Federal Data of 123M US Households Leaked in Latest AWS Breach
Federal data of 123m us households leaked in latest aws data breach – Federal Data of 123M US Households Leaked in Latest AWS Breach: Whoa, hold onto your hats, folks! We’re diving headfirst into a massive data breach affecting a staggering 123 million US households. This isn’t just another minor security hiccup; we’re talking potentially sensitive personal information, financial details, and location data potentially exposed. The implications are huge, impacting everything from individual identities to our collective trust in online services.
Let’s unpack this alarming situation and explore what it means for you and me.
This breach highlights some serious questions about data security in the cloud, particularly concerning the responsibility of major providers like AWS. We’ll examine their security protocols, their response to the crisis, and what improvements could prevent future catastrophes. We’ll also explore the legal ramifications, the potential for identity theft and financial fraud, and what steps we can all take to protect ourselves in this increasingly digital world.
Get ready for a deep dive into the complexities of data security and the unsettling reality of living in the age of massive data breaches.
Data Breach Overview

The recent alleged AWS data breach involving the exposure of data from 123 million US households is a significant event with potentially far-reaching consequences. The sheer scale of the breach underscores the vulnerability of sensitive personal information in the digital age and highlights the urgent need for robust data security measures across all sectors. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the importance of data protection and the potential ramifications of failing to adequately safeguard personal information.The breadth of the data potentially compromised is deeply concerning.
Reports suggest that the leaked information may include a wide range of personal details, potentially encompassing names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and possibly even financial information and location data. The exact nature and extent of the compromised data are still under investigation, but the potential for identity theft, financial fraud, and other forms of harm is substantial.
Impact on Affected Individuals
The potential impact on the 123 million individuals whose data may have been compromised is significant and multifaceted. Individuals face a heightened risk of identity theft, where malicious actors could use their personal information to open fraudulent accounts, obtain loans, or make unauthorized purchases. Financial fraud, including unauthorized access to bank accounts or credit cards, is another major concern.
Furthermore, the exposure of location data could lead to stalking, harassment, or even physical harm. The emotional distress and inconvenience associated with dealing with the aftermath of a data breach – such as credit monitoring, identity theft protection, and the time and effort required to resolve any resulting issues – should not be underestimated.
Timeline of Events
While a precise timeline is still emerging as investigations unfold, the initial reports suggest a relatively recent discovery of the breach. The timeframe between the initial compromise and the public disclosure will likely be a key focus of investigations, as will the steps taken (or not taken) to mitigate the damage. Understanding the sequence of events will be crucial in determining the extent of negligence, if any, and in identifying areas for improvement in data security protocols.
Future reports and investigations will likely provide a more detailed and accurate timeline of this significant data breach.
AWS’s Role and Responsibility
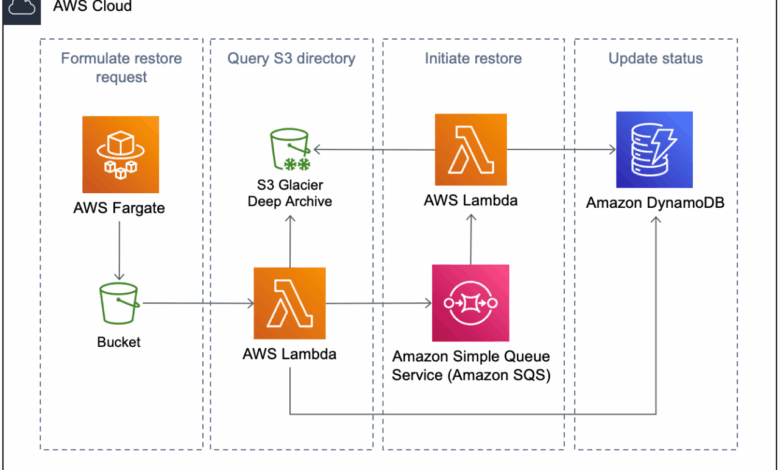
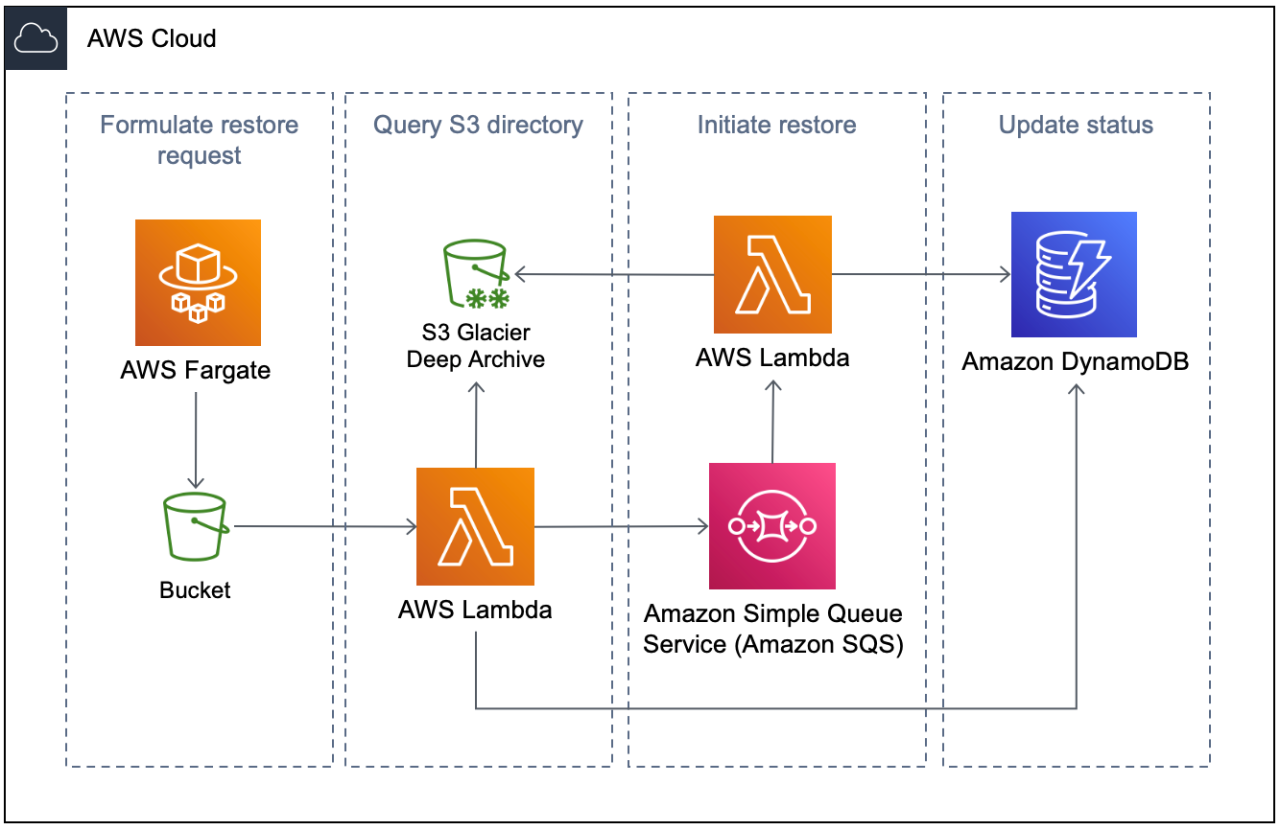
The recent data breach exposing the personal information of 123 million US households, allegedly stored on AWS servers, raises critical questions about the cloud provider’s security protocols and their effectiveness. While the precise details of the breach remain under investigation, analyzing AWS’s role and responsibility is crucial to understanding the scale of the incident and preventing future occurrences. This analysis will examine AWS’s security infrastructure, their response to the breach, and potential improvements to their security framework.AWS, as a leading cloud provider, boasts a sophisticated multi-layered security architecture.
This typically includes robust access control mechanisms, data encryption both in transit and at rest, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and regular security audits. However, the current breach suggests potential weaknesses within this system, possibly involving misconfigurations by the client storing the data, insufficient monitoring of access logs, or vulnerabilities in the specific services utilized. A thorough investigation is needed to pinpoint the exact failure points.
AWS’s Response to the Breach
Following the discovery of the breach, AWS initiated an internal investigation and collaborated with law enforcement agencies. They reportedly provided affected clients with support and guidance on mitigating the potential impact of the data exposure. The specific remedial actions taken by AWS, such as patching vulnerabilities, enhancing security controls, and improving incident response procedures, remain largely undisclosed pending the completion of the investigation.
Transparency in this process is vital to rebuilding trust and ensuring accountability. For example, a publicly available report detailing the identified vulnerabilities, implemented fixes, and lessons learned would significantly enhance confidence in AWS’s security posture.
Comparison with Other Major Cloud Providers
Comparing AWS’s security measures to those of other major cloud providers like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform is complex. All three offer robust security features, but their specific implementations and approaches differ. A direct comparison requires a detailed analysis of each provider’s security documentation, incident response procedures, and publicly available information on past breaches. Such a comparison should consider factors such as the frequency and severity of reported breaches, the transparency of their incident response processes, and the level of security certifications and compliance standards achieved.
While quantifying and directly comparing the effectiveness of security measures across different providers is difficult, analyzing publicly available information on past incidents and the respective responses can provide insights.
Hypothetical Improved Security Framework for AWS
An improved security framework for AWS could incorporate several enhancements. This could include implementing stricter default security settings, automating security configuration checks, leveraging advanced threat detection techniques such as machine learning and AI, and improving the visibility and granularity of security logging and monitoring. For example, mandating the use of multi-factor authentication for all accounts, implementing stricter access control lists (ACLs), and integrating automated security patching would reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Additionally, a more proactive approach to vulnerability discovery and remediation, coupled with robust penetration testing and security audits, would be crucial. The adoption of zero trust security principles, verifying every user and device before granting access regardless of location, could significantly enhance security. The hypothetical framework should also prioritize proactive security training for both AWS employees and clients to address human error, a significant factor in many data breaches.
The successful implementation of such a framework relies heavily on robust internal processes, continuous monitoring, and collaboration with clients.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
The leak of personal data from 123 million US households, allegedly stemming from an AWS data breach, triggers a complex web of legal and regulatory ramifications. Understanding the applicable laws and potential liabilities is crucial for both AWS and the affected individuals. This section will explore the legal landscape surrounding this significant data breach, outlining potential penalties and strategies for victims seeking redress.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Several federal and state laws in the US could apply to this data breach, depending on the specific nature of the compromised data and the location of the affected individuals. Key legislation includes the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) if protected health information (PHI) was involved; the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) if data on minors was compromised; and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and similar state laws, which grant consumers rights regarding their personal data.
The breach likely also falls under the purview of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Act, which prohibits unfair or deceptive acts or practices, and potentially state attorney general actions. Furthermore, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) may be relevant if financial information was among the leaked data. The scope of applicable regulations hinges on the precise type of data exposed and the affected individuals’ locations.
Potential Legal Liabilities for Implicated Parties
AWS, as the cloud service provider, faces potential liabilities for negligence, breach of contract, and violations of relevant data protection laws. Their responsibility extends to ensuring the security of their systems and the data entrusted to them. Depending on the terms of their service agreements with the affected party, they could face substantial financial penalties and reputational damage.
Other implicated parties, such as the organization whose data was breached and any third-party vendors involved, could also be held liable for their respective roles in the incident. The degree of liability depends on factors such as their level of negligence, the effectiveness of their security measures, and the extent to which they complied with relevant regulations. A critical factor will be determining whether the breach resulted from AWS’s failure to meet contractual obligations or from the client’s inadequate security practices.
Potential Penalties and Fines
The potential penalties for violating data protection laws vary widely depending on the specific legislation, the severity of the breach, and the number of affected individuals. The FTC, for example, can impose significant fines for violations of the FTC Act. State attorneys general can also pursue legal action, leading to substantial penalties and legal costs. Class-action lawsuits by affected individuals could result in massive payouts for damages, including compensation for identity theft, financial losses, and emotional distress.
The sheer scale of this breach – involving 123 million households – suggests the potential penalties could reach hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars. For instance, the Equifax data breach, involving a far smaller number of individuals, resulted in substantial fines and settlements.
Potential Legal Strategy for Victims Seeking Redress
Victims of this data breach can pursue several legal avenues to seek redress. Filing individual lawsuits is one option, though it can be expensive and time-consuming. A more efficient approach might be joining a class-action lawsuit, which allows multiple victims to pool their resources and share legal costs. This strategy offers economies of scale and increases the leverage against the implicated parties.
The recent AWS data breach exposing federal data from 123 million US households is a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities in our digital infrastructure. Building secure and robust applications is crucial, and that’s where exploring platforms like Domino and understanding the potential of low-code and pro-code development, as discussed in this insightful article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , becomes incredibly important.
Ultimately, stronger application development practices are key to preventing future breaches and protecting sensitive data like that of the 123 million households affected.
Victims should carefully document all damages suffered, including any financial losses, time spent mitigating the impact of the breach, and emotional distress. They should also consider seeking legal counsel specializing in data breach litigation to understand their rights and pursue the most effective legal strategy. Establishing negligence on the part of AWS or other involved parties is crucial for a successful claim.
Demonstrating a direct causal link between the breach and the victims’ losses will be critical to obtaining compensation.
Impact on Individuals and Society
The leak of personal data from 123 million US households represents a catastrophic breach of privacy with far-reaching consequences for individuals and society as a whole. The sheer scale of the data exposure means millions of people are now vulnerable to a range of serious threats, impacting their financial security, personal safety, and trust in online systems. The long-term effects could be profound and wide-ranging, requiring significant resources and effort to mitigate.The potential for identity theft and financial fraud is immense.
Stolen data, including Social Security numbers, addresses, financial account details, and even medical information, can be used to open fraudulent accounts, file false tax returns, or access existing accounts. Victims may face significant financial losses, credit damage, and the emotional distress of navigating the complex process of recovery. Beyond the immediate financial impact, the long-term consequences can include difficulty securing loans, renting property, or even obtaining employment.
The erosion of trust in online services and the increased fear of data breaches will likely lead to a decline in online engagement and transactions, potentially hindering economic growth and innovation.
Consequences for Affected Individuals
The leaked data could be used in a variety of malicious ways, leading to severe consequences for affected individuals. Identity theft is a primary concern, with criminals potentially using stolen information to access bank accounts, open credit cards, or even assume the victim’s identity for more serious crimes. Financial fraud, including phishing scams and loan applications under false pretenses, is another major risk.
Furthermore, the exposure of sensitive medical information could lead to medical identity theft, resulting in fraudulent billing or denial of legitimate healthcare services. The emotional toll on victims can be substantial, causing anxiety, stress, and a sense of vulnerability. Many individuals may spend countless hours rectifying the damage caused by the breach, impacting their personal and professional lives.
Consider the case of a victim who has to spend weeks freezing their credit, filing police reports, and contacting various agencies to resolve the issues arising from the breach – this represents a significant loss of time and emotional energy.
Societal Impact of the Breach
This data breach has significant implications for societal trust in online services and data privacy. The scale of the breach undermines public confidence in the ability of companies to protect sensitive personal information. This could lead to increased skepticism toward online transactions, a decrease in the use of online services, and a greater demand for stricter data privacy regulations.
The incident may also fuel public debate about the responsibilities of technology companies and government agencies in safeguarding personal data. Furthermore, the potential for misuse of leaked data for political manipulation or social engineering attacks represents a significant threat to societal stability. This could manifest in targeted disinformation campaigns or attempts to influence elections, further eroding public trust in institutions.
Types of Leaked Data and Potential Misuse, Federal data of 123m us households leaked in latest aws data breach
| Data Type | Potential Misuse | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Security Numbers (SSNs) | Identity theft, tax fraud, loan applications | Severe financial and legal consequences | Filing fraudulent tax returns, opening credit accounts |
| Addresses | Targeted mail fraud, physical theft, stalking | Financial loss, personal safety risks | Receiving fraudulent packages or experiencing home invasion |
| Financial Account Details | Unauthorized access to accounts, fraudulent transactions | Significant financial losses | Emptying bank accounts, making unauthorized purchases |
| Medical Information | Medical identity theft, fraudulent billing | Healthcare disruptions, financial burden | Receiving bills for services not rendered |
Financial Costs of the Breach
The financial costs associated with this breach are substantial and far-reaching. Individuals may face significant expenses related to credit monitoring, identity theft recovery services, and legal fees. Businesses will also incur costs related to notifying affected customers, providing credit monitoring services, and responding to legal actions. The long-term costs could include lost revenue due to decreased customer trust and the expenses associated with enhanced security measures.
The cost of this breach could easily run into the millions or even billions of dollars, impacting both individuals and businesses alike. For example, Equifax’s 2017 data breach, which exposed the personal information of 147 million people, resulted in billions of dollars in costs for the company, including legal settlements, regulatory fines, and credit monitoring services for affected customers.
This case serves as a stark reminder of the potential financial fallout from large-scale data breaches.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices: Federal Data Of 123m Us Households Leaked In Latest Aws Data Breach
The recent AWS data breach affecting 123 million US households underscores the critical need for robust data security measures at both the individual and organizational levels. Proactive steps are essential to mitigate future risks and protect sensitive information. This section Artikels best practices for individuals and businesses to enhance their data security posture.
The sheer scale of the recent AWS data breach, exposing federal data on 123 million US households, is truly alarming. It makes you wonder about the security of our personal information online, especially considering that Facebook is now reportedly asking for bank account info and card transactions from users, as detailed in this article: facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users.
This just underscores how vulnerable we are, and highlights the urgent need for stronger data protection measures in the face of these massive breaches.
Best Practices for Individuals to Protect Their Data
Protecting your personal data in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats requires a multi-layered approach. A proactive stance, incorporating the following practices, significantly reduces your vulnerability.
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use unique, complex passwords for each online account and enable MFA whenever possible. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone, beyond just a password.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your operating systems, applications, and antivirus software updated. These updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Learn to recognize and avoid phishing emails, text messages, and websites designed to steal your personal information. Never click on suspicious links or open attachments from unknown senders.
- Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Use strong passwords for your home Wi-Fi network and avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions. Consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) when connecting to public Wi-Fi.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Regularly check your bank statements, credit reports, and online accounts for any unauthorized activity. Report any suspicious activity immediately.
- Data Minimization: Only share personal information when absolutely necessary and limit the amount of data you share online.
Security Measures for Businesses to Safeguard Customer Data
Businesses have a legal and ethical responsibility to protect the data they collect from their customers. Implementing robust security measures is not merely a best practice; it’s a necessity.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit (while being transmitted) and at rest (while stored). This renders the data unreadable to unauthorized individuals even if a breach occurs. Examples include AES-256 for data at rest and TLS/SSL for data in transit.
- Access Control and Authorization: Implement strict access control measures, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. Use the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access they need to perform their jobs.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in your systems and applications. This proactive approach helps to identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan to handle data breaches effectively. This plan should Artikel steps to contain the breach, investigate its cause, and notify affected individuals.
- Employee Training: Train employees on security best practices, including password management, phishing awareness, and data handling procedures. Regular training reinforces good security habits.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: Implement DLP tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network without authorization.
Data Encryption Methods: A Comparison
Various encryption methods exist, each with varying levels of security and computational overhead. The choice depends on the sensitivity of the data and the resources available.
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. Examples include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard). Symmetric encryption is generally faster but requires secure key exchange.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Uses two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Examples include RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography). Asymmetric encryption is slower but eliminates the need for secure key exchange.
- Hashing: A one-way function that transforms data into a fixed-size string (hash). Hashing is used for data integrity checks, not for encryption as it cannot be reversed. Examples include SHA-256 and MD5.
The effectiveness of each method depends on factors such as key length, algorithm strength, and implementation. AES-256 is currently considered a highly secure symmetric encryption algorithm, while RSA with sufficiently large key sizes remains a strong asymmetric option. The choice often involves a balance between security and performance.
Public Awareness Campaign: Data Security and Privacy
A successful public awareness campaign requires a multi-pronged approach targeting diverse audiences through various channels.
- Educational Materials: Develop easily understandable educational materials, including infographics, videos, and articles, explaining data security concepts and best practices in simple terms.
- Social Media Campaigns: Utilize social media platforms to disseminate information and engage with the public. Run contests and share compelling stories to increase awareness.
- Partnerships with Influencers: Collaborate with trusted influencers and organizations to reach wider audiences and build credibility.
- Community Outreach Programs: Organize workshops and events in communities to educate individuals directly about data security and privacy issues.
- Government Collaboration: Work with government agencies to promote data security initiatives and disseminate public service announcements.
The Role of Data Brokers
Data brokers are companies that collect and compile personal information from various sources, then sell this aggregated data to businesses for marketing, risk assessment, and other purposes. This vast network of information, often unknowingly contributed by individuals through online activities and public records, creates a powerful but potentially dangerous resource. The recent AWS data breach highlights the critical vulnerabilities inherent in this system.Data brokers employ diverse methods to gather information.
This includes purchasing data from public records (like property records and court documents), scraping information from websites, and leveraging partnerships with other companies to gain access to user data. The sheer volume of data collected, combined with the often-opaque nature of their operations, makes it difficult to track and regulate their activities effectively.
Data Broker Vulnerabilities
The data broker industry’s structure presents several significant vulnerabilities. The reliance on numerous data sources increases the risk of breaches. A single compromised source can expose vast quantities of personal information, as seen in the recent incident. Furthermore, inadequate security measures, including outdated software and insufficient employee training, can make these companies easy targets for cyberattacks. The lack of comprehensive data governance and oversight across the industry exacerbates these vulnerabilities.
The aggregation of data from multiple sources creates a single point of failure with potentially catastrophic consequences. For example, a breach affecting a data broker with access to medical records, financial information, and social media activity would create a devastating combination of sensitive personal data for malicious actors.
Ethical Considerations in the Data Broker Industry
The ethical implications of the data broker industry are complex and far-reaching. The lack of transparency regarding data collection and usage practices raises serious concerns about individual privacy. Many individuals are unaware that their data is being collected and sold, and have little control over how it’s used. The potential for discriminatory practices, such as targeted advertising based on sensitive personal attributes, also raises ethical questions.
The recent AWS data breach exposing federal data from 123 million US households is a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities in cloud storage. This incident highlights the urgent need for robust security measures, and solutions like those offered by bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management are becoming increasingly crucial. Without proactive cloud security, the risk of similar massive data breaches impacting millions will only continue to grow.
Moreover, the use of data for surveillance and profiling purposes, without informed consent, represents a significant breach of trust. The potential for misuse of aggregated data by unscrupulous actors, leading to identity theft, fraud, and other harmful activities, is a major ethical concern.
Data Flow Visualization
Imagine a diagram with three main sections. The first section, labeled “Individuals,” depicts various sources of personal data: social media profiles, online purchases, public records, etc., each represented by a small icon. Arrows emanate from these icons, converging into a central box labeled “Data Brokers.” This box is larger and more complex, illustrating the aggregation process. From the “Data Brokers” box, multiple arrows point outwards to various recipients, such as “Marketing Firms,” “Insurance Companies,” “Credit Agencies,” and a final, ominous arrow leading to a box labeled “Malicious Actors.” This last arrow is thicker and darker than the others, visually emphasizing the potential for data misuse.
The overall design should convey a clear visual narrative of how personal data flows from individuals, through data brokers, and potentially into the hands of those who would exploit it for malicious purposes. The sheer volume of arrows converging on the “Data Brokers” box, and the diversity of arrows branching out from it, visually represents the scale and complexity of the data broker ecosystem.
Final Review
The AWS data breach affecting 123 million US households serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in our increasingly interconnected world. While the immediate fallout is concerning – potential identity theft, financial losses, and eroded trust – the long-term implications are even more profound. We need stronger regulations, more robust security protocols from tech giants, and increased public awareness about data privacy.
This isn’t just about technology; it’s about protecting our fundamental rights and building a safer digital future. Let’s use this wake-up call to demand better and proactively safeguard our personal information.
FAQ Overview
What types of data were potentially compromised?
Reports suggest the breach may have exposed a range of sensitive information, including names, addresses, social security numbers, financial account details, and potentially even location data. The exact scope is still being investigated.
What should I do if I think my data was compromised?
Monitor your credit reports closely for any suspicious activity. Consider placing a fraud alert or security freeze on your credit files. Change your passwords for all online accounts, and be wary of phishing scams targeting breach victims.
Is AWS solely responsible for this breach?
While AWS is a major player, the full extent of responsibility is still under investigation. The breach may involve other parties, including the client whose data was compromised and potentially even data brokers. Determining culpability will be a complex legal process.
How can I protect myself from future data breaches?
Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts. Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible. Be cautious about sharing personal information online, and regularly review your credit reports and bank statements.