
Data on Stolen Apple iPhones to Be Made More Secure Now
Data on stolen Apple iPhones to be made more secure now – that’s the exciting news! For years, the fear of data loss after iPhone theft has loomed large, leaving users vulnerable. But what if I told you that’s about to change? This post dives into the current state of iPhone data security, highlighting vulnerabilities and exploring innovative solutions that promise to revolutionize how we protect our personal information.
We’ll examine proposed hardware and software enhancements, Apple’s role in bolstering security, and the ethical considerations involved. Get ready for a deep dive into the future of iPhone data protection!
We’ll be looking at everything from enhanced encryption and remote wipe capabilities to the potential of biometric authentication and even blockchain technology. We’ll also discuss the legal implications of accessing data on a stolen phone and how Apple can better educate users on protecting their own data. It’s a complex issue, but the potential for a safer digital future is incredibly exciting.
The Current State of iPhone Theft Data Security
iPhone theft remains a significant concern, impacting both individuals and organizations. While Apple has implemented robust security features, vulnerabilities persist, and the effectiveness of these measures varies depending on user behavior and the sophistication of the thief. Understanding the current state of data security in stolen iPhones is crucial for mitigating risk.
Current Methods for Tracking and Securing Data on Stolen iPhones
Apple’s “Find My” network plays a central role in tracking and securing stolen iPhones. This service uses GPS and Bluetooth to pinpoint the device’s location, even when it’s offline. Activation Lock, another key feature, prevents anyone from using a stolen iPhone without the original owner’s Apple ID and password. Remotely wiping the device’s data is also possible through Find My, eliminating sensitive information.
However, these features are only effective if enabled before the theft. Furthermore, sophisticated thieves can sometimes circumvent these protections through techniques like jailbreaking or using cloned SIM cards.
Vulnerabilities in Existing Security Measures
Despite Apple’s efforts, several vulnerabilities remain. For example, if Activation Lock is disabled before theft, the device becomes easily usable by the thief. Similarly, physical access to the device, even briefly, can allow thieves to bypass security measures using specialized tools or techniques. Social engineering scams, where thieves trick owners into revealing their Apple ID and password, also represent a significant vulnerability.
The reliance on network connectivity for location tracking means that iPhones in areas with poor or no network coverage are harder to track. Finally, the sophistication of thieves is constantly evolving, necessitating continuous improvement in security measures.
Impact of Stolen iPhone Data on Individuals and Organizations
The impact of stolen iPhone data can be severe. Individuals may experience identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage due to the exposure of personal information such as banking details, contact lists, and private photos. Organizations, particularly those using iPhones for business purposes, face the risk of data breaches, intellectual property theft, and legal repercussions. The loss of confidential business data can lead to significant financial losses and damage to the organization’s reputation.
Hearing Apple’s tightening security around stolen iPhones is great news – less data breaches, fewer headaches. This improved security reminds me of the advancements in app development, particularly the exciting possibilities explored in domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , which could play a role in building even more robust security solutions. Ultimately, stronger security measures for our devices are crucial, and innovative development methods will only help enhance that protection further.
The potential for blackmail and extortion also exists if sensitive information is compromised.
Examples of Data Recovery Attempts Following iPhone Theft
The success of data recovery attempts following iPhone theft is highly variable and depends on several factors, including the time elapsed since the theft, the thief’s actions, and the user’s preparedness.
| Method | Success Rate | Time to Recovery | Data Compromised |
|---|---|---|---|
| Using Find My to locate and remotely wipe the device | High (if Activation Lock enabled) | Immediate to several hours (depending on network connectivity) | Potentially all data, depending on timing |
| Law enforcement investigation and recovery | Low to Moderate | Weeks to months | Potentially all data, depending on thief’s actions and investigation success |
| Data recovery services (forensic analysis) | Low to Moderate (depending on data encryption and device condition) | Days to weeks | Potentially partial data recovery, depending on the method used |
| No action taken | 0% | N/A | All data potentially compromised |
Proposed Enhancements to Data Security
Strengthening iPhone data security against theft requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing both hardware and software improvements. The goal is to make data recovery virtually impossible even if the device falls into the wrong hands, minimizing the impact of theft on users. This involves exploring new technologies and refining existing security measures to create a more robust and resilient system.The current state of iPhone security, while robust, still presents vulnerabilities that can be exploited by determined thieves.
Therefore, proactive enhancements are crucial to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Hardware-Based Security Enhancements
Hardware-based security offers a more tamper-resistant approach to data protection compared to software alone. Implementing dedicated hardware security modules (HSMs) within the iPhone could significantly improve data encryption and key management. These HSMs would act as secure enclaves, protecting cryptographic keys and sensitive data from unauthorized access, even if the device’s operating system is compromised. This approach builds on the existing Secure Enclave technology in iPhones, expanding its capabilities and resilience.
A further enhancement could be the integration of a physically unclonable function (PUF) circuit. PUFs generate unique, unpredictable identifiers based on the physical characteristics of the chip, making device cloning extremely difficult. This would add an additional layer of protection against sophisticated cloning attacks. The implementation would require miniaturization of these components to fit within the existing iPhone design constraints.
Software-Based Security Improvements
Software improvements play a vital role in bolstering iPhone security. One significant enhancement is implementing more robust encryption algorithms, such as post-quantum cryptography, which are designed to withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers. This would future-proof the data encryption against advancements in computing power. Furthermore, enhanced remote data wiping capabilities are needed. Currently, remote wipe functions can be circumvented in some scenarios.
Improved remote wipe functionality should ensure complete and irreversible data deletion, even if the device is offline or has its storage partially damaged. This requires a more sophisticated communication protocol that can function reliably under various network conditions and hardware limitations. The implementation of more sophisticated access control mechanisms, such as behavioral biometrics, which analyze user interaction patterns, could also be considered to prevent unauthorized access.
Implementation Challenges of Proposed Enhancements
Implementing these enhancements presents several challenges. Hardware modifications require significant engineering effort and may impact production costs and device size. Integrating new hardware components seamlessly into the existing iPhone architecture requires careful planning and extensive testing to avoid performance bottlenecks or compatibility issues. Software enhancements also require rigorous testing to ensure stability and security. Balancing security improvements with user experience is crucial; overly complex or intrusive security measures may deter users.
Furthermore, there’s a need for constant updates to address newly discovered vulnerabilities. The rapid pace of technological advancements requires continuous adaptation and refinement of security measures.
Comparison of Security Approaches
The effectiveness of different security approaches can be compared based on several factors:
- Resistance to Physical Attacks: Hardware-based solutions, especially those incorporating PUFs, offer superior resistance to physical tampering compared to software-only approaches.
- Resistance to Software Attacks: Software-based encryption and access control mechanisms are vulnerable to sophisticated software exploits. However, multi-layered software security, combined with hardware security, provides a strong defense.
- Cost and Complexity: Hardware enhancements generally incur higher development and manufacturing costs compared to software updates. Software updates, while less expensive, require continuous maintenance and updates.
- User Experience: Overly complex security measures can negatively impact the user experience. A balance must be struck between security and usability.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Data On Stolen Apple Iphones To Be Made More Secure Now
The increasing sophistication of iPhone theft necessitates a careful examination of the legal and ethical ramifications surrounding data access and security. Balancing the need for robust security measures with the fundamental right to privacy presents a complex challenge for both individuals and organizations. This section will explore the legal implications of accessing data on a stolen iPhone, identify ethical dilemmas, and discuss the delicate balance between user privacy and enhanced security.Accessing data on a stolen iPhone, even with the intention of recovering it, carries significant legal risks.
Depending on the jurisdiction, unauthorized access to personal data, even if done with good intentions, could be considered a violation of privacy laws. These laws often impose strict penalties for unauthorized access, regardless of the perpetrator’s motives. For example, accessing someone’s health records on a stolen phone could lead to serious legal repercussions under HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States.
Similarly, accessing financial data could violate various financial privacy regulations. The key takeaway is that good intentions do not excuse illegal actions.
Legal Implications of Accessing Data on a Stolen iPhone, Data on stolen apple iphones to be made more secure now
The legal landscape surrounding data access on stolen devices is complex and varies significantly by location. Generally, accessing data without the owner’s explicit consent is illegal. This applies even if the device is stolen and the data is being accessed for recovery purposes. Law enforcement agencies have specific procedures for accessing data on seized devices, often requiring warrants or court orders.
Private individuals or companies attempting to access data without proper authorization risk prosecution for offenses such as unauthorized access, data theft, or violation of privacy laws. The penalties can range from hefty fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the offense and the jurisdiction.
Ethical Dilemmas Surrounding Data Security and Privacy
The ethical considerations surrounding data security and privacy in the context of iPhone theft are multifaceted. While enhanced security measures are crucial for protecting sensitive data, they must not compromise individual privacy rights. For instance, implementing overly intrusive security features, such as constant surveillance or extensive data tracking, could raise serious ethical concerns. The balance lies in finding security solutions that are effective while respecting individual autonomy and the right to privacy.
The use of biometric data, for example, raises questions about data security and the potential for misuse. Companies must be transparent about how this data is collected, stored, and used, and they must implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
Balancing User Privacy and Enhanced Security Measures
The challenge lies in striking a balance between robust security measures that protect against theft and unauthorized access, and the preservation of user privacy. This necessitates a careful consideration of the types of data collected, the methods used to collect and store it, and the level of access granted to both users and third parties. For instance, implementing end-to-end encryption protects data even if the device is compromised, but it also raises challenges for law enforcement agencies in accessing data for investigations.
Therefore, the discussion must involve all stakeholders – individuals, organizations, and law enforcement – to find a solution that adequately addresses both security and privacy concerns.
Best Practices for Protecting Data on iPhones
Strong data protection requires a multi-faceted approach. Implementing the following best practices is crucial for both individuals and organizations:
The following points highlight essential steps to safeguard data on iPhones:
- Enable a strong passcode or use biometric authentication (Face ID or Touch ID).
- Enable Find My iPhone and keep it active at all times.
- Regularly back up your iPhone data to iCloud or a computer.
- Use two-factor authentication for all Apple accounts and other online services.
- Keep your iPhone software updated with the latest security patches.
- Be cautious about downloading apps from untrusted sources.
- Use strong and unique passwords for all your accounts.
- Consider using a reputable mobile device management (MDM) solution for organizational devices.
- Educate users about phishing scams and other social engineering attacks.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures to restrict access to sensitive data.
Future Directions in iPhone Data Security
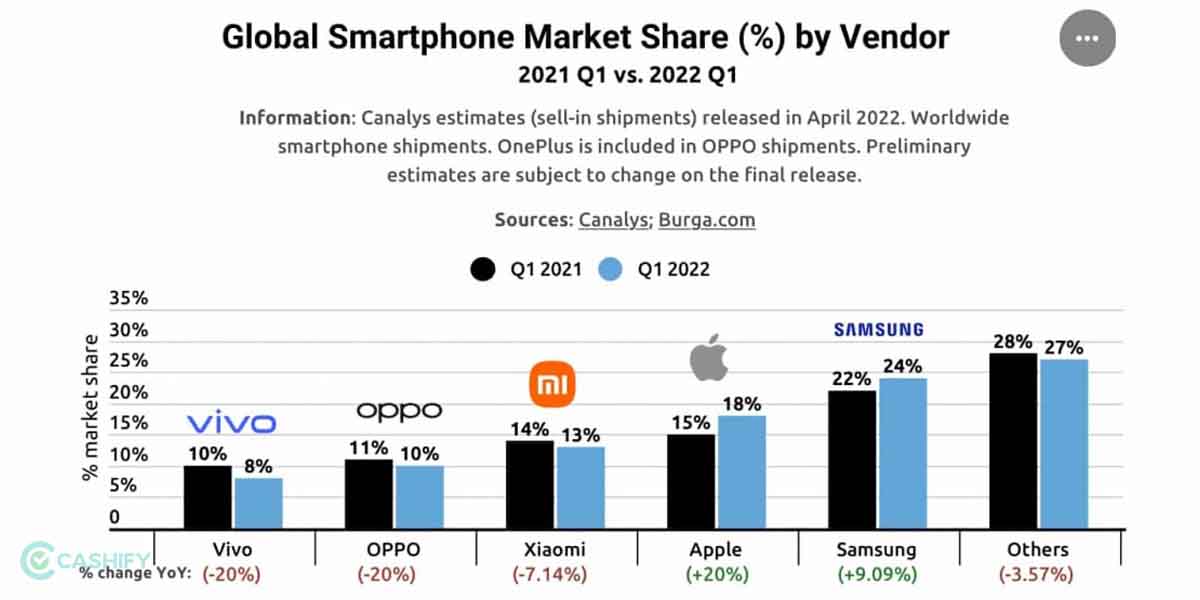
The current state of iPhone data security, while robust, is constantly evolving alongside the sophistication of cyber threats. Future advancements will need to leverage emerging technologies to stay ahead of these threats and offer users an even greater level of protection against data theft and unauthorized access. This necessitates a proactive approach focusing on enhancing existing security measures and exploring innovative solutions.
Biometric Authentication Enhancements
Biometric authentication, already a cornerstone of iPhone security, is poised for significant advancements. Current methods, like Face ID and Touch ID, are highly effective but can be vulnerable to sophisticated spoofing techniques. Future iterations could incorporate multi-modal biometric systems, combining facial recognition with other biometrics like fingerprint scanning and even iris or vein pattern recognition for a more robust and secure authentication process.
This layered approach would make it exponentially harder for attackers to bypass security measures. For example, a system combining Face ID with an under-display fingerprint sensor would require attackers to overcome two distinct biometric hurdles.
Blockchain Technology for Data Security
Blockchain technology, known for its immutability and transparency, offers significant potential for enhancing iPhone data security. A distributed ledger system could securely store user data, making it extremely difficult to alter or delete without detection. Imagine a scenario where sensitive user data, such as health records or financial information stored on the iPhone, is encrypted and recorded on a private blockchain.
Apple’s tightening security around stolen iPhones is a great step, but it highlights the broader need for robust data protection across all devices. This is where solutions like those discussed in this article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management become crucial. Improved cloud security ultimately strengthens the overall defense against data breaches, benefiting even the most secure individual devices like iPhones.
This would create a tamper-evident record of all data access and modifications, drastically reducing the risk of unauthorized changes or data breaches. The decentralized nature of blockchain also makes it more resilient to single points of failure, increasing overall system security. This approach could also be used to verify the authenticity of software updates, preventing malicious code from being installed.
Artificial Intelligence for Threat Detection and Prevention
Artificial intelligence (AI) can play a crucial role in proactively detecting and preventing data breaches on stolen iPhones. AI-powered systems could analyze user behavior patterns and device activity to identify anomalies indicative of malicious activity. For instance, unusual access attempts, data transfers to unauthorized locations, or rapid changes in device settings could trigger alerts. Furthermore, AI algorithms could learn from past attacks and adapt to new threats, improving their effectiveness over time.
This proactive approach could lead to faster detection of compromised devices, allowing for quicker intervention and mitigation of potential data loss. Real-time analysis of network traffic could also help identify and block suspicious connections before they can compromise the device. For example, an AI system could detect unusual outbound data transfers to a known malicious server and automatically block the connection.
Ending Remarks

The future of iPhone data security is bright, folks! While challenges remain in implementing these new technologies and balancing user privacy with enhanced security, the innovations discussed – from improved hardware encryption to AI-powered breach detection – paint a picture of significantly improved protection against data theft. Apple’s continued commitment to user privacy, coupled with ongoing technological advancements, offers a compelling vision of a future where stolen iPhones pose far less of a data security risk.
Stay tuned for further developments in this rapidly evolving field!
User Queries
What happens if my stolen iPhone is found?
If your iPhone is recovered, you can restore your data from a backup, assuming you had one enabled. If the data was encrypted, it will remain inaccessible to anyone without your passcode.
Can I track my stolen iPhone if I don’t have Find My iPhone enabled?
Unfortunately, without Find My iPhone activated, tracking your stolen device becomes significantly more difficult, if not impossible. Enabling this feature is crucial for recovery.
What is the difference between a hardware and software-based security solution?
Hardware solutions involve physical components within the iPhone itself, like improved encryption chips. Software solutions are upgrades to the iPhone’s operating system, like enhanced encryption algorithms or remote wipe features.
How secure is iCloud backup?
iCloud backups are generally secure, but using a strong password and enabling two-factor authentication is vital. Regular software updates are also crucial to patching any vulnerabilities.




