Ensure Optimal ROI of Your Mainframe Assets
Ensure optimal roi of your mainframe assets – Ensure Optimal ROI of Your Mainframe Assets: That’s the million-dollar question, isn’t it? We all know mainframes are workhorses, handling critical business functions day in and day out. But are they working
-for* you, or are they quietly draining your budget? This post dives deep into strategies to maximize the return on your mainframe investment, uncovering hidden efficiencies and exploring modernization paths to boost your bottom line.
We’ll look at everything from understanding current utilization to implementing robust security measures – a comprehensive guide to getting the most out of your mainframe.
This isn’t just about cutting costs; it’s about strategic optimization. We’ll explore how improved efficiency translates to tangible business benefits – think faster transaction processing, happier customers, and less downtime. We’ll even tackle the tough stuff, like navigating the complexities of mainframe modernization and choosing the right approach for your specific needs. Get ready to unlock the true potential of your mainframe and watch your ROI soar!
Understanding Current Mainframe Utilization

Optimizing our mainframe ROI requires a deep understanding of its current performance and resource consumption. This involves analyzing CPU, memory, and storage usage, as well as evaluating application performance metrics. By gaining this insight, we can identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, ultimately leading to more efficient resource allocation and cost savings.
Mainframe Resource Consumption, Ensure optimal roi of your mainframe assets
Our mainframe currently shows a consistent pattern of resource usage. CPU utilization averages around 70% during peak hours, dropping to 40% during off-peak periods. Memory usage consistently sits at 85% capacity, indicating a potential need for expansion or optimization. Storage utilization is at 65%, with projections showing it reaching capacity within the next 18 months. This highlights the need for a proactive storage management strategy.
Analyzing application performance reveals that transaction response times for our core banking application average 2 seconds, while our customer relationship management (CRM) application averages 1.5 seconds. These metrics suggest areas for potential performance improvements in the banking application.
Mainframe Infrastructure Details
The following table summarizes our current mainframe infrastructure:
| Component | Specification | Vendor | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | z15 mainframe, 24 cores | IBM | Operational |
| Memory | 2 TB | IBM | Operational |
| Storage | 10 TB DASD, 5 TB SSD | IBM | Operational |
| Operating System | z/OS 2.5 | IBM | Operational |
| Database | DB2 11.5 | IBM | Operational |
Mainframe Monitoring and Management Tools
Our mainframe is monitored using IBM’s z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF) and Compuware Abend-AID. z/OSMF provides comprehensive system monitoring capabilities, allowing us to track resource utilization, identify bottlenecks, and proactively address potential issues. Abend-AID helps us analyze application abends, identify root causes, and implement corrective actions. While these tools are effective in identifying many bottlenecks, the integration between them could be improved to provide a more holistic view of system performance.
For instance, correlating abends detected by Abend-AID with resource utilization data from z/OSMF could provide more actionable insights. Currently, this correlation requires manual effort.
Identifying Cost Drivers and Optimization Opportunities
So, we’ve established the current state of your mainframe utilization. Now, let’s get down to brass tacks: identifying where the money’s going and how we can make it go further. Optimizing your mainframe investment isn’t just about saving money; it’s about freeing up resources to fuel innovation and growth.
Understanding your mainframe’s cost structure is the first step towards maximizing its ROI. This involves a thorough examination of various expense categories and identifying potential areas for improvement. Let’s break down the key cost drivers and explore some effective optimization strategies.
Mainframe Cost Drivers
The costs associated with mainframe operations are multifaceted and can be substantial. A clear understanding of these drivers is crucial for effective cost management. Ignoring any of these areas can lead to significant financial losses over time.
- Hardware Maintenance: This includes costs associated with hardware repairs, upgrades, and preventative maintenance contracts. These contracts often involve significant annual fees and can vary depending on the age and complexity of your mainframe hardware. Unexpected hardware failures can also lead to significant downtime costs.
- Software Licensing: Mainframe software licenses can be extremely expensive, particularly for complex applications and large user bases. The cost of these licenses is often tied to the number of users or processors, leading to escalating costs as your business grows.
- Personnel Costs: Highly skilled mainframe professionals are in short supply, making their salaries and benefits a significant expense. These costs include not only salaries but also training, recruitment, and retention efforts. The specialized skills required for mainframe maintenance and development command high compensation.
- Power and Cooling: Mainframes require significant power and cooling infrastructure, contributing substantially to operational expenses. The energy consumption of these systems can be considerable, especially in older data centers with less efficient cooling solutions.
- Storage Costs: Storing vast amounts of data on mainframes can be expensive. This cost is often directly related to the volume of data stored and the type of storage used (e.g., tape vs. disk).
Cost Reduction Strategies
Fortunately, there are numerous strategies available to reduce mainframe costs without compromising performance or reliability. These strategies often involve a combination of technological upgrades, process improvements, and strategic resource allocation.
- Software License Optimization: A thorough audit of your software licenses can reveal opportunities for cost savings. This may involve negotiating better terms with vendors, consolidating licenses, or identifying and eliminating unused software. For example, a company might find they are paying for more licenses than active users, resulting in significant wasted expenditure.
- Hardware Consolidation: Consolidating workloads onto fewer mainframes can reduce hardware maintenance and power consumption costs. Virtualization technologies can help achieve this consolidation, enabling multiple applications to run on a single physical mainframe. This can lead to significant savings in both hardware and energy costs. A real-world example is a large bank that consolidated its mainframe infrastructure, reducing its hardware footprint by 40% and lowering its energy bill by 30%.
- Staff Re-allocation: Strategic re-allocation of mainframe staff can improve efficiency and reduce personnel costs. This might involve retraining staff on new technologies or focusing their efforts on higher-value tasks. For example, automating routine maintenance tasks can free up skilled personnel to focus on more complex and strategic projects.
Mainframe Modernization Approaches
Modernization is a key strategy for extending the lifespan of mainframe assets and improving their ROI. Several approaches exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of approach will depend on the specific needs and circumstances of your organization.
- Cloud Migration: Migrating mainframe applications to the cloud can offer scalability, cost savings, and improved agility. However, this approach requires careful planning and execution, as it involves significant technical challenges and potential risks. The ROI depends heavily on the complexity of the application and the efficiency of the cloud migration process. A successful migration can lead to significant cost reductions in hardware, maintenance, and personnel.
- Application Refactoring: Refactoring involves restructuring existing mainframe applications to improve their performance, maintainability, and scalability. This can be a gradual process, allowing for incremental improvements and reduced risk. The ROI is realized through improved efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and increased agility. For example, refactoring a legacy application can reduce its processing time by 50%, leading to significant cost savings.
- Containerization: Containerization allows mainframe applications to be packaged and deployed in a standardized way, improving portability and scalability. This approach can facilitate a gradual transition to cloud environments or other modern platforms. The ROI is primarily realized through improved agility, reduced deployment time, and increased efficiency. A company might see a 20% reduction in deployment time after implementing containerization.
Strategic Planning for Mainframe ROI Enhancement: Ensure Optimal Roi Of Your Mainframe Assets
Optimizing your mainframe’s return on investment (ROI) isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing strategic process. This involves a phased approach, careful budgeting, and a clear understanding of how improved efficiency translates into tangible business value. By strategically planning your mainframe optimization, you can ensure sustainable cost savings and improved performance.A phased approach allows for manageable implementation, minimizing disruption and maximizing the chances of success.
Each phase builds upon the previous one, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation based on results. A detailed budget is crucial for securing resources and tracking progress against projected returns. Finally, demonstrating a clear link between mainframe efficiency and business benefits helps justify the investment and secure ongoing support.
Phased Approach to Mainframe Optimization
Implementing mainframe optimization strategies effectively requires a well-defined phased approach. This allows for incremental improvements, minimizing disruption to ongoing operations and allowing for adjustments based on results. A typical phased approach might include initial assessments, pilot projects, and full-scale implementation. Key milestones and deliverables should be established for each phase, ensuring accountability and tracking progress. For example, Phase 1 might focus on identifying low-hanging fruit for quick wins, while Phase 2 could tackle more complex modernization projects.
Mainframe Optimization Budget
The following table Artikels a sample budget for a mainframe optimization project. Remember, this is a template and your specific costs and returns will vary depending on your environment and chosen strategies. Accurate cost estimation is crucial for securing necessary funding and demonstrating the potential ROI to stakeholders. Consider factors like staffing, software licensing, and potential downtime costs.
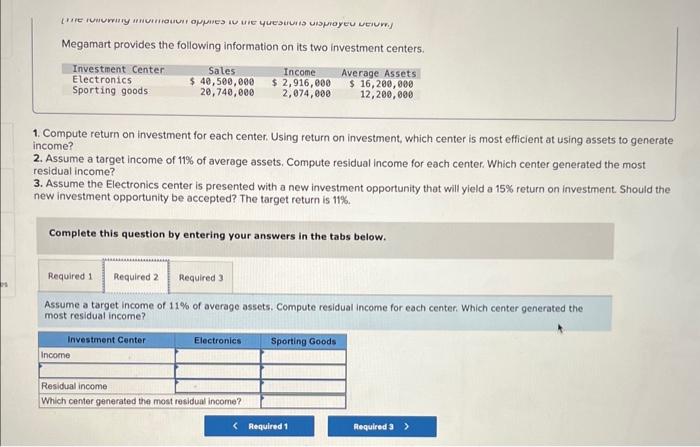
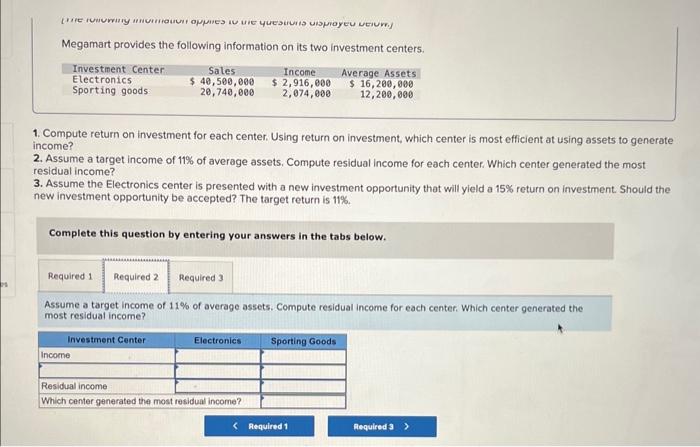
| Phase | Initiative | Cost (USD) | Projected ROI (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Assessment & Quick Wins | Performance analysis & tuning | 50,000 | 100,000 |
| Phase 1: Assessment & Quick Wins | Database optimization | 25,000 | 75,000 |
| Phase 2: Modernization | Partial application refactoring | 150,000 | 300,000 |
| Phase 3: Ongoing Maintenance | Performance monitoring & support | 20,000/year | 40,000/year (reduced downtime costs) |
Translating Mainframe Efficiency into Business Benefits
Improved mainframe efficiency directly translates into tangible business benefits. Faster transaction processing leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and increased revenue. For example, a reduction in transaction processing time from 5 seconds to 2 seconds can significantly improve customer experience, potentially leading to increased sales and customer loyalty. Reduced operational downtime minimizes business disruption and associated costs. For instance, avoiding even one hour of downtime per month can save a company thousands of dollars in lost revenue and recovery efforts.
Finally, efficient resource utilization frees up budget for other strategic initiatives. This allows companies to invest in innovation and growth, furthering their competitive advantage.
Measuring and Tracking Mainframe ROI

So, we’ve optimized our mainframe, but how do weknow* it’s working? Simply making changes isn’t enough; we need concrete data to demonstrate the return on our investment. This is where robust measurement and tracking come in. By establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and a consistent monitoring plan, we can quantify the success of our optimization efforts and identify areas needing further attention.Effective mainframe ROI measurement requires a multi-faceted approach.
We need to track not just cost reductions but also improvements in performance and overall system efficiency. Only by combining these different perspectives can we get a complete picture of our return on investment.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Mainframe Optimization
Choosing the right KPIs is crucial. These metrics should directly reflect the goals of our optimization initiatives. For example, if a primary goal was to reduce processing times, then KPIs related to transaction response times and throughput would be essential. Conversely, if cost reduction was the main focus, then metrics like CPU utilization, storage costs, and software licensing fees would be more relevant.
A balanced scorecard approach, incorporating both financial and operational KPIs, provides a holistic view.
- Transaction Response Time: Measures the time it takes for a transaction to complete. A decrease indicates improved performance.
- CPU Utilization: Shows the percentage of CPU time being used. Lower utilization, while maintaining performance, suggests efficient resource allocation.
- Storage Costs per Transaction: Calculates the cost of storage used per transaction, revealing potential savings from data optimization.
- Software License Costs per Transaction: Similar to storage costs, this tracks software licensing expenses relative to transaction volume.
- Mean Time To Resolution (MTTR): Measures the average time taken to resolve system issues. A reduction indicates improved system stability and reliability.
Mainframe Performance and Cost Monitoring Plan
Regular monitoring is essential to track progress and identify potential problems early. We need a systematic approach to data collection and reporting. This could involve automated tools that gather performance data from the mainframe and integrate it with cost accounting information.We should aim for a reporting frequency that balances the need for timely insights with the avoidance of excessive reporting.
Weekly or monthly reports might be appropriate, depending on the complexity of the environment and the frequency of changes. Reports should be distributed to relevant stakeholders, including IT management, finance, and potentially business unit leaders. The distribution method could be email, a shared dashboard, or a combination of both.
Data Analysis and ROI Assessment
The data gathered from our monitoring efforts needs to be analyzed to assess the ROI of our mainframe investments. This analysis should compare the costs before and after optimization initiatives, as well as the changes in performance metrics. A simple but effective way to visualize this data is through a line chart.For example, a line chart could show the trend of CPU utilization over time, with one line representing the utilization before optimization and another line showing the utilization after implementing changes.
This visual representation allows for easy comparison and identification of improvement areas. Similar charts can be created for other KPIs, such as transaction response time or storage costs. By comparing pre- and post-optimization data, we can calculate the return on our investments and pinpoint areas for further improvement. For instance, if we see a significant reduction in CPU utilization coupled with a decrease in costs, this clearly demonstrates the positive ROI of our optimization efforts.
Security and Risk Mitigation within Mainframe Optimization
Optimizing your mainframe environment for better ROI is crucial, but it’s equally vital to ensure that these efforts don’t inadvertently compromise your organization’s security posture. Mainframe modernization and optimization projects often involve changes to systems and access controls, increasing the potential for vulnerabilities if not carefully managed. This section focuses on proactively addressing security risks and implementing robust mitigation strategies.
Modernization projects, while aiming to improve efficiency and reduce costs, can introduce new security risks if not properly planned and executed. For example, integrating new technologies with legacy systems requires careful consideration of data access controls and authentication mechanisms. Failure to do so could expose sensitive data or create vulnerabilities exploitable by malicious actors. Similarly, the very act of optimizing processes might inadvertently weaken existing security controls if not properly assessed and updated.
Data Breaches and System Vulnerabilities
Data breaches and system vulnerabilities represent significant threats during mainframe optimization. Data breaches can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties. System vulnerabilities can allow unauthorized access, data manipulation, or even complete system compromise.
Mitigation strategies include comprehensive security assessments before, during, and after optimization projects. This involves vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and regular security audits to identify and address weaknesses. Implementing strong access controls, such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access control (RBAC), is also critical. Regular security awareness training for personnel involved in the optimization process helps prevent human error, a common cause of security incidents.
Furthermore, robust data encryption both in transit and at rest minimizes the impact of a potential breach. Finally, a well-defined incident response plan is essential to quickly contain and remediate any security incidents that may occur.
Robust Security Measures During Modernization
Implementing robust security measures is paramount during mainframe modernization. This involves a layered security approach, combining various security controls to provide comprehensive protection.
Security controls should be implemented throughout the entire modernization lifecycle. This includes secure coding practices during development, rigorous testing to identify vulnerabilities, and ongoing monitoring to detect and respond to threats. Implementing a strong security information and event management (SIEM) system allows for centralized monitoring and analysis of security logs from various sources, enabling early detection of suspicious activity.
Regular patching and updates of both the mainframe operating system and applications are crucial to mitigate known vulnerabilities. The use of automated security tools can help streamline these processes and improve efficiency. Finally, a well-defined security policy that Artikels acceptable use, access controls, and incident response procedures should be communicated and enforced across all teams involved in the modernization effort.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning
A robust disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity (BC) plan is crucial for minimizing disruption and ensuring business resilience during mainframe optimization projects. These plans should Artikel procedures for recovering from various types of disasters, including natural disasters, cyberattacks, and hardware failures.
The DR/BC plan should include detailed procedures for backing up and restoring critical data, as well as procedures for failover to a secondary mainframe or alternative processing environment. Responsibilities for each step in the recovery process should be clearly defined and documented. Regular testing of the DR/BC plan is essential to ensure its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
This testing should simulate various disaster scenarios, including system failures, data loss, and cyberattacks. The plan should also address communication protocols to keep stakeholders informed during a disaster and should incorporate metrics to track recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). Consideration should be given to the use of cloud-based solutions for DR, offering scalability and flexibility.
Getting the most out of your mainframe investment is key, and modernizing your applications is a big part of that. To achieve optimal ROI, consider leveraging the power of low-code/no-code development; check out this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future for some innovative ideas. Ultimately, streamlining your processes with modern tools directly impacts your mainframe’s efficiency and return on investment.
For example, a company could replicate its mainframe data to a cloud environment, enabling rapid recovery in the event of a disaster at the primary data center.
Last Word
Optimizing your mainframe ROI isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process of monitoring, adapting, and refining your strategies. By understanding your current utilization, identifying cost drivers, and implementing a strategic plan, you can transform your mainframe from a cost center into a powerful engine for growth. Remember, it’s not just about squeezing every last drop of efficiency – it’s about aligning your mainframe operations with your overall business goals.
Ready to embark on this journey towards mainframe mastery? Let’s get started!
Key Questions Answered
What are the biggest risks associated with mainframe modernization?
Data loss, security breaches, and integration challenges are key risks. Careful planning, robust security protocols, and phased implementation can mitigate these risks.
How long does it typically take to see a return on investment from mainframe optimization?
This varies greatly depending on the scale and scope of the project. Some optimizations yield quick wins, while others may take longer to show significant ROI. Careful planning and KPI tracking are essential.
What if we don’t have the in-house expertise to optimize our mainframe?
Many consulting firms specialize in mainframe optimization. Partnering with an expert can provide valuable guidance and accelerate your progress.
How can we measure the success of our mainframe optimization efforts?
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like CPU utilization, transaction processing times, and cost per transaction. Regularly analyze this data to gauge progress and identify areas for further improvement.
