FBI Issues Ransomware Cyber Attack Warning to US Businesses
FBI Issues Ransomware Cyber Attack Warning to US Businesses – Whoa, that headline grabbed my attention! The FBI isn’t issuing warnings lightly, and this one’s a serious wake-up call for American businesses of all sizes. We’re talking ransomware, the digital extortion racket that’s costing companies millions, crippling operations, and stealing sensitive data. This post dives into the specifics of the warning, the types of attacks we’re seeing, and – most importantly – how you can protect your business.
The FBI’s warning highlights a concerning rise in sophisticated ransomware attacks targeting US businesses across various sectors. They’re not just targeting large corporations; smaller businesses are increasingly vulnerable. The attacks are becoming more frequent and more damaging, utilizing advanced techniques to bypass traditional security measures. We’ll explore the common tactics used by these cybercriminals, the devastating consequences for victims, and the crucial steps businesses need to take to bolster their defenses.
This isn’t just about avoiding a hefty ransom; it’s about protecting your data, your reputation, and the future of your business.
FBI Warning Details
The FBI recently issued a stark warning to US businesses regarding the escalating threat of ransomware attacks. This isn’t just another cybersecurity advisory; it highlights a significant and evolving threat landscape demanding immediate attention from organizations of all sizes. The warning emphasizes the sophistication and pervasiveness of these attacks, urging proactive measures to mitigate the risk.The FBI’s warning detailed a range of ransomware attacks, emphasizing the increasingly sophisticated tactics employed by cybercriminals.
These attacks are no longer limited to simple file encryption; they now frequently involve data exfiltration, extortion, and the exploitation of vulnerabilities in widely used software. The warning stressed the need for robust cybersecurity practices and incident response planning.
Ransomware Attack Types Highlighted
The FBI’s warning specifically addressed several prevalent ransomware attack vectors. These included attacks leveraging phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links, exploiting known vulnerabilities in software applications (especially unpatched systems), and gaining initial access through compromised remote desktop protocol (RDP) credentials. The agency also highlighted the rise of double extortion attacks, where threat actors both encrypt data and threaten to publicly release sensitive information unless a ransom is paid.
This dual threat significantly increases the pressure on victims to comply.
Industries Most at Risk
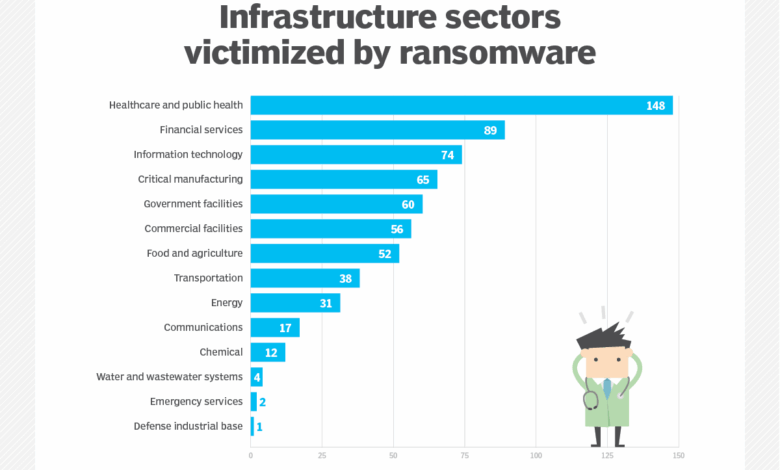
The FBI’s warning pinpointed several industries as being particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks. These include healthcare, manufacturing, finance, and education. These sectors often handle sensitive data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Furthermore, the critical infrastructure and essential services provided by many of these industries amplify the potential consequences of a successful ransomware attack. The interconnected nature of modern business also means that a successful attack on one organization can have ripple effects throughout its supply chain.
Examples of Successful Ransomware Attacks, Fbi issues ransomware cyber attack warning to us businesses
The FBI’s warning implicitly referenced numerous real-world examples of successful ransomware attacks against US businesses. While specific details of ongoing investigations are often kept confidential, the severity and frequency of these attacks are undeniable. The following table provides hypothetical examples, illustrating the diverse impact of ransomware across different sectors, based on publicly available information about real attacks:
| Industry | Attack Type | Impact | Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Phishing Email leading to Ryuk Ransomware | Disruption of patient care, data breach, significant financial losses, reputational damage | Employee security awareness training, multi-factor authentication, regular software patching, robust data backups |
| Manufacturing | Exploitation of unpatched software vulnerability (e.g., EternalBlue) leading to Conti Ransomware | Production downtime, supply chain disruption, loss of intellectual property, significant financial losses | Regular software patching, network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, incident response planning |
| Finance | RDP compromise leading to REvil Ransomware | Data breach, financial losses, regulatory fines, reputational damage, loss of customer trust | Strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, robust data encryption |
| Education | Phishing Email leading to LockBit Ransomware | Disruption of classes, data breach of student and faculty information, reputational damage | Employee security awareness training, data encryption, regular data backups, strong access controls |
Ransomware Tactics and Techniques
The FBI’s warnings about ransomware attacks targeting US businesses are serious. Understanding how these attacks unfold is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation. This section details the common methods used by ransomware actors, the encryption techniques employed, and the characteristics of prominent ransomware families. This knowledge empowers businesses to strengthen their defenses and reduce their vulnerability.Ransomware actors employ a variety of methods to infiltrate business systems, often exploiting known vulnerabilities or leveraging social engineering techniques.
The initial breach frequently serves as the gateway for the ransomware deployment and subsequent data encryption.
Ransomware Infiltration Methods
Successful ransomware attacks often begin with initial access, gained through various means. These include phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links, exploiting vulnerabilities in unpatched software, utilizing compromised credentials obtained through credential stuffing or brute-force attacks, and leveraging remote desktop protocol (RDP) weaknesses. Once initial access is achieved, attackers often move laterally within the network to identify valuable data and critical systems before deploying the ransomware payload.
The sophistication of these techniques varies, ranging from simple phishing scams to highly targeted attacks involving advanced persistent threats (APTs). For instance, a seemingly legitimate email prompting the user to update their software could be a vector for malware delivery.
Data Encryption and Ransom Demands
After gaining access, ransomware actors employ sophisticated encryption techniques to render data unusable. Common algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman). The encryption process typically targets critical files and data, such as databases, financial records, and customer information. Once the encryption is complete, a ransom note is displayed, demanding a payment in cryptocurrency, often Bitcoin, in exchange for a decryption key.
The ransom note usually includes a deadline, threats of data destruction or public release if the ransom is not paid, and instructions on how to make the payment. The amount demanded varies greatly depending on the size and perceived value of the affected organization.
Comparison of Ransomware Families
Several ransomware families have gained notoriety for their impact and sophistication. Ryuk, Conti, and REvil (also known as Sodinokibi) are prime examples. Ryuk is known for targeting large enterprises and critical infrastructure, often after initial access is gained through other malware. Conti, a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation, is known for its advanced capabilities and extensive operational security. REvil was known for its high-profile attacks against various organizations, often targeting intellectual property and confidential data.
While these groups share similarities in their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), they differ in their operational structures, ransom demands, and overall sophistication. For example, Conti utilized a sophisticated affiliate program, while REvil was characterized by its highly targeted and customized attacks.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs) is crucial for early detection and response. IOCs associated with ransomware attacks can include unusual network activity, such as encrypted communications to known command-and-control (C2) servers, unusual file creation or modification patterns, particularly involving encrypted files with specific extensions, and suspicious email activity, including phishing emails and malicious attachments. Specific IOCs vary depending on the ransomware family involved.
For example, certain file extensions or specific registry keys may be indicative of a particular ransomware variant. Monitoring these indicators is essential for proactive threat detection and response.
Impact on US Businesses
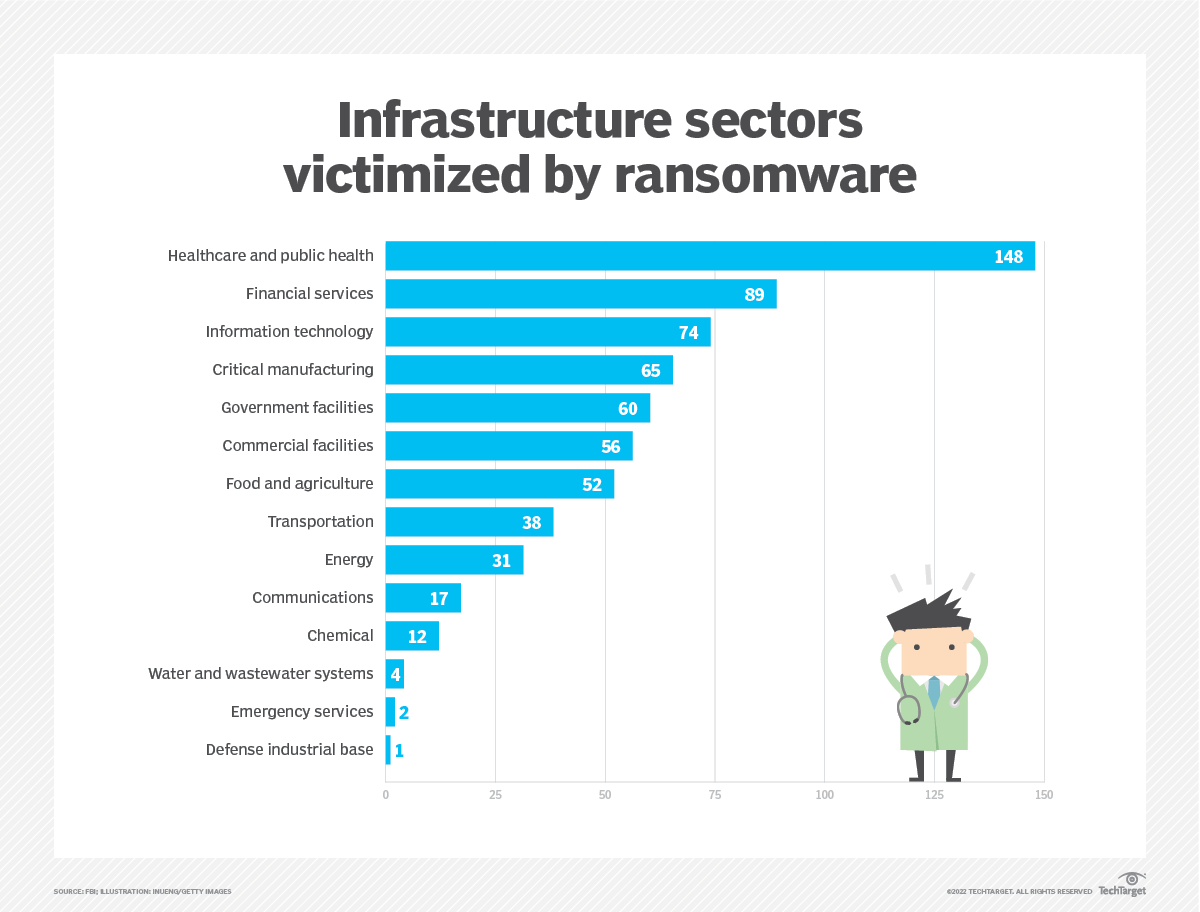
Ransomware attacks are inflicting devastating blows on US businesses, extending far beyond the immediate financial losses. The ripple effects impact operations, reputation, and legal standing, creating a complex and costly aftermath that can cripple even the most resilient companies. Understanding the full scope of these consequences is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation strategies.The financial burden of a ransomware attack can be staggering.
Direct costs include the ransom payment itself (if paid), which can range from thousands to millions of dollars depending on the sophistication of the attack and the size of the business. Beyond the ransom, businesses face significant expenses related to data recovery, system restoration, cybersecurity consulting, legal fees, and potential fines. Operational disruptions lead to lost productivity, missed deadlines, and damage to ongoing projects.
The inability to access critical data can halt operations entirely, resulting in lost revenue and potential contracts. For example, a small manufacturing company might lose thousands of dollars daily while its production line is offline due to an encrypted system. A large hospital facing a ransomware attack might experience even greater financial losses due to halted services and potential patient safety risks.
Financial and Operational Consequences
Ransomware attacks create a domino effect of financial and operational problems. Immediate losses stem from the inability to access critical data and systems. This downtime translates directly into lost revenue, particularly for businesses that rely on real-time transactions or continuous operations. The cost of restoring systems and data, often involving specialized IT services and potentially the purchase of new hardware, adds to the financial strain.
Long-term consequences include decreased productivity, damaged client relationships, and difficulty attracting new business due to a tarnished reputation. The hidden costs, such as lost opportunities and the potential for future attacks, are also significant. Consider the impact on a small business that loses client data and faces subsequent lawsuits; the costs can quickly spiral out of control.
Reputational Damage and Loss of Customer Trust
A ransomware attack can severely damage a business’s reputation and erode customer trust. News of a data breach, even if the ransom is paid and data is recovered, can spread quickly through media outlets and social networks, causing significant damage to brand image. Customers may lose confidence in the business’s ability to protect their sensitive information, leading to a decline in sales and customer loyalty.
This reputational damage can be long-lasting, even after the immediate crisis is resolved. For example, a financial institution suffering a ransomware attack that exposes customer data will likely experience a significant drop in customers and their trust. The impact can be amplified if the company is slow to respond or is perceived as being uncooperative with investigations.
Legal Ramifications and Regulatory Compliance
Businesses affected by ransomware attacks face potential legal ramifications and regulatory compliance issues. Depending on the type of data compromised and the applicable laws (such as HIPAA for healthcare providers or GDPR for businesses handling European citizen data), significant fines and penalties can be imposed. Furthermore, affected businesses may face lawsuits from customers or other parties affected by the breach.
Compliance with regulations like the CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) and other state-level data privacy laws adds another layer of complexity and potential liability. Failure to adequately address the security breach and comply with reporting requirements can lead to further legal repercussions. The legal costs associated with defending against lawsuits and navigating regulatory investigations can be substantial.
Immediate Actions After a Ransomware Attack
It is critical to act swiftly and decisively after a ransomware attack. A well-defined incident response plan is crucial.
The following steps should be taken immediately:
- Isolate affected systems: Disconnect infected computers and servers from the network to prevent further spread of the ransomware.
- Report the incident: Contact law enforcement (FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3)) and relevant regulatory bodies.
- Assess the damage: Determine the extent of the data breach and the systems affected.
- Secure backups: Verify the integrity of backups and initiate data recovery if possible.
- Engage cybersecurity experts: Seek professional help to investigate the attack, restore systems, and improve security measures.
- Communicate with stakeholders: Inform affected customers, employees, and business partners about the incident and the steps being taken to address it.
- Document everything: Maintain a detailed record of the attack, response efforts, and recovery process for legal and insurance purposes.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Ransomware attacks are a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. The financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruption caused by these attacks can be devastating. Fortunately, a proactive and multi-layered approach to cybersecurity can significantly reduce the risk. By implementing robust prevention and mitigation strategies, businesses can protect themselves from the crippling effects of ransomware.Implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is crucial for protecting your business from ransomware attacks.
This involves a combination of technical safeguards, employee training, and incident response planning. Neglecting any of these areas significantly weakens your overall security posture.
Robust Cybersecurity Measures
A strong cybersecurity foundation is built upon several key pillars. These measures work synergistically to create a robust defense against ransomware and other cyber threats. Failing to address any one of these areas leaves your business vulnerable.
The FBI’s ransomware warning to US businesses is a serious wake-up call. We need robust, secure systems, and that’s where advancements like domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , come in. These modern development approaches can help build more resilient and secure applications, ultimately mitigating the risk of these devastating cyberattacks. The FBI’s warning highlights the urgent need for businesses to prioritize cybersecurity upgrades.
- Regular Software Updates: Patching vulnerabilities in operating systems, applications, and firmware is paramount. Outdated software is a prime target for attackers. Automate updates whenever possible to ensure timely patching.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce the use of complex, unique passwords for all accounts. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible to add an extra layer of security. Consider password managers to help users create and manage strong passwords.
- Network Security: Utilize firewalls to control network traffic and prevent unauthorized access. Segment your network to limit the impact of a breach. Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor network activity for malicious behavior.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up critical data to an offline, secure location. Test your backup and recovery procedures regularly to ensure they are effective. The 3-2-1 backup rule (3 copies of data, on 2 different media, with 1 copy offsite) is a good guideline to follow.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities on individual endpoints (computers, servers, etc.). They can detect and prevent ransomware infections before they can spread.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources to identify and respond to security incidents. They provide a centralized view of your security posture and can help detect anomalous activity that may indicate a ransomware attack.
Cybersecurity Strategy for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs)
SMBs often lack the resources of larger organizations, but they are still highly vulnerable to ransomware. A tailored strategy is crucial.
The FBI’s ransomware warning to US businesses is a serious wake-up call. We’re seeing a massive increase in attacks, highlighting the urgent need for robust security measures. Understanding and implementing solutions like those discussed in this article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is crucial. Ultimately, proactive cloud security is no longer optional; it’s essential to prevent becoming another statistic in the FBI’s alarming reports.
A prioritized approach is recommended, focusing on the most critical assets and vulnerabilities first. This might involve starting with basic security hygiene (strong passwords, software updates) and gradually implementing more advanced measures as resources allow. Outsourcing some security functions to managed service providers (MSPs) can be a cost-effective solution.
- Prioritize Critical Assets: Identify and protect your most valuable data and systems first.
- Implement Basic Security Hygiene: Focus on foundational security practices like strong passwords, software updates, and regular backups.
- Consider Cloud Security: Leverage cloud-based security solutions to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Employee Training: Invest in employee training to increase awareness of phishing scams and other social engineering tactics.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a plan for responding to a ransomware attack, including steps for containment, recovery, and communication.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Human error is a major factor in ransomware attacks. Phishing emails, malicious links, and social engineering tactics are often successful because employees lack awareness or training.
Regular security awareness training is essential to mitigate this risk. This training should cover topics such as phishing scams, malware, safe browsing practices, and password security. Simulations and phishing tests can help reinforce learning and identify vulnerabilities in your employees’ security practices. Training should be ongoing and updated to reflect the latest threats.
Regular security awareness training is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process.
Government and Industry Response
The fight against ransomware is a multifaceted battle requiring a collaborative effort between government agencies, private industry, and individual businesses. The sheer scale and sophistication of modern ransomware attacks necessitate a coordinated strategy encompassing prevention, detection, response, and recovery. This collaborative approach is crucial because ransomware attacks often transcend national borders, requiring international cooperation to effectively track down and prosecute perpetrators.The FBI and other government agencies play a critical role in this fight, acting as a central point of coordination and information sharing.
Their expertise in investigations, threat intelligence, and cybersecurity provides invaluable support to businesses facing attacks. Furthermore, government initiatives are instrumental in setting cybersecurity standards and promoting best practices across industries.
FBI and Other Government Agency Roles in Combating Ransomware
The FBI’s role extends beyond investigations. They actively engage in public awareness campaigns, educating businesses and individuals about ransomware threats and preventive measures. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) works alongside the FBI, providing technical assistance and resources to organizations affected by ransomware attacks. Other agencies, such as the Department of Justice (DOJ), focus on prosecuting cybercriminals and recovering stolen funds.
This coordinated approach ensures a comprehensive response to the ransomware threat, leveraging the unique strengths of each agency. For example, the DOJ might prosecute individuals involved in a ransomware attack, while the FBI and CISA help affected businesses recover their systems and data.
Industry Group Initiatives to Address the Ransomware Threat
Industry groups like the Financial Services Information Sharing and Analysis Center (FS-ISAC) and the Healthcare Information Sharing and Analysis Center (H-ISAC) play a vital role in information sharing and collaborative threat intelligence. These organizations facilitate the exchange of threat information among their members, enabling early detection and response to ransomware attacks. They also develop and promote best practices and security standards, helping organizations strengthen their defenses.
Furthermore, industry groups often lobby for government policies that support cybersecurity initiatives and strengthen the legal framework for combating cybercrime. This collective action strengthens the overall security posture of entire sectors, making it more difficult for attackers to succeed.
Comparison of Cybersecurity Frameworks and Standards
Several cybersecurity frameworks and standards, such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), ISO 27001, and CIS Controls, offer guidance for organizations to improve their cybersecurity posture. While each framework has its strengths and weaknesses, they all share the common goal of mitigating risks and improving resilience against cyber threats, including ransomware. The NIST CSF, for example, provides a flexible framework that can be adapted to different organizational contexts, while ISO 27001 offers a comprehensive standard for information security management systems.
The CIS Controls focus on a prioritized set of actions that provide significant protection against common threats. The effectiveness of any framework depends on its proper implementation and integration into an organization’s overall security strategy. Choosing the right framework often depends on an organization’s size, industry, and specific risk profile.
Resources Available to US Businesses for Ransomware Prevention and Response
The fight against ransomware requires proactive measures. Here are key resources available to US businesses:The following list provides essential resources for ransomware prevention and response:
- FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3): Report ransomware incidents and access resources for victims.
- CISA’s website: Provides alerts, advisories, and guidance on cybersecurity best practices.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Offers a voluntary framework for improving cybersecurity.
- Industry-specific ISACs: Offer threat intelligence and best practices for specific sectors.
- Cybersecurity insurance providers: Can offer financial protection and incident response services.
Future Trends and Predictions: Fbi Issues Ransomware Cyber Attack Warning To Us Businesses
The ransomware landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-increasing sophistication of cybercriminals. Predicting the future of ransomware is challenging, but by analyzing current trends and technological developments, we can anticipate potential threats and develop proactive mitigation strategies. This necessitates a constant vigilance and adaptability within the cybersecurity community.The convergence of AI, IoT, and cloud computing presents both opportunities and vulnerabilities.
While these technologies offer enhanced security capabilities, they also introduce new attack vectors for malicious actors. For instance, the proliferation of IoT devices creates a larger attack surface, while AI can be leveraged to automate attacks and improve their effectiveness.
The FBI’s ransomware warning to US businesses is a serious wake-up call. We’re seeing a surge in sophisticated attacks, and it’s crucial to stay vigilant. This highlights the importance of data security, especially considering recent reports like this one detailing Facebook’s questionable request for bank account info and card transactions of users: facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users.
Such phishing attempts, combined with ransomware threats, create a perfect storm for businesses; proactive security measures are absolutely vital.
Emerging Ransomware Attack Vectors
The reliance on cloud services and the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) are significantly altering the attack landscape. Ransomware operators are increasingly targeting cloud environments, exploiting vulnerabilities in cloud configurations or gaining access through compromised credentials. Similarly, the sheer number of interconnected IoT devices, often lacking robust security measures, provides an easily exploitable entry point for ransomware attacks.
For example, a recent attack on a manufacturing facility involved ransomware infiltrating through an unsecured industrial control system (ICS) connected to the internet. The subsequent disruption caused significant financial losses and production delays.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Ransomware Attacks
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming both offensive and defensive capabilities in the cybersecurity realm. Attackers are utilizing AI to automate the identification of vulnerable systems, personalize phishing campaigns, and even develop more sophisticated encryption techniques. On the other hand, defensive technologies are also leveraging AI to detect anomalies, predict attacks, and automate incident response.
The development of quantum computing also poses a significant threat, potentially rendering current encryption methods obsolete. This necessitates a proactive approach to developing quantum-resistant cryptography.
New Defensive Technologies and Strategies
The cybersecurity industry is actively developing new defensive technologies to combat the evolving ransomware threat. These include advanced threat detection systems using AI and ML, improved endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and enhanced security information and event management (SIEM) capabilities. Blockchain technology is also being explored for its potential to enhance data security and resilience against ransomware attacks.
Furthermore, a strong focus on zero trust security architectures, which limit access to sensitive data based on least privilege principles, is becoming increasingly crucial. This approach aims to mitigate the impact of successful breaches by limiting lateral movement within a network.
Evolution of Ransomware Tactics and Techniques
We can expect ransomware tactics to become increasingly sophisticated and targeted. Double extortion attacks, where data is both encrypted and exfiltrated before a ransom demand, are likely to become more prevalent. Supply chain attacks, targeting software vendors or third-party providers, will continue to pose a significant threat. Furthermore, the use of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) platforms will likely facilitate easier access to ransomware tools for less technically skilled attackers.
The integration of ransomware attacks with other forms of cybercrime, such as data breaches and extortion, is also expected to increase. This creates a more complex and challenging threat environment requiring a multi-layered defensive approach.
Outcome Summary
The FBI’s ransomware warning serves as a stark reminder that the threat landscape is constantly evolving. While the prospect of a ransomware attack can feel daunting, proactive measures are key. By understanding the tactics used by attackers, implementing robust cybersecurity practices, and staying informed about emerging threats, businesses can significantly reduce their risk. Remember, prevention is far cheaper and less stressful than dealing with the aftermath of an attack.
Take the time to review your security protocols, train your employees, and invest in the right tools – your business’s future depends on it.
User Queries
What types of ransomware are most prevalent in these attacks?
The FBI warning doesn’t specify particular strains, but commonly used ransomware families like Ryuk, Conti (now largely defunct but its tactics live on), and others with similar capabilities are likely involved. The focus is on the attack methods rather than specific malware names.
What if my business is already infected?
Immediately disconnect from the network to prevent further spread. Do NOT pay the ransom. Contact law enforcement (the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) is a good starting point) and a cybersecurity professional for assistance with recovery and investigation.
How much does ransomware protection cost?
Costs vary widely depending on the size and complexity of your business and the level of protection needed. From basic antivirus software to comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) systems, the investment range is substantial, but significantly less than the potential cost of a ransomware attack.