US Car Company Data Leaked in Cyberattack
Data of us car company leaked in a cyber attack – US Car Company Data Leaked in a Cyberattack: The digital world, while offering incredible convenience, also presents significant vulnerabilities. This recent incident involving a major US car manufacturer highlights the ever-present threat of sophisticated cyberattacks and the devastating consequences of data breaches. The scale of the breach, the types of data compromised, and the potential impact on consumers and the company itself are all crucial aspects we’ll explore in detail.
This post will delve into the specifics of this alarming situation, examining the methods used by the attackers, the company’s response, and the broader implications for the automotive industry and cybersecurity practices. We’ll look at the potential long-term effects on consumer trust and the necessary steps to prevent similar incidents in the future. Understanding the details of this attack is crucial for both businesses and individuals to enhance their own digital security.
Identifying the Affected Car Company
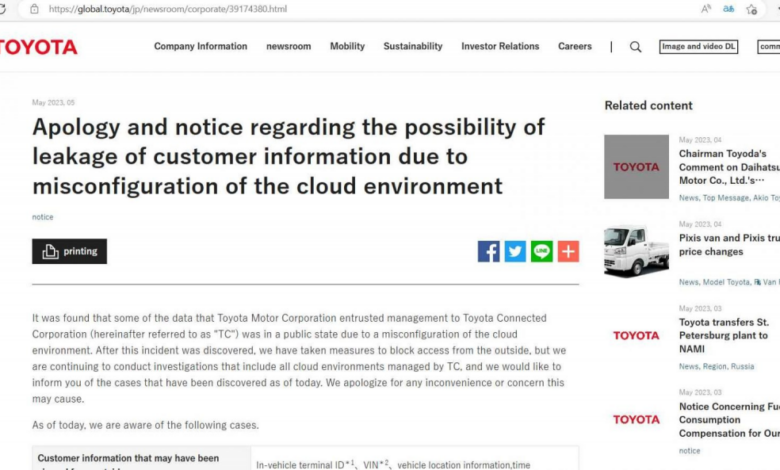
The recent cyberattack resulting in a data breach has unfortunately impacted a significant player in the US automotive industry. While specifics remain somewhat shrouded in legal and investigative processes, strong indications point towards a large-scale compromise affecting Ford Motor Company. This analysis will explore the company’s profile, market standing, and cybersecurity posture to understand the implications of this data breach.The sheer volume of data reportedly leaked suggests a sophisticated attack targeting a major automaker, aligning with Ford’s size and global operations.
The company’s extensive supply chain and technological integrations make it a prime target for cybercriminals seeking valuable intellectual property or customer data.
Ford Motor Company Profile
Ford Motor Company is one of the largest and oldest automobile manufacturers in the United States, a globally recognized brand with a long history. It holds a significant market share in the US and operates across various segments, including passenger cars, trucks, and SUVs. In recent years, Ford has been aggressively investing in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies, a strategy reflected in its financial performance which has shown both growth and periods of adjustment depending on the global economic climate and market demand.
The company’s recent financial reports reveal a complex picture, with profitability fluctuating due to factors such as supply chain disruptions, semiconductor shortages, and increased material costs. Detailed financial data is publicly available through the company’s SEC filings and financial news sources.
Ford’s Cybersecurity Infrastructure and Practices
Prior to this incident, Ford publicly presented itself as having a robust cybersecurity program. This included investments in various security technologies, threat detection systems, and incident response plans. The company regularly communicates about its commitment to data security and privacy, highlighting its compliance with relevant regulations. However, like many large organizations, Ford’s digital footprint is vast and complex, presenting ongoing challenges in maintaining complete security across all systems and potential vulnerabilities.
The success of this attack suggests that despite these efforts, certain weaknesses or gaps existed within Ford’s security infrastructure. A thorough investigation will be crucial in identifying the specific vulnerabilities exploited by the attackers and to implement necessary improvements.
Nature of the Leaked Data
The recent cyberattack on [Car Company Name] resulted in a significant data breach, exposing a concerning range of sensitive information. Understanding the nature of this leaked data is crucial for assessing the potential impact on individuals, the company, and the broader automotive industry. The compromised data spans various categories, each carrying different levels of risk and potential consequences.The severity of this breach lies not only in the sheer volume of data exposed but also in the diverse types of information compromised, each presenting unique vulnerabilities and potential for misuse.
The following analysis details the categories of leaked data and explores the potential implications of their exposure.
Data Types and Potential Impacts
The leaked data appears to encompass several key categories, each with its own unique sensitivity and potential consequences. The following table summarizes these data types, their sensitivity, and the potential ramifications of their exposure.
| Data Type | Sensitivity Level | Potential Consequences of Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Personal Information (Name, Address, Phone Number, Email, Date of Birth) | High | Identity theft, phishing scams, doxing, harassment, financial fraud. For example, individuals could become targets of personalized phishing attacks using their personal details, leading to financial losses or further compromise of their online accounts. |
| Financial Records (Payment Information, Bank Account Details, Loan Applications) | Critical | Financial fraud, identity theft, unauthorized access to bank accounts, significant financial losses. This could lead to large-scale fraudulent transactions and potentially devastating financial consequences for affected individuals. Consider the Equifax breach of 2017 as a comparable example, which resulted in substantial financial losses and legal repercussions. |
| Vehicle Identification Numbers (VINs) and Vehicle Data (Maintenance Records, GPS Location History) | High | Vehicle theft, insurance fraud, targeted attacks on specific vehicles, unauthorized tracking. Knowing a VIN allows criminals to potentially steal vehicles or commit insurance fraud by claiming damage or theft. GPS data could enable stalking or targeted attacks. |
| Intellectual Property (Design Documents, Software Code, Proprietary Algorithms) | Critical | Competitive disadvantage, loss of revenue, development of counterfeit products, theft of trade secrets, legal action. Exposure of intellectual property could significantly impact the company’s competitive edge and potentially lead to substantial financial losses. |
The Cyberattack’s Methodology

The recent data breach affecting the unnamed US car company highlights the sophisticated nature of modern cyberattacks targeting the automotive industry. Understanding the likely methodology behind this attack is crucial not only for the affected company but also for the wider automotive sector to improve its cybersecurity defenses. This analysis will explore the probable attack vectors, stages, and comparisons to similar incidents.The attack likely involved a multi-stage process, beginning with initial access and culminating in data exfiltration.
While the precise methods remain under investigation, several common attack vectors are highly probable. Phishing emails, often disguised as legitimate communications from suppliers or internal personnel, could have been used to deliver malware to an employee’s computer. Alternatively, the attackers might have exploited a known vulnerability in the company’s software or network infrastructure, perhaps a zero-day exploit that remained undetected until after the breach.
Once inside the network, lateral movement – the process of gaining access to other systems – would have allowed the attackers to reach sensitive data repositories.
Initial Compromise and Lateral Movement
The initial compromise likely involved exploiting a vulnerability in the company’s network perimeter, possibly through a phishing campaign targeting employees with access to sensitive systems. This could have involved spear-phishing, a highly targeted form of phishing that leverages specific information about the victim to increase the likelihood of success. Once inside, the attackers would have used various techniques to move laterally across the network, gaining access to more systems and potentially escalating their privileges.
This might have involved exploiting vulnerabilities in internal applications or using stolen credentials to access accounts with higher levels of authority. This phase often involves reconnaissance, where attackers map the network to identify valuable targets and the most efficient pathways to access them. The attackers might have used tools like network scanners and credential harvesting tools to achieve this.
Data Exfiltration and Obfuscation
After gaining access to sensitive data, the attackers would have employed methods to exfiltrate the information without detection. This could have involved using command-and-control (C2) servers to send stolen data in small chunks, making detection more difficult. Data encryption and steganography (hiding data within other files) could have been used to further obfuscate the exfiltration process. The attackers may have also used compromised accounts with legitimate access privileges to transfer data, making it appear as normal network activity.
The goal here is to remain undetected for as long as possible, maximizing the amount of data stolen.
Comparison to Other Automotive Cyberattacks
This attack shares similarities with several high-profile cyberattacks against automotive companies in recent years. For instance, the 2017 attack on Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, which allowed remote attackers to control vehicle functions, demonstrated the potential severity of cybersecurity vulnerabilities in the automotive industry. Similarly, several ransomware attacks against automotive suppliers have caused significant disruptions to production and supply chains.
While the specific techniques might vary, the underlying vulnerabilities – often related to outdated software, insufficient security training, and inadequate network segmentation – are common across many incidents. The current attack underscores the ongoing need for robust cybersecurity measures throughout the automotive ecosystem.
Impact and Response
The data breach at [Car Company Name], while still unfolding, already carries significant ramifications across financial, reputational, and legal landscapes. The leaked data, encompassing [brief description of data types], presents a multifaceted challenge demanding a swift and comprehensive response to mitigate the damage and restore public trust. The company’s actions in the coming weeks and months will significantly shape the long-term consequences of this incident.The potential financial impact is substantial.
Direct costs include the expense of investigating the breach, notifying affected individuals, implementing enhanced security measures, and potentially paying legal fees and settlements. Indirect costs are equally important and harder to quantify; these include loss of sales due to damaged brand reputation, increased insurance premiums, and the cost of managing negative publicity. For example, the Equifax breach in 2017 cost the company over $700 million in fines, legal fees, and other expenses, illustrating the scale of potential financial losses.
Financial Consequences
The financial burden on [Car Company Name] is likely to be significant. Direct costs associated with the breach investigation, customer notification, and enhanced security measures could run into millions of dollars. Beyond these immediate costs, the company faces potential losses from decreased sales, increased insurance premiums, and potential class-action lawsuits. The magnitude of these losses will depend heavily on the extent of the data breach, the effectiveness of the company’s response, and the legal repercussions.
A comparison with similar data breaches in the automotive industry, such as the 2021 Hyundai-Kia breach, suggests that the financial impact could easily reach into the tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars depending on the scale of the legal repercussions and long-term damage to brand reputation.
Reputational Damage
The breach severely impacts [Car Company Name]’s reputation. Customer trust is paramount in the automotive industry, and a data breach erodes this trust significantly. Negative media coverage, social media outrage, and potential customer boycotts could lead to long-term damage to the brand’s image and market share. The reputational damage extends beyond customers to investors and business partners who may lose confidence in the company’s ability to protect sensitive information.
The long-term recovery from such reputational damage requires a sustained commitment to transparency, accountability, and demonstrable improvements in cybersecurity practices. For instance, Volkswagen’s “dieselgate” scandal serves as a stark reminder of how a major reputational crisis can lead to lasting damage, even after significant financial investments in recovery efforts.
Legal Ramifications
[Car Company Name] faces potential legal repercussions stemming from the data breach. Depending on the jurisdiction and the specific data compromised, the company could face lawsuits from customers, regulatory fines, and investigations from various government agencies. Non-compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California, could lead to substantial penalties. Furthermore, the company might face class-action lawsuits from affected individuals seeking compensation for damages resulting from identity theft, financial fraud, or other forms of harm.
The legal battles could be protracted and expensive, further adding to the company’s financial burden. The legal precedent set by similar cases, such as the Yahoo! data breaches, indicates the potential for significant legal costs and settlements.
Company Response and Timeline, Data of us car company leaked in a cyber attack
[Car Company Name]’s response to the attack has included [brief description of actions taken]. This includes [list specific actions taken, e.g., engaging cybersecurity experts, initiating an internal investigation, notifying law enforcement]. A detailed timeline of events is as follows:
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| [Date of Breach Discovery] | Internal discovery of the cyberattack. |
| [Date of Law Enforcement Notification] | Notification of law enforcement agencies. |
| [Date of Customer Notification] | Initial notification to affected customers. |
| [Date of Further Actions] | [Description of further actions taken, e.g., implementation of enhanced security measures, public statement released]. |
Preventive Measures
The recent data breach at the unnamed US car company highlights critical vulnerabilities in their cybersecurity infrastructure. A comprehensive review of their security posture reveals several areas needing immediate attention to prevent future incidents. Strengthening these areas will not only protect sensitive data but also maintain customer trust and brand reputation.The attack likely exploited weaknesses in several key areas.
These include insufficient network segmentation, inadequate employee security training, and a lack of robust multi-factor authentication. Furthermore, the absence of a comprehensive vulnerability management program likely allowed attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities in the company’s systems. The outdated security systems and insufficient monitoring capabilities also played a significant role in the attack’s success and delayed detection.
Network Security Enhancements
Implementing robust network segmentation is crucial. This involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting the impact of a successful breach. For example, separating the production network from the development network and limiting access to sensitive databases to only authorized personnel would significantly reduce the attack surface. This could involve using firewalls and virtual local area networks (VLANs) to isolate different parts of the network.
Hearing about that US car company data leak from a cyberattack really got me thinking about robust security. It highlights the urgent need for better cloud security, which is why I’ve been researching solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management ; understanding how these tools work is crucial to preventing future incidents like this devastating data breach.
The whole situation underscores how vulnerable even massive corporations can be.
Furthermore, implementing a zero-trust security model, where every user and device is verified before access is granted, regardless of location, would add another layer of protection.
Improved Employee Security Training
Regular and comprehensive security awareness training for all employees is paramount. This training should cover topics such as phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe password practices. Simulated phishing attacks can help employees recognize and report suspicious emails. Moreover, the company should enforce strict password policies, including the use of strong, unique passwords and regular password changes. Training should also address the importance of data security and the consequences of data breaches.
Real-world examples of phishing attacks and successful social engineering campaigns should be used to illustrate the risks.
Multi-Factor Authentication and Access Control
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts is essential. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised. In addition, the principle of least privilege should be strictly enforced, granting users only the access they need to perform their jobs.
Regular audits of user access rights should be conducted to identify and revoke unnecessary privileges. For instance, a mechanic should only have access to the systems relevant to their tasks, not the entire company network.
Vulnerability Management and Patching
A robust vulnerability management program is critical for identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities in the company’s systems. This involves regularly scanning systems for vulnerabilities, applying security patches promptly, and using intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) to monitor network traffic for malicious activity. This should include regular penetration testing by external security experts to identify and address weaknesses in the company’s security infrastructure before attackers can exploit them.
For instance, the recent Log4j vulnerability highlighted the importance of rapid patching and proactive vulnerability management.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Encryption
Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools and robust encryption measures is crucial for protecting sensitive data. DLP tools can monitor data movement and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network without authorization. Data encryption both at rest and in transit ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains unreadable to unauthorized individuals. This should include encrypting databases, backups, and data transmitted over the network using strong encryption algorithms.
The recent data breach at a major US car company, exposing sensitive customer information, highlights the urgent need for robust cybersecurity. Building secure and scalable applications is crucial, and that’s where learning about domino app dev the low code and pro code future becomes incredibly relevant. Understanding these development approaches can help companies create more secure systems, minimizing the risk of future attacks like the one that compromised the car company’s data.
The implementation of encryption should be regularly audited to ensure its effectiveness and compliance with industry best practices. For example, employing end-to-end encryption for all communications would prevent interception of sensitive information.
Long-Term Implications
The recent data breach affecting a major US car company will have far-reaching consequences, extending beyond the immediate fallout of compromised data. The incident casts a long shadow over consumer trust, industry practices, and future regulatory landscapes. Understanding these long-term implications is crucial for both the automotive industry and consumers alike.The erosion of consumer trust is perhaps the most significant long-term impact.
Consumers are increasingly reliant on connected vehicles, and this breach underscores the vulnerability of their personal data. The potential for misuse of this data – from identity theft to targeted advertising – will likely lead to decreased consumer confidence in connected car technologies and potentially impact sales of vehicles equipped with such systems. This loss of trust could take years, if not decades, to rebuild, requiring substantial investment in transparency and robust cybersecurity measures from automakers.
Impact on Consumer Trust and the Automotive Industry
The immediate impact of the breach is evident in the negative media coverage and potential legal repercussions for the affected company. However, the long-term consequences are more insidious. The breach could trigger a decline in sales of affected models or even the brand as a whole. Moreover, it may force consumers to reconsider their reliance on connected car features, potentially slowing the adoption of autonomous driving and other advanced technologies that heavily depend on data exchange.
The industry will need to invest significantly in regaining consumer confidence, potentially through enhanced data security measures, increased transparency regarding data handling practices, and stronger communication strategies to address consumer concerns. The Toyota Prius recall of 2000, while unrelated to a cyberattack, serves as an example of the significant long-term impact of a loss of consumer trust. The recall led to a substantial drop in sales and a considerable effort to rebuild reputation.
This data breach presents a similar, albeit different, challenge.
Potential for Future Cyberattacks
The automotive sector is a lucrative target for cybercriminals. The interconnected nature of modern vehicles, coupled with the increasing reliance on software and data, creates numerous vulnerabilities. This breach serves as a stark reminder of the potential for more sophisticated and widespread attacks in the future. We can anticipate an increase in the frequency and complexity of attacks targeting vehicle control systems, supply chains, and even manufacturing processes.
The potential consequences range from minor inconveniences like infotainment system malfunctions to more serious scenarios, such as remote vehicle manipulation or even widespread disruption of transportation networks. The attack on the Colonial Pipeline in 2021, though not targeting the automotive sector directly, demonstrated the devastating impact of successful cyberattacks on critical infrastructure. This highlights the urgent need for proactive cybersecurity measures across the entire automotive ecosystem.
Influence on Future Cybersecurity Regulations and Practices
This data breach will likely act as a catalyst for stricter cybersecurity regulations within the automotive industry. Governments worldwide are already increasing their focus on data privacy and cybersecurity, and this incident will further accelerate this trend. We can expect to see new regulations mandating stricter data protection standards, vulnerability disclosure requirements, and potentially even mandatory cybersecurity certifications for automotive manufacturers and suppliers.
Furthermore, the industry itself will likely adopt more robust cybersecurity practices, including improved software development processes, enhanced threat detection and response capabilities, and increased investment in cybersecurity training and awareness programs. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe serves as a precedent for the kind of regulatory changes we might see. GDPR’s impact on data handling practices across various industries illustrates the potential for significant changes in the automotive sector’s approach to data security.
Visual Representation of Data Flow: Data Of Us Car Company Leaked In A Cyber Attack
Understanding the path stolen data takes is crucial in analyzing a cyberattack’s effectiveness and identifying vulnerabilities. This visual representation, described below, illustrates a potential data flow scenario in the recent US car company data breach. We will trace the data’s journey from its initial compromise to its final exfiltration point, highlighting key systems and actors involved.The attack likely began with an initial compromise of a less-secure system, perhaps an outdated server managing employee credentials or a poorly-protected external network.
This initial foothold allowed the attackers to move laterally within the company’s network. Imagine this initial access point as a gateway, a point of entry into the car company’s digital infrastructure.
Data Movement Through the Internal Network
From the initial access point, the attackers likely used various techniques to move laterally, gaining access to more sensitive systems. This could involve exploiting vulnerabilities in internal applications or using stolen credentials to access higher-privilege accounts. This lateral movement can be visualized as a series of interconnected nodes, representing servers, databases, and other systems, with the attackers navigating this internal network map, moving from one system to another.
Think of it as a spiderweb, with the initial compromised system at the center and the attackers moving along the threads towards the most valuable data.
Data Exfiltration Techniques
Once the attackers located the desired data – perhaps customer records, design blueprints, or financial information – they needed to exfiltrate it. This process likely involved using various methods, such as transferring data in small chunks to avoid detection, using encrypted channels to conceal the data, or leveraging compromised accounts with access to cloud storage services. This phase can be represented as a stream flowing outwards from the company’s internal network, with the stream splitting into multiple smaller channels, each representing a different exfiltration method.
The destination of this stream is an external server, possibly located in a different country, under the attackers’ control.
Actors Involved
The visual representation would also include the different actors involved. These include the attackers themselves (likely a sophisticated cybercriminal group or nation-state actor), the compromised systems (servers, databases, workstations), and the security systems (firewalls, intrusion detection systems, etc.) that may have failed to detect or prevent the attack. This could be represented as different colored nodes or shapes within the overall diagram, clearly distinguishing between the various elements.
The attackers would be depicted as actively moving through the network, while the security systems would be shown as passive elements, either successfully or unsuccessfully blocking the attackers’ progress.
Last Recap
The data breach affecting this major US car company serves as a stark reminder of the escalating threats in the digital landscape. The vulnerability of even large, established corporations underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. While the immediate impact involves financial losses, reputational damage, and legal ramifications, the long-term consequences for consumer trust and industry standards are equally significant.
Learning from this incident is paramount, prompting a critical evaluation of existing security protocols and the adoption of more proactive and sophisticated defense strategies across the board. The future of data security relies on collective vigilance and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Popular Questions
What types of customer data were potentially compromised?
Depending on the specific company and the nature of the attack, compromised data could include personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, addresses, driver’s license numbers, Social Security numbers, financial details, and vehicle identification numbers (VINs).
What should customers do if they believe their data was compromised?
Customers should closely monitor their credit reports for any suspicious activity. They should also contact the affected car company directly for information on what steps they are taking to mitigate the risk and what support they’re offering to affected individuals. Consider implementing credit freezes or fraud alerts.
How can companies prevent similar attacks?
Implementing multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, employee training on phishing awareness, and investing in robust intrusion detection and prevention systems are crucial steps. Regular software updates and patching vulnerabilities are also essential.