Bazarcall Ransomware Warning Insurance Firms at Risk
Bazarcall ransomware warning to all insurance firms: This isn’t just another cybersecurity threat; it’s a wake-up call. Insurance companies, with their treasure trove of sensitive data, are prime targets for ransomware attacks. This post dives deep into the Bazarcall threat, exploring its tactics, the devastating consequences for insurers of all sizes, and most importantly, how to protect your firm from becoming the next victim.
We’ll cover everything from preventative measures to incident response planning, ensuring you’re equipped with the knowledge to navigate this dangerous landscape.
We’ll examine the specific vulnerabilities that make insurance firms attractive targets, detail the potential financial ruin and operational chaos a Bazarcall attack can unleash, and even discuss the legal and regulatory fallout. From understanding Bazarcall’s infiltration methods to crafting a robust incident response plan, we’ll arm you with the insights needed to safeguard your business and your clients’ data.
Bazarcall Ransomware
Bazarcall ransomware, a significant threat in the cybercrime landscape, poses a considerable risk to insurance firms of all sizes. Its sophisticated techniques and the sensitive nature of data held by insurance companies make them a particularly attractive target. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities and potential consequences is crucial for effective mitigation strategies.
Bazarcall Ransomware: Target Profile of Vulnerable Insurance Firms
Insurance firms are prime targets for Bazarcall due to their possession of valuable, sensitive data. Smaller firms might lack robust cybersecurity infrastructure, making them easier targets. Larger firms, while possessing more resources for security, often hold significantly larger volumes of sensitive data, making a successful attack potentially more devastating. Factors like outdated software, insufficient employee training on cybersecurity best practices, and a lack of multi-factor authentication significantly increase vulnerability.
Firms relying heavily on legacy systems are particularly at risk, as these systems often lack the security patches and updates found in more modern infrastructure. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of some insurance operations, with multiple offices and remote workers, can create vulnerabilities that are harder to manage centrally.
Financial and Operational Consequences of a Bazarcall Attack on Insurance Firms
A successful Bazarcall ransomware attack can lead to substantial financial losses. The direct costs include the ransom payment itself (which can reach millions of dollars), incident response costs (hiring cybersecurity experts, legal counsel, and public relations firms), and recovery costs (restoring data and systems). Indirect costs include lost business revenue due to operational downtime, potential regulatory fines for data breaches (especially if personal or confidential client data is compromised), and the costs associated with notifying affected clients and repairing damaged reputations.
Operational disruptions can range from minor delays in processing claims to complete system shutdowns, impacting policyholder services and potentially leading to legal action. The disruption of critical business processes like claims processing, underwriting, and policy administration can severely impact an insurer’s profitability and operational efficiency.
Reputational Damage and Client Loss Following a Bazarcall Incident
The reputational damage from a Bazarcall attack can be severe and long-lasting. A ransomware attack reveals vulnerabilities in an insurance firm’s security posture, raising concerns about their ability to protect sensitive client data. This can erode client trust and lead to significant client churn. Negative media coverage and public perception of inadequate security measures can further exacerbate reputational damage.
The loss of clients, combined with the negative impact on brand reputation, can translate into significant long-term financial losses, making recovery even more challenging.
The BazarCall ransomware warning to all insurance firms is a serious wake-up call. We need robust, secure systems, and that’s where advancements like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future become crucial. Investing in secure, adaptable tech is no longer optional; it’s essential for insurance firms facing the BazarCall threat and similar future cyberattacks.
Impact of Bazarcall on Insurance Firms of Different Sizes
| Size | Financial Impact | Operational Disruption | Reputational Damage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Potentially crippling; ransom may exceed available resources; high recovery costs relative to revenue. | Significant; complete shutdown likely; lengthy recovery time. | Severe; loss of client trust and potential business failure. |
| Medium | Substantial; significant ransom payment; high incident response and recovery costs. | Moderate to significant; partial or complete system outages; recovery time varies. | Moderate to severe; damage to reputation; potential loss of clients. |
| Large | High; substantial ransom payment possible; high incident response and recovery costs; but greater resources for recovery. | Moderate; localized outages possible; recovery time varies depending on redundancy and preparedness. | Moderate; significant reputational impact; potential loss of market share. |
Bazarcall Ransomware Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
Bazarcall ransomware, a significant threat to businesses, particularly in the insurance sector, utilizes a range of sophisticated techniques to infiltrate systems, exfiltrate data, and encrypt valuable information. Understanding these tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) is crucial for effective prevention and response. This section details the common methods employed by Bazarcall, focusing on its impact on insurance firms.
Common Infiltration Vectors
Bazarcall, like many ransomware operations, relies on several entry points to compromise target systems. These often involve exploiting vulnerabilities in software, using phishing emails, or leveraging compromised credentials. Insurance firms, with their complex IT infrastructure and sensitive data, are particularly vulnerable. For example, spear-phishing emails targeting specific employees with tailored malicious attachments or links are frequently used.
Exploiting known vulnerabilities in outdated software, such as unpatched versions of common applications or operating systems, provides another easy pathway for Bazarcall’s entry. Finally, the theft or purchase of legitimate user credentials through various means allows attackers to bypass security measures and gain direct access to the network.
Data Exfiltration Methods, Bazarcall ransomware warning to all insurance firms
Once inside the network, Bazarcall operators focus on identifying and exfiltrating sensitive insurance data. This includes policyholder information (names, addresses, social security numbers, etc.), financial records, claims data, and internal documents containing proprietary information or strategic plans. Data exfiltration often occurs gradually over time, using techniques like command and control (C2) servers to upload stolen data in small chunks, avoiding detection by security systems.
This can involve compromised accounts with elevated privileges, allowing attackers to transfer data directly from internal servers or databases to external locations. Data may be compressed and encrypted during transfer to further hinder detection and recovery efforts.
Bazarcall Ransomware Encryption Process
The encryption process employed by Bazarcall typically involves a multi-stage approach. First, the ransomware identifies target files based on file extensions and potentially file types. Then, a strong encryption algorithm, often AES or RSA, is used to encrypt the identified files. The encryption key is then encrypted with a public key and sent to the C2 server.
Simultaneously, a ransom note is placed on the compromised system, detailing the demands and instructions for payment. The encryption process itself can be highly efficient, targeting large volumes of data within a relatively short period. This speed increases the difficulty of recovery and increases the pressure on victims to pay the ransom.
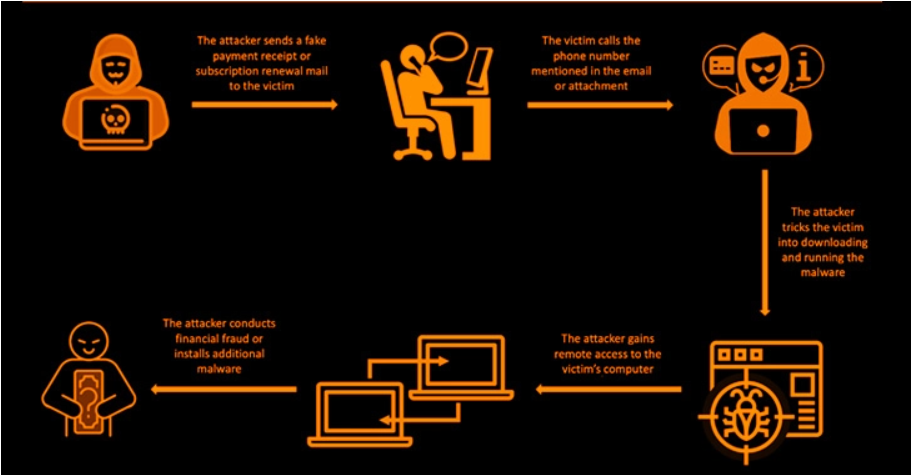
Stages of a Bazarcall Ransomware Attack
The following flowchart illustrates the typical stages of a Bazarcall ransomware attack:[Descriptive Flowchart]Imagine a flowchart with the following boxes connected by arrows:
1. Initial Access
This box represents the initial compromise, achieved through phishing, exploited vulnerabilities, or stolen credentials.
2. Internal Reconnaissance
This box depicts the attackers exploring the network to identify valuable data and systems.
3. Data Exfiltration
This box illustrates the process of stealing sensitive data.
4. Ransomware Deployment
This box shows the deployment of the Bazarcall ransomware to encrypt target files.
5. Ransom Note Delivery
This box indicates the appearance of the ransom note demanding payment.
6. Data Recovery (or Not)
This box represents the final outcome, either data recovery after payment (or negotiation) or permanent data loss.The arrows connecting these boxes clearly show the progression of the attack.
Cybersecurity Measures for Insurance Firms Against Bazarcall: Bazarcall Ransomware Warning To All Insurance Firms
The insurance industry, with its vast troves of sensitive personal and financial data, is a prime target for ransomware attacks like Bazarcall. Protecting against this threat requires a multi-layered, proactive approach that goes beyond basic security measures. This involves strengthening network defenses, implementing robust data protection strategies, and investing in advanced security technologies. Failing to adequately protect against Bazarcall could result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
Network Security Hardening
Strengthening the network infrastructure is paramount in mitigating Bazarcall’s impact. This includes implementing strong access controls, regularly patching vulnerabilities in software and operating systems, and utilizing robust firewalls to filter malicious traffic. Network segmentation, isolating critical systems and data from less sensitive areas, is also crucial to limit the lateral movement of ransomware within the network. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify and address weaknesses before attackers exploit them.
A zero trust security model, where every user and device is verified before access is granted, regardless of location, should also be considered.
Data Protection and Backup Strategies
Robust data backups and a well-defined recovery plan are essential for any organization facing a ransomware attack. The 3-2-1 backup rule—three copies of data, on two different media types, with one copy offsite—is a widely accepted best practice. Regular backups should be tested to ensure data can be quickly and reliably restored. Immutable backups, which cannot be altered or deleted, provide an additional layer of protection against ransomware encryption.
Data loss prevention (DLP) tools can help monitor and control sensitive data movement, minimizing the impact of a successful breach. Insurance firms should also have a comprehensive incident response plan detailing the steps to be taken in the event of a ransomware attack, including communication protocols with stakeholders, law enforcement, and potentially cybersecurity insurance providers.
Security Technologies for Detection and Response
Investing in advanced security technologies is crucial for detecting and responding to Bazarcall attacks. A layered approach is recommended, combining multiple technologies to provide comprehensive protection.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions monitor endpoint activity for malicious behavior, providing real-time alerts and enabling rapid incident response.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, identifying patterns and anomalies indicative of a ransomware attack.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: These platforms provide up-to-date information on emerging threats, including Bazarcall’s TTPs, enabling proactive security measures.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: While not a complete solution, robust antivirus and anti-malware software remains an essential first line of defense against ransomware.
- Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, blocking malicious connections and alerting security personnel to potential threats.
Implementing these security measures requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation. Regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices is vital, as human error remains a significant vulnerability. Staying informed about evolving ransomware tactics, like those employed by Bazarcall, is also crucial for maintaining effective defenses. By combining robust network security, comprehensive data protection, and advanced security technologies, insurance firms can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to Bazarcall and similar ransomware attacks.
Incident Response Planning and Mitigation Strategies

A robust incident response plan is crucial for insurance firms facing the threat of Bazarcall ransomware. Such a plan should not only Artikel steps to take during an attack but also incorporate preventative measures and post-incident recovery strategies. Failing to prepare adequately can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
Key Components of a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan for Bazarcall ransomware attacks should include several key components. Firstly, it needs to define clear roles and responsibilities for each team member involved in the response. Secondly, it must detail procedures for identifying and containing the attack, including isolating infected systems and preventing further spread. Thirdly, it should Artikel strategies for data recovery, encompassing backups and restoration processes.
Finally, it must address communication protocols with stakeholders, including clients, regulators, and law enforcement. A well-rehearsed plan, tested through regular drills, is far more effective than a theoretical document.
Immediate Actions Following Bazarcall Ransomware Detection
Upon detecting a Bazarcall ransomware attack, immediate action is paramount. The first step is to isolate all affected systems from the network to prevent further lateral movement and encryption. This involves disconnecting from the internet and any shared network resources. Simultaneously, a forensic investigation should commence to determine the extent of the breach and the attack vector. This investigation should include analyzing logs, identifying compromised accounts, and assessing the encrypted data.
Finally, the incident response team should activate the pre-defined incident response plan, notifying relevant stakeholders and initiating data recovery procedures. Speed and decisiveness are crucial in minimizing the impact of the attack.
Negotiating with Bazarcall Ransomware Operators
Negotiating with ransomware operators is a complex decision with significant ethical considerations. Paying a ransom doesn’t guarantee data recovery and may embolden future attacks. It can also be illegal in some jurisdictions. However, in situations where critical data is irretrievable through other means and the business impact of data loss is catastrophic, negotiation may be considered. This should only be undertaken with the advice of legal counsel and cybersecurity experts.
The negotiation process itself requires careful planning, secure communication channels, and a clear understanding of the potential risks and rewards. Transparency with law enforcement is essential throughout this process.
Roles and Responsibilities During a Bazarcall Ransomware Incident
| Team | Role | Responsibilities | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incident Response Team | Incident Commander | Overall management of the incident response; coordination of all teams; decision-making authority. | [Contact details] |
| IT Security Team | Security Analyst | Network isolation, malware analysis, system recovery, vulnerability assessment. | [Contact details] |
| Legal Team | Legal Counsel | Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements; guidance on ransom payments; communication with law enforcement. | [Contact details] |
| Public Relations Team | Communications Manager | Internal and external communications; managing reputation; stakeholder engagement. | [Contact details] |
Legal and Regulatory Implications for Insurance Firms

A Bazarcall ransomware attack on an insurance firm triggers a cascade of legal and regulatory repercussions, extending far beyond the immediate financial losses. The sensitive nature of the data held by insurance companies—including personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, and medical histories—makes them prime targets, and a successful attack carries significant legal liabilities. Understanding these implications is crucial for proactive risk management and effective incident response.
Data Breach Notification Laws and Regulations
Insurance firms are subject to a complex web of data breach notification laws, varying by jurisdiction. These laws mandate notification to affected individuals, regulatory bodies, and sometimes even credit reporting agencies within specific timeframes following a confirmed data breach. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the New York SHIELD Act impose stringent notification requirements, including specific details about the breach and steps taken to mitigate further harm.
Failure to comply with these notification laws can result in significant penalties, including class-action lawsuits and regulatory fines. The GDPR in Europe adds another layer of complexity, with its own stringent notification requirements and hefty penalties for non-compliance. Navigating this multifaceted legal landscape is paramount for any insurance firm.
Regulatory Fines and Penalties for Non-Compliance
The potential for regulatory fines and penalties following a Bazarcall ransomware attack is substantial. Regulatory bodies like the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and state insurance departments can impose significant financial penalties for failures in cybersecurity practices that lead to data breaches. These penalties are often determined based on the severity of the breach, the number of individuals affected, and the insurance firm’s demonstrable efforts (or lack thereof) in preventing and mitigating the attack.
For instance, a failure to implement adequate security measures, such as multi-factor authentication or regular security audits, could significantly increase the severity of the penalties imposed. Furthermore, a lack of a comprehensive incident response plan, leading to a delayed or inadequate response, could also contribute to heavier fines.
Complying with Data Privacy Regulations After a Bazarcall Attack
Effective compliance with data privacy regulations following a Bazarcall attack requires a multi-pronged approach.
- Immediate Notification: Promptly notify affected individuals and relevant regulatory bodies according to applicable laws, providing clear and concise information about the breach and steps taken to mitigate its impact.
- Forensic Investigation: Conduct a thorough forensic investigation to determine the extent of the breach, identify the source of the attack, and assess the compromised data.
- Data Remediation: Implement measures to remediate the compromised systems and data, including data restoration from backups and system patching.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Strengthen security measures to prevent future attacks, including implementing multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
- Employee Training: Conduct regular employee training programs to raise awareness about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response to future incidents.
- Cooperation with Authorities: Fully cooperate with law enforcement and regulatory authorities during the investigation.
Insurance and Cyber Insurance Coverage for Bazarcall Attacks
The devastating impact of a ransomware attack like Bazarcall on an insurance firm can be catastrophic, affecting not only operational continuity but also financial stability and reputation. Cyber insurance has become a crucial risk mitigation strategy, offering financial protection against such events. Understanding the nuances of these policies is paramount for effective risk management.Cyber insurance policies designed to cover losses from ransomware attacks, such as Bazarcall, typically fall under several categories.
These include First-Party Coverage (covering the insured’s direct losses), Third-Party Coverage (covering losses incurred by others due to the insured’s actions), and Crime Insurance (potentially covering losses if the attack constitutes a criminal act). The specific coverage offered varies widely between providers and policy types.
Types of Cyber Insurance Policies Covering Bazarcall Attacks
Different cyber insurance policies offer varying levels of protection against Bazarcall attacks. Some policies may cover the costs of data recovery and restoration, while others may also cover business interruption losses, legal expenses, and public relations costs associated with managing the aftermath of an attack. Comprehensive policies often combine several types of coverage to provide a more holistic approach to risk mitigation.
For example, a policy might cover the cost of incident response services, ransom payments (subject to policy limitations and exclusions), and notification costs to affected individuals. Less comprehensive policies may only cover certain aspects, such as data breach notification or system restoration.
Comparison of Cyber Insurance Providers and Coverage Options
The cyber insurance market is diverse, with numerous providers offering a wide range of coverage options. Comparing providers requires careful consideration of several factors, including policy limits, deductibles, exclusions, and the specific services included. Some providers specialize in certain industries, such as insurance, and may offer more tailored coverage options. It is crucial to review policy documents carefully to understand the extent of coverage offered for ransomware attacks, including the specifics related to Bazarcall.
Factors like the insurer’s financial strength and claims handling process should also be assessed. For instance, one provider might offer higher coverage limits for ransom payments but have a higher deductible, while another might offer a lower limit but a lower deductible.
Cyber Insurance Claim Process Following a Bazarcall Attack
Filing a cyber insurance claim after a Bazarcall attack involves a structured process. Prompt notification to the insurer is crucial, often within a specified timeframe Artikeld in the policy. Detailed documentation of the attack, including incident response reports, forensic analysis findings, and financial losses, is necessary to support the claim. The insurer will typically investigate the claim to verify the validity of the losses and ensure compliance with policy terms.
The claim process may involve interaction with various specialists, including forensic investigators, legal counsel, and public relations experts, depending on the scope of the incident. Timely and thorough documentation is vital for a smooth and efficient claims process.
Exclusions and Limitations in Cyber Insurance Policies Related to Ransomware
Cyber insurance policies often include exclusions and limitations that affect coverage for ransomware attacks. Common exclusions might include losses resulting from pre-existing conditions, failure to maintain adequate security measures, or attacks originating from an insured’s own employees. Limitations may include caps on coverage for specific types of losses, such as ransom payments or business interruption. Policies may also exclude coverage for certain types of data, such as intellectual property or sensitive personal information, if specific requirements regarding data security and protection are not met.
Careful review of the policy’s exclusions and limitations is essential to understand the extent of actual coverage. For example, a policy might exclude coverage for losses resulting from a known vulnerability that the insured failed to patch despite having received a security alert.
End of Discussion
The Bazarcall ransomware threat to insurance firms is real and potent. Ignoring it is not an option. By understanding Bazarcall’s tactics, implementing strong cybersecurity measures, and developing a comprehensive incident response plan, insurance companies can significantly reduce their risk. Remember, proactive security is far more cost-effective than reactive recovery. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay protected.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the average ransom demanded by Bazarcall?
The ransom amount varies greatly depending on the size and sensitivity of the stolen data. There’s no set amount, and negotiations are often involved.
Can I recover my data without paying the ransom?
Data recovery is possible without paying, but it’s significantly more challenging and time-consuming. It often involves restoring from backups, and success depends heavily on the robustness of your backup strategy.
What if my cyber insurance doesn’t cover a Bazarcall attack?
Carefully review your policy’s exclusions and limitations. Many policies cover ransomware attacks, but there might be specific exclusions or conditions you need to be aware of. Consult with your insurance provider immediately.
How can I report a Bazarcall ransomware attack?
Report the incident to law enforcement (such as the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3)) and relevant regulatory bodies. You should also notify your insurance provider and potentially affected clients, depending on your legal obligations.