Five Mobile Security Concerns Usually Ignored
Five mobile security concerns which are usually ignored are silently chipping away at our digital safety. We’re so busy tapping, swiping, and scrolling that we often overlook the crucial steps needed to protect our precious data and privacy. This post dives into five common oversights – from outdated software to the dangers of public Wi-Fi – and offers practical advice to help you bolster your mobile security.
Think of your phone as a digital wallet, holding everything from banking apps and personal photos to sensitive work documents. Leaving it vulnerable is like leaving your physical wallet open on a park bench – a recipe for disaster. Let’s explore these frequently ignored vulnerabilities and learn how to protect ourselves from the digital pickpockets lurking online.
Outdated Software & Operating Systems
Ignoring updates is a common mistake, but leaving your mobile software and operating system outdated exposes your device to significant security risks. These outdated systems become vulnerable to various attacks, potentially leading to data breaches, malware infections, and even complete device compromise. Regular updates are crucial for maintaining a secure mobile environment.Outdated software and operating systems are riddled with security vulnerabilities.
We often overlook crucial mobile security issues like weak passwords, unsecured Wi-Fi use, and outdated software. But managing these risks becomes even more critical when considering the cloud’s expanding role in our mobile lives. Understanding this is key, which is why I recently dove into an article about bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management , helping to contextualize the importance of addressing those often-ignored mobile vulnerabilities in the age of cloud computing.
Ultimately, proactive security measures are essential to mitigate these five mobile security concerns.
These vulnerabilities are often exploited by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to your personal data, install malicious software, or even take control of your device. The longer you delay updates, the greater your risk.
Common Vulnerabilities in Outdated Mobile Software, Five mobile security concerns which are usually ignored
The following table illustrates common vulnerabilities found in outdated mobile software and their potential impact. Remember, these are examples and not an exhaustive list. The specific vulnerabilities vary depending on the manufacturer, operating system version, and the specific software in question.
| Manufacturer | OS Version | Vulnerability Type | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generic Android Manufacturer | Android 7.0 Nougat | Remote Code Execution | Complete device compromise, data theft |
| Apple | iOS 12 | Wi-Fi vulnerability | Man-in-the-middle attacks, data interception |
| Generic Android Manufacturer | Android 4.4 KitKat | Unpatched security flaw | Malware installation, data breaches |
| Samsung | Samsung Experience 9.0 (based on Android 8.0 Oreo) | Privilege escalation | Unauthorized access to sensitive data |
Updating Mobile Software and Operating Systems
Updating your mobile device is a straightforward process, although the exact steps may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and operating system. Generally, the process involves:
1. Checking for Updates
Go to your device’s settings menu. Look for a section labeled “Software Update,” “System Update,” or something similar.
2. Downloading the Update
We often overlook crucial mobile security issues, like weak passwords or public Wi-Fi usage. One alarming example highlighting this negligence is the recent news of Facebook requesting bank account details and card transaction information from users, as detailed in this article: facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users. This underscores the importance of being vigilant about where we share our sensitive data, reminding us to prioritize the other often-ignored mobile security concerns.
Once an update is available, the system will usually prompt you to download it. This requires a stable internet connection.
3. Installing the Update
After the download completes, you’ll be prompted to install the update. This often requires a device restart. Ensure your device is adequately charged before starting the update process.
4. Restarting Your Device
After the installation is complete, your device will typically restart automatically. Once it restarts, the updated software and operating system will be active.
Security Features of Different Mobile Operating Systems Regarding Updates
iOS and Android have different approaches to software updates. Apple generally provides updates to a wider range of devices for a longer period than Android manufacturers. iOS updates are typically released simultaneously for all compatible devices. However, Android’s update rollout varies significantly between manufacturers and device models, with some devices receiving updates more quickly than others. This disparity in update frequency and duration creates a more significant security risk for Android users overall, even though individual Android versions might have equally strong security features.
Android’s fragmented update landscape leads to a higher proportion of vulnerable devices compared to iOS.
Public Wi-Fi Risks

Free Wi-Fi is tempting, but connecting to public networks exposes your mobile device to a range of security threats. The convenience often overshadows the significant risks involved, making it a frequently overlooked security concern for many mobile users. Understanding these risks and implementing preventative measures is crucial for protecting your data and privacy.Public Wi-Fi networks, unlike those secured in your home or office, are often unsecured or poorly secured.
This lack of security creates opportunities for malicious actors to intercept your data and compromise your device.
Common Security Threats on Public Wi-Fi
Using public Wi-Fi exposes your mobile device to several threats. These include man-in-the-middle attacks, where hackers intercept communication between your device and the website you’re visiting; data breaches, where sensitive information like login credentials and financial details are stolen; malware infections, where malicious software is downloaded onto your device without your knowledge; and phishing attacks, where you are tricked into revealing personal information through deceptive websites or emails.
These threats can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and significant privacy violations.
Methods Hackers Exploit Unsecured Wi-Fi
Hackers employ various methods to exploit users on unsecured Wi-Fi. One common technique is creating rogue access points that mimic legitimate Wi-Fi networks. Users unknowingly connect to these fake networks, allowing hackers to monitor their online activity and steal data. Another method is using packet sniffing, where hackers capture data packets transmitted over the network, potentially revealing sensitive information.
They might also employ sophisticated techniques like DNS spoofing to redirect users to malicious websites, leading to malware infections or phishing attacks. The lack of encryption on many public Wi-Fi networks makes these attacks significantly easier to execute.
Best Practices for Securing Mobile Devices on Public Wi-Fi
Several best practices can significantly reduce the risks associated with using public Wi-Fi. One of the most effective is using a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it much more difficult for hackers to intercept your data. Avoid accessing sensitive accounts like banking or email while on public Wi-Fi. Enable your device’s firewall to block unauthorized access attempts.
Keep your operating system and apps updated to patch known security vulnerabilities. Finally, be cautious about the websites you visit and only use trusted and secure websites when conducting sensitive transactions.
Identifying a Secure Wi-Fi Network: A Step-by-Step Guide
Identifying a secure Wi-Fi network requires careful attention. First, look for networks with a strong password protection, indicated by a padlock icon next to the network name. Avoid networks with names that seem suspicious or generic. Consider the location; if the network is in a public place like a coffee shop, verify its legitimacy with staff before connecting.
Check the network’s encryption protocol; WPA2 or WPA3 are considered secure, while WEP is outdated and easily cracked. If unsure, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and avoid connecting to a public Wi-Fi network altogether. Remember, a seemingly innocuous public Wi-Fi network could be a gateway to serious security risks.
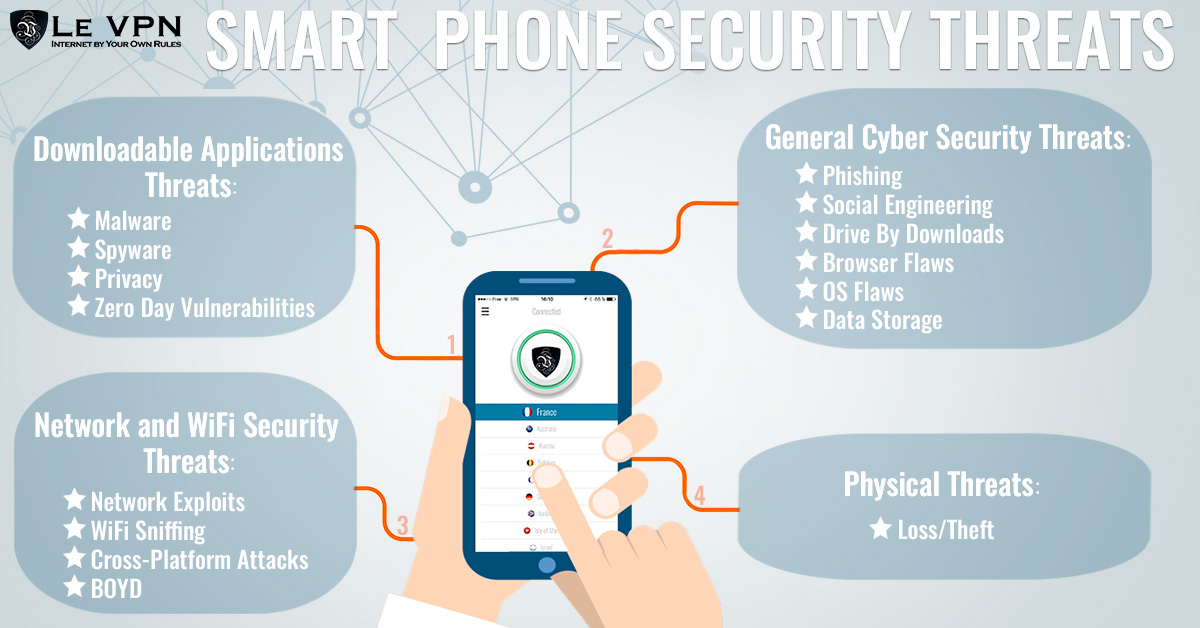
Unsecured Apps & Permissions: Five Mobile Security Concerns Which Are Usually Ignored
We all love downloading apps to make our lives easier, but little do many realize the potential security risks lurking within seemingly harmless applications. Downloading apps from untrusted sources or failing to carefully review app permissions can expose your mobile device to malware, data theft, and privacy violations. Understanding these risks and taking proactive steps is crucial for maintaining your mobile security.Many people don’t fully grasp the implications of granting apps extensive permissions.
While some permissions are necessary for an app’s functionality, others might be unnecessary and potentially dangerous. Reviewing and understanding these permissions before installation is a critical step in protecting your data and privacy.
Security Risks of Untrusted App Sources
Downloading apps from sources other than official app stores, such as unofficial websites or third-party marketplaces, significantly increases your risk of installing malicious software. These apps often lack proper security checks and may contain malware designed to steal your personal information, track your activity, or even take control of your device. The consequences can range from financial loss to identity theft.
Importance of App Permission Review
Before installing any app, carefully review the permissions it requests. Many apps request access to far more data than is strictly necessary for their function. For example, a flashlight app might request access to your contacts, location, or microphone – permissions that are completely unrelated to its core functionality. Granting unnecessary permissions allows apps to collect and potentially misuse your personal information.
Examples of Malicious Apps and Their Impact
Several examples illustrate the dangers of unsecured apps.
- Fake antivirus apps: These apps often mimic legitimate antivirus software but instead install malware, slowing down your device and stealing your data. They might display fake warnings about viruses, prompting you to pay for a “solution” that actually exacerbates the problem.
- Spyware apps: These apps secretly monitor your activity, collecting your location data, messages, and other sensitive information. This data can then be sold to third parties or used for malicious purposes such as identity theft or blackmail.
- Apps with hidden trackers: Some seemingly harmless apps might include hidden trackers that collect your browsing history, app usage, and other personal data without your knowledge or consent. This data is often used for targeted advertising, but it can also be misused for more sinister purposes.
Checklist for Evaluating App Permissions and Security
Before downloading an app, consider this checklist:
- Source: Download only from trusted app stores like Google Play Store or Apple App Store.
- Permissions: Carefully review all requested permissions. If an app requests permissions that seem unrelated to its function, reconsider downloading it.
- Reviews: Read user reviews to see if others have reported any issues or suspicious activity.
- Developer: Research the app developer. Look for reputable developers with a history of creating secure and trustworthy apps.
- Privacy Policy: Review the app’s privacy policy to understand how your data will be collected, used, and protected.
Weak or Reusable Passwords
In today’s interconnected world, our mobile devices hold a treasure trove of personal information – from banking details and social media accounts to photos and emails. Protecting this data hinges on strong password security, a frequently overlooked aspect of mobile security. Using weak or reusable passwords leaves you incredibly vulnerable to various threats, including account takeovers and identity theft.
Let’s delve into the dangers and best practices.Weak passwords, often easily guessable combinations like “password123” or “123456,” provide minimal protection against determined attackers. Reusing the same password across multiple accounts amplifies the risk exponentially. If one account is compromised, attackers gain access to all accounts using that password, creating a domino effect of security breaches. This can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal ramifications.
Strong Password Creation
Creating strong passwords involves incorporating a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Aim for a password length of at least 12 characters. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays, pet names, or common words. A helpful mnemonic technique is to create a memorable phrase and then weave it into a complex password. For example, the phrase “My dog loves green apples” could be transformed into “MyD0gL0v3sGr33nAppI3s!”.
Regularly updating passwords, especially for critical accounts, is also crucial.
Password Manager Benefits
Password managers are invaluable tools for enhancing mobile security. They generate strong, unique passwords for each account, eliminating the need to remember numerous complex combinations. They securely store these passwords, often using encryption, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized individuals to access them. Many password managers also offer features like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and security audits, adding an extra layer of protection.
Seriously, folks, we often overlook crucial mobile security issues like weak passwords and unsecured Wi-Fi. But building robust apps is key, and that’s where understanding the development process comes in. Check out this insightful article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future to see how secure coding practices can help mitigate those five mobile security concerns which are usually ignored, ultimately making our digital lives safer.
Popular examples include LastPass, 1Password, and Bitwarden.
Password Management Strategies Comparison
| Strategy | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Password Manager (e.g., LastPass, 1Password) | Generates strong passwords, secure storage, multi-factor authentication, cross-platform compatibility | Requires trust in the provider, potential vulnerability if the master password is compromised, subscription fees for premium features |
| Password Vault (e.g., physical notebook, encrypted file) | Offline storage, potentially higher level of control | Difficult to manage many passwords, risk of physical loss or theft, less convenient than password managers |
| Spreadsheet (with strong encryption) | Centralized storage | Requires manual password creation, vulnerability if the spreadsheet is compromised, less user-friendly |
Phishing & Social Engineering
Mobile devices are incredibly personal, holding everything from banking details to intimate photos. This makes them prime targets for sophisticated attacks that exploit human psychology as much as technological vulnerabilities. Phishing and social engineering are two sides of the same coin, manipulating users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software. They leverage our trust and often prey on our urgency or fear.Phishing and social engineering tactics on mobile devices frequently mimic legitimate communications, creating a sense of urgency or fear to trick users into acting quickly without thinking.
These attacks often exploit the convenience and immediacy of mobile communication, making them particularly effective.
Examples of Phishing Scams and Social Engineering Tactics
Mobile phishing attacks often arrive disguised as text messages (SMS phishing or “smishing”) or seemingly legitimate emails. These messages might claim to be from your bank, a delivery service, or a social media platform, urging you to update your account information, verify a transaction, or claim a prize. Social engineering on mobile devices can involve more direct interaction.
For instance, a scammer might pose as tech support, gaining access to your device under the guise of troubleshooting a problem. Another tactic involves creating fake apps that mimic popular services, which, once downloaded, steal your data.
Identifying and Avoiding Phishing Attempts
Before clicking any link or providing information, carefully examine the message’s sender. Look for inconsistencies in email addresses, phone numbers, or website URLs. Legitimate organizations rarely use generic greetings or threaten immediate account suspension. Suspicious links should never be clicked directly; instead, type the website address manually into your browser. If you’re unsure about a message’s authenticity, contact the organization directly using a verified phone number or email address found on their official website, not the one provided in the suspicious message.
Enable two-factor authentication wherever possible, adding an extra layer of security to your accounts. Finally, be wary of unexpected messages requesting personal information. Legitimate organizations rarely ask for sensitive details via text or email.
Visual Representation of a Phishing SMS Message
Imagine a text message on your phone. The sender appears to be “YourBank.” The message reads: “Urgent Security Alert! Your account has been compromised. Click here [link to a fake website] to verify your details immediately.” The link looks legitimate at first glance, but a closer inspection reveals a slightly misspelled URL or a domain name that doesn’t quite match the bank’s official website.
The message creates a sense of panic, urging immediate action, which is a hallmark of a phishing attempt. The overall tone is formal and urgent, attempting to bypass critical thinking.
Summary
Securing your mobile device isn’t about becoming a cybersecurity expert; it’s about implementing simple, effective habits. By staying updated on software, being mindful of Wi-Fi networks, carefully vetting apps, using strong passwords, and recognizing phishing attempts, you can significantly reduce your risk. Remember, a little vigilance goes a long way in protecting your digital life. Take control of your mobile security today – your peace of mind will thank you for it!
FAQ Section
What’s the biggest risk of using an outdated operating system?
Outdated OS versions often contain known security vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit to gain access to your data. These vulnerabilities can be patched in newer versions, making updates crucial.
How can I tell if a public Wi-Fi network is safe?
Look for networks with strong passwords, HTTPS encryption (indicated by a padlock icon in your browser), and avoid connecting to open, unencrypted networks whenever possible. A VPN adds an extra layer of protection.
Why are app permissions important?
Apps request permissions to access various aspects of your phone (camera, location, contacts, etc.). Carefully review these permissions before installing an app; if an app requests access that seems unnecessary, it could be malicious.
What’s a good password strategy?
Use long, unique passwords for each account, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. A password manager can help you generate and securely store these complex passwords.
How can I spot a phishing attempt?
Look for suspicious links, grammatical errors, urgent requests for personal information, and unfamiliar sender addresses. If something feels off, don’t click any links or respond.