow of goods and people.
The consequences extend far beyond simple inconvenience; they can lead to societal chaos and even loss of life. The Stuxnet worm, a sophisticated piece of malware believed to have been developed by the US and Israel, targeted Iranian nuclear facilities, demonstrating the potential for cyberattacks to inflict significant physical damage.
Disruption of Essential Services
The potential for cyberattacks to disrupt essential services is a major concern. Communication networks, including internet and telephone systems, are vulnerable to denial-of-service attacks, which can overwhelm systems and render them unusable. This can hinder emergency response efforts, impede communication between government agencies, and disrupt business operations. Imagine a scenario where emergency services are unable to communicate during a natural disaster due to a cyberattack – the consequences could be catastrophic.
Furthermore, attacks on supply chains can disrupt the flow of essential goods, leading to shortages and economic instability.
Vulnerabilities in National Cybersecurity Systems
Numerous vulnerabilities exist within national cybersecurity systems that cyber attackers can exploit. Outdated software, insufficient security protocols, and a lack of adequate cybersecurity training for personnel all contribute to this risk. The reliance on interconnected systems, while beneficial in many ways, also creates a larger attack surface, making it easier for attackers to gain access to sensitive information and critical systems.
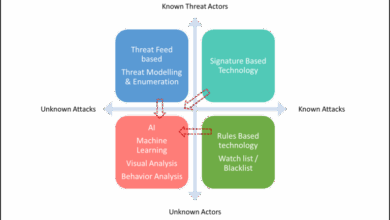
Human error, such as clicking on malicious links or falling prey to phishing scams, remains a significant vulnerability. Furthermore, the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, utilizing techniques like AI-driven malware and advanced persistent threats, makes it increasingly difficult to defend against them.
Foreign Actors and Undermining National Security
Foreign actors utilize cyberattacks to undermine national security in various ways. State-sponsored hacking groups can steal intellectual property, disrupt critical infrastructure, spread disinformation, and interfere with elections. These actions can weaken a nation’s economic competitiveness, destabilize its political system, and erode public trust. The SolarWinds attack, a large-scale cyber espionage operation attributed to Russian actors, demonstrated the potential for foreign actors to gain access to sensitive government and private sector data on a massive scale.
These attacks can be used for espionage, sabotage, or to sow discord and instability within a nation. The increasing use of cyberattacks as a tool of geopolitical power projection underscores the need for robust national cybersecurity strategies.
Governmental Response to Cyber Threats

President Biden’s emphasis on the gravity of cyberattacks on national security underscores the urgent need for robust governmental responses. The US government, recognizing this threat, has implemented a multi-faceted approach involving various agencies and departments, each contributing specialized expertise and resources to the overall effort. This approach, however, continues to evolve in response to the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.Current strategies and policies focus on prevention, detection, response, and recovery.
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) plays a crucial role, coordinating national cybersecurity efforts and providing guidance and support to both government agencies and private sector entities. The National Security Agency (NSA) focuses on intelligence gathering and defensive measures, working to identify and mitigate potential threats before they materialize. The FBI investigates cybercrimes, bringing perpetrators to justice and helping victims recover from attacks.
These agencies collaborate extensively, sharing information and resources to improve overall effectiveness. However, the scale and sophistication of cyberattacks constantly challenge these established methods.
Current US Cybersecurity Strategies and Policies
The US government utilizes a layered approach to cybersecurity, combining legislative initiatives, technological advancements, and international collaborations. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) plays a key role in disseminating threat intelligence, providing vulnerability assessments, and coordinating incident response efforts across the nation. Legislation such as the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) aims to standardize cybersecurity practices within the defense industrial base.
Furthermore, the government invests heavily in research and development of cutting-edge cybersecurity technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to improve threat detection and response capabilities. International partnerships are crucial for sharing information and collaborating on tackling transnational cybercrime.
Hypothetical National Cybersecurity Strategy
A comprehensive national cybersecurity strategy should prioritize a proactive, preventative approach. This would involve a significant investment in cybersecurity education and workforce development to address the current skills gap. A nationwide cybersecurity awareness campaign could educate individuals and organizations on best practices, significantly reducing vulnerabilities. Furthermore, strengthening public-private partnerships is vital, fostering collaboration and information sharing between government agencies and the private sector.
This would facilitate a rapid response to emerging threats and allow for the sharing of best practices. Finally, the strategy must incorporate robust incident response plans, ensuring a coordinated and effective response to large-scale cyberattacks, including clear lines of communication and well-defined roles and responsibilities. This should include regular simulations and exercises to test the effectiveness of these plans.
President Biden’s warning about cyberattacks posing grave risks to national security really hits home. We’re seeing a massive shift to the cloud, making robust security crucial. That’s why understanding solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is so important in the fight against these threats. Ultimately, strengthening our cloud defenses is key to mitigating the dangers Biden highlighted.
Recommendations for Improving National Cybersecurity Defenses
Improving national cybersecurity requires a multi-pronged approach. First, a significant increase in funding for cybersecurity research and development is crucial to stay ahead of evolving threats. This includes investing in innovative technologies and fostering the development of new cybersecurity talent. Second, strengthening legal frameworks and international cooperation is necessary to effectively prosecute cybercriminals and deter malicious activity. This would involve enhancing existing laws and creating new ones to address the evolving nature of cybercrime, while simultaneously working with international partners to establish common standards and legal frameworks.
Third, mandatory cybersecurity standards for critical infrastructure should be implemented and regularly updated to ensure consistent levels of protection across sectors. This would involve creating a system for auditing and enforcing these standards, ensuring compliance and improving overall security.
Comparative Analysis of National Cybersecurity Approaches
Different nations adopt varied approaches to cybersecurity, influenced by their unique geopolitical contexts and technological capabilities. Some nations, like Israel, prioritize proactive defense strategies, emphasizing strong national cybersecurity agencies and robust intelligence gathering capabilities. Others, like China, may focus on state-sponsored cyber operations, using them for both offensive and defensive purposes. The European Union, on the other hand, is increasingly focused on collaborative efforts, promoting data privacy regulations and establishing common cybersecurity standards across member states.
These diverse approaches highlight the complexities and challenges of creating a globally coordinated response to cyber threats. The lack of a unified global framework often hinders effective international cooperation in addressing transnational cybercrime.
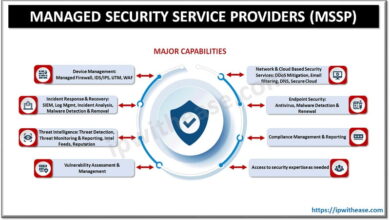
The Role of Private Sector in National Cybersecurity
The private sector plays a dual role in national cybersecurity: it’s both a critical component of our national infrastructure and a potential source of vulnerability. From the financial institutions managing our money to the energy companies powering our homes, private entities control systems vital to our national security. Their security practices, therefore, directly impact our overall national resilience to cyberattacks.
Understanding this complex relationship is paramount to effective national cybersecurity strategy.The private sector’s contribution to national cybersecurity vulnerabilities stems from several factors. Many companies, especially smaller ones, lack the resources or expertise to implement robust cybersecurity measures. This leaves them susceptible to attacks, which can then cascade to larger systems and critical infrastructure. Additionally, the interconnected nature of modern systems means a breach in one company can quickly compromise others, creating a domino effect.
Outdated software, insufficient employee training, and a lack of proactive threat detection are also common weaknesses. Finally, the constant evolution of cyber threats means companies must constantly adapt their defenses, a challenge many struggle to meet.
Private Sector Responsibilities in Protecting National Infrastructure
Private sector companies bear a significant responsibility for protecting the national infrastructure they control. This responsibility extends beyond simply safeguarding their own data and systems; it includes proactively identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities that could impact the broader national infrastructure. This requires investment in advanced security technologies, comprehensive employee training programs, and robust incident response plans. Companies must also cooperate with government agencies and share information about threats to enhance collective defense.
Failure to do so not only puts their own businesses at risk but also jeopardizes the security of the nation.
Examples of Successful Private-Public Partnerships in Cybersecurity
Successful collaboration between the public and private sectors is crucial for effective cybersecurity. One example is the Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs), which are industry-specific organizations that facilitate information sharing about cyber threats among member companies and with government agencies. These partnerships allow for faster identification and response to threats, improving overall national security. Another example is the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)’s collaboration with various private sector companies on vulnerability disclosure programs.
These programs incentivize security researchers to responsibly report vulnerabilities to companies, allowing them to be patched before they can be exploited by malicious actors. These initiatives demonstrate the effectiveness of coordinated efforts in mitigating cyber risks.
Best Practices for Enhancing Private Sector Cybersecurity Posture
The following best practices are crucial for private sector organizations to improve their cybersecurity posture and contribute to national security:
- Implement a robust cybersecurity framework, such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework, tailored to the specific needs and risks of the organization.
- Invest in advanced security technologies, including intrusion detection and prevention systems, endpoint detection and response, and security information and event management (SIEM) tools.
- Regularly update software and systems to patch known vulnerabilities. This includes operating systems, applications, and firmware.
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify and address weaknesses in security controls.
- Develop and implement comprehensive incident response plans to effectively manage and recover from cyberattacks.
- Provide comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training to all employees to educate them about common threats and best practices.
- Establish strong access control measures, including multi-factor authentication, to limit unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
- Regularly back up critical data and systems to ensure business continuity in the event of a cyberattack.
- Actively participate in information sharing initiatives, such as ISACs, to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices.
International Cooperation in Combating Cyberattacks
President Biden’s emphasis on the grave national security risks posed by cyberattacks underscores the urgent need for a global response. No single nation, regardless of its technological prowess, can effectively combat the sophisticated and increasingly transnational nature of these threats alone. International cooperation is paramount to building a more resilient and secure cyberspace.The interconnectedness of the global digital landscape makes international collaboration essential.
Cyberattacks often originate from, transit through, or target multiple countries, requiring coordinated efforts to trace origins, disrupt operations, and prosecute perpetrators. Without a unified front, cybercriminals and state-sponsored actors can exploit jurisdictional gaps and weaknesses in national cybersecurity defenses, hindering effective investigation and prosecution.
Challenges in Establishing International Norms and Regulations for Cyberspace
Creating effective international norms and regulations for cyberspace presents significant challenges. Differing national interests, legal frameworks, and technological capabilities often impede the development of universally accepted standards. The ambiguity surrounding the application of existing international law to cyberspace further complicates the issue. Disagreements on what constitutes a legitimate cyber operation versus an act of aggression pose a significant obstacle to creating binding agreements.
Additionally, the rapid evolution of technology makes it difficult to create regulations that remain relevant and effective over time. The challenge lies in finding a balance between promoting international cooperation and respecting national sovereignty.
Key International Organizations and Treaties Involved in Cybersecurity Efforts
Several international organizations and treaties play a vital role in fostering cybersecurity cooperation. The United Nations, through its Group of Governmental Experts (GGE) on cybersecurity, has worked to develop norms of responsible state behavior in cyberspace. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has issued guidelines on cybersecurity best practices for governments and the private sector. The Council of Europe’s Convention on Cybercrime provides a framework for international cooperation in investigating and prosecuting cybercrime.
While these efforts represent significant progress, they often lack the force of international law, relying instead on voluntary adherence. The Budapest Convention on Cybercrime, for instance, is a legally binding instrument, but its effectiveness depends on the ratification and implementation by individual states.
Examples of Successful International Collaborations in Combating Cybercrime
Despite the challenges, several successful examples of international collaboration in combating cybercrime exist. Joint investigations into large-scale cyberattacks, such as those targeting critical infrastructure or financial institutions, often involve the sharing of intelligence and expertise between multiple countries. The takedown of notorious botnets, which are networks of compromised computers used to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, often requires the coordinated efforts of law enforcement agencies from various jurisdictions.
President Biden’s warning about cyberattacks as grave national security risks really hit home. We need robust, secure systems, and that’s where advancements like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future become crucial. Developing secure applications efficiently is key to mitigating these threats and protecting our national infrastructure from increasingly sophisticated attacks.
The stakes are simply too high to ignore.
Furthermore, initiatives promoting information sharing and capacity building among nations, particularly those with less developed cybersecurity infrastructure, have proven beneficial in strengthening global cybersecurity defenses. The sharing of threat intelligence, for example, allows countries to proactively defend against emerging threats and improve their overall cybersecurity posture. These collaborative efforts demonstrate the potential for significant progress when nations work together to address this shared challenge.
Public Awareness and Education on Cybersecurity

President Biden’s emphasis on the gravity of cyberattacks highlights the urgent need for a robust national cybersecurity strategy. A crucial, often overlooked, component of this strategy is public awareness and education. Without informed citizens, even the most sophisticated technological defenses are vulnerable. A well-educated populace acts as a first line of defense, reducing the success rate of phishing scams, malware infections, and other cyber threats.Public awareness campaigns are essential for strengthening national cybersecurity.
These campaigns must effectively communicate the risks associated with cyberattacks and empower individuals with the knowledge and skills to protect themselves and their data. A successful campaign will not only reduce the number of successful attacks but also foster a culture of cybersecurity responsibility.
The Importance of Public Awareness Campaigns
Effective public awareness campaigns are vital because they bridge the gap between technical expertise and everyday understanding. They translate complex cybersecurity concepts into easily digestible information, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their online safety. This, in turn, reduces the overall vulnerability of the nation’s digital infrastructure. For example, a campaign that successfully teaches individuals to recognize and avoid phishing emails significantly reduces the number of successful phishing attacks, which are a primary vector for many larger cybercrimes.
Designing a Public Awareness Campaign, Cyber attacks are grave risks to national security says us president joe biden
A comprehensive public awareness campaign should utilize a multi-pronged approach, incorporating various media channels to reach a diverse audience. This could include television and radio public service announcements (PSAs) featuring relatable scenarios and clear, concise instructions. Online resources, such as interactive websites and easily accessible guides, should be developed to provide detailed information and practical advice. Social media campaigns, leveraging the power of influencers and targeted advertising, can further extend the reach of the message.
Finally, educational programs in schools and community centers can instill good cybersecurity practices from a young age. A hypothetical campaign might feature a series of short videos depicting common cyber threats, like phishing emails and malicious websites, followed by demonstrations of how to identify and avoid them.
Examples of Effective Public Education Initiatives
Several successful public education initiatives have demonstrated the power of targeted outreach. The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) in the UK, for instance, regularly publishes clear and concise guidance on various cyber threats, offering practical advice for individuals and businesses. Similarly, the US Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) provides resources and alerts to keep citizens informed about current threats and best practices.
These initiatives emphasize simplicity and clarity, making complex information accessible to a wide range of individuals. These campaigns often use memorable slogans and visuals to reinforce key messages.
Types of Cyber Threats and Mitigation Strategies
| Cyber Threat | Description | Mitigation Strategies | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Attempts to trick users into revealing sensitive information (passwords, credit card details) | Verify sender authenticity, avoid suspicious links, use strong passwords | An email appearing to be from a bank requesting login details. |
| Malware | Malicious software designed to damage or disable computer systems | Install antivirus software, keep software updated, avoid suspicious downloads | A virus infecting a computer and stealing data. |
| Ransomware | Malware that encrypts a victim’s files and demands a ransom for decryption | Regular backups, strong passwords, avoid suspicious links and attachments | Files encrypted and a ransom demanded for their release. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks | Attempts to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users | Investing in robust network infrastructure and security protocols | A website becoming inaccessible due to overwhelming traffic. |
Closing Summary: Cyber Attacks Are Grave Risks To National Security Says Us President Joe Biden
President Biden’s stark warning about cyberattacks highlights a critical need for a multi-pronged approach to national cybersecurity. Strengthening our defenses requires not only robust government policies and increased investment in technology but also a concerted effort from the private sector and informed citizenry. We must move beyond reactive measures and adopt a proactive strategy that anticipates and neutralizes threats before they can inflict damage.
The future of our national security, quite literally, depends on it.
FAQ Overview
What types of cyberattacks are most concerning to national security?
Attacks targeting critical infrastructure (power grids, water systems), data breaches revealing sensitive government information, and attacks disrupting essential services are particularly worrisome.
How can individuals contribute to national cybersecurity?
Practicing good online hygiene (strong passwords, vigilance against phishing scams), staying informed about cybersecurity threats, and reporting suspicious activity can make a difference.
What role does international cooperation play in combating cyberattacks?
Sharing intelligence, establishing common standards, and collaborating on investigations are crucial for effectively countering transnational cybercrime.
What are the potential economic consequences of a major cyberattack?
The economic impact could be devastating, ranging from widespread business disruptions and financial losses to increased insurance premiums and a decline in investor confidence.