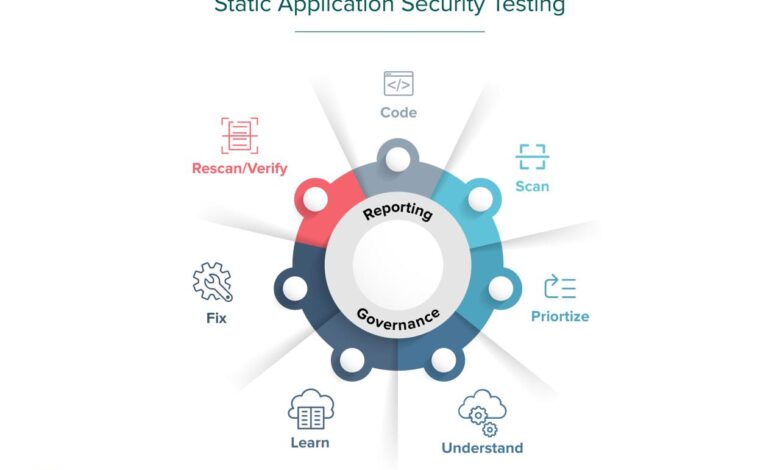
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) Explained
Static application security testing sast – Static Application Security Testing (SAST) is your secret weapon in the fight against software vulnerabilities. Before you even run your code, SAST tools meticulously analyze your source code for potential security flaws, identifying weaknesses like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and more. This proactive approach saves time, money, and prevents costly security breaches down the line, making it an essential part of any modern development pipeline.
Imagine having a super-powered code reviewer that catches errors before they become real-world problems. That’s essentially what SAST offers. It works by examining the code’s structure and logic, looking for patterns and anomalies that indicate potential security vulnerabilities. Different tools use various techniques, from simple pattern matching to complex control flow analysis, to pinpoint these issues. By integrating SAST early in your development lifecycle, you shift security left, making it a continuous process rather than a last-minute scramble.
Introduction to Static Application Security Testing (SAST)

Static Application Security Testing (SAST) is a crucial method for identifying security vulnerabilities within the source code of an applicationbefore* it’s deployed. Unlike dynamic testing, which analyzes the running application, SAST examines the code itself, looking for flaws in the logic, design, and implementation that could be exploited by attackers. This proactive approach helps developers address security risks early in the development process, reducing the cost and effort required to fix them later.SAST offers numerous benefits when integrated into the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC).
By incorporating SAST early, organizations can significantly reduce the number of vulnerabilities present in released software, minimizing the risk of breaches and improving overall application security posture. Early detection translates to lower remediation costs; fixing a bug in the initial stages is far less expensive than patching a production system. Furthermore, SAST contributes to faster release cycles by identifying and resolving security issues before they become major roadblocks.
Vulnerability Detection Capabilities of SAST
SAST tools are capable of detecting a wide range of vulnerabilities. These include common flaws such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), insecure authentication mechanisms, buffer overflows, and path traversal vulnerabilities. More sophisticated tools can also identify more complex issues like race conditions, insecure use of cryptographic libraries, and potential denial-of-service (DoS) weaknesses. The specific vulnerabilities a SAST tool can detect depend on its capabilities and the type of code it analyzes.
The ability to identify vulnerabilities early significantly improves the overall security and reliability of the application.
Examples of Common SAST Tools
Several commercial and open-source SAST tools are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of tool depends on factors such as budget, the types of applications being developed, and the level of integration required with the existing SDLC. Below is a comparison of four popular SAST tools.
| Name | Features | Pricing Model | Supported Languages |
|---|---|---|---|
| SonarQube | Static code analysis, vulnerability detection, code quality analysis, integration with various IDEs and CI/CD pipelines. Offers both open-source and commercial versions with varying capabilities. | Open-source (free) and commercial (subscription-based) | Java, C#, C++, JavaScript, Python, PHP, Ruby, and many more. |
| Checkmarx | Comprehensive SAST capabilities, including support for various programming languages and frameworks. Provides detailed vulnerability reports and remediation guidance. | Commercial (subscription-based) | Java, .NET, C++, Python, PHP, JavaScript, and more. |
| Coverity | Advanced static analysis engine, focusing on identifying critical security vulnerabilities and code quality issues. Integrates with various development workflows. | Commercial (subscription-based) | C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, and more. |
| Fortify Static Code Analyzer | Comprehensive SAST solution offering deep code analysis, vulnerability detection, and remediation guidance. Strong integration with other security tools and workflows. | Commercial (subscription-based) | Java, .NET, C++, C, Python, PHP, JavaScript, and more. |
SAST Techniques and Methods
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) employs a variety of sophisticated techniques to analyze source code and identify potential security vulnerabilities. Understanding these methods is crucial for effectively leveraging SAST tools and interpreting their findings. This section delves into the core techniques and approaches used in modern SAST solutions.
Static Analysis Techniques
SAST tools don’t simply scan for s; they use powerful algorithms to understand the code’s structure and behavior. Several key techniques contribute to their effectiveness. These techniques allow the tools to go beyond simple pattern matching and delve into the logic of the application.
- Control Flow Analysis: This technique examines the order in which code executes. By mapping the possible paths of execution, SAST tools can identify unreachable code, infinite loops, and other control flow issues that might indicate vulnerabilities. For example, it can detect if a critical security check is bypassed under certain conditions.
- Data Flow Analysis: This tracks the flow of data through the application. It identifies how data is used, modified, and propagated throughout the codebase. This is vital for detecting vulnerabilities like SQL injection, where user-supplied data is improperly handled and incorporated into database queries.
- Taint Analysis: This focuses on tracking potentially dangerous data, often referred to as “tainted” data, from its origin (e.g., user input) to its final destination. The analysis flags instances where tainted data reaches sensitive operations (e.g., database queries, command execution) without proper sanitization. This is incredibly effective in identifying cross-site scripting (XSS) and other injection flaws.
SAST Testing Approaches: White-Box, Black-Box, and Grey-Box
The level of access a SAST tool has to the application’s internal workings influences its effectiveness and the type of vulnerabilities it can detect.
- White-Box Testing: In this approach, the SAST tool has complete access to the source code, including internal APIs and implementation details. This allows for a deep analysis, uncovering a wider range of vulnerabilities. White-box SAST is highly effective but requires access to the entire codebase.
- Black-Box Testing: Here, the SAST tool only has access to the compiled application or a limited interface. This mimics an attacker’s perspective, focusing on vulnerabilities exposed through external interactions. Black-box testing is less thorough than white-box but valuable for assessing the application’s external security posture.
- Grey-Box Testing: This approach sits between white-box and black-box. The SAST tool has partial access to the internal workings, perhaps through limited API documentation or access to certain internal modules. It offers a balance between thoroughness and accessibility.
SAST Approaches: Abstract Interpretation and Symbolic Execution
Different SAST tools employ various underlying analysis engines. Two prominent approaches are:
- Abstract Interpretation: This technique approximates the program’s behavior without actually executing it. It uses abstract values to represent data and over-approximates the possible program states to identify potential vulnerabilities. This approach is computationally efficient, allowing for analysis of large codebases.
- Symbolic Execution: This explores all possible execution paths of the program by using symbolic values instead of concrete inputs. It systematically explores different input combinations to identify vulnerabilities triggered by specific input patterns. While more computationally intensive, symbolic execution can uncover vulnerabilities that abstract interpretation might miss.
SAST Vulnerability Identification Examples
SAST tools are designed to identify a broad range of vulnerabilities. Here are some examples:
- SQL Injection (Java): A SAST tool might flag a vulnerable Java statement like
String query = "SELECTbecause it directly concatenates user input (
- FROM users WHERE username = '" + username + "'";username) into the SQL query, making it susceptible to SQL injection attacks. The tool would recommend parameterized queries or prepared statements to mitigate this risk. - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) (JavaScript): A SAST tool could identify a vulnerable JavaScript snippet like
document.write(". Directly embedding user input (" + userInput + "
");
userInput) into the HTML output without proper encoding leaves the application vulnerable to XSS attacks. The tool would suggest using appropriate encoding functions (likeencodeURIComponent()) to prevent XSS vulnerabilities.
Integrating SAST into the SDLC: Static Application Security Testing Sast
Seamlessly integrating Static Application Security Testing (SAST) into your Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is crucial for building secure applications. It’s no longer enough to simply add SAST as an afterthought; a proactive, integrated approach is key to preventing vulnerabilities from ever reaching production. This involves strategically placing SAST within your existing workflows and tailoring its use to the specific needs of each phase.SAST Workflow Integration Across the SDLC
SAST Integration Across SDLC Stages
Effective SAST integration requires a well-defined workflow that spans the entire SDLC. This means incorporating SAST checks from the initial requirements phase through to testing and deployment. A typical workflow might involve:
- Requirements Gathering: While seemingly early, this is a crucial phase. Security requirements should be clearly defined, and the scope of SAST analysis should be established. This ensures that the SAST tool’s capabilities align with the project’s security goals.
- Design Phase: Architectural design reviews can identify potential security weaknesses before coding begins. SAST can indirectly contribute here by providing insights into common vulnerability patterns that inform design choices.
- Coding Phase: This is where SAST tools shine. Integrate SAST scans into the Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline to automatically analyze code for vulnerabilities as it’s committed. This provides immediate feedback to developers.
- Testing Phase: SAST results should inform the testing strategy, guiding the focus of penetration testing and other security assessments. This ensures that resources are targeted effectively at the most critical vulnerabilities.
- Deployment: While less directly involved, SAST helps ensure that only code that has passed a security threshold is deployed to production. This reduces the risk of introducing vulnerabilities into live systems.
Managing SAST Results and Prioritizing Vulnerabilities
SAST tools often generate a large number of findings. Effective management is essential to avoid alert fatigue and focus on the most critical issues. This involves:
- Prioritization based on severity and likelihood: SAST reports typically assign severity levels (e.g., critical, high, medium, low) to vulnerabilities. Combine this with an assessment of the likelihood of exploitation to prioritize remediation efforts. A critical vulnerability with high likelihood of exploitation should be addressed immediately.
- False positive reduction: SAST tools aren’t perfect and can produce false positives. Implement strategies to minimize these, such as configuring the tool appropriately, using code analysis best practices, and regularly reviewing the results with experienced developers.
- Centralized vulnerability management system: Use a dedicated system to track vulnerabilities, assign them to developers, and monitor their remediation status. This improves transparency and accountability.
Challenges of Integrating SAST and Proposed Solutions
Integrating SAST into existing development processes can present challenges.
- Tool integration with existing CI/CD pipelines: Integrating SAST tools requires technical expertise and can be time-consuming. Solutions include using pre-built integrations or consulting with DevOps engineers.
- Addressing false positives: False positives can overwhelm developers and lead to wasted time. Solutions include fine-tuning the SAST tool’s configuration, using code analysis best practices, and establishing clear processes for handling false positives.
- Developer buy-in: Developers may resist SAST integration if they perceive it as an extra burden. Solutions include demonstrating the value of SAST through concrete examples of vulnerabilities found and highlighting its role in improving code quality.
- Cost of SAST tools and expertise: SAST tools can be expensive, and specialized expertise is often required for effective implementation. Solutions include exploring open-source alternatives (like SonarQube), gradually phasing in SAST, and investing in training for developers.
Setting up a Basic SAST Pipeline with SonarQube
SonarQube is a popular open-source platform for continuous inspection of code quality. Setting up a basic SAST pipeline involves:
- Install SonarQube: Download and install SonarQube according to the official documentation. This involves setting up the database and configuring the server.
- Install SonarQube Scanner: Download and install the SonarQube Scanner, which analyzes your code and sends the results to the SonarQube server.
- Configure SonarQube Project: Create a new project in SonarQube and configure it to use the appropriate language analyzers (e.g., Java, Python, C#).
- Integrate with CI/CD: Integrate the SonarQube Scanner into your CI/CD pipeline (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI). This ensures that code is automatically scanned upon each commit.
- Analyze and review results: Regularly review the results from SonarQube to identify and address vulnerabilities.
False Positives and Mitigation Strategies in SAST
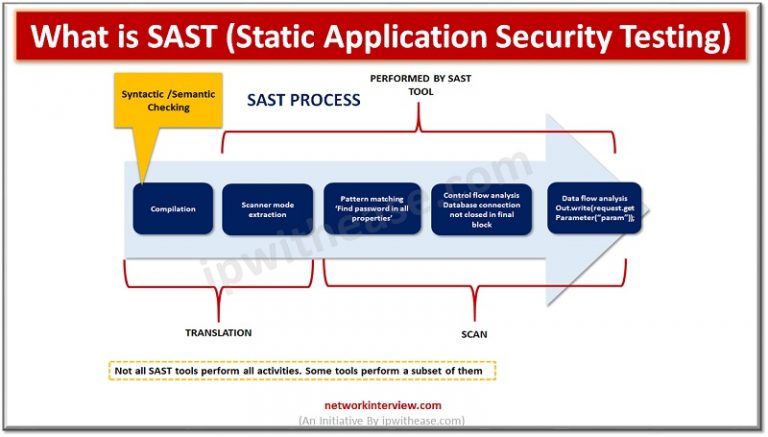
SAST tools, while incredibly valuable for identifying security vulnerabilities, are not perfect. They often flag potential issues that are not actually vulnerabilities, leading to the frustrating phenomenon of false positives. These false positives can significantly impact developer productivity and the overall effectiveness of your security program if not properly managed. Understanding their causes and implementing effective mitigation strategies is crucial for maximizing the benefits of SAST.False positives arise from a variety of factors, ranging from limitations in the SAST engine’s ability to understand complex code logic to issues with the tool’s configuration and the codebase itself.
The cost of investigating and resolving these false positives can be substantial, consuming developer time and potentially delaying project timelines. Effective strategies for reducing false positives are essential for maintaining developer morale and ensuring the efficiency of your SAST integration.
Common Causes of False Positives
Several factors contribute to the generation of false positives. These include overly sensitive rules, limitations in the SAST engine’s understanding of context, and issues within the codebase itself that trigger rules unintentionally. Understanding these root causes allows for more targeted mitigation strategies. For instance, a rule designed to detect SQL injection might flag a perfectly safe parameterized query if the tool isn’t sophisticated enough to recognize the parameterization technique.
Similarly, custom code that mimics known vulnerability patterns can inadvertently trigger false positives.
Techniques for Reducing False Positives
Reducing the number of false positives requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing both tool configuration and code practices. Effective configuration adjustments can significantly improve the accuracy of SAST analysis. This involves carefully reviewing and potentially adjusting the sensitivity levels of various rules, suppressing rules known to produce frequent false positives for specific code sections, and regularly updating the SAST tool to leverage the latest improvements in vulnerability detection and false positive reduction algorithms.
Code refactoring, focusing on improving code clarity and adhering to secure coding practices, also plays a significant role. For example, rewriting complex code segments to be more straightforward can help reduce the likelihood of false positives.
Impact of False Positives on Developer Productivity
The sheer volume of false positives can overwhelm developers, leading to alert fatigue and a diminished trust in the SAST tool. Developers may start ignoring alerts, even legitimate ones, leading to a significant decrease in the effectiveness of the SAST program. This ultimately impacts the overall security posture of the application. The time spent investigating and dismissing false positives is time that could have been spent addressing actual vulnerabilities.
This lost productivity translates directly into increased development costs and project delays.
Best Practices for Managing and Resolving False Positives
Effective management of false positives requires a structured approach.
- Prioritize alerts: Focus on high-severity alerts first, addressing the most critical potential vulnerabilities before investigating lower-priority issues. This helps to ensure that the most significant risks are addressed promptly.
- Categorize false positives: Track the types of false positives encountered, noting the specific rules and code patterns involved. This helps identify recurring issues and refine SAST tool configurations or coding practices.
- Implement a feedback loop: Regularly review and update the SAST tool’s configuration based on feedback from developers. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement in the tool’s accuracy.
- Use suppression strategically: Suppress false positives only when absolutely necessary and with clear justification. Overuse of suppression can mask genuine vulnerabilities. Document each suppression with a detailed explanation of why it is justified and any planned remediation steps.
- Regularly review suppressed alerts: Periodically review suppressed alerts to ensure they remain valid and haven’t become actual vulnerabilities due to code changes.
- Invest in developer training: Educate developers on secure coding practices and how to interpret SAST reports effectively. This improves their ability to distinguish between true positives and false positives, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the SAST program.
SAST and Security Standards Compliance
SAST plays a crucial role in helping organizations meet various security standards and regulations. By proactively identifying vulnerabilities early in the software development lifecycle (SDLC), SAST tools significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and help demonstrate compliance with industry best practices. This ultimately translates to reduced costs associated with remediation and potential legal repercussions.SAST’s contribution to compliance stems from its ability to detect vulnerabilities that directly violate the requirements Artikeld in many security frameworks.
The automated nature of SAST ensures consistent and thorough scanning, providing comprehensive evidence of compliance efforts.
SAST and the OWASP Top 10
The OWASP Top 10 is a regularly updated list of the most critical web application security risks. SAST tools are designed to identify many of these vulnerabilities, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure direct object references. By configuring the SAST tool to specifically target the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, organizations can systematically address these critical risks and demonstrate their commitment to secure coding practices.
A successful SAST scan with minimal or no critical vulnerabilities identified related to the OWASP Top 10 provides strong evidence of compliance.
SAST and PCI DSS Compliance
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to ensure that ALL companies that accept, process, store or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. SAST can contribute significantly to PCI DSS compliance by identifying vulnerabilities that could expose sensitive cardholder data. For example, SAST can detect insecure coding practices that could lead to SQL injection attacks, which could compromise databases containing payment information.
Regular SAST scans, coupled with remediation of identified vulnerabilities, provide verifiable evidence of ongoing efforts to maintain PCI DSS compliance. Detailed reports demonstrating the absence of critical vulnerabilities related to data protection and access control are key to successful audits.
SAST Reporting and Compliance Demonstrations
SAST tools generate detailed reports outlining the vulnerabilities identified during the scan. These reports typically include the vulnerability type, severity level, location in the code, and recommended remediation steps. This information is invaluable for demonstrating compliance. For example, a report showing zero critical vulnerabilities related to authentication and authorization mechanisms would strongly support an organization’s claim of compliance with relevant standards.
These reports can be used to support security audits and compliance reviews by providing concrete evidence of the organization’s proactive approach to security. Furthermore, tracking the remediation of identified vulnerabilities over time demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement and ongoing compliance.
Using SAST Reports in Security Audits and Compliance Reviews, Static application security testing sast
SAST reports serve as critical documentation during security audits and compliance reviews. Auditors can use these reports to verify the organization’s claims of compliance, assess the effectiveness of its security measures, and identify areas for improvement. For example, an auditor reviewing compliance with the OWASP Top 10 can directly compare the SAST report to the list of vulnerabilities, verifying that the organization has addressed the critical risks.
The detailed nature of SAST reports, including precise code locations and remediation recommendations, significantly streamlines the audit process and provides a clear picture of the organization’s security posture. A well-maintained history of SAST scans and remediation efforts further strengthens the evidence presented during these reviews.
Future Trends in SAST
The field of Static Application Security Testing (SAST) is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing complexity of software applications and the ever-growing sophistication of cyber threats. We’re seeing a shift towards more intelligent, automated, and integrated solutions that aim to improve accuracy, reduce false positives, and seamlessly fit into modern development workflows. This evolution is promising a more secure and efficient software development lifecycle.SAST’s future hinges on leveraging advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance vulnerability detection and remediation.
The sheer volume and complexity of codebases make manual analysis increasingly impractical, highlighting the crucial role of automation in ensuring comprehensive security assessments.
AI-Powered Vulnerability Detection
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing SAST by enabling more accurate and efficient vulnerability detection. Traditional rule-based SAST tools often struggle with complex code patterns and produce a high number of false positives. AI-powered systems, however, can learn from vast datasets of code and vulnerabilities, identifying subtle patterns and anomalies that might be missed by rule-based approaches. For example, an AI-powered SAST tool might learn to recognize specific code sequences associated with SQL injection vulnerabilities, even if those sequences are slightly obfuscated or vary from standard patterns.
This allows for more precise identification of genuine vulnerabilities, reducing the burden on security teams and accelerating the remediation process. Furthermore, AI can help prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact, enabling security teams to focus their efforts on the most critical issues.
Addressing the Challenges of Increasing Software Complexity
The increasing complexity of modern software applications, including microservices architectures, serverless functions, and the integration of third-party libraries, presents significant challenges for SAST. These complex architectures often involve multiple languages, frameworks, and deployment environments, making it difficult for traditional SAST tools to provide comprehensive coverage. Future SAST tools will need to adapt to these complexities by incorporating support for a wider range of languages and frameworks, as well as improved interoperability with other security tools and DevOps processes.
For instance, SAST tools might need to integrate seamlessly with containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes to analyze applications within their runtime environment. Furthermore, addressing the security challenges of open-source components and third-party libraries will be crucial.
The Evolving Role of SAST in Application Security
SAST is expected to become even more deeply integrated into the software development lifecycle (SDLC), shifting from a purely security-focused activity to a proactive and integral part of the development process. This integration will involve the use of SAST tools earlier in the development cycle, potentially even during the design and planning phases. This shift towards “shift-left” security testing will allow developers to identify and address vulnerabilities early in the process, significantly reducing the cost and effort required for remediation.
SAST will also play a more prominent role in DevSecOps, working in conjunction with other security tools and automation processes to create a more robust and efficient security posture. We can expect to see SAST tools increasingly integrated with CI/CD pipelines, automatically triggering security scans upon code commits and providing immediate feedback to developers.
Visual Representation of SAST Evolution
Imagine a graph charting the evolution of SAST. The X-axis represents time, spanning the past decade and projecting into the future. The Y-axis represents key features and capabilities. The graph begins in 2014 with a relatively low line representing basic rule-based SAST tools with limited language support and high false positive rates. The line gradually ascends over the years, reflecting improvements in accuracy, language support, and integration with DevOps.
Around 2018, a steeper incline is observed, representing the emergence of AI-powered SAST tools. The line continues to rise sharply, projecting into the future with advanced capabilities like automated remediation suggestions, enhanced support for complex architectures, and seamless integration with other security tools. The overall shape suggests an exponential growth in SAST capabilities, highlighting its increasingly important role in application security.
The projection into the future shows the line continuing to ascend at an even steeper rate, indicating a rapid expansion of capabilities and adoption within the industry.
Final Conclusion
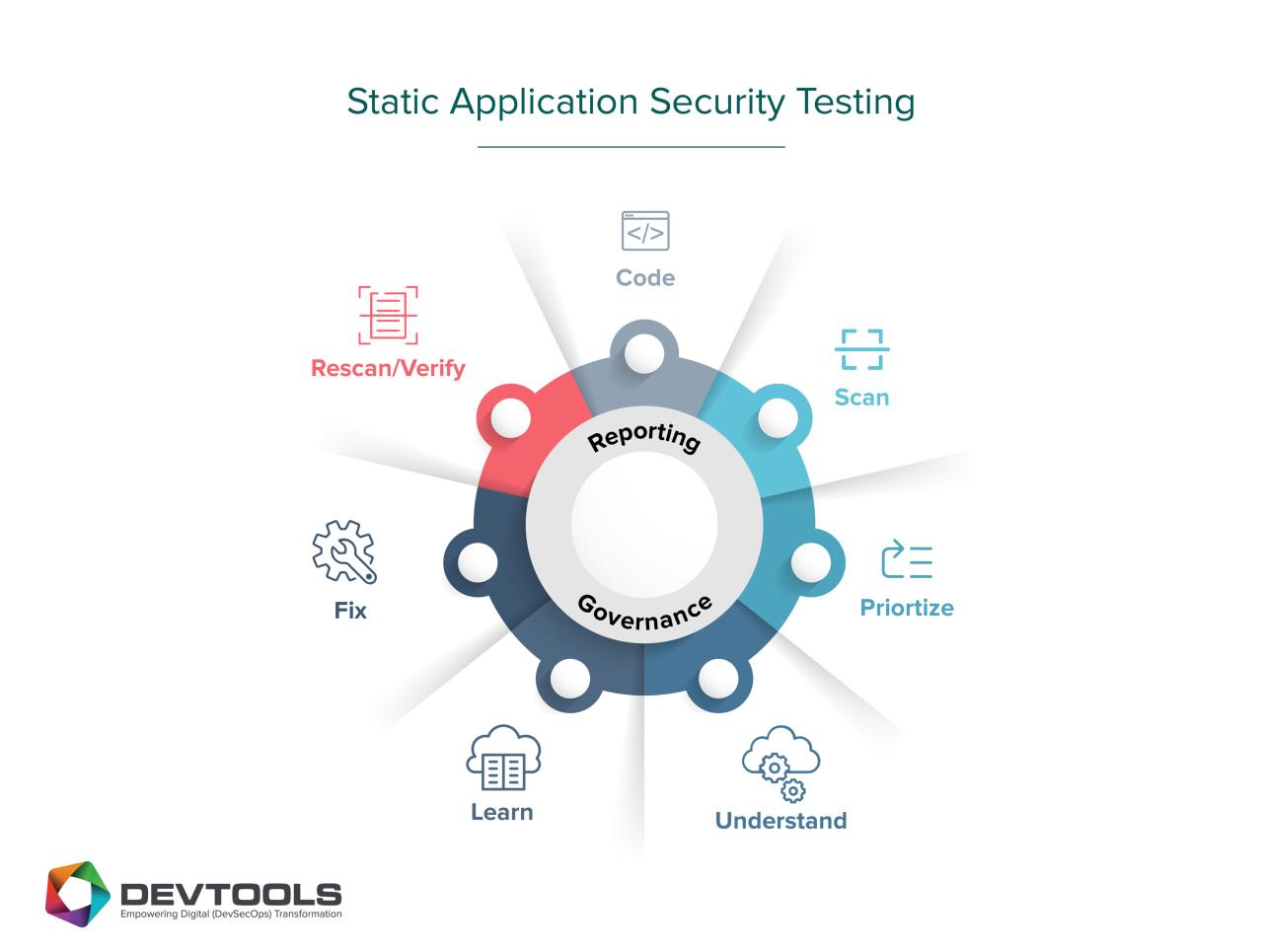
Incorporating Static Application Security Testing (SAST) into your workflow isn’t just about finding bugs; it’s about building a culture of security. By proactively identifying vulnerabilities early in the development process, you drastically reduce the risk of costly breaches and enhance the overall security posture of your applications. While managing false positives and integrating SAST into existing processes can present challenges, the long-term benefits of improved security and developer productivity far outweigh the initial hurdles.
Embrace SAST, and build safer, more secure software.
FAQ Section
What’s the difference between SAST and DAST?
SAST (Static Application Security Testing) analyzes source code without executing it, while DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) tests a running application to find vulnerabilities.
Can SAST find all vulnerabilities?
No, SAST primarily focuses on code-level vulnerabilities. It may miss runtime or environment-specific issues that DAST can detect.
How much does SAST software cost?
SAST tools range from free open-source options to expensive enterprise solutions, depending on features and scalability.
Is SAST suitable for all programming languages?
Most SAST tools support a wide range of programming languages, but coverage and effectiveness can vary.





