Email Security in the Remote Work Era
Email security in the remote work era is more critical than ever. The shift to distributed workforces has dramatically expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals, making robust email security a non-negotiable aspect of modern business. This isn’t just about protecting company data; it’s about safeguarding individual employees and maintaining trust with clients. We’ll delve into the evolving threat landscape, practical security measures, and emerging technologies designed to keep your remote team and their communications safe.
From phishing scams cleverly disguised as legitimate emails to sophisticated malware attacks, the threats are constantly evolving. Understanding these threats and implementing effective preventative measures is crucial for maintaining a secure and productive remote workforce. We’ll explore various strategies, from multi-factor authentication and strong password policies to employee training and advanced threat protection solutions. The goal? To create a secure email environment that allows for seamless collaboration without compromising security.
The Evolving Threat Landscape: Email Security In The Remote Work Era
The shift to remote work has dramatically reshaped the cybersecurity landscape, creating new vulnerabilities and expanding the attack surface for malicious actors. The reliance on personal devices and unsecured home networks, coupled with the increased use of cloud-based services, has significantly amplified the risk of email-borne threats. These threats, once primarily targeting corporate networks, now directly impact individual employees, potentially compromising sensitive data and disrupting business operations.The rise in remote work has fundamentally altered how cybercriminals approach their attacks.
They are leveraging the increased reliance on email communication for both personal and professional purposes to exploit vulnerabilities and gain access to valuable information. This increased reliance on email for communication creates a fertile ground for various sophisticated attacks.
Types of Email Attacks Targeting Remote Workers
Remote workers are particularly vulnerable to a range of email-based attacks. These attacks often exploit the trust employees place in email communication, leveraging social engineering tactics to bypass security measures.
- Phishing: These attacks involve deceptive emails that mimic legitimate organizations or individuals to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card details, or social security numbers. A common example is an email appearing to be from a bank, requesting users to update their account information by clicking a malicious link.
- Spear Phishing: A more targeted and sophisticated form of phishing, spear phishing attacks leverage specific information about the target to increase their effectiveness. Attackers may research their victims online, gathering personal details to craft highly personalized emails that appear authentic and trustworthy. For example, an attacker might impersonate a colleague or supervisor, sending an email requesting urgent action with a malicious attachment.
- Malware: Malicious software, or malware, can be delivered via email attachments or links. Once opened, this malware can infect the victim’s device, allowing attackers to steal data, install ransomware, or gain control of the system. Examples include viruses, trojans, and spyware, which can cause significant damage and disruption.
Traditional vs. Remote-Work-Focused Email Security Solutions
Traditional email security solutions, often focused on perimeter-based defenses, are proving insufficient in the remote work environment. These solutions often rely on centralized gateways and may struggle to effectively protect employees working outside the traditional corporate network. They may also lack the advanced threat detection capabilities needed to identify and mitigate sophisticated attacks like spear phishing.In contrast, email security solutions designed for remote work environments often incorporate advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to detect and prevent a wider range of threats.
These solutions typically leverage cloud-based infrastructure, offering flexible and scalable protection regardless of the employee’s location. They also often incorporate features such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to further enhance security. For instance, a remote-work focused solution might detect unusual login attempts from unfamiliar locations or identify suspicious email content based on patterns and anomalies.
These solutions offer more comprehensive protection tailored to the unique challenges posed by remote work.
Implementing Robust Email Security Measures

Securing email communication is paramount in today’s remote work environment, where employees access sensitive data from various locations and devices. A robust, multi-layered approach is essential to mitigate the ever-increasing risks associated with phishing, malware, and data breaches. This involves a combination of technological safeguards and employee education. Ignoring these measures leaves your organization vulnerable to significant financial and reputational damage.Implementing a comprehensive email security strategy requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply installing antivirus software.
It necessitates a combination of advanced technologies and a strong commitment to employee training and awareness. This strategy should proactively identify and neutralize threats before they can compromise sensitive information or disrupt operations.
Multi-Layered Email Security Strategy, Email security in the remote work era
A multi-layered strategy utilizes several security controls to create a defense-in-depth approach. This means that even if one layer fails, others are in place to protect against threats. Key components include:
- Authentication: Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are crucial. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a code from a mobile app, before granting access. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
- Encryption: Encrypting emails both in transit (using TLS/SSL) and at rest (using encryption at the server level) protects sensitive data from interception by unauthorized individuals. This is especially important for emails containing confidential information, such as financial data or personal details.
- Filtering: Email filtering systems use various techniques to identify and block malicious emails, including spam, phishing attempts, and malware. These systems should be regularly updated to stay ahead of evolving threats and utilize techniques such as Bayesian filtering and heuristic analysis.
Implementing Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication
A step-by-step guide to implementing strong password policies and MFA:
- Define a strong password policy: Require passwords to be at least 12 characters long, containing a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Prohibit the use of easily guessable passwords, such as names or dates. Regular password changes should also be enforced.
- Implement MFA: Choose an MFA method that suits your organization’s needs, such as time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) using authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy, or security keys. Ensure that MFA is mandatory for all remote employees accessing sensitive systems and data.
- Provide clear instructions: Provide comprehensive instructions to employees on how to set up and use MFA, and offer support for those who need assistance.
- Regularly review and update policies: Password policies and MFA methods should be reviewed and updated regularly to stay ahead of evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
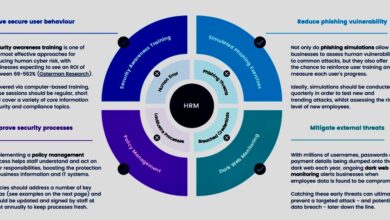
Email Security Threat Education and Safe Practices
Regular training is vital to reinforce safe email practices among remote employees. This training should cover various threat types, prevention methods, and response procedures. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of successful attacks.
| Threat Type | Prevention Method | Employee Training | Response Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Email filtering, security awareness training, suspicious email reporting | Identify phishing attempts (malformed URLs, suspicious sender addresses, urgent requests), never click on suspicious links or download attachments from unknown sources. | Report suspicious emails immediately to IT; do not interact with the email or its attachments. |
| Malware | Antivirus software, email filtering, regular software updates, secure browsing habits | Understand the risks of malware, avoid downloading attachments from untrusted sources, and practice safe browsing habits. | Report suspected malware infections immediately to IT; isolate affected devices. |
| Data Breaches | Encryption, access controls, strong password policies, MFA | Understand data security policies, avoid sharing sensitive information via email, and use strong passwords and MFA. | Report any suspected data breaches immediately to IT; follow incident response procedures. |
| Spear Phishing | Advanced threat protection, security awareness training, employee verification | Recognize sophisticated phishing attempts that target specific individuals or departments; verify requests through alternative communication channels. | Report suspicious emails immediately to IT; verify the legitimacy of requests before taking any action. |
Securing Email Communication Channels

In today’s remote work landscape, securing email communication channels is paramount. The shift to distributed workforces has expanded the attack surface, making email a prime target for cybercriminals. Understanding the risks associated with various email access methods and platforms is crucial for maintaining data integrity and organizational security.
The reliance on diverse communication methods and devices introduces complexities that necessitate a multi-layered security approach. This includes not only robust email security software but also careful consideration of the devices and platforms used to access corporate email.
Security Implications of Using Personal Devices for Work Email
Using personal devices for work email introduces significant security risks. Personal devices often lack the robust security measures implemented on company-managed devices. This includes the absence of endpoint detection and response (EDR) software, regular security updates, and strong password policies enforced by IT departments. Furthermore, personal devices are more susceptible to malware infections due to less restrictive app installation policies and potentially weaker user security awareness.
The risk of data breaches increases significantly if a personal device is lost, stolen, or compromised, potentially exposing sensitive company information. For example, a remote employee using a personal laptop without up-to-date antivirus software could easily fall victim to phishing attacks, leading to malware infection and data theft. The lack of centralized management makes it difficult for IT to enforce security policies and monitor activity, increasing the vulnerability of the organization.
Remote work exploded email security concerns, forcing us to rethink our approach. Building robust, secure internal communication systems is crucial, and that’s where innovative solutions like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future become invaluable. By leveraging these advancements, we can create secure, custom applications to better manage sensitive information and bolster email security in our increasingly distributed workforce.
Comparison of Email Clients and Their Security Features
Various email clients offer different levels of security. Desktop clients like Outlook and Thunderbird generally offer better security features than webmail interfaces, especially when properly configured. Desktop clients allow for the implementation of more robust encryption protocols and integration with other security tools. However, webmail clients like Gmail and Outlook on the web are convenient and accessible from any device, but they rely heavily on the security measures provided by the email provider.
Some email clients offer features like two-factor authentication (2FA), which adds an extra layer of security. Others may support S/MIME or PGP encryption for securing email content, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring message confidentiality. The choice of email client should align with the organization’s security policies and risk tolerance.
Security Protocols of Different Email Platforms
Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, two leading email platforms, offer different approaches to security. Microsoft 365, for example, incorporates features like Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) to identify and block malicious emails before they reach the user’s inbox. It also provides data loss prevention (DLP) tools to prevent sensitive information from leaving the organization’s network. Google Workspace utilizes its own robust security infrastructure, including machine learning algorithms to detect and filter spam and phishing attempts.
Both platforms offer various levels of encryption, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) for securing email transmission and data encryption at rest. However, the specific security features and their effectiveness can vary based on the chosen subscription plan and the organization’s configuration. A direct comparison reveals subtle differences in their approach to threat detection and response, data encryption, and user access controls.
For instance, while both offer 2FA, the implementation and user experience may differ slightly. The optimal platform choice depends on the specific security needs and budget of the organization.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) in Remote Work
The rise of remote work has dramatically expanded the attack surface for organizations, significantly increasing the risk of data loss through email. Employees accessing company resources from diverse and often less secure personal networks introduce vulnerabilities that traditional office-based security measures can’t fully address. Understanding and mitigating these risks is crucial for maintaining data integrity and regulatory compliance.The potential for data breaches stemming from compromised email accounts, accidental exposure of sensitive data, or malicious insiders is significantly heightened in remote work environments.
Data loss can lead to hefty financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. Implementing robust DLP strategies is no longer a luxury, but a necessity.
Key Risks Associated with Email Data Loss in Remote Work
Remote work introduces several unique challenges to data security. Unsecured home Wi-Fi networks, the use of personal devices for work, and a lack of consistent IT oversight all contribute to increased vulnerability. Employees might inadvertently share sensitive information via unencrypted email or fall victim to phishing attacks leading to data exfiltration. Furthermore, the lack of physical security controls over company assets, such as laptops containing sensitive data, expands the potential for loss or theft.
The risk is further amplified by the increased use of cloud-based services, which, while offering flexibility, require careful configuration and access controls to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures
Effective DLP requires a multi-layered approach combining technical controls and employee training. Email encryption is a cornerstone of this strategy. Implementing end-to-end encryption ensures that only the intended recipient can decrypt and read the email’s contents, even if intercepted. This is particularly important for highly sensitive data like financial information, personal health information (PHI), or intellectual property. Access controls, such as role-based access and multi-factor authentication (MFA), limit who can access sensitive emails and data.
MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods (e.g., password and a one-time code) before accessing emails or company systems. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are crucial to identify and address potential weaknesses in the system. Data loss prevention tools, capable of scanning emails for sensitive information and blocking or alerting users on potential violations, are also an important part of a comprehensive strategy.
Best Practices for Handling Sensitive Information via Email in a Remote Work Setting
Implementing robust DLP requires more than just technology; it demands a culture of security awareness. Here are some essential best practices:
- Never send sensitive information via unencrypted email: Always use encryption for emails containing confidential data.
- Use strong passwords and enable MFA: Protect your email account with robust passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Be cautious of phishing attempts: Never click on suspicious links or attachments in emails.
- Use company-approved devices and networks: Avoid using personal devices and unsecured networks for work-related emails.
- Report suspicious activity immediately: Report any suspected security breaches or phishing attempts to your IT department without delay.
- Regularly update software and security patches: Ensure your devices and software are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Implement data loss prevention tools: Utilize DLP tools to monitor and control the flow of sensitive data.
- Regularly back up important data: Maintain regular backups of sensitive information to mitigate the impact of data loss.
- Train employees on security best practices: Conduct regular security awareness training for all employees.
Monitoring and Incident Response
Effective monitoring and a well-defined incident response plan are crucial for mitigating the risks associated with email security breaches in a remote work environment. The distributed nature of remote work expands the attack surface, making proactive monitoring and swift incident handling paramount. Failing to address these aspects leaves your organization vulnerable to significant data loss, reputational damage, and financial penalties.A robust monitoring and incident response strategy should encompass both preventative measures and reactive procedures.
This proactive approach significantly reduces the impact of successful attacks and ensures business continuity. Effective strategies also help minimize downtime and the associated costs.
Email Activity Monitoring
Implementing comprehensive email activity monitoring involves utilizing various tools and techniques to detect suspicious activities. This includes analyzing email traffic for malicious content, tracking user behavior, and monitoring for unusual login attempts or access patterns. A multi-layered approach, combining advanced threat protection solutions with internal security monitoring, provides the best defense. For instance, a system could flag emails containing unusual attachments, links to suspicious websites, or communication with known malicious IP addresses.
Further analysis could involve examining email content for s associated with phishing or malware, and tracking the volume and frequency of emails sent and received by individual users. Anomalies in these patterns could signal a potential breach.
Incident Response Procedure
A detailed incident response procedure should be established and regularly tested. This procedure should Artikel clear steps for containment, eradication, and recovery in the event of an email-related security incident. The procedure should be easily accessible to all relevant personnel and should include contact information for key individuals. For example, the containment phase might involve immediately quarantining affected email accounts, isolating infected systems from the network, and blocking malicious IP addresses.
Eradication would focus on removing malware, restoring compromised systems, and patching identified vulnerabilities. The recovery phase would involve restoring data from backups, reviewing security policies, and implementing preventative measures to avoid future incidents. Regular simulations and training exercises are essential to ensure the effectiveness of the response plan.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical for identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses in remote work email systems. These assessments should cover all aspects of the email infrastructure, including email servers, client software, and network security. Vulnerability assessments should leverage automated scanning tools to identify known vulnerabilities, while penetration testing can simulate real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of security controls.
A comprehensive audit should review security policies, access controls, and incident response procedures, ensuring they are up-to-date and effectively implemented. Findings from these assessments should be prioritized and addressed promptly to minimize the risk of exploitation. For example, an audit might reveal outdated email client software on employee machines, which would then be prioritized for updating to address potential vulnerabilities.
The Role of Security Awareness Training
In today’s remote work environment, where employees access sensitive company data from various locations and devices, security awareness training is no longer a luxury—it’s a critical necessity. A well-structured program is the cornerstone of a robust email security strategy, empowering employees to identify and avoid phishing scams, malware, and other email-borne threats. Without it, even the most sophisticated technical security measures can be rendered ineffective by a single click from an unsuspecting employee.Effective security awareness training goes beyond simply providing information; it fosters a security-conscious culture.
This involves regularly reinforcing best practices, making learning engaging and memorable, and providing clear, actionable steps employees can take to protect themselves and the company. The goal is to transform employees from potential vulnerabilities into active participants in maintaining email security.
Developing a Comprehensive Security Awareness Training Program
A comprehensive program should cover various aspects of email security. It should begin with an overview of common email threats, such as phishing, spear phishing, whaling, and malware attachments. The training should then detail best practices, including how to identify suspicious emails (e.g., unexpected attachments, unusual sender addresses, urgent requests for information), how to report suspicious emails, and what to do if an employee suspects they have fallen victim to an attack.
Regular refresher training, incorporating updated threats and techniques, is crucial to maintain effectiveness. The program should also emphasize the importance of strong password management and the risks associated with clicking on unknown links. Finally, it’s essential to clearly define the company’s email security policies and procedures.
Examples of Engaging Training Materials
Engaging training materials are key to successful security awareness. Scenarios that realistically portray phishing attempts can be highly effective. For example, a scenario could involve an email seemingly from the CEO requesting immediate wire transfer of funds, with subtle clues highlighting its fraudulent nature (incorrect grammar, unusual urgency, unusual request). Short, informative videos demonstrating common attack vectors, like a video showing the subtle differences between a legitimate email from a known sender and a cleverly disguised phishing email, can also be very effective.
Interactive quizzes at the end of each module allow for immediate feedback and assessment of employee understanding. Gamification techniques, such as awarding points or badges for completing training modules or identifying phishing attempts correctly, can significantly boost engagement and retention.
Measuring Training Effectiveness and Identifying Areas for Improvement
Measuring the effectiveness of the training program is crucial to ensure its ongoing success. Pre- and post-training assessments can measure the increase in knowledge and understanding of email security best practices. Simulated phishing campaigns, where employees receive test phishing emails, can effectively measure the program’s impact on real-world behavior. Analyzing the results of these campaigns provides valuable data on the effectiveness of the training and helps identify areas where additional focus is needed.
Regular feedback from employees through surveys or focus groups can provide valuable insights into their perception of the training and suggest improvements to content and delivery methods. Tracking the number of reported phishing attempts and successful attacks after the training is implemented can also be used as a key performance indicator (KPI) to evaluate the program’s overall success.
A reduction in reported incidents would indicate a positive impact.
Email security is paramount in today’s remote work landscape, with threats constantly evolving. To combat this, robust cloud security is essential, and that’s where solutions like Bitglass come in. Learning more about bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is crucial for understanding how to effectively protect sensitive email data; ultimately strengthening your overall remote work security strategy.
Emerging Technologies and Email Security
The rise of remote work has dramatically expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals, making robust email security more critical than ever. Fortunately, emerging technologies offer powerful new tools to combat these evolving threats, enhancing protection for remote workers and their organizations. These advancements leverage the power of artificial intelligence, advanced threat detection, and cloud-based solutions to create a more secure email environment.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is revolutionizing email security.
These technologies are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time to identify and neutralize threats that traditional methods often miss. This includes detecting sophisticated phishing attempts, identifying malicious attachments, and flagging suspicious sender behavior. The continuous learning capabilities of AI and ML allow for adaptation to new and emerging threats, ensuring ongoing protection against ever-evolving attack vectors.
AI and Machine Learning in Email Security
AI and ML algorithms analyze email content, sender reputation, and behavioral patterns to identify suspicious activity. For example, an AI system might detect an email with unusual language or formatting, or one sent from an unfamiliar IP address, even if the email itself contains no malicious code. This proactive approach helps prevent threats before they can cause damage. ML algorithms improve their accuracy over time by learning from past incidents, making them increasingly effective at identifying and blocking malicious emails.
This contrasts sharply with older, rule-based systems that rely on pre-defined criteria and struggle to keep pace with the rapidly evolving tactics of cybercriminals. For instance, a sophisticated phishing campaign might employ a technique never encountered before, which a rule-based system might miss entirely, while an AI system could potentially identify the subtle anomalies suggesting malicious intent.
Advanced Threat Protection Solutions
Advanced threat protection solutions such as sandboxing and behavioral analysis provide an extra layer of security against sophisticated email attacks. Sandboxing involves isolating suspicious attachments or links in a controlled virtual environment to analyze their behavior without exposing the user’s system to potential harm. This allows security systems to detect malicious code that might otherwise go undetected by traditional antivirus software.
Behavioral analysis monitors the activity of emails and their attachments to identify unusual patterns that might indicate malicious intent, such as attempts to access sensitive data or communicate with external command-and-control servers. For example, an attachment that attempts to connect to a known malicious IP address would be flagged, even if the attachment itself doesn’t contain readily identifiable malware.
Cloud-Based Email Security Solutions
Cloud-based email security solutions are particularly well-suited for remote work environments. These solutions offer centralized management, scalability, and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. This centralized approach allows organizations to easily deploy and manage security policies across all their users, regardless of their location. Moreover, cloud providers often invest heavily in security infrastructure and expertise, providing access to advanced threat protection capabilities that might be cost-prohibitive for individual organizations to implement on their own.
This means remote workers benefit from the same level of protection as those working in a traditional office environment, ensuring consistent security across the entire workforce. A company migrating to a cloud-based email security platform can benefit from automatic updates and improved threat detection capabilities, reducing the burden on internal IT staff.
Final Conclusion
Securing email in the age of remote work isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process requiring vigilance, adaptation, and a multi-faceted approach. By combining robust security measures, comprehensive employee training, and a proactive approach to threat detection and response, organizations can significantly mitigate the risks associated with email-borne attacks. Remember, the human element is key – empowered and informed employees are your best defense against cyber threats.
Stay vigilant, stay informed, and stay secure.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the biggest email security challenges facing remote workers?
The biggest challenges include increased exposure to phishing attacks, lack of secure network access, and the use of unmanaged personal devices for work email. Also, employees working from home may be less aware of security best practices.
How can I ensure my employees are using strong passwords?
Implement a strong password policy that includes length requirements, character complexity, and regular password changes. Encourage the use of password managers and provide training on creating secure passwords.
What is the role of email encryption in remote work security?
Email encryption protects sensitive information by scrambling it so only authorized recipients with the decryption key can read it. This is vital for protecting confidential data shared via email.
How often should security awareness training be conducted?
Regular, ideally quarterly, security awareness training is essential to keep employees updated on the latest threats and best practices. It should be interactive and engaging to maintain employee interest and knowledge.