Encryptionless Ransomware Desais Defense Strategies
Encryptionless ransomware attacks and defense strategies an interview with zscalers deepen desai – Encryptionless ransomware attacks and defense strategies an interview with Zscaler’s Deepen Desai – that’s a mouthful, right? But it’s a crucial topic. Forget the fancy encryption; this new breed of ransomware is all about disruption and data extortion, leveraging other methods to cripple your systems. This interview dives deep into the tactics, the motivations behind these attacks, and most importantly, how to fight back.
Get ready to learn about a rapidly evolving threat landscape and the strategies you need to protect your business.
We’ll explore Deepen Desai’s expert insights from Zscaler, a leading cybersecurity firm, to understand the mechanics of these attacks, why they’re so effective, and how they differ from traditional ransomware. We’ll also delve into practical defense strategies, from layered security approaches to robust data backup and recovery plans. Finally, we’ll discuss the crucial role of human awareness in preventing these attacks and look at the future of this threat landscape.
Buckle up, it’s going to be an informative ride!
Introduction to Encryptionless Ransomware
Encryptionless ransomware represents a disturbing evolution in cybercrime, shifting away from the traditional method of encrypting victim data. Instead, these attacks leverage different tactics to disrupt operations and extort payments, focusing on data exfiltration and the threat of public release rather than rendering data unusable through encryption. This shift necessitates a reevaluation of existing security strategies and a deeper understanding of the attackers’ motivations.Encryptionless ransomware attacks bypass the complexities of encryption by directly stealing sensitive data from a victim’s system.
This stolen data is then used as leverage for extortion. Attackers typically gain unauthorized access through various methods, such as phishing emails, exploiting vulnerabilities in software, or utilizing compromised credentials. Once inside the network, they locate valuable data, exfiltrate it, and then threaten to publicly release this information unless a ransom is paid. This differs from traditional ransomware, which renders data unusable by encrypting it, requiring a decryption key from the attackers to regain access.
Attacker Motivations
The motivations behind encryptionless ransomware attacks are primarily financial. Attackers seek monetary gain by leveraging the fear and reputational damage associated with a data breach. For example, a company might face significant financial losses if sensitive customer data, intellectual property, or financial records are leaked. The reputational damage resulting from such a breach could also lead to loss of customer trust and legal repercussions.
Furthermore, some attackers might target specific organizations for political or ideological reasons, using the leaked data to embarrass or damage the target’s reputation.
Impact Comparison: Encryptionless vs. Traditional Ransomware
The impact of encryptionless ransomware can differ significantly from that of traditional ransomware. While traditional ransomware primarily disrupts operations by rendering data inaccessible, encryptionless ransomware focuses on the potential for reputational damage and financial loss from data exposure. The impact on victims often includes immediate operational disruption due to the compromise, followed by the longer-term damage of potential legal action, regulatory fines, and loss of customer trust.
The cost of remediation, including forensic investigation, public relations management, and credit monitoring for affected individuals, can be substantial. In contrast, traditional ransomware’s primary impact is the immediate loss of access to critical data and systems, with recovery efforts centered around decryption or data restoration. While both types of attacks lead to financial losses, the nature and timing of those losses differ considerably.
The threat of public exposure inherent in encryptionless attacks adds a layer of complexity and urgency absent in traditional ransomware attacks.
Deepen Desai’s Expertise and Perspective
Deepen Desai brings a wealth of experience to the discussion of encryptionless ransomware. His background and insights, combined with Zscaler’s position at the forefront of cybersecurity, offer a unique perspective on this evolving threat. This section delves into Desai’s expertise, Zscaler’s role in mitigating ransomware, and his analysis of the changing landscape of encryptionless attacks.Zscaler’s role in combating ransomware is significant, given its position as a leading cloud security provider.
The company’s security cloud architecture allows for real-time threat detection and prevention, a crucial element in stopping encryptionless ransomware before it can inflict damage. Desai’s contributions to Zscaler’s strategy, coupled with his understanding of attacker methodologies, provide valuable insight into the complexities of this emerging threat. His perspective is shaped by years of experience analyzing attack vectors and developing proactive security measures.
Deepen Desai’s Background and Experience
Deepen Desai’s extensive career in cybersecurity has equipped him with a deep understanding of the ever-shifting threat landscape. His expertise encompasses various aspects of security, including threat intelligence, incident response, and security architecture. This broad knowledge base allows him to effectively analyze the nuances of encryptionless ransomware and its implications for organizations. His experience likely includes working with numerous organizations across various sectors, providing him with a broad perspective on how different industries are impacted by these attacks.
For example, his experience might encompass analyzing attacks targeting healthcare providers, financial institutions, or manufacturing companies, highlighting the unique vulnerabilities of each sector.
Zscaler’s Role in Combating Ransomware Attacks
Zscaler’s cloud-based security platform plays a critical role in preventing and mitigating ransomware attacks. Its architecture, built around the principle of “never trust, always verify,” enables real-time inspection of traffic before it reaches the organization’s network. This prevents malicious code from ever reaching endpoints, effectively neutralizing encryptionless ransomware attacks that rely on exploiting vulnerabilities to gain initial access. Zscaler’s advanced threat detection capabilities, including machine learning algorithms, are instrumental in identifying and blocking suspicious activities indicative of ransomware deployment.
This proactive approach minimizes the risk of successful attacks, unlike traditional security solutions that often react to an attack after it has already begun. The speed and scale of Zscaler’s cloud-based system allow it to adapt to the constantly evolving tactics used by ransomware actors.
Desai’s Perspective on the Evolving Threat Landscape of Encryptionless Ransomware
Desai’s perspective on encryptionless ransomware likely emphasizes the shift from data encryption to data exfiltration and extortion. He probably highlights the increased sophistication of these attacks, where attackers focus on stealing sensitive data before deploying ransomware, creating a double extortion scenario. This approach increases the pressure on victims to pay the ransom, as the threat of data exposure is equally damaging, if not more so, than the loss of encrypted data.
His analysis likely includes the observation that encryptionless ransomware is more difficult to detect because it doesn’t immediately disrupt operations, allowing attackers to remain undetected for longer periods. This extended dwell time increases the potential damage and the complexity of remediation efforts. He likely emphasizes the need for robust security posture including preventative measures and incident response planning to mitigate the risk of these evolving attacks.
For instance, he may point to the critical role of security awareness training for employees in preventing initial infection through phishing or other social engineering attacks, a common entry point for encryptionless ransomware.
Deepen Desai’s interview on encryptionless ransomware attacks highlighted the urgent need for robust defenses. Building secure applications is key, and that’s where understanding the evolving landscape of application development comes in; check out this insightful piece on domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , to see how modern development practices can enhance security. Ultimately, combining strong security practices with efficient development methods is crucial in the fight against increasingly sophisticated ransomware threats.
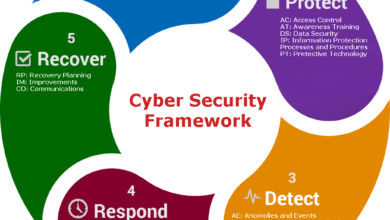
Defense Strategies Against Encryptionless Ransomware: Encryptionless Ransomware Attacks And Defense Strategies An Interview With Zscalers Deepen Desai

Encryptionless ransomware attacks, while less common than their encrypting counterparts, pose a significant threat due to their reliance on data exfiltration and extortion. These attacks aim to disrupt operations and steal sensitive data, leveraging the fear of public exposure to pressure victims into paying ransoms. Effective defense requires a multi-layered approach focusing on prevention, detection, and response.
Key Defense Strategies
Three key defense strategies are crucial in mitigating the impact of encryptionless ransomware: robust data protection, proactive threat hunting, and a well-defined incident response plan. These strategies, when implemented effectively, significantly reduce the risk and potential damage caused by these attacks.
Data Protection Strategies
Robust data protection forms the bedrock of any defense against encryptionless ransomware. This involves implementing strong access controls, data loss prevention (DLP) measures, and regular backups. Strong access controls, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access, limit unauthorized access to sensitive data. DLP solutions monitor data movement and prevent sensitive information from leaving the network without authorization.
Regular backups, ideally stored offline or in an immutable storage location, ensure data can be recovered even if the primary systems are compromised. This minimizes the impact of data exfiltration and reduces the leverage of attackers.
Proactive Threat Hunting
Proactive threat hunting plays a vital role in early detection. This involves actively searching for malicious activity within the network rather than passively waiting for alerts. Security teams should utilize security information and event management (SIEM) systems and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to monitor network traffic and system activity for suspicious patterns. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing identify weaknesses that attackers could exploit.
This proactive approach allows for the timely detection and mitigation of threats before they can cause significant damage. Early detection is critical in limiting the scope of a data breach.
Incident Response Planning
A well-defined incident response plan is paramount in minimizing the impact of an encryptionless ransomware attack. This plan should Artikel clear steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity. This includes establishing communication protocols, identifying key personnel, and defining roles and responsibilities. Regular testing and updates ensure the plan remains effective and adaptable to evolving threats. A well-rehearsed plan ensures a coordinated and efficient response, limiting the duration and severity of the incident.
Consider including legal counsel in your response plan to guide decisions regarding reporting requirements and potential legal ramifications.
Layered Security Approach
| Defense Layer | Method | Implementation Details | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perimeter Security | Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) with Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) | Deploy a NGFW to inspect all inbound and outbound traffic, blocking known malicious traffic and applying IPS rules to detect and prevent attacks. | High – Prevents initial access attempts. |
| Endpoint Security | Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Deploy EDR agents on all endpoints to monitor system activity, detect malicious behavior, and respond to threats in real-time. | High – Detects and responds to malware and suspicious activity on endpoints. |
| Data Security | Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Encryption | Implement DLP tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network unauthorized. Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. | High – Protects sensitive data from exfiltration. |
| Backup and Recovery | Regular backups to immutable storage | Implement a robust backup and recovery strategy with regular backups to offline or immutable storage, ensuring data can be recovered quickly in case of an attack. | Critical – Enables rapid recovery and minimizes downtime. |
| Security Awareness Training | Regular employee training | Conduct regular security awareness training to educate employees about phishing, social engineering, and other attack vectors. | Medium – Reduces the likelihood of successful phishing attacks. |
| Threat Intelligence | Subscription to threat intelligence feeds | Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities. | Medium – Enables proactive mitigation of known threats. |
Incident Response Plan Steps, Encryptionless ransomware attacks and defense strategies an interview with zscalers deepen desai
A robust incident response plan should include the following steps:
- Preparation: Develop and regularly test the plan, identifying roles, responsibilities, and communication channels.
- Detection and Analysis: Implement monitoring systems to detect suspicious activity and analyze the nature and scope of the incident.
- Containment: Isolate affected systems to prevent further spread of the attack.
- Eradication: Remove the malware and restore affected systems to a clean state.
- Recovery: Restore data from backups and resume normal operations.
- Post-Incident Activity: Conduct a thorough post-incident review to identify weaknesses and improve security measures.
The Role of Data Backup and Recovery

In the face of encryptionless ransomware attacks, which focus on data exfiltration and disruption rather than encryption, a robust data backup and recovery strategy becomes the first line of defense. Without the ability to restore data quickly and easily, organizations face significant operational downtime, financial losses, and reputational damage. The speed and efficiency of recovery directly impact the severity of the attack’s consequences.The core principle is to maintain multiple copies of your critical data, stored in different locations and using different methods.
This redundancy ensures that even if one backup method fails, you still have viable options for restoring your data. The effectiveness of your backup and recovery plan is not merely about having backups; it’s about the ability to quickly and seamlessly restore data to a usable state, minimizing disruption to business operations.
Backup and Recovery Methods
Choosing the right backup and recovery methods requires careful consideration of factors like data volume, sensitivity, budget, and recovery time objectives (RTOs). A multi-layered approach, combining different methods, is often the most effective.
- The 3-2-1 Rule: This widely accepted guideline recommends keeping at least three copies of your data, on two different media types, with one copy stored offsite. This provides a high degree of protection against data loss from various threats, including ransomware, hardware failure, and natural disasters. For example, you might have one copy on a local server, one on an external hard drive, and one in the cloud.
- Cloud Backups: Cloud-based backup solutions offer scalability, accessibility, and often built-in disaster recovery capabilities. However, security and data sovereignty concerns must be carefully addressed. Selecting a reputable cloud provider with strong security measures is crucial. For instance, using a cloud provider with multi-factor authentication and data encryption at rest and in transit would significantly enhance security.
- Air-Gapped Backups: Air-gapped backups are stored on media that is completely disconnected from any network. This provides an extremely high level of protection against ransomware attacks that spread through network connections. The trade-off is that restoring data from an air-gapped backup requires physically transporting the media, which can take time. An example would be a set of external hard drives stored in a secure, offsite location with no network connectivity.
Testing and Validating Backup and Recovery Processes
Regular testing and validation are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of your backup and recovery strategy. A plan that hasn’t been tested is essentially useless in a real-world emergency.Testing should involve a simulated recovery scenario. This means selecting a portion of your data (perhaps a non-critical dataset), deleting it from your primary system, and then attempting to recover it from your backups.
This process should be documented and should include:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) measurement: How long did it take to restore the data?
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) measurement: How much data was lost during the recovery process?
- Data integrity verification: Was the restored data identical to the original?
- Documentation of the entire process: This includes all steps taken, any challenges encountered, and the time taken for each step.
Regular, scheduled testing—at least quarterly—is recommended to ensure that your backups remain valid and your recovery processes remain efficient. This proactive approach ensures preparedness and minimizes disruption during a real ransomware attack. Furthermore, documenting and regularly reviewing the procedures ensures that staff is well-versed in the process, reducing confusion and delays during a crisis.
Human Factors and Social Engineering
Encryptionless ransomware attacks, while technically sophisticated, often hinge on the simplest of vulnerabilities: human error. Social engineering exploits the human element, manipulating individuals into actions that compromise security, providing attackers with the necessary access to wreak havoc. Understanding these human factors is crucial in developing effective defense strategies.Social engineering techniques rely on deception and manipulation to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that benefit the attacker.
This can range from seemingly innocuous phishing emails to more elaborate schemes involving impersonation and pretexting. The success of these attacks often depends on the victim’s lack of awareness, trust in the attacker, or pressure to act quickly. The consequences, especially with encryptionless ransomware, can be devastating, as the focus shifts from data encryption to data exfiltration and extortion.
A Social Engineering Scenario Leading to Encryptionless Ransomware Infection
Imagine Sarah, a mid-level accountant at a small manufacturing company. She receives an email seemingly from her company’s IT department, requesting immediate access to a shared drive containing sensitive financial data. The email cites an urgent audit and includes a link to a seemingly legitimate login portal. Unbeknownst to Sarah, the email is a sophisticated phishing attack.
The link leads to a fake login page designed to steal her credentials. Once Sarah enters her login details, the attacker gains access to the company’s network. They then deploy encryptionless ransomware, targeting specific financial records. The attackers don’t encrypt the data; instead, they exfiltrate it, threatening to release it publicly unless a ransom is paid. Sarah’s trust in the email, coupled with the perceived urgency, made her vulnerable to this attack.
The attacker’s tactic was simple yet effective: leveraging a sense of urgency and the appearance of legitimacy to bypass security protocols.
Security Awareness Training Program Elements
A comprehensive security awareness training program is essential to mitigate the risk of social engineering attacks. This program should include several key elements:
The program should begin with an overview of social engineering tactics and techniques. This section should cover various attack vectors, including phishing emails, pretexting calls, and malicious websites. Real-world examples of successful attacks should be used to illustrate the potential consequences of falling victim to social engineering.
Next, the program should provide practical training on how to identify and avoid social engineering attempts. This should include training on identifying suspicious emails, recognizing phishing attempts, and verifying the legitimacy of requests for sensitive information. Role-playing exercises can be particularly effective in simulating real-world scenarios.
Finally, the program should emphasize the importance of reporting suspicious activity. Employees should be encouraged to report any suspicious emails, phone calls, or other communications to the IT department. A clear and accessible reporting mechanism should be established to facilitate this process. Regular refresher training and simulated phishing exercises will reinforce learned behaviors and help keep employees vigilant.
The Future of Encryptionless Ransomware and Defense
Encryptionless ransomware, while currently less prevalent than its encrypting counterpart, presents a concerning evolution in the threat landscape. Its focus on data exfiltration and disruption rather than encryption necessitates a shift in defensive strategies. Predicting its future trajectory requires understanding the motivations behind its use and the technological advancements that could fuel its growth.The future will likely see a rise in sophisticated, targeted encryptionless ransomware attacks.
This prediction stems from the increasing profitability of data breaches and the relative ease of exfiltrating data compared to encrypting and decrypting large datasets. Attackers will likely leverage advanced techniques like living-off-the-land (LOL) attacks, using legitimate system tools to avoid detection, and focus on high-value targets with sensitive data. The anonymity offered by the dark web and the growing sophistication of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operations will further fuel this trend.
Trends in Encryptionless Ransomware Attacks
Encryptionless ransomware attacks will increasingly exploit vulnerabilities in supply chains and third-party vendors. This is because compromising a single vendor can grant access to a wide network of clients, maximizing the potential for data exfiltration and disruption. We can expect to see a rise in double extortion attacks, where attackers both exfiltrate data and disrupt operations, demanding payment to prevent both data release and operational downtime.
The use of automation and artificial intelligence will also improve the efficiency and scale of these attacks, allowing attackers to target more victims simultaneously. For example, a hypothetical scenario could involve an attacker compromising a managed service provider (MSP) and gaining access to numerous small businesses, all of which become victims simultaneously.
Emerging Technologies for Defense
Advanced threat detection and response technologies, such as extended detection and response (XDR), will play a crucial role in mitigating the risk. XDR integrates data from various security tools to provide a holistic view of the threat landscape, enabling faster identification and response to attacks. Improved endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions will also be critical in identifying malicious activities on endpoints before they can exfiltrate data.
Furthermore, the implementation of robust zero trust security models will limit lateral movement within a network, even if an attacker gains initial access. This approach assumes no implicit trust and verifies every user and device attempting to access resources.
Proactive Security Measures
Proactive security measures are paramount in reducing the likelihood and impact of encryptionless ransomware attacks. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential to identify and address potential weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. Implementing strong access controls, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access, will significantly limit the damage an attacker can inflict. Furthermore, robust data loss prevention (DLP) solutions can monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network.
Finally, comprehensive security awareness training for employees is vital in reducing the risk of social engineering attacks, a common vector for ransomware infections. Regular simulated phishing exercises and training on identifying suspicious emails and attachments are crucial components of this strategy.
Final Wrap-Up

So, there you have it – a glimpse into the world of encryptionless ransomware and the crucial strategies to combat it. The conversation with Deepen Desai highlighted the urgent need for a multi-layered approach to security, emphasizing not just technology, but also human awareness and proactive planning. While the threat landscape continues to evolve, understanding the mechanics of these attacks and implementing robust defense mechanisms are key to staying ahead.
Don’t just react; be proactive. Your data’s future depends on it.
FAQ Summary
What are the common methods used in encryptionless ransomware attacks besides data encryption?
Encryptionless ransomware often employs methods like data deletion, system disruption (through malware), or simply holding data hostage through access denial. They aim to cripple operations rather than encrypting files.
How can I tell if I’m under an encryptionless ransomware attack?
Look for signs like system unresponsiveness, data inaccessibility (without encryption indicators), unusual network activity, or ransom demands without mention of encryption. A sudden inability to access critical systems is a strong indicator.
Are there any specific regulations or compliance standards relevant to encryptionless ransomware attacks?
Yes, depending on your industry and location, regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or others may apply. These regulations often mandate specific data security and incident response protocols, making effective ransomware defense crucial for compliance.
What’s the difference between a backup and a recovery strategy?
A backup strategy Artikels
-how* you create and store copies of your data. A recovery strategy details
-how* you restore your systems and data from those backups in case of an attack. Both are essential and interconnected.