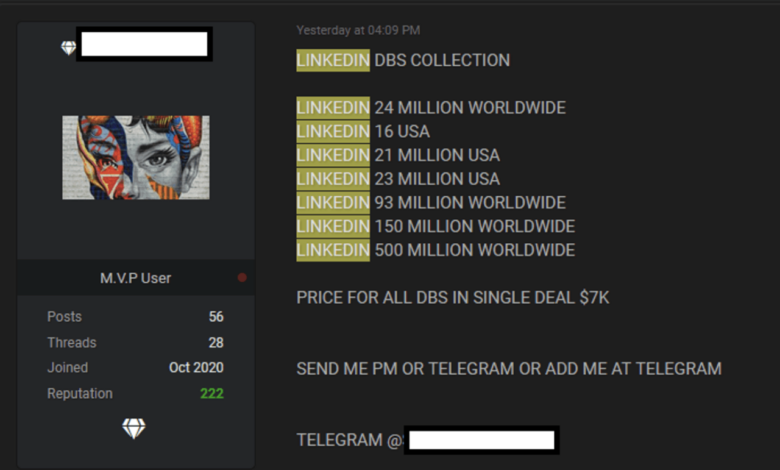
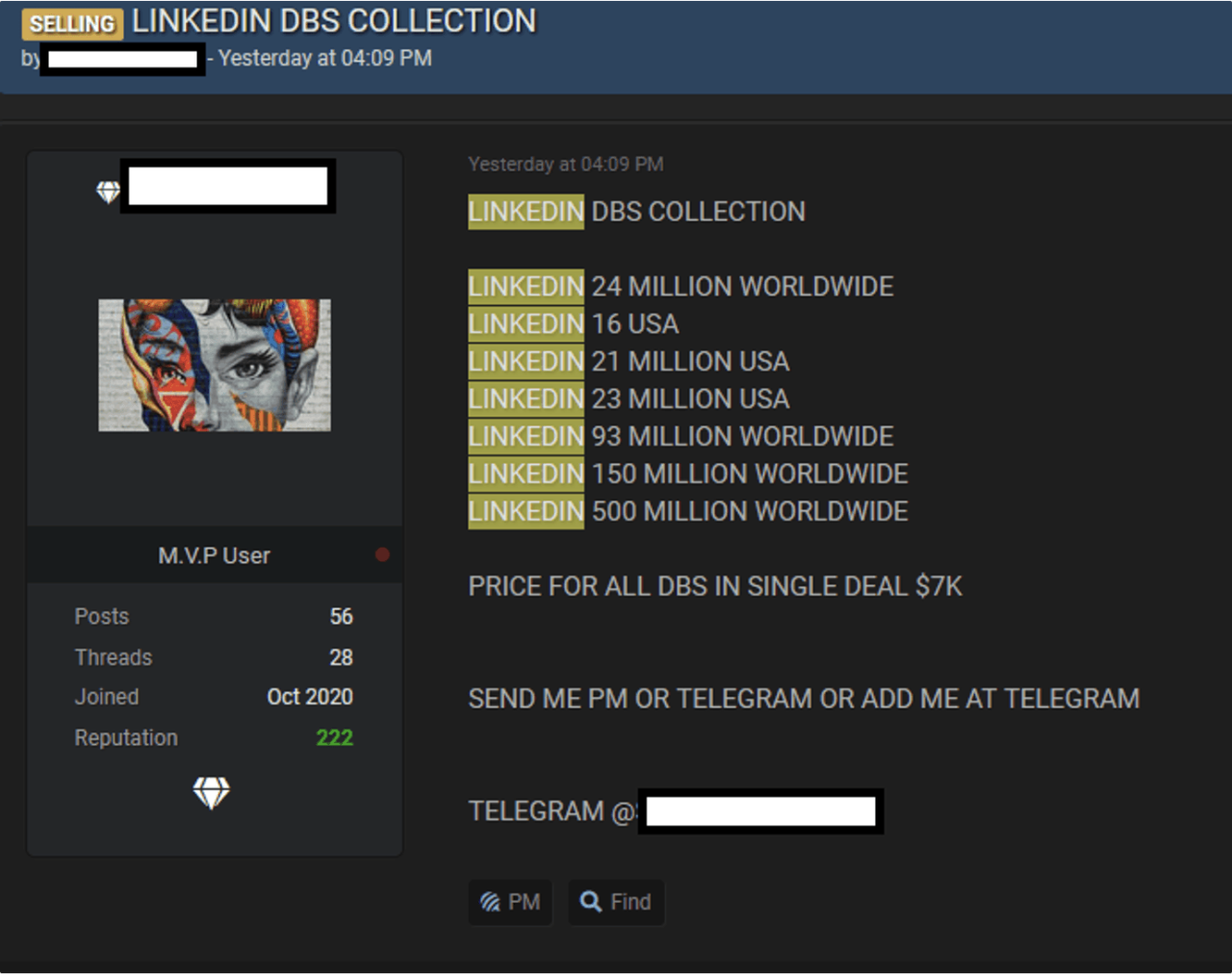
700 Million LinkedIn Users Data Leaked, For Sale
Data of 700 million linkedin users leaked and put for sale on dark web – Data of 700 million LinkedIn users leaked and put for sale on the dark web – it’s a headline that sends shivers down your spine, right? This massive data breach isn’t just another statistic; it’s a stark reminder of how vulnerable our personal information is in the digital age. Imagine the potential fallout: identity theft, financial fraud, and the erosion of trust in online platforms.
This post dives deep into this alarming situation, exploring the scale of the breach, the dark web’s role, and what we can do to protect ourselves.
The sheer volume of data—700 million user profiles—is staggering. We’re talking about names, emails, phone numbers, and potentially even more sensitive information. This isn’t just a minor inconvenience; it’s a potential catastrophe for millions of individuals. The dark web marketplace, where this data is being sold, operates in a shadowy realm, making it incredibly difficult to track down the perpetrators and recover the stolen information.
This breach highlights the critical need for stronger cybersecurity measures and greater transparency from companies handling our personal data.
The Scale of the Breach
The recent leak of 700 million LinkedIn user records represents a massive data breach, potentially impacting millions of individuals globally. The sheer volume of data involved underscores the increasingly sophisticated nature of cyberattacks and the vulnerability of even large, established platforms. This breach necessitates a serious examination of its implications and a proactive approach to data security.The potential impact of this data leak is significant and far-reaching.
The leaked data, combined with other publicly available information, could be used for various malicious purposes, leading to serious consequences for the affected users.
Data Types Included in the Leak
The leaked dataset likely contains a variety of sensitive personal information. This could include usernames, email addresses, phone numbers, physical addresses, job titles, company names, and potentially even LinkedIn profile URLs and connection information. While the exact contents haven’t been fully verified, the potential for identity theft, financial fraud, and targeted phishing attacks is substantial. The combination of different data points allows for highly personalized and effective attacks, making this breach particularly dangerous.
Consequences for Affected Individuals
Individuals whose data was compromised face a range of potential consequences. Identity theft, where criminals use stolen information to open fraudulent accounts or make purchases, is a major concern. Phishing attacks, leveraging the leaked data to craft highly targeted and convincing scams, pose another significant threat. Furthermore, the release of personal and professional details could lead to reputational damage, harassment, and even blackmail attempts.
The long-term effects of such a breach can be devastating, both financially and emotionally.
Comparison with Other Major Data Breaches
This LinkedIn data breach ranks among the largest in history. To illustrate its scale, we can compare it to other significant breaches:
| Date | Company | Number of Records | Data Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| September 2017 | Equifax | 147 million | Names, Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, driver’s license numbers |
| May 2020 | First American Financial Corporation | 88.5 million | Bank account numbers, mortgage and tax records, Social Security numbers |
| 2013 | Yahoo! | 3 billion | Names, email addresses, phone numbers, security questions and answers, dates of birth, hashed passwords |
The table above shows that while the Yahoo! breach involved a larger number of records, the LinkedIn breach is still exceptionally significant due to the detailed nature of the personal and professional information exposed. The consequences for individuals affected by these breaches are broadly similar, encompassing identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage. The scale of the LinkedIn breach underscores the ongoing need for robust data security measures and user awareness regarding online privacy.
Dark Web Marketplace Dynamics
The dark web, a hidden layer of the internet accessible only through specialized software and configurations, operates with its own unique economic rules, particularly regarding the buying and selling of illicit data. The recent leak of 700 million LinkedIn user records exemplifies the complex dynamics at play in these underground marketplaces. Understanding these dynamics is crucial to comprehending the scale and potential impact of such breaches.The sale of data on the dark web is a highly specialized process, driven by both supply and demand.
Data is often packaged and sold in various formats and sizes, depending on its perceived value and the seller’s strategy. The quality and completeness of the data also heavily influence its price. Furthermore, the seller’s reputation within the dark web community can significantly affect the transaction’s success.
The news about 700 million LinkedIn users’ data being sold on the dark web is seriously unsettling. It highlights the urgent need for robust security measures, especially considering how much sensitive information is often stored in apps. Building secure applications is crucial, and that’s where understanding the capabilities of platforms like Domino, as described in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , becomes essential.
Ultimately, the LinkedIn breach underscores the importance of prioritizing data security in every stage of app development.
Data Pricing and Payment Methods
Pricing mechanisms on dark web marketplaces are often opaque and negotiated. The price for a dataset like the leaked LinkedIn data would depend on several factors: the volume of data, the quality of the information (e.g., including passwords, email addresses, or professional details), and the perceived market demand. Prices are typically expressed in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Monero, or other privacy-focused coins, allowing for untraceable transactions.
Escrow services, managed by trusted third parties within the dark web community, are often used to ensure both the buyer and seller are protected from fraud. Payment is usually released to the seller only after the buyer verifies the data’s authenticity and completeness. Negotiations might involve samples of the data being provided upfront to build trust and demonstrate the data’s quality.
Buyer Profiles for LinkedIn Data, Data of 700 million linkedin users leaked and put for sale on dark web
Several types of buyers would be interested in this specific data breach. Cybercriminals could use the data for phishing campaigns, creating highly targeted attacks that leverage the professional details within the dataset to increase their success rate. Competitive intelligence firms, operating ethically or unethically, might be interested in the data to gain insights into competitors’ employees and strategies.
Researchers studying cybercrime or data breaches might also seek to acquire the data for analytical purposes, although ethical considerations would be paramount. Finally, unscrupulous recruiters might use the data to identify potential candidates, bypassing traditional recruitment channels. The price they would be willing to pay would depend on their specific needs and how valuable they perceive the information to be.
Dark Web Infrastructure for Data Sales
The sale of this data likely involved several layers of infrastructure. The initial leak might have been facilitated through compromised servers or insider access. The seller would then utilize hidden services, typically hosted on the Tor network, to advertise and sell the data. These hidden services provide anonymity and obfuscation, making them difficult to track and detect by law enforcement.
Communication between buyer and seller would likely occur through encrypted messaging platforms common within the dark web ecosystem, ensuring secrecy and preventing interception. The actual transfer of the data would likely occur through encrypted channels, further protecting the transaction from unauthorized access. The entire process is designed to minimize the seller’s and buyer’s digital footprints, maximizing their anonymity and reducing the risk of detection.
Vulnerabilities and Security Gaps
The massive LinkedIn data breach, exposing the details of 700 million users, highlights significant weaknesses in the platform’s security infrastructure. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial not only for LinkedIn but also for other platforms facing similar threats in the ever-evolving landscape of cybercrime. This section delves into potential security flaws, likely attack methods, and necessary improvements to prevent future incidents.
The scale of the breach suggests a sophisticated attack, likely exploiting multiple vulnerabilities. While the exact methods remain undisclosed, several possibilities exist, ranging from exploiting known vulnerabilities in LinkedIn’s systems to leveraging compromised credentials or social engineering tactics. The sheer volume of data obtained points towards a well-planned and executed operation, potentially involving insider access or the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities—flaws unknown to the developers and security teams.
Potential Vulnerabilities Exploited
Several potential vulnerabilities could have contributed to this breach. These include, but are not limited to, outdated software, insufficient input validation, weak password policies, and a lack of robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) enforcement across all user accounts. The attackers may have exploited a specific vulnerability in LinkedIn’s API, a common target for data breaches, or leveraged vulnerabilities in third-party applications integrated with the platform.
Furthermore, insufficient monitoring and logging could have allowed attackers to operate undetected for an extended period.
Likely Attack Methods
Considering the scale of the breach, the attackers likely employed a multi-pronged approach. This might have involved credential stuffing—using lists of stolen usernames and passwords obtained from other breaches to attempt logins—combined with more sophisticated techniques. SQL injection attacks, targeting vulnerabilities in LinkedIn’s databases, are another possibility. Furthermore, exploiting vulnerabilities in LinkedIn’s API could have allowed the attackers to extract large amounts of data directly, bypassing many standard security controls.
Finally, a targeted phishing campaign, aimed at employees with access to sensitive data, could have provided initial access to the network.
Recommended Security Enhancements
To prevent future breaches, LinkedIn needs to significantly bolster its security posture. This involves a multi-faceted approach focusing on proactive measures, rather than solely reactive patching.
- Implement robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) as a mandatory requirement for all users, significantly reducing the impact of compromised credentials.
- Regularly conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify and address security weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. This should include both internal and external assessments.
- Strengthen password policies, enforcing strong, unique passwords and potentially implementing password managers to aid users in creating and managing complex passwords.
- Invest in advanced threat detection and response systems, including intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools, to monitor network traffic and detect suspicious activity in real-time.
- Enhance data encryption both in transit and at rest, protecting sensitive user information even if a breach occurs.
- Implement a comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) strategy to prevent sensitive data from leaving the network unauthorized.
Hypothetical Improved Security Architecture
A significantly improved security architecture for LinkedIn would incorporate several key components and processes. This architecture should prioritize a layered security approach, with multiple layers of defense to mitigate the impact of any single security failure.
- Zero Trust Security Model: Assume no user or device is inherently trustworthy. Verify every access request, regardless of origin, using strong authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Enhanced API Security: Implement robust API gateways with rate limiting, input validation, and authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and abuse of the API.
- Advanced Threat Intelligence: Proactively monitor threat intelligence feeds to identify and address emerging threats and vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Automated Security Orchestration and Response (SOAR): Automate security tasks, such as incident response and vulnerability remediation, to improve efficiency and reduce response times.
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about phishing attacks, social engineering tactics, and other security threats to reduce the risk of human error.
Legal and Ethical Implications
The massive LinkedIn data breach, exposing the personal information of 700 million users, raises significant legal and ethical concerns for both LinkedIn and the affected individuals. This situation highlights the critical need for robust data protection measures and underscores the legal ramifications of failing to uphold user privacy. The sheer scale of the breach necessitates a thorough examination of the responsibilities of the involved parties and the available recourse for those affected.LinkedIn’s legal responsibilities are multifaceted.
Depending on the jurisdiction and applicable data protection laws (like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California), they may face significant penalties for failing to adequately protect user data. This includes demonstrating negligence in security practices, insufficient data encryption, and a lack of proactive measures to prevent and mitigate such breaches. Investigations by regulatory bodies are likely, potentially resulting in substantial fines and reputational damage.
Furthermore, class-action lawsuits from affected users are highly probable.
LinkedIn’s Legal Responsibilities
LinkedIn’s legal responsibilities stem from its role as a data controller under various data protection regulations. This means they are obligated to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect user data from unauthorized access, loss, or alteration. Failure to meet these obligations can lead to legal action under laws like the GDPR, which mandates stringent data protection standards and allows for significant fines for non-compliance.
The CCPA in California offers similar protections for residents of that state, allowing them to sue for data breaches that result in financial harm. Furthermore, other jurisdictions have their own data protection laws, and LinkedIn’s legal obligations will vary based on where the affected users reside. The company’s adherence to these laws will be scrutinized extensively following this breach.
Potential Legal Actions for Affected Individuals
Individuals whose data was compromised in the LinkedIn breach have several potential legal avenues for recourse. They may be able to file individual lawsuits against LinkedIn, alleging negligence and seeking compensation for damages such as identity theft, financial loss, or emotional distress. More likely, given the scale of the breach, class-action lawsuits will be filed, consolidating the claims of numerous affected individuals and potentially leading to larger settlements or judgments.
The success of these lawsuits will depend on demonstrating that LinkedIn failed to meet its legal obligations to protect user data and that the breach caused them direct harm.
Ethical Considerations for Companies Handling User Data
The ethical implications of this breach extend beyond the legal ramifications. Companies handling large amounts of user data have a moral obligation to prioritize user privacy and security. This breach underscores the ethical failure to adequately protect sensitive information, potentially leading to significant harm to individuals. Transparency is crucial; companies should be upfront about data breaches and promptly inform affected users.
Moreover, a proactive approach to data security, including regular security audits and robust encryption protocols, is ethically necessary. The prioritization of profit over user well-being is an ethical concern that this breach starkly illustrates. Ethical data handling goes beyond legal compliance; it requires a commitment to responsible data stewardship.
Best Practices for Data Security and User Privacy Protection
The following best practices are essential for companies to protect user data and maintain ethical standards:
- Implement robust data encryption at rest and in transit.
- Regularly conduct security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance account security.
- Develop and regularly update comprehensive data security policies and procedures.
- Provide comprehensive employee training on data security best practices.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and prevent data exfiltration.
- Establish clear data retention policies and securely dispose of data when no longer needed.
- Maintain transparent communication with users about data security practices and any breaches.
- Invest in advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
- Comply with all relevant data privacy regulations and industry best practices.
Impact on User Trust and Reputation
The exposure of 700 million LinkedIn user records represents a catastrophic blow to user trust and severely damages LinkedIn’s reputation. This breach goes beyond simple data exposure; it undermines the fundamental promise of security and privacy that underpins the platform’s entire business model. The scale of the leak is unprecedented, potentially impacting millions of users worldwide and causing widespread anxiety about the safety of their personal and professional information.The potential consequences for LinkedIn are far-reaching and could significantly impact its long-term viability.
Loss of user trust translates directly into decreased user engagement, potential regulatory penalties, and reputational damage that could take years to repair. The immediate impact will likely be seen in a drop in user activity, decreased advertiser confidence, and a potential exodus of users to competing professional networking platforms. The long-term effects depend heavily on LinkedIn’s response and its ability to regain user confidence.
LinkedIn’s Diminished Credibility
The sheer volume of data leaked significantly erodes user trust in LinkedIn’s security infrastructure. Users will question the effectiveness of LinkedIn’s security measures, leading to decreased confidence in the platform’s ability to protect their sensitive information. This damage extends beyond individual users; it also impacts the credibility of LinkedIn as a trusted professional networking platform. The breach casts doubt on LinkedIn’s commitment to data security and its ability to prevent future incidents.
This loss of credibility could negatively affect LinkedIn’s relationships with businesses and recruiters who rely on the platform for talent acquisition and professional networking. The Yahoo! data breach, for instance, resulted in a significant loss of user trust and a protracted period of recovery for the company. LinkedIn faces a similar challenge, needing to demonstrate concrete and substantial improvements to regain lost confidence.
Rebuilding User Trust: Necessary Steps
Rebuilding user trust requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on transparency, accountability, and demonstrable improvements to security infrastructure. LinkedIn must proactively communicate with affected users, providing clear and concise information about the breach, the data compromised, and the steps being taken to mitigate the risks. This includes offering credit monitoring services and identity theft protection to affected users. Furthermore, LinkedIn needs to invest heavily in improving its security protocols, demonstrating a tangible commitment to data protection.
This could involve independent security audits, enhanced data encryption, and improved user authentication methods. Finally, LinkedIn should actively engage with users, addressing their concerns and demonstrating a commitment to learning from the mistakes made. Transparency and accountability are paramount in this process. The lack of proactive communication and swift action following the Equifax breach, for example, resulted in significant public backlash and long-term reputational damage.
LinkedIn must avoid repeating this mistake.
Long-Term Effects on User Engagement and Platform Usage
The long-term effects on user engagement and platform usage are difficult to predict precisely but will likely be negative in the short to medium term. Many users may choose to deactivate their accounts or significantly reduce their activity on the platform due to concerns about data privacy and security. This decrease in user engagement could negatively impact LinkedIn’s advertising revenue and its overall value proposition.
The platform’s ability to attract new users may also be hampered, as potential users may be hesitant to join a platform with a history of significant data breaches. The long-term impact will depend on LinkedIn’s success in implementing effective remedial measures and restoring user trust. The Cambridge Analytica scandal demonstrated how a data breach can lead to long-term damage to user trust and platform usage, resulting in significant legal and reputational consequences for Facebook.
LinkedIn must learn from this example and take proactive steps to prevent a similar fate.
The news about 700 million LinkedIn users’ data being sold on the dark web is seriously unsettling. It highlights the urgent need for robust security measures, especially with the increasing reliance on cloud services. That’s why understanding solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is crucial. Ultimately, strengthening cloud security is our best defense against these kinds of massive data breaches and the subsequent fallout for individuals and companies alike.
The Role of Data Brokers and Aggregators

The recent leak of 700 million LinkedIn user records highlights a critical issue: the often-unseen role of data brokers and aggregators in the proliferation of personal data on the dark web. These entities, which collect and compile personal information from various sources, inadvertently (or sometimes intentionally) contribute to the risk of large-scale breaches and the subsequent sale of this sensitive data.
Understanding their involvement is crucial to addressing the problem.Data brokers and aggregators build extensive profiles on individuals by combining information from public records, online activity, and purchased datasets – datasets that might include leaked data from previous breaches. Their business model often relies on the aggregation and sale of this compiled information to various clients, including marketing firms, credit agencies, and even researchers.
The sheer volume of data they handle makes them attractive targets for hackers, and a breach at a data broker can expose the personal information of millions of individuals simultaneously, far exceeding the impact of a single company’s data breach. Furthermore, the aggregated nature of the data makes it even more valuable to malicious actors.
Data Broker Involvement in the LinkedIn Data Sale
The sale of the LinkedIn data likely involved data brokers and aggregators in several ways. The leaked data itself might have been initially sold on the dark web by the original perpetrators, but it’s highly probable that data brokers subsequently purchased and incorporated it into their existing datasets. This integration enhances the value of their existing profiles by adding new data points, potentially enriching the information already held on individuals.
This enriched data is then repackaged and sold to other clients, unknowingly spreading the compromised information further. Alternatively, some data brokers might have actively sought to purchase the data directly from the initial source, aware of its value in the marketplace.
Regulatory Measures to Control Data Brokers and Aggregators
Several regulatory measures could be implemented to control the activities of data brokers and aggregators. Stricter data security standards, including mandatory breach notification requirements, would hold these entities accountable for protecting the data they collect and process. Regulations could also limit the types of data they can collect and the purposes for which they can use it, particularly concerning sensitive personal information.
Increased transparency, requiring data brokers to disclose their data collection practices and provide individuals with the ability to opt out, is also essential. Finally, robust enforcement mechanisms are needed to penalize non-compliance and deter future breaches.
Data Flow Visualization
Imagine a flow chart. At the starting point is the initial data breach at LinkedIn (or another source). The data then flows to the dark web, where it’s sold. From there, several paths emerge. One path leads to individual buyers on the dark web (e.g., identity thieves).
Another path shows the data being purchased by data brokers and aggregators. These brokers then integrate the data into their existing databases, enriching their profiles on individuals. Finally, this enriched data is sold to various downstream clients, such as marketing firms, researchers, or credit agencies. Each step increases the potential for misuse and further dissemination of the compromised information.
The end result is the widespread availability of the originally leaked data, often without the knowledge or consent of the affected individuals.
Final Wrap-Up
The leak of 700 million LinkedIn user profiles serves as a chilling wake-up call. It underscores the urgent need for stronger data protection measures, both from companies and individuals. While the immediate impact is devastating for those affected, the long-term consequences could be even more far-reaching. The erosion of trust in online platforms, the rise of sophisticated cybercrime, and the ever-evolving landscape of the dark web all demand our attention.
Staying informed, practicing good online hygiene, and advocating for stronger data privacy regulations are crucial steps we can take to protect ourselves in this increasingly digital world.
Commonly Asked Questions: Data Of 700 Million Linkedin Users Leaked And Put For Sale On Dark Web
What type of data was leaked?
Reports suggest the leaked data included names, email addresses, phone numbers, and potentially other personal information, depending on the user’s LinkedIn profile settings.
How can I check if my data was compromised?
There’s no official way to definitively check if your data was included in this specific leak. However, you can monitor your accounts for suspicious activity and change your passwords regularly.
What should I do if I think my data was compromised?
Immediately change your LinkedIn password, enable two-factor authentication, and monitor your financial accounts and credit reports for any unusual activity. Consider reporting the incident to LinkedIn and the relevant authorities.
Is LinkedIn responsible for this breach?
While the investigation is ongoing, LinkedIn has a legal responsibility to protect user data. The extent of their liability will depend on the investigation’s findings.